Choosing the Right PCB Soldering Company: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's interconnected world, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of almost every electronic device. The process of soldering, which joins electronic components to a PCB, is crucial for product performance and reliability. Choosing the right pcb soldering company is therefore a critical decision. This article will guide you through the essential considerations for this crucial step.
Understanding Different PCB Soldering Methods

The selection of the appropriate PCB soldering method is crucial for achieving reliable and high-quality electronic assemblies. PCB soldering companies employ various techniques, each suited to specific applications, production volumes, and design complexities. These methods include hand soldering, wave soldering, reflow soldering, and selective soldering, each offering distinct advantages and disadvantages.
| Soldering Method | Description | Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hand Soldering | Manual process using a soldering iron. | Prototypes, rework, small batches, through-hole components. | Flexibility, low initial setup cost, suitable for intricate jobs and rework. | Slow, labor-intensive, variable quality, not suitable for large-scale production, requires skilled operator. |
| Wave Soldering | Molten solder wave is used to solder through-hole components. | Large-scale production of through-hole components and mixed-technology boards. | Fast, cost-effective for high volume, good for through-hole components. | Not suitable for surface mount components (SMT) on the solder side of the board, thermal shock risk, requires masking, less precise than reflow. |
| Reflow Soldering | Solder paste is heated in a reflow oven to solder SMT components. | Mass production of surface mount components. | High precision, excellent for SMT components, high production volume, automation possible. | Requires initial setup cost (stencil, oven), less suitable for through-hole components, requires careful temperature control. |
| Selective Soldering | Automated soldering of specific areas using solder jet or mini wave. | Mixed-technology boards, precise soldering for specific components. | Precise and repeatable, reduces thermal stress, suitable for complex boards, good for mixed SMT/Through hole. | Higher setup cost, slower than wave soldering, more complex setup. |
Hand Soldering vs. Automated Soldering for PCB Assembly

Selecting the appropriate soldering method is critical for PCB assembly, with hand soldering and automated soldering representing two distinct approaches tailored for different production needs. Hand soldering is often employed for prototyping and small-batch runs, while automated soldering is the go-to method for mass production due to its efficiency and consistency.
| Feature | Hand Soldering | Automated Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Application | Prototypes, small batches, rework, and repair | Mass production, large volume assembly |
| Cost | Lower setup cost, higher per-unit cost | Higher initial cost (equipment), lower per-unit cost |
| Precision | Dependent on operator skill, potential for human error | High precision and repeatability, minimal human error |
| Turnaround Time | Slower for large volumes, faster for small volumes | Faster for large volumes, may have longer setup time |
| Equipment | Soldering iron, solder wire, basic tools | Reflow ovens, wave soldering machines, pick-and-place machines |
| Skill Level | Requires skilled and experienced operators | Requires skilled technicians for setup and maintenance, less manual labor |
| Consistency | Variable due to manual processes | Highly consistent results due to machine precision |
The choice between hand soldering and automated soldering significantly impacts project cost, precision, and turnaround time. A pcb soldering company will assess these factors based on your specific requirements.
Key Factors When Selecting a PCB Soldering Company

Selecting the right PCB soldering company is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of your electronic products. Several key factors must be carefully considered to make an informed decision that aligns with your specific needs and industry standards. These factors range from the company's certifications and industry experience to their component handling and quality control capabilities.
- Certifications
Verify that the company holds relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 (for quality management) or AS9100 (for aerospace applications). These certifications are indicative of a commitment to quality and adherence to industry best practices. They demonstrate that the company has implemented robust quality management systems and processes, ensuring a high standard of service. - Industry Experience
Assess the company's experience within your specific industry. A PCB soldering company with experience in sectors like medical, aerospace, automotive, or consumer electronics will be better equipped to handle your unique requirements and adhere to specific industry standards. Industry-specific experience means they likely understand the nuances of materials, tolerances, and reliability requirements that are pertinent to your products. - Component Handling Capabilities
Evaluate the company's ability to handle a wide range of components, including surface mount technology (SMT), through-hole, and mixed technology components. Their capability should also extend to handling sensitive or delicate components with appropriate methods and tools. The company should also have robust inventory management to minimize risk of component damage or loss. - Quality Control Measures
Inquire about the company's quality control processes, including testing and inspection methodologies. Stringent quality control is crucial to maintaining high reliability and reducing defects. This includes documentation and adherence to best practices at every step of the manufacturing process. Look for a company that actively monitors and documents quality from incoming materials to the final soldered product. - Lead-Free Soldering Capabilities
Ensure that the company is proficient in lead-free soldering, adhering to the Restriction of Hazardous Substances (RoHS) directive. This is essential for environmental compliance and meeting global regulations. It also assures that products are compliant with standards that prohibit lead in electronic products
Assessing the Capabilities of a PCB Soldering Company

Evaluating the capabilities of a PCB soldering company is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of your electronic products. This assessment encompasses their equipment, expertise, and ability to handle various soldering techniques and PCB design complexities. A thorough evaluation will determine if the company can meet your specific needs and quality standards.
Key areas to assess include:
- Equipment and Technology
A well-equipped PCB soldering company should possess modern machinery for automated soldering processes like reflow and wave soldering, along with selective soldering capabilities. They should also have the equipment for manual soldering and rework when necessary. Furthermore, inspect their use of ancillary tools such as pick-and-place machines for SMT assembly and automated optical inspection (AOI) systems. - Component Compatibility
The company must demonstrate competence in handling various surface mount technology (SMT) components, through-hole components, and mixed technology boards. Their processes must minimize the risk of damage or misalignment during component placement and soldering, considering the sensitivity of electronic components to thermal stress and electrostatic discharge. - Soldering Expertise
Assess the company's expertise in SMT, through-hole, and mixed technology soldering. SMT involves smaller components, requiring very precise soldering techniques. Through-hole, on the other hand, requires secure, reliable connections through the PCB layers. A capable company should be able to perform all these efficiently and also be able to implement mixed-technology soldering techniques, combining SMT and through-hole methods to meet your particular design needs. - Complex PCB Design Handling
A capable PCB soldering company should be able to handle complex designs, including multi-layered PCBs, high-density boards, and those with unique geometries. Their engineers must be adept at interpreting design specifications and translating them into a quality finished product, and adept at handling heat dissipation issues, via designs, and other complexities.
| Capability Area | Key Considerations | Evaluation Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment | Automated soldering machines, rework tools, AOI systems | Check for calibration, maintenance records, and technology level. |
| Component Handling | SMT, through-hole, mixed technologies | Verify expertise with various types, sizes, and sensitivities. |
| Soldering Expertise | SMT, through-hole, mixed tech | Review training, certifications of personnel, and process control. |
| PCB Design Complexity | Multilayer PCBs, high-density designs | Assess experience with similar complex designs and their success rate. |
Cost and Pricing Models of PCB Soldering Services
Understanding the cost drivers and pricing models for PCB soldering services is crucial for effective budgeting and project planning. These factors vary significantly, influencing the final price and your overall project expenses. A thorough grasp of these aspects enables you to make informed decisions when selecting a PCB soldering company.
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of PCB soldering. These include:
- Volume
The quantity of PCBs to be soldered directly impacts the price. Larger volumes often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. - Complexity
The number of components, board layers, and the density of the design all contribute to the complexity of the soldering process. More complex designs typically incur higher costs. - Materials
The types of components, solder paste, and board materials used influence pricing. Specialized components or materials may increase the cost. - Turnaround time
Expedited turnaround times for quick prototyping or tight production schedules generally result in increased costs due to the resources allocated to meet the shorter timeline.
PCB soldering companies utilize various pricing models, each suited to different project requirements and budget considerations:
| Pricing Model | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Per Unit Pricing | A fixed price is charged for each PCB soldered. | Simple and easy to understand, suitable for large production runs with consistent designs. | Less cost-effective for small quantities or complex designs; may not be flexible for design changes or prototypes. |
| Hourly Rate | Charges based on the time spent on the soldering process. | Flexible for small batches, prototypes, and complex designs where time estimates are difficult; provides better visibility of time-consuming tasks. | Total cost can be unpredictable if time estimates are inaccurate; may be more expensive for large production runs. |
| Project Based Pricing | A fixed price is quoted for the entire project, regardless of time or units. | Cost is predictable and budget planning is straightforward; favorable for projects with well-defined specifications. | Less flexible for project changes; may not accurately reflect actual time spent; less cost effective on large-volume orders. |
Selecting the appropriate pricing model is crucial and depends on your project's specific requirements. For large production runs of a standard design, per-unit pricing may offer cost benefits, whereas complex designs or prototypes might be more cost-effectively addressed using an hourly rate or project-based pricing model. Transparent communication with the PCB soldering company is essential to understand all cost drivers and secure the most advantageous pricing arrangement.
Quality Assurance and Inspection Processes
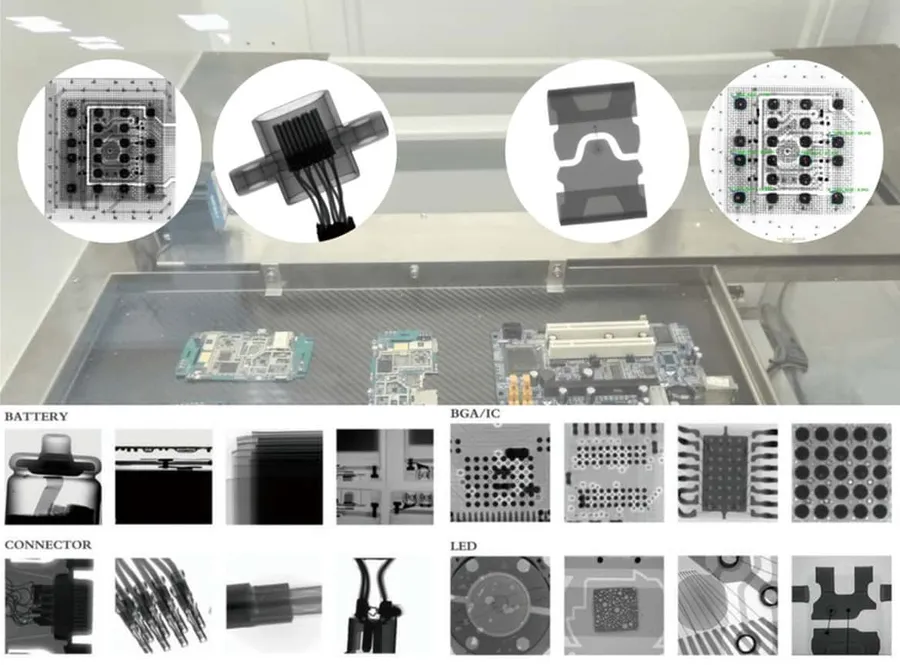
Rigorous quality assurance and inspection processes are paramount in PCB soldering to guarantee high reliability and minimize defects. These processes utilize advanced techniques to scrutinize solder joints and overall board integrity.
A robust quality control system typically encompasses multiple stages of inspection, including:
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI systems use high-resolution cameras to analyze solder joints for proper placement, alignment, and overall quality, identifying issues such as missing components, solder bridges, and insufficient solder. - X-ray Inspection
X-ray inspection techniques are used to examine hidden solder joints, such as those beneath BGA (Ball Grid Array) packages, detecting voids, misalignments, and other internal defects that would not be visible through traditional visual inspection methods. - Functional Testing
Functional testing validates the PCB’s operational performance according to design specifications, verifying that the assembled board behaves as intended within its operational parameters and ensuring the electronic components are performing as expected. This can include power-up tests, signal integrity checks, and compliance with performance criteria. - In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
ICT uses electronic probes to access test points on the PCB, verifying the correct assembly and values of individual components. This process identifies faulty or incorrectly placed components, shorts, and opens, providing feedback for immediate corrective action.
These methods, when used in conjunction, offer a multi-faceted approach to defect detection, thereby ensuring the long-term performance of the assembled PCBs.
When selecting a PCB soldering company, it is critical to inquire about their quality control processes to ensure they meet your reliability expectations. Ask detailed questions regarding their inspection equipment, the frequency of checks performed, and how they handle non-conformances.
Turnaround Time and Production Capacity
A critical factor in selecting a PCB soldering company is its ability to meet your production timelines. This involves evaluating their production capacity, lead times, and flexibility to handle projects of varying scales, from initial prototypes to large-scale manufacturing runs, ensuring your project progresses smoothly without unnecessary delays.
| Factor | Description | Implication for PCB Soldering Company Selection |
|---|---|---|
| Production Capacity | The volume of PCBs a company can solder within a given timeframe. | Ensures the company can handle your project's scale without bottlenecks or delays. |
| Lead Time | The time between placing an order and receiving the finished PCBs. | Impacts your overall project timeline and time to market; shorter lead times are generally preferable. |
| Flexibility | Ability to adjust to changing project specifications, urgent orders, or different order volumes. | Essential to manage unexpected project changes and maintain production efficiency. |
| Scalability | Ability to handle both prototype and high-volume production efficiently. | Indicates the company's long-term capabilities and suitability for growing production requirements. |
To effectively assess a PCB soldering company's turnaround time and production capacity, inquire about their typical lead times for various order sizes and complexity, their scheduling process, and their capacity planning approach. Request data on their historical on-time delivery performance and understand their processes for managing unforeseen circumstances. Choose a company that offers transparent communication, realistic delivery timelines, and the capacity to grow with your production needs. A well-planned production schedule contributes directly to a successful product launch.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Soldering
This section addresses frequently asked questions regarding PCB soldering, providing clear and concise answers to common queries about the process, costs, and industry landscape, focusing on the perspective of a PCB soldering company.
- What are the different terms used for PCB soldering?
PCB soldering is often referred to as circuit board soldering or electronics assembly soldering. While the end goal is to create reliable electrical connections between components on a PCB, the specific terminology may depend on the context within the industry. - Which PCB soldering company is considered the best?
The 'best' PCB soldering company varies depending on individual project needs, including factors such as complexity, volume, industry, and required certifications. There isn't a universally 'best' company; instead, the optimal choice should align with the specific requirements and technical demands of the project. Factors such as certifications (ISO, AS9100), experience, equipment, and testing capabilities should be evaluated to determine suitability. - What factors influence PCB assembly cost?
PCB assembly costs are influenced by several factors, including the complexity of the board design, the quantity of components, type of components (SMT or through-hole), the number of boards required (volume), material costs, special handling requirements (such as lead-free soldering), the required turnaround time, and specific testing or quality control protocols. A higher complexity or smaller batch sizes typically increases per-unit cost. - Who are the largest PCB suppliers in the industry?
While there are many significant players in the PCB supply chain, the term 'largest' can be defined by several criteria, such as revenue, volume, or global presence. Key industry players include both manufacturers of bare PCBs and companies that provide full-service assembly and soldering. Some examples include industry giants such as TTM Technologies and those with a strong global presence such as Foxconn. It is important to note that focusing on the capabilities of the soldering service provider rather than the bare board supplier is a more practical approach to ensure the quality of your product. - What are the main methods used by a PCB soldering company?
The primary methods employed by PCB soldering companies include hand soldering, wave soldering, reflow soldering, and selective soldering. Hand soldering is typically used for prototyping and small production runs, while wave soldering is suitable for through-hole components. Reflow soldering is the standard for SMT components, and selective soldering is used for more complex boards that require specific areas to be soldered. The method selected is determined by the design, volume, and technology used on the PCB. - Why is it important to check the quality and inspection process of a PCB soldering company?
Rigorous quality control and inspection is critical to ensure high reliability, reduce defects, and meet industry standards. Quality checks such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), X-ray inspection and functional testing are necessary to detect imperfections in solder joints or component placement. A comprehensive inspection process reduces the risk of faulty PCBs and prevents costly recalls. - What does it mean for a PCB soldering company to be certified?
Certification indicates that a company meets the standards specified by an independent body in their field. Common certifications for PCB soldering companies include ISO 9001 (Quality Management System), AS9100 (aerospace and defense industry), and IATF 16949 (Automotive Industry). These certifications demonstrate that the company has established processes and standards, and is commited to consistently providing quality services.
The Future Trends in PCB Soldering Technologies
The PCB soldering landscape is continually evolving, driven by the demand for increased precision, efficiency, and miniaturization. Emerging trends are leveraging robotics, artificial intelligence, and advanced materials to transform soldering processes.
These advancements not only improve the quality and reliability of soldered connections but also address the challenges of handling increasingly complex PCB designs and component packages. The integration of these technologies is expected to significantly impact the future of PCB assembly and manufacturing.
- Robotics and Automation
The incorporation of robotic systems in soldering is increasing, particularly for high-volume production. Robots enhance precision, speed, and repeatability, thereby decreasing error rates and improving output consistency. Automated soldering systems are becoming more sophisticated with advanced vision systems, ensuring accurate component placement and solder application. - Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML algorithms are being developed for solder joint inspection and quality control. AI-driven systems can detect minute soldering defects that might escape human detection. Furthermore, machine learning algorithms can optimize soldering parameters by predicting and preventing failures. These capabilities lead to higher yields, reduced rework, and more reliable products. - Advanced Soldering Materials
Research and development into new solder alloys are ongoing. These include alloys with improved mechanical properties, higher melting points, and better compatibility with lead-free regulations. Nanomaterials are being explored to enhance the solder's conductivity and joint reliability, particularly for fine-pitch components and advanced applications. These developments lead to more robust and reliable PCB connections. - Smart Soldering Systems
Emerging smart soldering systems integrate sensors, software, and network connectivity. These systems offer real-time monitoring of soldering parameters (e.g., temperature profiles) and allow for dynamic adjustments based on process feedback. This data-driven approach is a shift from static soldering protocols to a more adaptable and predictive strategy that enhances efficiency and optimizes results - Laser Soldering
Laser soldering uses focused light energy to precisely melt the solder joint, offering highly localized and controlled heating. This method is particularly valuable for extremely small or heat-sensitive components. The advantages include reduced heat stress to components, precise control of heat application, and faster processing, making it increasingly applicable in advanced electronics manufacturing. - 3D Soldering Technologies
With the rise of 3D electronics and vertically stacked devices, novel soldering technologies are being explored to ensure reliable connections in three-dimensional configurations. These technologies focus on materials, processes, and equipment capable of handling multi-layer interconnects and intricate geometries, enabling more sophisticated electronic devices.
Choosing the right pcb soldering company is critical to ensuring the quality and reliability of your electronic products. By carefully considering the soldering methods, the company's capabilities, pricing, quality measures, turnaround times, and future trends, you can select a reliable partner that helps you deliver top-tier results in the competitive market. Always do your due diligence and make an informed choice to secure your product's success. [pcb soldering company] is an important factor in your supply chain.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA