Choosing the Right SMT Assembly Company: A Comprehensive Guide

In today's technology-driven world, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is the backbone of modern electronics manufacturing. Selecting the right SMT assembly company is crucial for ensuring the quality and efficiency of your products. This article delves into the key factors to consider when choosing an SMT assembly partner, exploring leading companies and providing actionable advice to guide your decision. We will explore the nuances of SMT assembly process and its impact on product development, helping you better understand the significance of choosing an experienced and reliable partner in this domain.
Understanding SMT Assembly Basics

Surface Mount Technology (SMT) is the dominant method for assembling electronic circuits, facilitating the direct mounting of components onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). This approach, crucial in modern electronics, contrasts with older through-hole technology and enables higher component density, reduced board size, and improved manufacturing efficiency.
- SMT Component Types
SMT encompasses a variety of components including resistors, capacitors, inductors, diodes, transistors, and integrated circuits, all designed with flat terminations for surface mounting. - PCB Design for SMT
Effective SMT assembly hinges on a well-planned PCB layout, where the footprint of each component is accurately designed to ensure reliable soldering. - SMT Assembly Process Overview
The process typically involves applying solder paste, placing components with automated machinery, reflow soldering, and inspection, all of which are crucial for a successful final assembly.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting an SMT Assembly Company
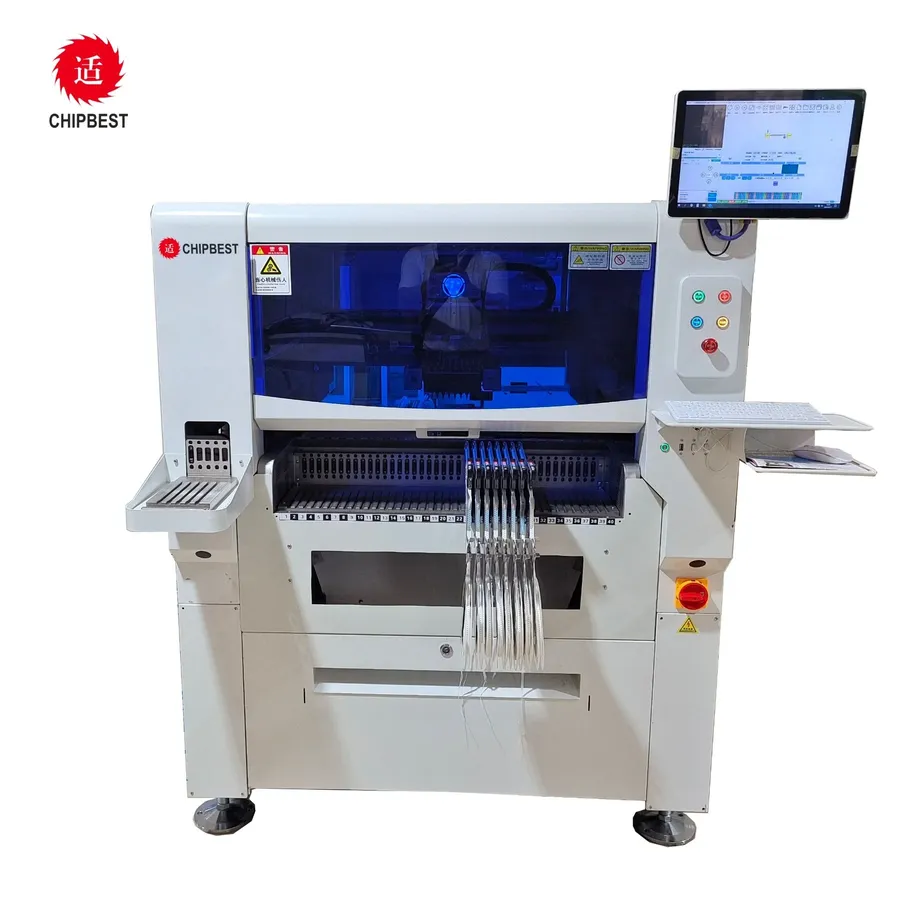

Selecting the right SMT (Surface Mount Technology) assembly company is crucial for ensuring the quality and reliability of your electronic products. This section outlines the key factors you should consider to make an informed decision, focusing on technological capabilities, experience, certifications, quality control, and production flexibility. Evaluating these aspects thoroughly can help you choose a partner that aligns with your specific project needs and long-term goals.
- Technological Capabilities
Assess the company's equipment and technology. Do they use modern pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens, and inspection systems? Their technology should be capable of handling your specific component types and assembly requirements, including fine-pitch components and specialized packages. Consider whether they offer advanced technologies like X-ray inspection for BGA packages and automated optical inspection (AOI) for quality assurance. - Experience and Expertise
Inquire about the company's experience in assembling similar types of boards or products. A seasoned SMT assembly partner will have a deep understanding of manufacturing challenges and best practices, ensuring they can efficiently navigate the complexities of your project. Verify that they have a qualified team of engineers and technicians skilled in PCB assembly. - Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that the company possesses relevant industry certifications, such as ISO 9001 or IATF 16949, which demonstrate a commitment to quality management. Certifications ensure that the company adheres to established standards for manufacturing processes, ensuring the consistency and reliability of their services. It indicates their compliance with environmental and safety regulations. - Quality Control Measures
Evaluate the SMT assembly company's quality control processes, including incoming material inspection, in-process checks, and final product testing. Rigorous quality control minimizes defects and ensures the reliability of assembled boards. A good quality system should be in place from the beginning of the process until the final product. - Production Flexibility
Assess the company's ability to handle different production volumes. Determine if they can accommodate your project needs, from prototyping and low-volume runs to mass production. A versatile company should also be able to manage changes in your project scope or requirements effectively, ensuring they can meet your fluctuating demands with consistent quality.
Top SMT Assembly Companies and Their Strengths
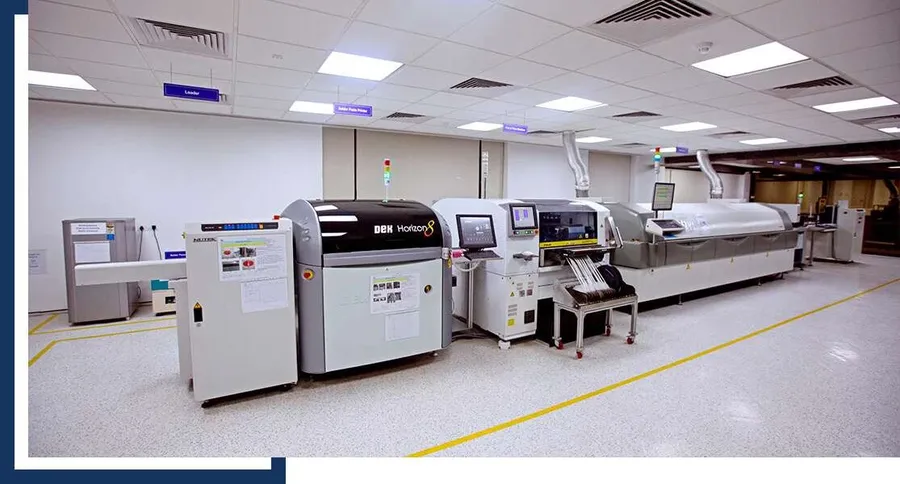

Selecting an SMT assembly company requires careful consideration of their capabilities, specialization, and reputation within the industry. This section provides a comparative analysis of several leading companies, highlighting their unique strengths and areas of expertise to help guide decision-making.
| Company | Specialization | Geographical Reach | Industry Focus | Key Strengths | Customer Base |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Company A | High-mix, low-volume production | North America, Europe | Aerospace, Medical, Industrial | Rapid prototyping, complex assemblies, strong quality control | Mid-sized and large companies with demanding quality and lead time requirements |
| Company B | High-volume, cost-effective solutions | Asia, Europe | Consumer electronics, Automotive | Scalable production capacity, competitive pricing, mature supply chain | High-volume manufacturers seeking cost-effectiveness |
| Company C | Specialized in fine-pitch and advanced assembly | Global | Telecommunications, High performance computing | Expertise in advanced technologies, R&D support, flexible solutions | Companies with specialized technology requirements |
| Company D | Prototype to small production runs | North America, Europe | Startup, Research & Development, IoT | Low volume production, fast turnaround times, strong engineering support | Emerging technology companies |
| Company E | Turnkey PCB assembly | Asia, North America | Consumer electronics, LED lighting | Component sourcing, manufacturing, assembly, and testing | Companies that need fully integrated turnkey services |
SMT Assembly Process: A Detailed Overview

The Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly process is a complex, multi-stage procedure that transforms bare printed circuit boards (PCBs) into functional electronic assemblies. This process involves precise application of solder paste, accurate placement of surface mount components, and carefully controlled reflow soldering, all facilitated by advanced equipment and rigorous process control.
- Solder Paste Application
The initial stage involves the application of solder paste, a mixture of solder alloy and flux, onto the PCB pads. This is typically achieved through a stencil printing process, where a thin stencil with apertures corresponding to the PCB pad locations is used to precisely deposit the paste. Automated screen printers are commonly employed, ensuring consistent and accurate solder paste deposition. Key considerations here include solder paste viscosity, stencil design, and printer settings, all of which significantly influence solder joint quality. - Component Placement
Following solder paste application, surface mount components are placed onto the PCB. This stage leverages pick-and-place machines, sophisticated robotic systems that select components from tape-and-reel feeders and precisely position them onto the designated locations on the PCB. These machines are programmed with detailed component placement data, ensuring high accuracy and speed. Component orientation, placement accuracy, and machine calibration are critical factors for avoiding defects at this stage. - Reflow Soldering
Once the components are placed, the PCB assembly is transferred to a reflow oven. This oven subjects the PCB to a controlled temperature profile, heating the solder paste to its melting point, allowing the solder to wet the component leads and form reliable solder joints. The reflow temperature profile is carefully designed to ensure proper soldering while preventing thermal damage to components and the PCB. This profile usually includes preheating, soaking, reflow, and cooling zones, each with specific temperature and time parameters. - Inspection and Testing
After reflow soldering, the assembled PCBs are thoroughly inspected for defects. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) systems are used to identify issues such as missing components, misaligned components, and solder joint defects. Further electrical testing, such as in-circuit testing (ICT) or functional testing, may be conducted to ensure that the assembled boards meet the required performance specifications. These tests can reveal defects not readily apparent through visual inspection. - Cleaning and Final Assembly
Depending on the application and quality standards, the assembled PCBs may be cleaned to remove flux residues left over from the soldering process. Finally, the assembled PCBs may undergo additional assembly operations like adding through-hole components, connectors, or enclosures. These steps depend on the design and intended function of the final electronic product.
Cost Factors in SMT Assembly
Understanding the cost drivers in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly is crucial for effective project planning and budget management. SMT assembly costs are influenced by a multitude of factors, each contributing to the overall expense. Optimizing these factors is key to achieving cost-effective, high-quality electronic products.
| Cost Factor | Description | Optimization Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Component Costs | The price of electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, integrated circuits (ICs), and connectors. | Design for availability; use standard, non-specialized parts; source components from reliable suppliers. |
| Labor Costs | Expenses related to manual labor involved in various stages, including machine operation, inspection, and testing. | Automate processes where feasible; optimize work flow; train personnel to improve efficiency; leverage experienced operators. |
| PCB Design Complexity | The intricacy of the printed circuit board (PCB), including layer count, trace density, and component density. | Simplify board design; reduce layers; use standard footprints; optimize component placement; collaborate closely with design team. |
| Assembly Volume | The number of units produced. | Negotiate favorable pricing for higher volumes; utilize batch processing and assembly lines; choose flexible partners. |
| Setup Costs | Initial expenses for setting up assembly lines, such as stencil creation, machine programming, and testing protocols. | Minimize variations in component footprint and design to reduce multiple setups; reuse programs where feasible; choose partners with flexible setup options |
| Testing and Quality Control | Expenses associated with various testing methodologies, including in-circuit testing (ICT) and automated optical inspection (AOI), and functional testing. | Implement design for testing (DFT) methodologies; optimize testing process; use reliable testing equipment; and incorporate testing at each stage of the assembly line. |
| Material Procurement | Costs associated with ordering components, storing parts, and logistics management. | Use vendor managed inventory; forecast demands accurately; reduce inventory carrying costs and time. |
| Rework and Repair | Expenses associated with diagnosing and correcting assembly errors. | Implement rigorous testing process; optimize the manufacturing process; choose partners with strong quality control measures. |
Frequently Asked Questions About SMT Assembly Companies
This section addresses common queries regarding SMT (Surface Mount Technology) assembly, offering clear and concise answers to help you better understand the industry and its processes.
- What exactly is an SMT assembly company?
An SMT assembly company specializes in the manufacturing of printed circuit boards (PCBs) using Surface Mount Technology. They handle the process of placing electronic components onto the surface of PCBs and soldering them in place, a method prevalent in modern electronics manufacturing. - What is the core meaning of SMT assembly?
SMT assembly refers to the process of mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB. Unlike through-hole technology, SMT components are smaller and are soldered onto the board surface, allowing for higher component density and automated manufacturing. - What are the typical costs involved in SMT assembly?
The cost of SMT assembly is influenced by several factors including the number of components, complexity of the PCB design, labor costs, materials, testing and order volume. Higher volumes usually result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Complex designs that require more advanced component placement or testing can increase costs. - Who are some of the largest SMT assembly companies globally?
Identifying the definitive 'top 10' can vary based on different market analyses. However, some of the leading players include Foxconn, Flex, Jabil, Pegatron, and others known for their extensive scale and global reach. These companies often have facilities across multiple countries. - How does SMT assembly differ from through-hole technology?
Surface Mount Technology (SMT) places components directly on the surface of the PCB, while through-hole technology requires components to have leads that pass through holes drilled in the board. SMT allows for higher density and smaller designs, making it suitable for modern electronics. - What are essential considerations when selecting an SMT assembly partner?
When choosing an SMT assembly company, consider their technology capabilities, experience in handling similar project types and volumes, certifications like ISO 9001, rigorous quality control, and their ability to communicate effectively and adapt to your specific requirements. They should also demonstrate a strong track record of timely delivery and customer satisfaction.
Future Trends in SMT Assembly

The landscape of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) assembly is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology, increasing automation, and the strategic integration of artificial intelligence. These trends are not only reshaping production processes but are also influencing the design, cost, and overall efficiency of electronic manufacturing.
- Advanced Automation and Robotics
The adoption of sophisticated robotic systems for component placement, soldering, and inspection is increasing. This leads to higher throughput, improved accuracy, and reduced human error, enhancing overall productivity and consistency. - Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Integration
AI and ML are being incorporated into various aspects of SMT assembly, including predictive maintenance of equipment, automated optical inspection (AOI) for defect detection, and process optimization to minimize waste and improve yield rates. - Miniaturization and High-Density Interconnect (HDI)
As electronic devices continue to shrink, SMT assembly must adapt to accommodate increasingly smaller components and higher densities. Techniques such as micro-BGA and chip-scale packaging are becoming more prevalent to meet these demands. - Enhanced Traceability and Data Analytics
Improved data collection and analytics throughout the assembly process allow manufacturers to monitor performance in real-time, identify bottlenecks, and implement process improvements. This level of transparency also enhances traceability and quality control, which are critical in highly regulated industries. - Flexible Manufacturing Systems
The need for agility and adaptability in production is driving the adoption of flexible manufacturing systems that can quickly switch between different products and production volumes. This trend supports the rise of high-mix, low-volume manufacturing environments. - Sustainable SMT Assembly Practices
Environmental concerns are pushing manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices such as using lead-free solders, reducing waste, conserving energy, and implementing closed-loop recycling systems. These green initiatives aim to minimize the environmental impact of SMT assembly processes.
These evolving trends are converging to define a new era of SMT assembly, one that is characterized by enhanced efficiency, improved product quality, and a greater ability to meet the dynamic needs of the electronics industry. Companies that embrace these changes are best positioned for long-term success.
Practical Tips for Working with an SMT Assembly Company
Effective collaboration with an SMT assembly company hinges on several key areas: design optimization for manufacturing, maintaining clear and consistent communication, implementing rigorous quality control, and establishing strong, long-term partnerships. These elements ensure a smooth and efficient production process, leading to high-quality results and reduced costs.
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Optimization
Implement DFM principles early in the design phase. This involves considering component placement, pad design, and routing to minimize assembly challenges. Share your design files and consult with the assembly company for design feedback. This iterative process helps to avoid costly revisions later. - Establish Clear Communication Channels
Maintain open and frequent communication with your SMT assembly partner. Clearly specify your requirements, including BOM accuracy, preferred components, required standards, and delivery timelines. Use clear documentation and utilize channels like email, project management software, or regular meetings to avoid misunderstandings. Consistent updates and prompt responses are essential. - Implement Robust Quality Control Measures
Define clear quality control criteria and expectations up front. Ensure that the assembly company has well-defined quality control procedures during production. Consider requesting inspection reports, functional testing at the assembly company, and perform thorough acceptance testing on your end. Regular quality audits can be valuable. - Build Long-Term Partnerships
View your relationship with an SMT assembly company as a long-term partnership rather than a transactional engagement. Foster a collaborative relationship by understanding their processes, expertise, and any limitations. This approach can lead to more streamlined processes, improved cost efficiency, and better overall project outcomes. Consistent engagements allow for the development of a reliable, high quality production pipeline. - Component Procurement Strategy
Discuss component procurement early and decide whether the assembly company or you will handle this process. Align on quality and sourcing practices. If you’re procuring components, verify they align to your BoM and are traceable back to the original manufacturer or authorized reseller. Also, specify component reel requirements. This can help eliminate errors during placement. - Detailed Assembly Documentation
Ensure the assembly company has all necessary documentation, including the Bill of Materials (BOM), Gerber files, pick-and-place files, and assembly drawings. Any special instructions or requirements should be clearly stated. Verify the accuracy and completeness of this documentation before starting any production.
Comparing SMT Assembly Company Services
Selecting the ideal SMT assembly partner requires a careful evaluation of their service offerings. This section provides a detailed comparison of common services provided by SMT assembly companies, enabling you to make an informed decision based on your specific project requirements. The key is to understand which company's strengths align with your project's needs in terms of scale, complexity, and required testing.
| Service | Description | Prototyping | Low Volume Production | High Volume Production | Testing Services | Material Procurement |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prototyping Services | Quick-turn assembly of small batches of PCBs for testing and design validation. | Yes | Often | Rarely | Limited | Often |
| Low Volume Production | Production of small to medium-sized batches, suitable for initial market releases or specialized applications. | Sometimes | Yes | Sometimes | Standard | Yes |
| High Volume Production | Large-scale production runs catering to products with significant market demand. | Rarely | Sometimes | Yes | Comprehensive | Yes |
| Testing Services | Includes functional testing, in-circuit testing (ICT), and other quality assurance checks. | Limited | Standard | Comprehensive | Yes | N/A |
| Material Procurement | Sourcing and management of all necessary components for assembly, reducing customer logistical burden. | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | Yes |
| Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Review | Analysis of PCB designs to identify and correct issues that could hinder the assembly process. | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | N/A |
| Supply Chain Management | Coordination and management of the component supply chain to ensure on-time delivery and prevent delays. | Yes | Yes | Yes | N/A | Yes |
Choosing the correct SMT assembly company is vital for the success of any electronics project. This article has provided a comprehensive overview of key factors, processes, cost considerations, and practical tips to help guide your selection process. By understanding the nuances of SMT assembly, and having a clear picture of the services offered by leading SMT assembly companies, businesses can make informed decisions to ensure high-quality and cost effective production of their electronic products. Partnering with a reputable [smt assembly company] can elevate your product and streamline your business operations.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA