Navigating the Landscape of Top Electronics Assembly Companies
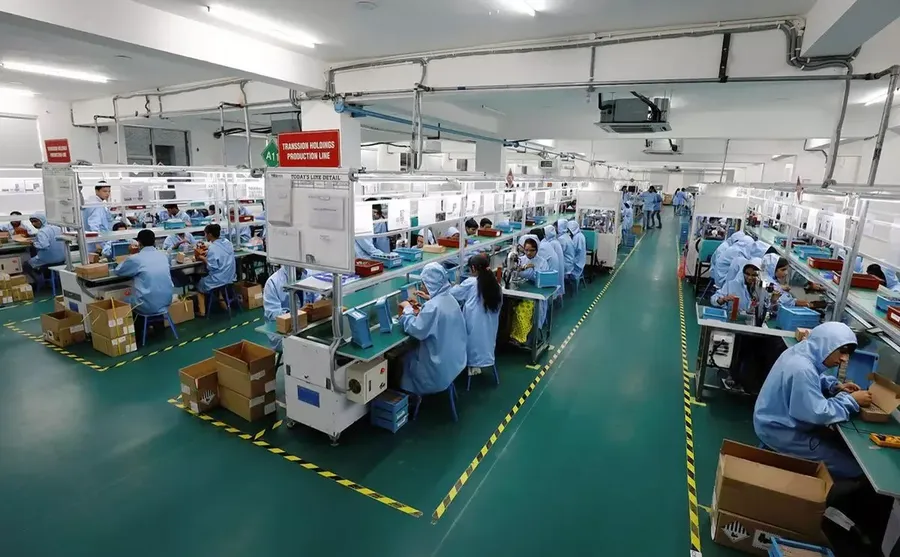

In today's interconnected world, the role of electronics assembly companies is more critical than ever. From smartphones to medical devices, these companies are the unsung heroes, transforming designs into tangible products. This article will delve into the intricacies of the electronics assembly industry, offering a guide to the top players, their services, and key considerations when selecting a partner. Think of these companies as the engine that turns the wheels of modern technological advancements.
Understanding the Electronics Assembly Industry

The electronics assembly industry is the backbone of modern technology, encompassing the intricate processes required to manufacture electronic devices. This crucial sector involves assembling various components onto printed circuit boards (PCBs), transforming raw materials into functional electronic products through precise techniques like Surface Mount Technology (SMT), Through-Hole Technology (THT), and mixed assembly methods. Quality, precision, and efficiency are paramount, given the complexity and sensitivity of the products, directly influencing performance and reliability, and highlighting the critical role these companies play in the global supply chain.
The processes involved in electronics assembly are diverse, each having specific applications and requirements:
- Surface Mount Technology (SMT)
SMT involves mounting electronic components directly onto the surface of a PCB. This method is widely used for high-density assemblies due to its efficiency and suitability for automated manufacturing processes, allowing for smaller, more compact devices. Components are soldered to the PCB using automated machinery, ensuring precise placement and consistent connections. - Through-Hole Technology (THT)
THT involves inserting component leads through pre-drilled holes on the PCB and soldering them on the opposite side. This technology is often used for larger or more robust components that require stronger physical connections and is generally better suited for handling higher mechanical stresses. - Mixed Technology Assembly
Mixed technology assembly combines both SMT and THT methods on the same PCB. This approach is often used in more complex devices that have a variety of components with differing assembly requirements. It requires a flexible and skilled assembly process.
The electronics assembly industry is heavily reliant on advanced machinery and skilled labor. The overall process involves several stages, each requiring careful planning and execution, it is not just about assembling components, it's about ensuring the entire product lifecycle, from design to finished product, meets the stringent quality and performance requirements.
Key Services Offered by Electronics Assembly Companies
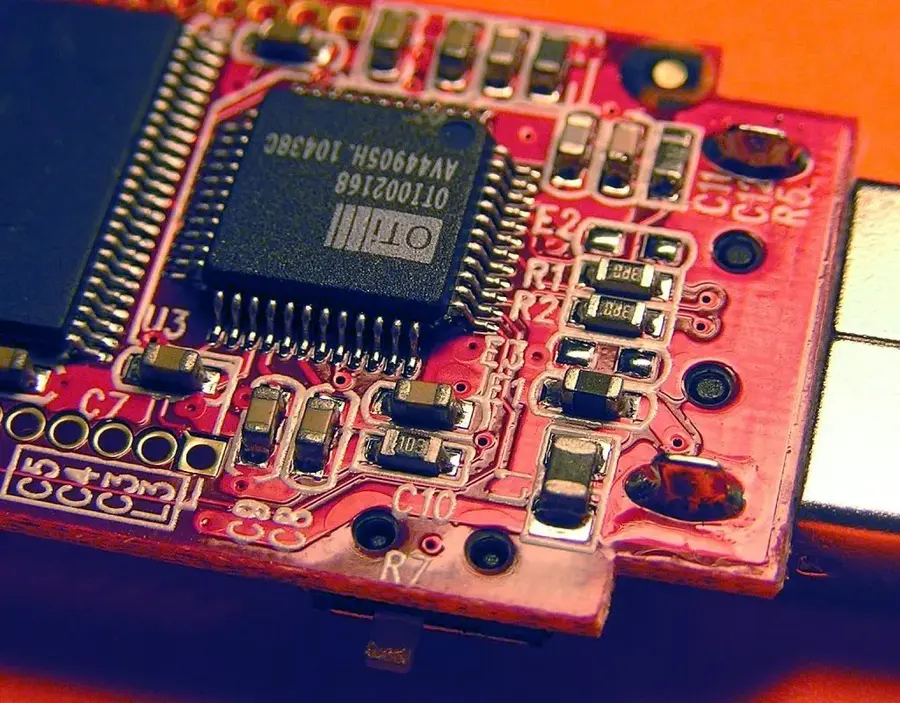
Electronics assembly companies provide a diverse array of services essential for the creation of modern electronic devices. These services encompass the entire product lifecycle, from initial design and prototyping to full-scale manufacturing and testing, playing a crucial role in bridging the gap between circuit design and functional electronic products.
| Service | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| PCB Assembly | Population of printed circuit boards with electronic components using Surface Mount Technology (SMT), Through-Hole Technology (THT), or a combination. | Fundamental to creating functional electronic devices; ensures components are correctly placed and soldered onto the board. |
| Prototyping | Creation of initial models or samples to test designs, functionality, and feasibility before mass production. | Crucial for identifying design flaws and making necessary adjustments, minimizing risks in full-scale manufacturing. |
| Testing and Quality Control | Rigorous testing of assembled boards and devices to verify performance and compliance with standards. | Ensures the reliability and quality of the final product, safeguarding against defects and failures. |
| Full Turnkey Solutions | Comprehensive services that cover all aspects of manufacturing, from component sourcing to final product assembly and shipping. | Streamlines the manufacturing process, reducing management overhead and timelines for clients. |
| Design Services | Assistance with circuit board design, component selection and layout optimization, addressing manufacturability. | Ensures that the designs are optimized for manufacturability, reducing the risks of production errors and streamlining manufacturing process. |
| Component Sourcing | Procurement of electronic components from various suppliers, managing supply chain logistics. | Reduces client's effort in sourcing components, while leveraging company's existing supplier relationships and negotiation power. |
| End-to-End Assembly | Complete management of the assembly process from initial component kitting to final product packaging. | Simplifies the supply chain process, minimizing logistical complexities and ensuring smooth production flow. |
Top Global Electronics Assembly Companies
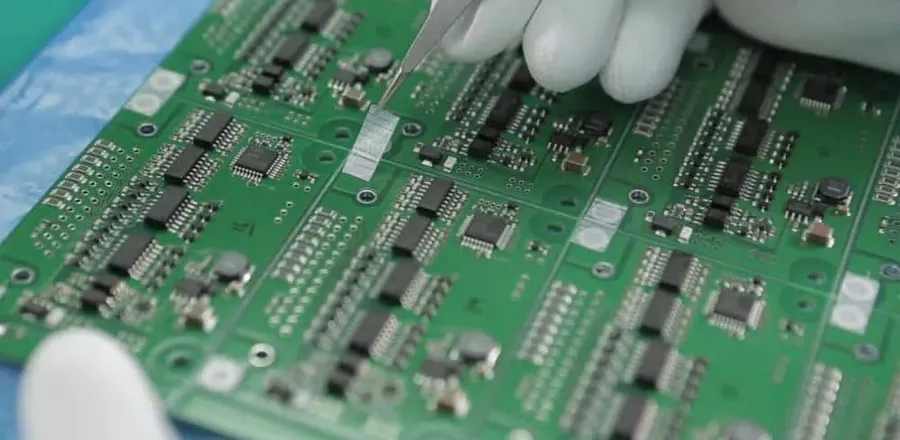
The global electronics assembly landscape is dominated by a few key players that provide comprehensive manufacturing solutions to various industries. These companies not only offer assembly services but also often extend their capabilities to design, prototyping, and supply chain management, demonstrating a commitment to quality, precision, and efficient production on a large scale.
| Company | Specialization | Strengths | Geographical Reach |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rayming Technology | Printed Circuit Board (PCB) assembly, SMT & Through-Hole | Offers comprehensive PCB assembly services with a focus on quality and flexibility. Known for its competitive pricing and fast turnaround times, excellent customer service. | Global, primarily serving North America, Europe, and Asia |
| Universal Scientific Industrial (USI) | System assembly, module design and manufacturing | Renowned for its expertise in miniaturization, advanced testing capabilities, and large-scale manufacturing capacity. Strong global presence with a diverse client base across multiple sectors. | Global, with manufacturing facilities across Asia, Europe, and the Americas |
| Flex | End-to-end supply chain, design & manufacturing | A leader in providing innovative solutions for diverse industries, leveraging its vast global network and technological expertise. Flex's focus on supply chain optimization and sustainability provides them an advantage. | Extensive global presence with manufacturing operations across multiple continents |
| Jabil | Full turnkey manufacturing, product design & supply chain | Known for its extensive global footprint and robust technological capabilities, specializing in highly complex assembly and engineering solutions. Jabil's strength lies in its scalability and ability to handle diverse product requirements. | Global, with facilities in North America, Europe, and Asia |
Leading Electronics Assembly Companies in the USA
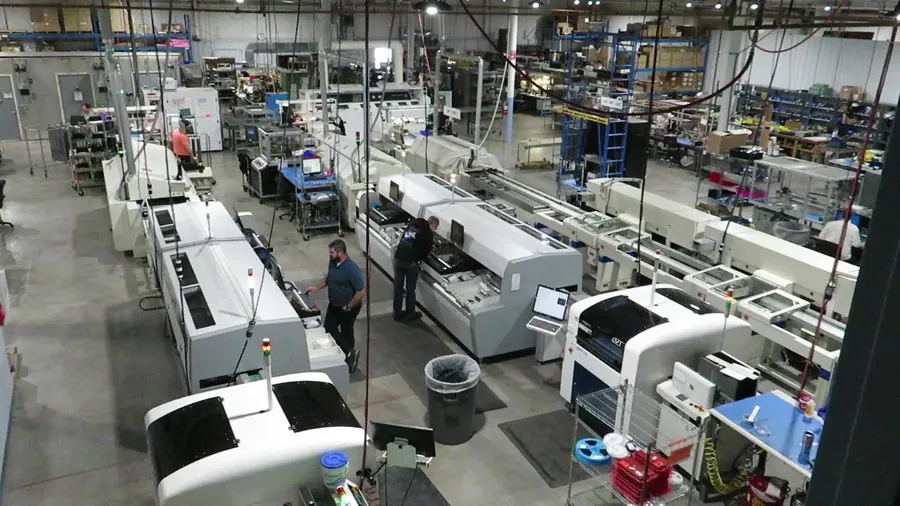

The United States boasts a robust electronics assembly sector, featuring a mix of large multinational corporations and specialized smaller firms. These companies are crucial in the production of a wide array of electronic products, from consumer devices to sophisticated industrial and aerospace components. Their regional strengths are diverse, catering to various industry niches and technological advancements.
Key players in the US market demonstrate varying expertise. Large tech companies such as Apple, Dell Technologies, Hewlett-Packard (HP), Cisco Systems, Intel, and Qualcomm, while primarily known for their own branded products, often have significant internal assembly operations and also contract out assembly work to other companies. Other companies specializing in electronics assembly services are crucial to the supply chain, offering their assembly services to these large technology companies, as well as other industries.
| Company | Industry Focus | Assembly Services | Regional Strength | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Apple | Consumer Electronics | Primarily Internal Assembly; Contract Manufacturing for some products | California | Known for high-volume manufacturing and innovative products; also contracts out to large EMS providers. |
| Dell Technologies | Computer Hardware | Primarily contract manufacturing | Texas | Specializes in PC assembly and server hardware. |
| Hewlett-Packard (HP) | Computer Hardware & Printing | Primarily contract manufacturing | California | Focus on PC and printer assembly. |
| Cisco Systems | Networking Equipment | Primarily contract manufacturing | California | Leading manufacturer of routers, switches, and other network products. |
| Intel | Semiconductors | Primarily internal assembly of their chips; some external assembly through other companies | California | Integrated device manufacturer that focuses on semiconductors. |
| Qualcomm | Semiconductors | Primarily internal assembly of their chips; some external assembly through other companies | California | Fabless semiconductor company specializing in wireless technologies. |
The service landscape in the US electronics assembly sector is diverse. Companies provide everything from basic PCB assembly to comprehensive turnkey solutions, encompassing design, component sourcing, and final product testing. Regional strengths vary, with California housing many tech giants, while other states host specialized assembly firms. The US market is characterized by a high demand for quality and innovation, with companies adapting to new trends in automation and miniaturization. Many of the companies in the US also provide services that comply with stringent quality standards, and specific industry regulations like medical, aerospace and military applications.
Factors to Consider When Choosing an Electronics Assembly Company
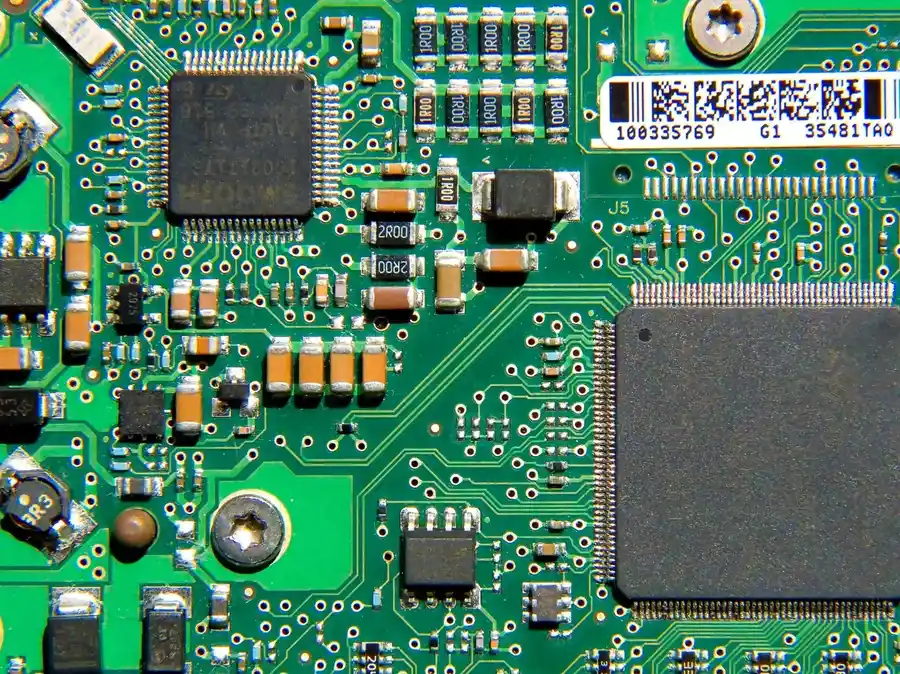
Selecting the right electronics assembly company is crucial for the success of any electronics project. This decision requires a thorough evaluation of several key factors, each of which can significantly impact project timelines, budget, and the overall quality of the final product. The checklist below provides a structured approach to evaluate potential partners, ensuring alignment with your project's unique requirements.
- Certifications (ISO, AS9100)
Verify that the company holds relevant certifications, such as ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 13485 (medical devices), or AS9100 (aerospace). These certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality and adherence to industry standards. - Technology Capabilities (SMT, Through-Hole, Mixed)
Ensure the company has the necessary technology for your specific assembly requirements, such as Surface Mount Technology (SMT), Through-Hole Technology (THT), or a mix of both. Confirm their ability to handle the complexity and density of your PCB designs. - Prototyping Services
Assess the company's capabilities in prototyping. Rapid prototyping is essential for design validation and iterative improvements. A capable partner will offer quick turnaround times, flexibility in design changes, and support to refine the design for manufacturability. Companies that can provide Design for Manufacturing (DFM) feedback are particularly valuable. - Scalability
Evaluate the company's capacity to scale production according to your needs, from small-batch prototyping to large-scale manufacturing. Verify that their infrastructure and processes can adapt to increasing demands without compromising quality or delivery times. - Cost
Consider the overall cost, not just the unit price. Evaluate the total cost, including material sourcing, assembly, and potential rework. Opt for transparency in pricing and a cost structure aligned with your budget. A low-cost provider may lead to hidden costs and delays. Focus on overall value rather than the lowest initial bid. - Lead Times
Inquire about lead times for both prototyping and mass production. Assess whether their timelines align with your project schedule. The ability to deliver on time is crucial to minimizing delays and ensuring project milestones are met.
Each of these considerations directly impacts the project timeline and budget. For example, a company with outdated technology may lead to poor assembly quality and rework, driving up costs and delaying production. Similarly, a lack of scalable infrastructure can disrupt long-term plans. Therefore, a comprehensive evaluation of these factors is essential before selecting an electronics assembly partner.
Cost-Effective Solutions in Electronic Assembly
Achieving cost-effectiveness in electronics assembly requires a multifaceted approach that considers various factors from design to supply chain management. By strategically optimizing processes and making informed decisions, companies can significantly reduce expenses without compromising quality or performance. This section outlines key strategies for minimizing costs in the electronics assembly process.
Key strategies for cost reduction include optimizing designs for manufacturing, leveraging volume discounts, managing material costs effectively, and establishing a robust and efficient supply chain.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Implementing DFM principles during the design phase can significantly reduce assembly costs. This involves simplifying designs, reducing component counts, using standard components, and optimizing layouts for automated assembly processes. Addressing potential manufacturing issues early can prevent costly redesigns and production delays. - Volume and Scale Benefits
Larger production volumes typically translate to lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Negotiating volume discounts with component suppliers and assembly partners can substantially lower expenses. Planning for future scalability is essential to maximize cost-effectiveness over time. - Material Cost Management
Careful component selection is crucial. Opting for cost-effective yet reliable components, exploring alternative sourcing options, and optimizing bill of materials (BOM) can lower overall material costs. Forecasting and inventory management help prevent shortages and overstocking, minimizing wastage and associated expenses. - Efficient Supply Chain
A robust and efficient supply chain is vital for cost reduction. Developing relationships with reliable suppliers, implementing just-in-time (JIT) inventory, and optimizing logistics can minimize lead times, reduce storage costs, and ensure a consistent supply of components. Diversifying the supply base can also mitigate risks related to price fluctuations and shortages.
| Strategy | Description | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Design for Manufacturability (DFM) | Optimizing design for easier assembly, reduced component count, and standard parts. | Lowers assembly costs, reduces errors, and simplifies production. |
| Volume Discounts | Negotiating lower per-unit costs with suppliers for larger orders. | Significant cost reduction for mass production. |
| Material Cost Management | Selecting cost-effective components and optimizing the Bill of Materials. | Reduces raw material costs and waste. |
| Supply Chain Efficiency | Optimizing supplier relations, implementing JIT inventory and logistics. | Minimizes lead time, storage costs, and inventory management expenses. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Electronics Assembly Services
This section addresses common inquiries regarding electronics assembly, focusing on key aspects such as minimum order quantities, turnaround times, testing procedures, and adherence to industry standards. We also consider questions arising from related searches about local companies, company lists, and regional variations in service.
- What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) for electronics assembly?
MOQs vary significantly depending on the assembly company and the complexity of the project. Some companies specialize in high-volume production, while others cater to smaller runs. It's crucial to discuss your needs with potential partners to find one that matches your production volume requirements. Generally, SMT assembly often has higher minimums due to setup costs, whereas THT might offer more flexibility. - How long does the electronics assembly process usually take?
Turnaround time is influenced by various factors, including the complexity of the PCB, component availability, and the assembly company's current workload. Prototyping usually has a faster turnaround than mass production. It is critical to confirm expected lead times at the outset, factoring in potential delays from unforeseen issues. A well planned project should include time for possible adjustments. - What kind of testing is performed during and after the assembly process?
Testing protocols usually encompass several stages of the assembly process. This includes visual inspection, automated optical inspection (AOI) for solder joints and component placement, in-circuit testing (ICT) to verify connectivity, and functional testing to validate overall performance of the assembled PCB. Additional tests might be specific to your product requirements and regulatory standards. - How do electronics assembly companies ensure quality control and compliance with industry standards?
Reputable electronics assembly companies adhere to stringent quality control measures such as ISO 9001, and specific industry standards like IPC. They will usually have certifications in place to demonstrate their compliance with relevant benchmarks. These standards ensure that the production process is both consistent and meets the quality levels required for their customers and the applications of the produced devices. - Do electronics assembly companies offer component sourcing services?
Many electronics assembly companies offer component sourcing as a value-added service. This can significantly simplify the process for clients, reducing lead times and cost, in some cases. However, it's vital to confirm the sourcing process and the company's ability to supply reliable, high-quality components. This service is invaluable, especially with current disruptions in the global supply chain. - Are there electronics assembly companies near me, and what are the benefits of using a local provider?
The advantages of using local electronics assembly companies include easier communication, faster response times, and the ability to visit the facility directly for quality checks. However, you need to evaluate the capabilities and cost structures of local providers, versus those that might offer superior value despite being further away. Location is only one variable in the choice of an assembly partner, expertise, and capacity are far more important. - Can electronics assembly companies provide design for manufacturability (DFM) feedback?
Many electronics assembly companies offer DFM analysis as part of their service. This is essential to optimize the design for effective and efficient manufacturing, potentially reducing costs and turnaround times. DFM feedback can be invaluable for first time production, and should be sought even if you think your design is perfect. It is often an overlooked advantage of a good assembly partner.
Emerging Trends in the Electronics Assembly Sector
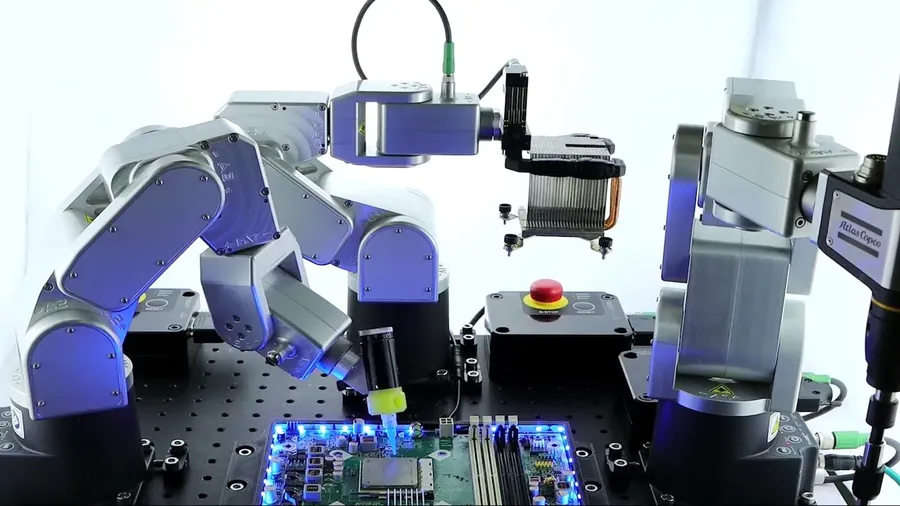
The electronics assembly sector is undergoing a rapid transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. These trends not only reshape manufacturing processes but also open new avenues for innovation and growth.
- Increased Automation
The adoption of robotics and automated systems in assembly lines is accelerating. This leads to higher precision, reduced labor costs, and increased production efficiency. Automated optical inspection (AOI) and automated guided vehicles (AGVs) are becoming commonplace. - Growth of Internet of Things (IoT)
The proliferation of IoT devices has spurred demand for specialized assembly services. These services often require high-volume manufacturing of small, complex devices with advanced connectivity features, thereby driving the demand for specific and tailored assembly techniques. - Wearable Technology Advancements
Wearable technology like smartwatches, fitness trackers, and medical sensors is driving demand for miniaturized and flexible electronic components. This trend requires assembly processes that can handle these ultra-small form factors. - Medical Device Innovation
The medical device industry is seeing significant advancements, with increasing demand for sophisticated electronic assemblies in diagnostic and therapeutic equipment. This leads to a demand for companies that are compliant with rigorous industry-specific standards and have high precision assembly capabilities. - Demand for Flexible Electronics
Flexible substrates and printed electronics are gaining traction, requiring specialized assembly techniques and materials. These types of assemblies are increasingly being adopted in displays, wearable technology, and automotive electronics. - Advanced Materials Integration
The use of advanced materials in electronics assembly is on the rise. This involves utilizing materials like graphene, conductive inks, and composite substrates, requiring adapted assembly methods. - Sustainability and Green Manufacturing
There is an increasing focus on sustainable manufacturing practices, including the use of eco-friendly materials and processes. These require energy-efficient assembly practices and reduced waste throughout the manufacturing lifecycle.
Looking ahead, the electronics assembly industry will continue to evolve driven by these trends. Companies that adapt and invest in new technologies and methodologies are positioned to achieve success. This includes not only adoption of automation but also incorporating sustainable manufacturing, and developing capabilities in handling flexible, miniaturized, and advanced materials.
Comparative Analysis of Different Types of Electronic Assembly Services
The electronics assembly sector offers a variety of service models tailored to different client needs and project scopes. Understanding the distinctions between Contract Manufacturing, Original Equipment Manufacturer (OEM) services, and Electronics Manufacturing Services (EMS) is crucial for selecting the right partner for your electronic product assembly needs. Each model offers unique benefits, operational structures, and levels of involvement in the product lifecycle.
| Service Model | Description | Benefits | Typical Client | Pros | Cons | Ideal Situation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Contract Manufacturing | Manufacturing products based on the client's designs and specifications. | Cost-effective for high-volume production; focus on manufacturing efficiency. | Companies with established designs looking for scalable production. | Lower production costs, high scalability. | Less control over the manufacturing process, may require detailed documentation. | When a company has mature, well-defined designs and requires efficient and cost effective production. |
| OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) | Manufacturing products to be sold under the client's brand name. | Brand control; custom product design; potential for high profit margins. | Companies looking to sell branded products with specific requirements. | Full control over design and branding, ability to create unique products. | Potentially higher development costs; reliance on the OEM for all aspects. | When a company desires to sell a branded product and requires the manufacturer to be a comprehensive partner. |
| EMS (Electronics Manufacturing Services) | Providing a broad range of services, from design and component sourcing to assembly and testing. | Comprehensive support; faster time to market; reduced capital investment. | Companies seeking a turnkey solution for their electronic product. | End-to-end service, from design to manufacturing; greater flexibility and scalability. | Potential for less direct oversight in the production process; may require long-term partnership. | When a company needs a full-service partner and does not have the infrastructure for manufacturing or product development. |
The electronics assembly industry is a critical component of modern technology, driving innovation and enabling countless applications. By understanding the diverse landscape of electronics assembly companies, the services they offer, and the key factors for selection, businesses can choose the right partner to ensure success. As the industry continues to evolve with new technologies, strategic partnerships with qualified electronics assembly companies will be essential for companies in the electronics sectors. These companies stand at the forefront of the technological revolution, continuously pushing the boundaries of what is possible.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA