Choosing the Right Company PCB Partner: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's interconnected world, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of virtually every electronic device. From smartphones to medical equipment, PCBs play a vital role, and choosing the right company PCB partner is crucial for ensuring the success of any product. This article will guide you through the essential aspects of selecting a reliable company PCB manufacturer, covering key elements such as manufacturing capabilities, quality standards, and assembly options, helping you navigate the complex landscape of PCB production to find the perfect fit for your needs.
Understanding Your Company PCB Needs

Before engaging a PCB manufacturer, a thorough assessment of your project's requirements is crucial. This initial step dictates the type of PCB needed, influencing the manufacturing process, material selection, and overall cost. A clear understanding at this stage will streamline the selection process and ensure that your chosen company PCB partner aligns with your needs.
- PCB Type
The complexity of your project determines the type of PCB needed, be it single-layer for simpler applications, multi-layer for intricate designs, or flexible PCBs for dynamic environments. - Material Requirements
Consider the thermal and electrical characteristics required for your PCB. Material choice impacts performance, durability, and cost, with options ranging from standard FR-4 to high-performance materials. - Volume Requirements
Production volume is a key consideration, as it affects manufacturing processes and costs. Whether you need prototypes, small batches, or mass production runs will determine which manufacturer is a better fit. - Timeline
A realistic project timeline is necessary for coordinating design, manufacturing, and assembly, ensuring the manufacturer can meet your deadlines. - Budget
Your allocated budget needs to be balanced against performance and quality. Balancing these will drive decision making and allow for identifying potential cost efficiencies early in the process.
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| PCB Type | Single-layer, multi-layer, flex, rigid-flex |
| Material | FR-4, aluminum, ceramic, polyimide, etc. |
| Volume | Prototype, small batch, mass production |
| Timeline | Design, manufacturing, assembly |
| Budget | Cost vs. performance |
PCB Manufacturing Capabilities: What to Look For
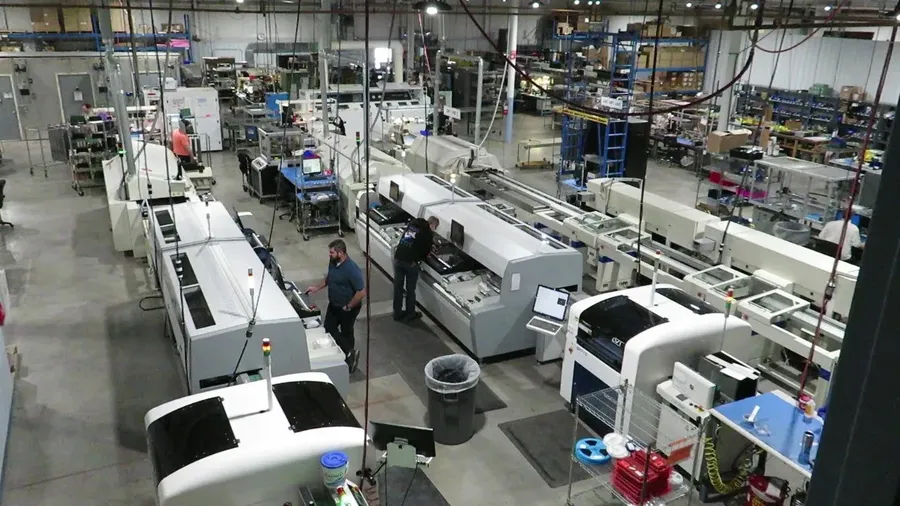

Selecting a PCB manufacturer requires a thorough evaluation of their manufacturing capabilities to ensure they can meet the specific demands of your project. Key considerations include their precision in trace width and spacing, their proficiency in various via types, the range of surface finish options they offer, and their capacity to handle your required layer counts. Additionally, it's crucial to confirm their adoption of advanced PCB manufacturing technologies.
| Capability | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Trace Width/Spacing | The smallest conductor width and the space between them that the manufacturer can reliably produce. | Critical for high-density designs and signal integrity. |
| Via Types | The different types of vias (through-hole, blind, buried) the manufacturer can create. | Essential for multi-layer designs and complex routing. |
| Surface Finish Options | The variety of surface finishes available (e.g., HASL, ENIG, Immersion Silver). | Crucial for solderability and environmental protection. |
| Layer Count | The maximum number of copper layers the manufacturer can produce in a single PCB. | Determines the complexity and functionality of the PCB. |
| Advanced Technologies | The latest manufacturing capabilities including microvias, high-speed materials, and fine-line technologies. | Necessary for cutting-edge designs and high-performance applications. |
PCB Assembly Services: Turnkey vs. Consignment
When it comes to PCB assembly, understanding the nuances between turnkey and consignment services is crucial for efficient project management. These two models differ significantly in how components are sourced and managed, impacting both cost and logistics.
| Feature | Turnkey Assembly | Consignment Assembly |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Manufacturer handles all component procurement | Customer provides all necessary components |
| Inventory Management | Manufacturer manages component inventory | Customer manages and ships component inventory |
| Lead Time | Potentially shorter due to streamlined sourcing | Can vary greatly based on component availability |
| Cost | Often higher due to component procurement fees | Potentially lower initial cost, but may incur additional risk |
| Responsibility | Manufacturer has increased responsibility for project | Customer has higher responsibility for material quality and delivery |
| Suitability | Ideal for projects with a large BOM (Bill of Materials) or limited in-house resources | Ideal for projects with strict component control and cost management focus |
The decision between turnkey and consignment assembly hinges on your project's specific needs, resources, and priorities. Evaluating these aspects will lead you to the ideal PCB assembly service.
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
SMT involves mounting components directly onto the surface of the PCB. This technique is used for high-density applications, allowing smaller, more compact boards. - Through-Hole Technology
Through-hole technology involves inserting components with leads through holes in the PCB, and then soldering them on the other side. This method is more robust, offering stronger connections, and is typically used for components that need to withstand mechanical stress. - Mixed Technology Assembly
Mixed technology refers to the use of both SMT and through-hole components on a single PCB, which is typical for designs that require components with varying performance demands. This is a versatile approach combining the advantages of both assembly techniques.
Quality Standards and Certifications for Company PCBs
Selecting a company PCB manufacturer requires careful consideration of their adherence to quality standards and certifications. These certifications are not mere badges; they represent a commitment to consistent manufacturing processes, material quality, and overall reliability of the produced PCBs. Compliance with recognized standards assures clients that the PCBs meet the necessary performance and safety criteria for their intended applications.
| Certification/Standard | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 9001 | International standard for quality management systems. | Indicates the company has robust processes for quality control, from design to manufacturing and delivery. |
| IPC Standards (e.g., IPC-A-600, IPC-A-610) | Industry standards for acceptability of PCBs and electronic assemblies. | Ensures that the manufactured PCBs meet specific performance and reliability criteria regarding features such as solder joints, via fill, and trace characteristics. |
| UL Compliance | Certification for product safety by Underwriters Laboratories. | Confirms that the PCBs meet stringent safety requirements, preventing hazards like electrical shock, fire, etc.,. |
| RoHS Compliance | Restriction of Hazardous Substances directive. | Guarantees the PCB contains minimal amounts of hazardous materials like lead, mercury, and cadmium, important for environmental and health safety. |
| REACH Compliance | Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and Restriction of Chemicals regulation. | Ensures the PCB manufacturer identifies and manages the risks linked to the substances they produce and market. |
Beyond certifications, it's crucial to assess a company’s quality control (QC) procedures. These procedures should include inspections at various production stages, material traceability, and the use of advanced testing equipment. Transparency in quality control processes is vital. A reputable company should be willing to share its QC protocols and metrics, demonstrating their dedication to maintaining high standards.
Comparing Costs and Lead Times
Selecting a company PCB manufacturer requires a thorough cost and lead time comparison to ensure the best value for your project. This involves more than just looking at the price tag; it's about evaluating the total cost of ownership, including lead times and shipping, to guarantee that project timelines and budgetary constraints are met without compromising quality.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Project |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Price | Cost per PCB, which may vary by quantity and complexity. | Directly impacts overall project cost. |
| Lead Time | Time required for the manufacturer to produce the PCBs. | Can affect project schedules and deadlines. Shorter lead time may come with higher cost. |
| Shipping Costs | Expenses associated with transporting the PCBs to your location. | Can significantly impact overall cost, especially for international shipments. |
| Tooling Costs | One-time expenses for setting up the manufacturing process. | May increase upfront cost, especially for complex designs or small production runs. |
| Payment Terms | Terms of payment and credit options offered by the manufacturer. | Can affect cash flow and financial planning. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | The smallest number of PCBs that a manufacturer is willing to produce. | Can be a critical factor for small projects and prototypes. |
Evaluating Communication and Customer Support
A dependable company PCB partner is characterized by its ability to provide responsive communication and robust technical support, going beyond merely processing orders. This includes readily available channels for clear communication, proactive updates, and the capability to offer design assistance and quick resolutions for any manufacturing issues that may arise during the production process.
- Communication Channels
Assess the availability and responsiveness of different communication channels, such as phone, email, live chat, and project management portals. A diverse range of channels can accommodate different communication preferences and urgency levels. - Technical Support Availability
Evaluate the availability of technical support engineers who possess expertise in PCB design, manufacturing processes, and material science. This should include accessibility during different phases of the project, from initial design to final assembly. - Design Assistance
Confirm whether the company provides design assistance and Design for Manufacturability (DFM) reviews. This process should provide insight into whether any design changes are needed to optimize manufacturability and reduce costs. This shows proactive partnership, rather than simply fulfilling order requests. - Issue Resolution
Evaluate the company's approach to issue resolution. In manufacturing, production issues are inevitable, thus it is critical that the company PCB partner have established process in place to resolve any issues with speed and effectiveness. - Responsiveness
Measure response times and the overall helpfulness of support. This can be achieved through direct communication tests, requesting quotes, asking for technical information, and checking the turnaround time for issue resolution. This should give you a good sense of overall responsiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions About Company PCBs
This section addresses common questions regarding company PCBs, clarifying their role in various organizational contexts, differentiating between PCB manufacturers, and guiding the selection process. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effective PCB procurement and project management.
- What does PCB stand for in a company context?
In a business setting, PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board. It is a fundamental component of most electronic devices, serving as the foundation for mounting and connecting electronic components. PCBs are essential for enabling the functionality of electronic products. - What is the role of a PCB in a company's operations?
The role of a PCB within a company's operations is multifaceted. PCBs are integral to manufacturing electronic goods, and it enables product functionality. The choice of PCB and the company producing it directly impacts product quality, performance, and overall cost. - What is the meaning of PCB in business?
In business, PCBs represent a critical part of the supply chain for electronic product companies. They are not just components; they are essential for the functionality of a final product. Therefore, efficient PCB procurement is vital for product development and market competitiveness. - What does a 'PCB job' entail?
A 'PCB job' typically refers to roles involving the design, fabrication, assembly, and testing of printed circuit boards. These roles can range from PCB design engineers to manufacturing technicians, depending on the stage of the PCB production process. Each role requires specialized knowledge to ensure PCB quality and reliability. - What are the key differences between various PCB manufacturers?
PCB manufacturers can vary significantly in terms of their technology capabilities, production capacity, quality standards, and specialization. Some may focus on high-volume manufacturing, while others may specialize in prototyping or specific PCB types such as flexible circuits or high-density interconnects (HDI) and other advanced PCB designs. It is vital to choose a PCB manufacturer that aligns with project specifications. - How does selecting a specific PCB manufacturer affect cost and quality?
The choice of a PCB manufacturer has a direct impact on project costs and product quality. Manufacturers with advanced technology and rigorous quality control might have higher prices but offer better reliability and precision. Conversely, lower-cost options may lack the same level of quality control and have limitations with advanced specifications. A balance is required based on project priorities and budget. - What considerations are key when choosing the right PCB partner?
The primary considerations when choosing a PCB partner include: their manufacturing capabilities in terms of layer count, trace width, materials, and certifications, their ability to meet quality standards and project timelines, their communication and customer support services, and their pricing strategy. Ultimately, it is vital to find a PCB manufacturing partner that can meet your specific needs consistently.
Actionable Tips for Selecting a Company PCB Partner
Selecting the right company PCB partner is crucial for the success of your electronic projects. This section outlines actionable tips to guide you in making an informed decision, focusing on critical factors that impact quality, cost, and efficiency.
- Assess Specialization
Determine if the manufacturer specializes in the type of PCBs you require (e.g., single-sided, multilayer, flex). A specialized manufacturer is more likely to have the necessary expertise and equipment for your project, ensuring higher quality and fewer production issues. Companies with diverse manufacturing capabilities can also offer scalability should your project evolve. - Evaluate Location
Consider the geographical location of the PCB manufacturer relative to your facilities or assembly location. Proximity can significantly reduce shipping costs and lead times, particularly for prototypes and small-batch production. However, carefully weigh the benefits of reduced logistics against the quality and cost offered by manufacturers in other regions. - Technical Support
A strong technical support team can be an asset throughout the PCB manufacturing process. Ensure that the company offers design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback to prevent errors. Evaluate how quickly the support team responds to queries. Prompt and helpful assistance can prevent costly delays. - Ease of Communication
Choose a company that maintains clear and efficient communication. Regular updates, prompt responses, and effective problem-solving are essential. Verify if they use project management tools and whether communication is direct with their engineers and production team. - Financial Stability of the PCB Supplier
Before you commit, it is recommended to take the time to review the financial standing of your PCB manufacturer. This can be done through credit reports, bank references, or business ratings. This can help reduce the risk of business interruptions which can result from a supplier with financial problems. - Review Production Capabilities
Examine their production equipment, processes, and the technology they use. Make sure they can handle all the specifications and requirements that are important to you, and that they are following standards of practice. The right production equipment can reduce defects and costs while also keeping timelines accurate.
By evaluating these actionable tips, you will be in a better position to choose a company PCB partner that can meet the specific requirements of your project and ensure a successful outcome. This will help in balancing cost and quality, as well as helping you select a company that is a good long-term partner.
Future Trends and Technologies in Company PCB Manufacturing

The printed circuit board (PCB) industry is undergoing rapid evolution, driven by technological advancements and increasing demands for sophisticated electronic devices. Understanding these future trends is crucial when selecting a company PCB partner, ensuring they are equipped to meet current and future requirements.
- Flexible PCBs (Flex PCBs)
Flex PCBs are gaining popularity due to their ability to conform to complex shapes and fit into compact electronic devices, offering greater design freedom and reliability. - Miniaturization
The trend towards smaller and more powerful devices continues to drive PCB miniaturization, requiring manufacturers with capabilities in fine-line circuitry, microvias, and advanced packaging techniques. - Advanced Materials
The use of advanced materials, like high-frequency laminates and thermally conductive substrates, is becoming more common in PCBs, improving performance in high-speed and high-power applications. - Sustainable Manufacturing Practices
There is growing emphasis on environmentally friendly PCB manufacturing, including the use of lead-free solders, water-based cleaning solutions, and recycling programs, thus reducing the environmental footprint. - 3D Printing of PCBs
Additive manufacturing technologies like 3D printing are emerging as a potential disruptor, enabling rapid prototyping and customizable PCB production. - High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs
HDI PCBs are becoming increasingly necessary to accommodate higher component density and performance demands, characterized by fine lines, microvias, and multi-layer designs. - Embedded Components
The technology of embedding components directly into the PCB layers is advancing, leading to more compact, efficient, and reliable electronic assemblies, requiring advanced manufacturing capabilities.
These trends require company PCB partners to invest in new technologies and continuously upgrade their manufacturing processes to deliver high-quality and innovative PCB solutions.
Choosing the right company PCB manufacturer is a critical decision that impacts your electronic product's quality, reliability, and overall success. By carefully evaluating your needs, the manufacturer’s capabilities, and long-term vision, you can ensure your PCBs are produced to the highest standards, giving you a competitive edge. Selecting a company PCB is not just about cost and lead times, but also about building a valuable partnership that can drive your business forward through consistent high-quality PCB products.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA