Finding the Cheapest PCB: A Comprehensive Guide for Makers and Engineers
In today's fast-paced world of electronics, the need for cheap PCBs is more prevalent than ever. Whether you're a hobbyist working on a personal project or an engineer developing a new product, affordable PCB manufacturing is essential for bringing your designs to life. This article dives deep into the world of cheap PCBs, exploring various manufacturers, comparing their offerings, and providing insights to help you make informed decisions. Like the gears that power a watch, PCBs are the unsung heroes of modern technology. Let's unlock how to get them without breaking the bank.
Understanding Your PCB Needs

Before embarking on the journey of finding the cheapest PCB, it is crucial to meticulously define the specific requirements of your project. These requirements will directly influence the manufacturing cost and the final product's performance.
Key factors to consider include:
- Board Size
The dimensions of your PCB will determine the amount of material needed and, therefore, the cost. Standard sizes may be cheaper due to easier handling during manufacturing. - Layer Count
The number of conductive layers on your PCB is a key cost driver. Single or double-layer PCBs are significantly cheaper than multi-layer boards. - Material Requirements
The base material (e.g., FR-4, aluminum) and its thickness affect the price. Standard FR-4 is the most common and cost-effective choice for most applications. For higher performance needs, you might consider materials with better thermal or dielectric properties, but they will come at a higher price. - Quantity
The number of boards you order will impact the per-unit cost. Ordering in larger batches typically results in a lower price per PCB due to economies of scale. - Turnaround Time
The time required for manufacturing and delivery of your PCBs will affect cost. Express or expedited manufacturing services will often come at a premium, whereas slower service might offer cost savings.
By carefully assessing these factors before selecting a manufacturer, you can make informed decisions that will ensure the final product meets your project’s requirements, performance expectations and budget.
Let's dive deeper into understanding these elements:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Board Size | Directly Proportional | Larger boards require more material and processing time, increasing costs. Optimize board dimensions. |
| Layer Count | Exponential | More layers mean more complexity in manufacturing, causing a significant price hike. Evaluate your needs, consider using single-layer if possible. |
| Material | Variable | Standard FR-4 is cheapest, specialized materials like aluminum or high-Tg FR-4 are more expensive. Select the right material for your application |
| Quantity | Inversely Proportional | Higher quantities lead to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Consider batch sizes, calculate total cost, and reduce your order if possible |
| Turnaround Time | Directly Proportional | Faster manufacturing and delivery mean higher prices. Plan your schedule, and be flexible about the delivery time if possible. |
Major Players in the Cheap PCB Market
The landscape of cheap PCB manufacturing is dominated by a few key players, each offering varying strengths, weaknesses, and pricing structures. Understanding these nuances is crucial for selecting the best fit for your project. This section provides an overview of some of the most popular manufacturers.
- JLCPCB
Known for its extremely competitive pricing, especially for small quantities and simple designs. Offers a wide range of services, including PCB assembly. Their online platform is user-friendly, providing instant quotes and order tracking. They are a popular choice for hobbyists and small-scale projects but have been criticized for occasional quality inconsistencies and longer shipping times for some regions. Data suggests they maintain a price advantage for prototype quantities below 100 boards and are frequently used for 2-4 layer PCB's. (Source: Numerous maker forums and online comparisons) - PCBWay
A strong contender in the cheap PCB market, PCBWay provides a balance between cost and quality. They have a more extensive selection of advanced materials and technologies compared to JLCPCB and have a strong reputation for good customer support. Their pricing is often slightly higher but are known for their faster shipping, particularly for those based in North America. PCBWay provides excellent documentation and has a highly responsive support team, making them more appealing for complex or higher reliability projects. (Source: Industry reviews and independent benchmarking sites) - Seeed Studio
Seeed Studio is a well established manufacturer popular for its emphasis on open-source hardware. Seeed Studio also facilitates direct sales of various components, which can be beneficial when the design includes parts outside standard vendor libraries. While their pricing is typically higher than JLCPCB, Seeed Studio has a good reputation for quality and is a frequent choice for boards that require a higher level of precision. They also offer a variety of assembly services and development boards. (Source: User community feedback and their business model) - Others
Other manufacturers in the cheap PCB market include ALLPCB, Elecrow, and more region specific manufacturers. While these may have some benefits including unique offerings, most of the market share is held by the aforementioned companies. As pricing fluctuates, It’s beneficial to compare all options before making a decision.
| Manufacturer | Typical Pricing | Strengths | Weaknesses | Best Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JLCPCB | Very competitive for small quantities | Lowest Prices, user-friendly platform, wide range of services. | Occasional quality inconsistencies, longer shipping times. | Hobbyist projects, prototyping, simple PCB designs |
| PCBWay | Competitive, slightly higher than JLCPCB | Good balance of cost and quality, wider range of materials, good customer support. | Slightly higher cost than JLCPCB. | More complex projects, medium-scale production, when reliable delivery is needed. |
| Seeed Studio | Higher than JLCPCB | Strong quality, component sourcing, supports open source. | More expensive, less focused on extremely low costs. | Higher precision projects, open-source projects, projects that require components from their catalog. |
| Other Manufacturers | Varies based on manufacturer | Some unique offerings, can be good for very niche circumstances | Can be less reliable, can have poor customer support. | Research the company to find out before committing to a board. |
Price Comparison: A Detailed Look
Understanding the cost structure of PCB manufacturing is crucial for selecting the most economical option. This section provides a detailed comparison of pricing across various manufacturers, taking into account key factors that influence the final cost, such as board dimensions, production volume, layer count, and shipping fees.
The cost of a PCB is not uniform across manufacturers. It's essential to perform a comparative analysis to make an informed decision. This analysis will demonstrate the variations in pricing models.
| Feature | JLCPCB | PCBWay | Seeed Studio | Other (Hypothetical Manufacturer) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Basic 2-Layer Board (100mm x 100mm) | $2 (5 boards) | $5 (5 boards) | $6 (5 boards) | $8 (5 boards) |
| 4-Layer Board (100mm x 100mm) | $7 (5 boards) | $12 (5 boards) | $15 (5 boards) | $18 (5 boards) |
| 10 Boards (100mm x 100mm, 2-Layer) | $4 | $8 | $10 | $15 |
| 10 Boards (100mm x 100mm, 4-Layer) | $12 | $18 | $22 | $25 |
| Additional Setup Costs | Minimal | Variable | Moderate | High |
| Shipping Costs (to USA, estimated) | $8-$15 | $10-$20 | $12-$25 | $15-$30 |
| Turnaround Time (Typical, days) | 3-7 | 5-10 | 7-12 | 7-14 |
Note: All prices are approximate and subject to change. Shipping costs and turnaround times may vary based on destination and current service levels. This table provides a general guideline for cost comparisons.
Key Factors Affecting PCB Pricing:
- Board Size
Larger boards require more material and processing, leading to higher costs. - Layer Count
PCBs with more layers are more complex to produce, resulting in increased expenses. - Quantity
Ordering in larger quantities often reduces the per-unit cost due to economies of scale. - Material
Specialized materials or substrates can substantially raise the price. FR-4 is the standard but specific needs might require more expensive materials. - Finishes
Different finishes like ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) or HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) have different costs associated with them. - Turnaround Time
Faster turnaround times usually come with premium prices. Rush services incur higher fees. - Shipping Location
The cost and time to ship PCBs will vary by location.
Quality vs. Cost: Striking the Right Balance

Finding the cheapest PCB shouldn't mean sacrificing essential quality and performance. This section explores the necessary trade-offs between cost and quality, providing guidelines for ensuring your cheap PCB meets minimum specifications without compromising your project’s functionality.
The pursuit of the absolute lowest cost can sometimes lead to compromises in quality. Understanding where you can afford to cut back and where you must maintain standards is key. Some of the key areas to focus on include material quality, fabrication tolerances, and surface finish.
- Minimum Specifications Checklist:
Consider these areas carefully when evaluating a low-cost PCB manufacturer: - Material Grade:
Ensure the PCB material (e.g., FR-4) meets the required temperature and mechanical stress. Lower grade materials may affect the longevity and reliability of your board. - Fabrication Tolerances:
Verify minimum track width/spacing tolerances to avoid short circuits or opens. Cheaper fabs may have less accurate processes which could impact your designs. - Via Quality:
Inspect the quality of vias, ensuring proper plating and no broken connections. Poor via plating can lead to intermittent failures. - Solder Mask and Silkscreen:
Confirm that the solder mask is well aligned and silkscreen is legible. Poor alignment can make assembly difficult, and if silkscreen is missing or incorrectly placed you may have difficulties assembling your components - Surface Finish:
Evaluate the surface finish and its suitability for your application. The cheapest finish may not always be the best. HASL may work great in some cases but in others, you may require ENIG, Immersion Tin, etc.
It's important to recognize potential red flags that can indicate quality issues. These may include:
- Poor Communication:
A manufacturer with poor communication may also have poor processes or standards. If they are not easy to communicate with, you may run into issues should something not come out as you'd expect. This means you should look at customer service reviews. - Inconsistent Manufacturing:
If a company has inconsistent manufacturing you may have some boards that work well but others that don't. Check for reviews indicating inconsistent manufacturing. - Unwilling to Share Specifications:
A legitimate manufacturer will be open to sharing their manufacturing specifications. - Unusually Low Pricing:
If a price seems too good to be true, it is often best to be cautious. Such a low price may indicate that the manufacturer is cutting corners somewhere in production
| Feature | High-Quality PCB | Low-Cost PCB | Potential Tradeoffs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material | High-grade FR-4, Rogers | Standard FR-4, lower grade | Mechanical strength, temperature resistance |
| Fabrication Tolerances | Tighter tolerances, higher accuracy | Wider tolerances, lower accuracy | Circuit performance, reliability |
| Via Quality | Precise plating, reliable connections | Potential for poor plating, intermittent connections | Signal integrity, reliability |
| Surface Finish | ENIG, Immersion Tin, HASL | HASL (potentially low-grade) | Solderability, environmental resistance |
| Quality Control | Comprehensive quality checks | Potentially minimal checks | Defect rate, final product yield |
In summary, choosing the right PCB involves a balance. While cost is important, it should not be the only factor. By understanding the necessary specifications and potential trade-offs, you can make informed decisions that result in a cost-effective yet functional and reliable PCB.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cheap PCBs
Navigating the world of cheap PCBs can raise many questions. This section addresses some of the most common inquiries, providing clear and concise answers to help you make informed decisions about your PCB manufacturing needs.
- What is the most economical PCB finish?
Among the various PCB finishes, HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) is generally the most cost-effective. It's a reliable finish that provides good solderability, making it a popular choice for budget-conscious projects. However, it may not be ideal for very fine-pitch components or where surface planarity is critical, in which case ENIG is generally the cheapest option for a more flat surface finish. - What's the least expensive method for making a PCB?
The cheapest method for creating PCBs typically involves ordering from budget-friendly overseas manufacturers, like JLCPCB or PCBWay, especially when opting for standard specifications and larger production quantities, which benefit from economies of scale. DIY methods, such as etching your own boards, can seem cheaper initially, but often incur more cost due to the required chemicals, equipment, and time investment, often at the sacrifice of quality. - How much does a single PCB generally cost?
The cost of a single PCB can vary dramatically based on its size, layer count, complexity, and the manufacturer you choose. It could be as low as a few dollars for a small, single-layer board from a budget manufacturer like JLCPCB in the context of a larger order, to several hundred for a complex, multilayer board with specialty features. For small orders, the cost per board is significantly higher due to setup and handling costs. - What should a reasonable cost for a PCB be?
A 'reasonable' cost for a PCB depends heavily on the board's specifications and the intended application. For hobbyists or simple projects, a few dollars to tens of dollars per board is reasonable when ordering in a small quantity. For professional applications demanding high precision, multilayer PCBs, specialized materials and finishes, the cost per board could range from tens to hundreds of dollars. Benchmarking against industry standards and comparing quotes from multiple manufacturers is recommended to determine a reasonable price. - Do larger PCBs cost more than smaller PCBs?
Yes, generally larger PCBs cost more than smaller ones. This is because the cost of raw materials increases with the board area and it takes more time to process larger PCB's in manufacturing, therefore increasing cost. Also, larger PCBs will incur higher shipping costs due to the larger size and weight. - How does the number of layers impact the cost of a PCB?
The cost of a PCB increases with the number of layers. Each additional layer requires more manufacturing steps, increasing the time, materials, and complexity of the manufacturing process. This translates to a significant increase in cost. Typically, a four-layer board is considerably more expensive than a two-layer one, and this increase continues for boards with more layers. Therefore, for cost-conscious projects, keeping the number of layers to a minimum is crucial. - Does the PCB material affect the price?
Yes, the type of PCB material used significantly impacts the price. Standard FR-4 material is the most common and cost-effective option. Materials such as Aluminum, Rogers or high-Tg FR-4, used for high-frequency or high-temperature applications, are more expensive due to their specialized properties, greater material costs and additional manufacturing requirements.
Beyond Price: Other Factors to Consider When Choosing a PCB Manufacturer
While price is a significant factor when sourcing PCBs, several other elements critically influence the overall experience and the final product's suitability for your project. These factors encompass not just cost but also the practical aspects of production, delivery, and long-term reliability.
- Customer Support
Responsive and knowledgeable customer support can be invaluable, especially when dealing with complex designs or unexpected issues. Look for manufacturers who offer multiple communication channels and have a reputation for timely and helpful assistance. - Shipping Time and Reliability
The time it takes for your PCBs to arrive can significantly impact your project timeline. Consider both the manufacturer's production time and the shipping duration, as well as the reliability of their shipping methods. Some manufacturers offer expedited shipping options for urgent projects. - Available PCB Finishes
The choice of surface finish affects the solderability, corrosion resistance, and overall durability of the PCB. Common finishes include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative). The appropriate finish depends on the specific application and performance requirements. ENIG, for example, offers superior corrosion resistance but at a higher cost. - Design Rule Checks (DRC)
A comprehensive DRC process ensures that your design meets the manufacturer's capabilities and identifies potential issues before production. This process helps prevent errors, reduces the risk of manufacturing failures, and ultimately saves time and money. Manufacturers with robust DRC systems can offer valuable design feedback. - Component Sourcing and Assembly Services
Some manufacturers offer component sourcing and PCB assembly services, which can simplify the production process. This service can be particularly useful for larger projects or when you need a complete turnkey solution. Evaluate the costs, quality, and turnaround times associated with these services.
These factors, alongside cost, collectively determine the overall value and suitability of a PCB manufacturer. Ignoring them may lead to unexpected delays, quality problems, or increased overall project costs. A holistic evaluation is essential to secure the best result.
Optimizing Your PCB Design for Cost-Effectiveness
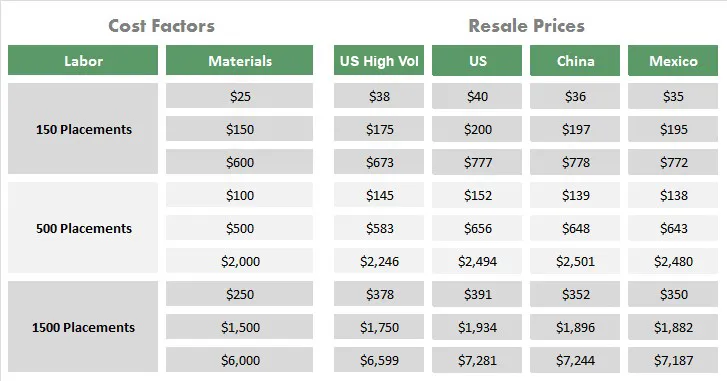
Smart PCB design choices significantly impact manufacturing costs. This section provides practical strategies to minimize expenses without compromising functionality, focusing on design elements that directly influence production efficiency and material usage.
By understanding the manufacturing process and making informed design decisions, you can significantly reduce the cost of your PCBs. Let's explore some actionable strategies.
- Panelization
Maximize board space on the manufacturer's panel by panelizing your designs. Combining multiple instances of your board or different designs into a single production panel reduces per-unit costs. Consider the manufacturer's panel sizes and required spacing for efficient panelization. - Standard Component Selection
Utilize readily available standard components. Using standard sizes, packages, and common values helps reduce the cost due to reduced setup time and readily available stocks at the manufacturers. Avoid obscure or hard-to-find components. - Minimize Layers
The number of layers significantly impacts cost. Use fewer layers whenever possible. Complex designs often require multi-layer boards, but simpler circuits should be designed for single or double-layer PCBs. - Simplify Board Shape
Complex board shapes increase manufacturing time and material waste, leading to higher cost. Opt for simple rectangular or square shapes unless absolutely necessary for your application. - Adequate Spacing and Traces
Adhere to the manufacturer’s recommended spacing for traces and vias. Violating minimum spacing rules increases the risk of defects and can add extra cost if the design is not manufacturable. Consistent spacing avoids unnecessary extra manufacturing steps. - Minimize the use of Vias
Each via requires drilling and plating. Reduce the number of vias to lower costs. Consider layer routing strategies to minimize vias. - Standard Trace Widths and Spacing
Stick to standard trace widths and spacing, which are usually 6 mils. Deviation can increase fabrication costs. For example, extremely fine traces may increase the cost. - Efficient Layout Techniques
Optimize your component placement for easy routing. Avoid complex routing patterns which might need advanced manufacturing techniques. Proper layout technique saves time and resources. - Avoid Unnecessary Features
Eliminate any features that are not critical to the functionality of the PCB. Any unneeded features will increase the production time and increase costs.
| Design Choice | Impact on Cost | How to Optimize |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Layers | Increased cost with more layers | Use single or double layers for simpler designs |
| Board Shape | Complex shapes increase costs | Use simple rectangular shapes |
| Component Choice | Special or non-standard parts increase costs | Stick to common, readily available components |
| Panelization | Panelization reduces cost per board | Use manufacturers guidelines for optimum panelization |
| Vias | Excess vias increase cost | Optimize layer routing to minimize vias |
| Trace Width/Spacing | Non-standard trace width and spacing increase costs | Use standard 6 mils trace width and spacing unless application specific |
| Unnecessary Features | Extra features can increase the production cost | Remove any non-essential features from the PCB. |
Geographic Considerations: Local vs. Overseas for Cheap PCBs

The decision of where to manufacture your PCBs—locally or overseas—extends beyond mere cost, significantly impacting lead times, shipping expenses, communication, and even environmental footprints. This section delves into the multifaceted aspects of this choice when seeking a cheap PCB solution.
When sourcing PCBs, especially with an eye on budget, geographical location presents a crucial trade-off. While overseas manufacturers often boast lower unit costs, local producers may offer advantages in turnaround time, communication clarity, and, potentially, reduced total cost when factoring in all variables.
| Factor | Local Manufacturers | Overseas Manufacturers |
|---|---|---|
| Unit Cost | Often higher | Often lower |
| Shipping Costs | Generally lower, faster, and more predictable | Generally higher, slower, and with less predictable timelines |
| Lead Time | Shorter lead times, faster turnaround | Longer lead times, potential for delays |
| Communication | Direct communication, fewer language barriers | Communication challenges, potential language barriers |
| Quality Control | Easier quality control, more direct oversight | Quality control challenges, longer correction loops |
| Minimum Order Quantity | Potentially lower, more flexible options | May have higher minimum order quantities (MOQs) |
| Customs and Importation | Minimal customs issues within the same country | May encounter customs delays and tariffs |
| Environmental Impact | Lower carbon footprint due to reduced transportation | Higher carbon footprint from international shipping |
| Support Local Business | Directly supports local economies | Does not contribute to local economic growth |
The perceived cost advantage of overseas manufacturers is not always the final outcome when all associated costs and potential delays are considered.
- Local PCB Manufacturing Advantages:
Often allows for rapid prototyping and faster design iterations due to shortened communication and shipping times. The ability to readily visit the facility and communicate directly with staff enables better quality control and reduces the risk of miscommunication. - Local PCB Manufacturing Disadvantages:
Unit costs are generally higher than their overseas counterparts. This difference may be due to higher labor costs, environmental regulations, or other factors related to domestic production. - Overseas PCB Manufacturing Advantages:
Often provides significantly lower unit costs due to lower labor and production expenses. This can be especially important when large production volumes are needed. - Overseas PCB Manufacturing Disadvantages:
Longer lead times from production to delivery, often several weeks, which can impact project timelines. Communication difficulties may arise due to language or time-zone differences. Shipping issues such as delays, damages, or customs issues may add unexpected costs.
Ultimately, the choice between a local and overseas manufacturer hinges on a balance between cost, time, quality, and communication. If rapid turnaround and direct communication are paramount, local manufacturers may be the better choice despite higher unit costs. However, if unit costs are the primary concern and longer lead times are acceptable, overseas manufacturers often offer a more economical solution.
Evaluate your project's specific requirements and weigh the pros and cons of each option to make an informed decision.
Choosing the Right PCB Manufacturer: Step-by-Step Guide
Selecting the optimal PCB manufacturer is crucial for project success, balancing cost with required quality and service. This step-by-step guide will help navigate the decision process, ensuring you choose a manufacturer that meets your specific needs and project scope.
- Define Your Project Requirements
Start by clearly outlining your PCB specifications: dimensions, layer count, material (e.g., FR-4, aluminum), copper thickness, required finishes (HASL, ENIG), tolerances, and impedance control needs. Also, determine the quantity required and your desired lead time. - Shortlist Potential Manufacturers
Based on your project requirements, create a list of potential manufacturers. Consider those discussed previously (JLCPCB, PCBWay, etc.) and others you may have found, and verify if they offer the required capabilities, technologies and materials. - Request Quotes
Submit your design files (Gerber files, BOM) to the shortlisted manufacturers. Be precise and ensure you include all your requirements and specifications in the request for quotation (RFQ) process. Comparing costs is crucial and ensure all factors like manufacturing cost, shipping and duty if any, are considered. - Evaluate Quotes & Compare
Carefully analyze the received quotes. Don't just focus on the base price; consider shipping costs, potential tooling fees, and lead times. Compare total costs, not just the per-unit price and make sure there are no hidden or unexpected costs. Factor in shipping time and your own timelines for PCB assembly and project completion. - Assess Quality and Reviews
Investigate the quality assurance processes of each manufacturer. Look for certifications (e.g., ISO 9001) and read customer reviews or testimonials. Verify the manufacturer’s reputation, looking for feedback on their adherence to schedules and the quality of their output. Sample production is usually advisable. - Check Customer Support and Communication
Evaluate the responsiveness and quality of their customer support. Clear, professional, and effective communication is essential, especially if issues arise during manufacturing. A robust support system should be available with effective communication channels. - Consider Shipping and Lead Time
Evaluate shipping options, including costs and transit times. This is critical to meet deadlines. The manufacturer should be able to consistently adhere to agreed timelines, and be able to provide real time updates on shipping if requested. - Select a Manufacturer and Place Your Order
Once you are satisfied with the chosen manufacturer, proceed with placing the order and making all the relevant payments. Always review final order and documentation to avoid errors.
By following these structured steps, you can make an informed decision and choose a PCB manufacturer that aligns with both your project's budget and technical requirements, ensuring the best possible outcomes.
Finding a cheap PCB doesn't mean sacrificing quality. By understanding your needs, carefully comparing manufacturers, and optimizing your designs, you can get the PCBs you need without draining your resources. The world of cheap pcb manufacturing is constantly evolving, so staying informed and adapting your strategies is key. As technology progresses, so do the options for creating the boards that power our innovations. We hope this guide has given you the knowledge to select a cheap PCB source for your next project.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA