Selecting the Right PCB Assembly Services Supplier: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's fast-paced world, electronics play an integral role in our daily lives, from the smartphones in our pockets to the complex systems driving industries. The heart of these electronic marvels lies in the printed circuit board (PCB), and the quality of PCB assembly services directly impacts the functionality and reliability of the final product. Choosing the right PCB assembly services supplier is a critical decision that can make or break your project. This guide delves into the nuances of selecting a competent supplier, considering everything from prototyping to mass production, ensuring that you are empowered to make an informed choice.
Understanding Your PCB Assembly Needs

Selecting the appropriate PCB assembly services supplier hinges on a clear understanding of your project's specific needs. This foundational step ensures that the chosen supplier is well-equipped to meet your requirements effectively, from initial prototyping to large-scale production.
Key considerations during this phase include production volume, complexity of the PCB design, any specific certifications, and necessary testing procedures. Each of these aspects plays a crucial role in determining the capabilities a suitable supplier should possess.
- Production Volume
Determine whether your project requires prototype quantities, low-volume runs, medium-scale production, or high-volume manufacturing. This will impact the supplier's production process and associated costs. - PCB Design Complexity
Assess the complexity of your PCB design, including the number of layers, component types, and specific technologies (e.g., SMT, through-hole). Suppliers should have the necessary equipment and expertise to handle your particular design. - Certifications and Standards
Identify any mandatory certifications, such as ISO 9001 or IPC standards, that your PCB assembly must meet. This is critical for quality assurance and compliance. - Testing Requirements
Define the necessary testing procedures, such as in-circuit testing (ICT), functional testing, or automated optical inspection (AOI). Confirm that the supplier can perform these tests to verify the functionality and reliability of the assembled PCBs.
Key Factors to Evaluate in PCB Assembly Services Suppliers

Selecting the right PCB assembly services supplier is critical for ensuring the quality, reliability, and timely delivery of your electronic products. This section details the key factors that should be thoroughly evaluated to make an informed decision, covering areas from experience and certifications to manufacturing capabilities and sourcing strategies.
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Experience | Years of operation, project portfolio, and industry knowledge. | Indicates the supplier's ability to handle complex projects and adapt to diverse client needs. |
| Certifications (ISO, IPC) | Compliance with international standards for quality management and PCB manufacturing. | Ensures adherence to established best practices and quality control measures. |
| Manufacturing Capabilities (SMT, Through-Hole) | Availability of Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole assembly capabilities. | Alignment with project requirements, ensuring the ability to process a wide range of board designs and component types. |
| Turnaround Time | The typical time needed from order placement to the delivery of assembled PCBs. | Crucial for meeting project deadlines and managing time-sensitive projects effectively. |
| Component Sourcing Strategies | Supplier's ability to procure components reliably and cost-effectively. | Impacts the overall cost and timelines of the assembly process and supply chain integrity. |
- Experience & Reputation
Assess the supplier's track record in the industry. A long-standing presence, coupled with a robust portfolio, indicates a level of expertise that can be relied upon. - Certifications
Certifications such as ISO 9001 and IPC standards compliance are not just badges; they are indicators of the supplier's commitment to quality and consistent processes. - Assembly Technology
Evaluate the assembly technology. The ability to handle both SMT and through-hole technology means the supplier is adaptable to various board types and design complexity. - Turnaround Capabilities
Understand the average turnaround time. This is crucial for project planning, where delays can be costly. Consider if they offer quick-turn services for prototyping or expedited projects. - Supply Chain
A transparent and reliable supply chain ensures the quality and availability of components. Ask about their sourcing strategies and any component traceability systems they have in place.
Cost Considerations in PCB Assembly
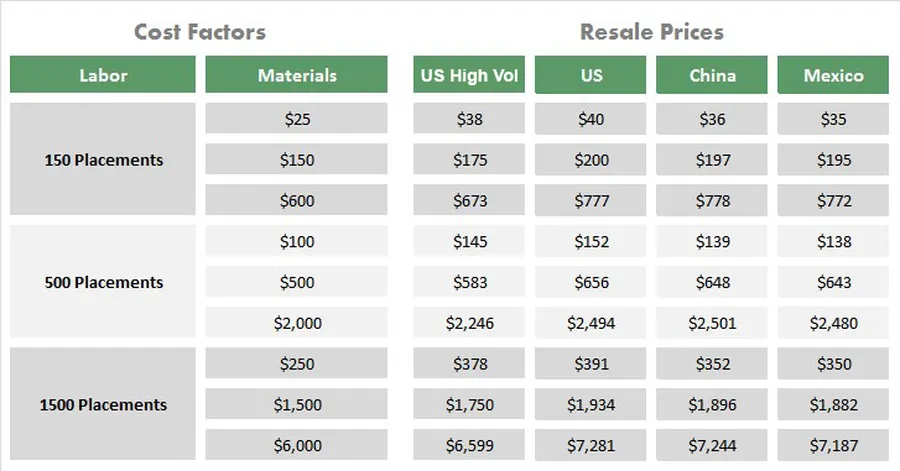
Understanding the cost structure of PCB assembly is crucial for effective budgeting and supplier selection. It's not solely about the per-unit price; a comprehensive view includes tooling, non-recurring engineering (NRE), and logistical expenses.
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of PCB assembly. Here's a breakdown:
| Cost Category | Description | Factors Influencing Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Per-Unit Assembly Cost | The cost to assemble one PCB, including component placement and soldering. | Volume, component type, assembly complexity (SMT, through-hole), technology used, precision of placement, inspection requirements. |
| Tooling Costs | Expenses for setup tools such as stencils for solder paste application. | Complexity of the board design, fine pitch components, production volume. |
| NRE (Non-Recurring Engineering) Fees | One-time costs for design review, initial setup, and programming of assembly machines. | Complexity of design, supplier’s process, design modifications |
| Component Costs | The price of individual components. | Market availability, component type, supply chain factors, purchasing volumes. |
| Testing and Inspection Costs | Expenses for quality control, including AOI, ICT, and functional testing. | Required level of testing and inspection, complexity of circuit, testing method. |
| Shipping Costs | The price of transporting PCBs, both components and finished products. | Distance, shipping speed, packaging requirements, weight and size of the shipment. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Minimum quantity the supplier is willing to assemble. | Supplier’s processes and production capacity. |
Understanding how these costs interact is crucial. For instance, higher NRE costs might be justified for complex boards, but they can be amortized over larger production runs. Similarly, choosing a supplier closer geographically might reduce shipping costs but can impact per unit assembly cost. The trade-offs need to be considered based on the specific project requirements.
Geographic Location vs. Offshore Suppliers for PCB Assembly

The decision between domestic and offshore PCB assembly services suppliers significantly impacts project timelines, costs, and quality. This section examines the trade-offs to help you make an informed choice aligned with your specific needs, including lead times, communication effectiveness, quality control rigor, and overall cost implications.
| Factor | Domestic Suppliers | Offshore Suppliers |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Times | Typically shorter; faster turnaround times are often achievable. | Generally longer due to shipping and customs procedures. |
| Communication | Easier communication; often in the same language and time zone, facilitating real-time interaction and issue resolution. | Potential for language and time zone differences, which can lead to delays and miscommunications. |
| Quality Control | Often easier to oversee quality due to proximity; potential for on-site inspections and direct interaction. | Quality control can be challenging to manage directly; reliance on supplier's quality assurance processes. |
| Cost | Generally higher due to higher labor and operational costs. | Typically lower due to lower labor and overhead costs. |
| Intellectual Property Protection | Stronger legal frameworks and protection of intellectual property. | Potential risks of intellectual property infringement and weaker legal protection. |
| Supply Chain Transparency | Greater transparency and visibility into the supply chain. | Supply chains may be more opaque and harder to trace. |
| Logistics and Shipping | Simpler logistics with lower shipping costs and faster delivery. | More complex logistics with higher shipping costs and longer delivery times; potential customs issues |
Prototyping to Production: Scaling with Your PCB Assembly Supplier
Selecting a PCB assembly services supplier capable of scaling from prototype runs to full-scale production is critical for long-term project success. A supplier that demonstrates flexibility and consistent quality throughout the product lifecycle is essential to avoid costly supplier changes.
The transition from prototyping to mass production requires a PCB assembly partner who can adapt to evolving project needs. This includes an increase in manufacturing volume, potential adjustments to component sourcing, and changes to testing protocols. A reliable supplier is one who can seamlessly manage these shifts without compromising quality or lead times.
- Key considerations for scaling include:
The flexibility of the assembly line and equipment is needed to handle an increase in production volume. - Component Sourcing:
A supplier should maintain a reliable supply chain that can meet volume demands. - Quality Assurance:
Consistent quality control and testing must be maintained at all production levels. - Communication:
Clear and consistent communication to address the changes during scaling process is essential.
| Phase | Volume | Focus | Supplier Requirement |
|---|---|---|---|
| Prototyping | Low | Design validation and testing | Fast turnaround time, flexibility in process. |
| Low-Volume Production | Low to Medium | Initial market introduction | Consistent quality and reliability. |
| Medium-Volume Production | Medium | Scaling and cost optimization | Capacity to increase output without compromising quality |
| High-Volume Production | High | Full market saturation | Large-scale capacity, robust supply chain, and efficient logistics. |
Ensuring Quality in PCB Assembly: Testing and Inspection
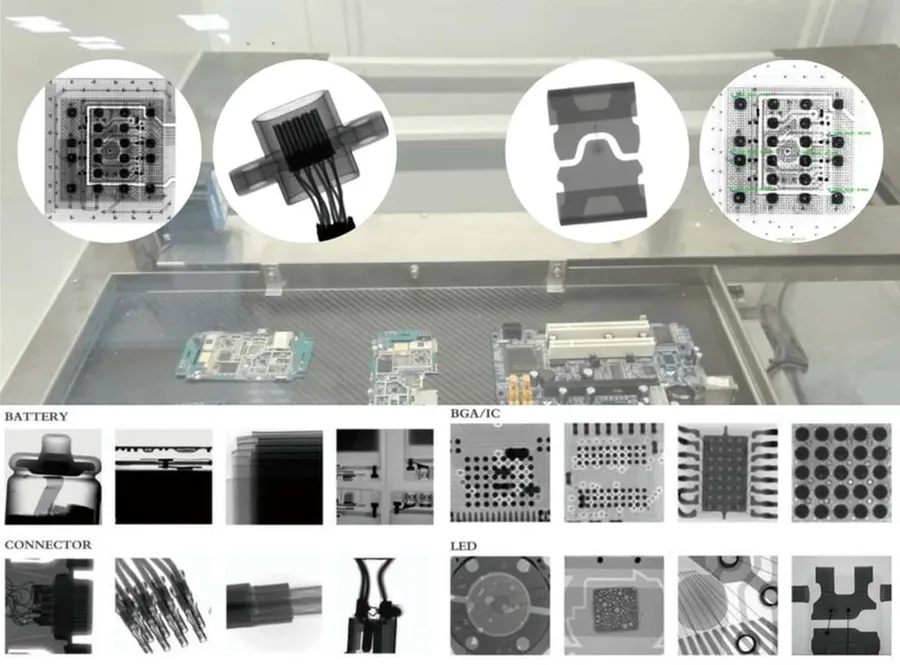
Rigorous testing and inspection are paramount in PCB assembly to guarantee the reliability and functionality of the final product. These processes identify potential defects early in the production cycle, minimizing costly rework and ensuring that assembled PCBs meet the required performance standards.
- Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI uses high-resolution cameras to visually inspect PCBs for defects such as missing components, incorrect orientation, solder shorts, and opens. It is a critical step that significantly reduces the chance of defects passing undetected to later stages. - X-Ray Inspection
X-ray inspection is crucial for examining solder joints, especially under BGAs (Ball Grid Arrays) and other components where visual inspection is not possible. This method can detect hidden voids, solder bridges, and other internal defects. - In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
ICT verifies the electrical performance of each component on the board. Using test probes, it checks for short circuits, open circuits, resistance values, and other electrical parameters. This test is essential for detecting component-level faults. - Functional Testing
Functional testing involves testing the assembled PCB under real-world operating conditions. This test is critical to ensure that the finished product functions correctly. It simulates the application environment and checks for the complete operation of the circuit according to its specifications. - Visual Inspection
Even with automated processes, manual visual inspection by trained personnel is crucial, particularly for checking aspects like component placement and solder quality that might be overlooked by machines. This final step serves as a critical human confirmation of the overall quality.
| Testing Method | Purpose | Defects Detected |
|---|---|---|
| AOI | Visual inspection for surface defects | Missing components, misalignment, solder defects |
| X-Ray | Inspection of hidden solder joints | Voids, bridges, insufficient solder |
| ICT | Electrical testing of components | Shorts, opens, incorrect component values |
| Functional Testing | Verification of board functionality | Performance issues, application failures |
Frequently Asked Questions about PCB Assembly Services
This section addresses common concerns and queries regarding PCB (Printed Circuit Board) assembly services. Understanding these aspects is crucial for effective project planning and supplier selection. We aim to provide clear, concise answers based on fundamental principles and industry best practices.
- How much does it cost to get a PCB assembled?
The cost of PCB assembly is highly variable and depends on several factors including the complexity of the board, the number of layers, the types of components used (surface mount, through-hole, BGA etc.), the assembly volume (prototype, low, medium, or high), and whether components need to be sourced. Expect prototype assembly to have higher per-unit costs due to setup charges, while larger volumes benefit from economies of scale. Material costs can also vary significantly, so it's imperative to obtain detailed quotes based on specific project requirements. PCB assembly pricing can range from a few dollars for simple boards to hundreds of dollars for high-density, complex designs. - Who is the biggest PCB supplier?
Identifying the single 'biggest' PCB supplier is challenging due to the fragmented nature of the market and variations in criteria such as revenue, production volume, and geographical footprint. However, large multinational corporations like TTM Technologies, Samsung Electro-Mechanics, and Unimicron consistently rank among the top PCB manufacturers globally in terms of production capacity and market share. Regionally, there are also numerous large suppliers that hold significant market positions. Therefore, the best approach is to consider the specific criteria most important to your requirements when choosing a suitable supplier. - Why is PCB assembly so expensive?
The expense of PCB assembly stems from several contributing factors. High precision machinery, such as pick-and-place equipment and reflow ovens, are required, along with skilled technicians to operate and maintain this equipment. The use of advanced components, particularly those with small footprints, contributes to cost increases. Additionally, strict quality control measures, including automated optical inspection (AOI) and functional testing, are standard practices that also factor into overall expenses. Furthermore, set-up costs, including stencil preparation and programming, also contribute to the total cost. Finally, the cost of component sourcing and potential material waste adds to the overall price. - Who manufactures PCBs?
PCBs are manufactured by a wide range of companies, from small, specialized shops to large, global corporations. Many PCB manufacturers, often termed 'fabricators,' focus on creating the bare boards according to the customer’s design specifications. A separate set of companies are PCB assembly service providers (also known as 'assemblers' or 'contract manufacturers'). These companies place and solder electronic components onto the fabricated PCBs. Some companies perform both PCB fabrication and assembly. The decision on which provider to use depends on project scope and complexity. Regional PCB fabrication providers will often be focused on local supply and quick turn production. - What is a quick-turn PCB assembly?
Quick-turn PCB assembly is a service focused on rapidly assembling printed circuit boards, generally for prototype or urgent needs. It emphasizes minimal lead times and quick turnaround of PCB assemblies, which is crucial for rapid product development. While quick-turn typically carries higher costs, its advantages of rapid iteration are vital for many projects. Quick-turn assembly service providers often utilize in-stock components, efficient processes and flexible shifts to meet expedited delivery times. This is often a high-mix low-volume approach that will not apply for larger production runs. - What certifications should PCB assembly suppliers hold?
Reputable PCB assembly suppliers will hold several important certifications, demonstrating a commitment to quality and industry standards. ISO 9001 certification is essential, demonstrating effective quality management systems. IPC certifications, particularly IPC-A-610 (Acceptability of Electronic Assemblies), and IPC-J-STD-001 (Requirements for Soldered Electrical and Electronic Assemblies) are crucial for ensuring consistent assembly quality. Additionally, industry-specific certifications like AS9100 for aerospace or ISO 13485 for medical devices may also be required for some applications. Choosing suppliers with relevant certifications offers assurance of their capabilities and processes. - What are the common issues in PCB Assembly?
PCB assembly is a complex process with several potential failure points. Common issues include component placement errors, insufficient or excessive solder, bridging (short circuits between pins), tombstoning (components standing on one end), and cold solder joints. Other problems arise from incorrect component orientation or damage from handling and thermal shock. In addition, incorrect stencil alignment can lead to solder paste misapplication, resulting in defective joints. It is therefore crucial that stringent quality control and inspection are implemented by the PCB assembly service provider.
Tools and Technology Used in PCB Assembly

Modern PCB assembly relies on a sophisticated array of tools and technologies to ensure precision, quality, and efficiency. These advanced systems automate and optimize the assembly process, enabling the production of complex electronic devices with high reliability and speed. Understanding these tools provides insight into the capabilities of different PCB assembly services suppliers.
- Solder Paste Printing
Solder paste printers accurately apply solder paste onto the PCB pads, a critical step for ensuring proper component soldering. These machines use stencils to control the amount and placement of solder paste. Advanced printers can handle fine-pitch components and complex board layouts with high precision. - Pick-and-Place Machines
Pick-and-place machines are the workhorses of PCB assembly, automatically placing components onto the board. These machines use vacuum nozzles or grippers to pick components from reels or trays and place them accurately on the pre-printed solder paste. They handle a wide range of component sizes and types, from small surface mount devices (SMDs) to larger integrated circuits (ICs), greatly speeding up assembly process. - Reflow Ovens
Reflow ovens are used to melt the solder paste, creating electrical connections between the components and the PCB. These ovens precisely control the temperature profile throughout the reflow process, preventing damage to the components and ensuring reliable solder joints. Different zones within the oven preheat, reflow, and cool the board according to the thermal requirements. - Wave Soldering Machines
Wave soldering is primarily used for through-hole components. These machines pass the PCB over a wave of molten solder, ensuring that solder fills the holes and creates reliable connections. While less common than reflow for surface-mount, wave soldering is essential for certain components. - Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Systems
AOI systems use high-resolution cameras to visually inspect the assembled boards, detecting common assembly defects such as missing components, misaligned parts, and solder joint issues. AOI is a key part of the quality control process, catching errors early in the production cycle. - X-Ray Inspection Machines
X-ray machines are used to inspect solder joints underneath components and within multi-layer boards, which cannot be visually inspected by AOI systems. This technology detects issues like voids and opens that could affect the reliability of the board. - Functional Testing Equipment
Functional testing verifies that the assembled PCB functions as intended, typically using a test jig or in-circuit test (ICT) equipment. These tests confirm the electrical integrity of the board and its ability to perform its designed function, ensuring that only functional boards are shipped to customers.
| Tool | Purpose | Impact on Quality and Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Solder Paste Printer | Applies solder paste accurately | Ensures proper solder application; minimizes shorts and opens |
| Pick-and-Place Machine | Places components onto PCB | Speeds up assembly; enhances placement precision and consistency |
| Reflow Oven | Melts solder paste | Creates reliable solder joints; prevents component damage with controlled heating |
| Wave Soldering Machine | Solders through-hole components | Provides reliable connections for specific components. |
| Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Visually inspects assembled boards | Detects defects early in the process; improves overall quality |
| X-Ray Inspection | Inspects solder joints under components | Ensures reliability of hidden solder connections; identifies defects not visible by AOI |
| Functional Testing Equipment | Verifies board functionality | Ensures correct electrical function; reduces defective outputs |
Building a Strong Relationship with Your PCB Assembly Supplier
Establishing a robust relationship with your PCB assembly services supplier is paramount for long-term success and consistent quality. This goes beyond transactional interactions and focuses on fostering a collaborative partnership built on mutual trust and open communication.
- Open Communication Channels
Establish clear and consistent communication channels. Regular meetings, whether in-person or virtual, are crucial to keep projects on track and address potential issues proactively. Utilize project management tools to share design files, track progress, and maintain transparency. - Proactive Feedback Loops
Implement a system for regular feedback throughout the assembly process. Share both positive feedback and areas for improvement with your supplier. This feedback loop allows them to refine their processes and tailor their services to meet your needs. - Collaborative Engagement
Engage your supplier as a partner, not just a vendor. Share design specifications, project goals, and any potential challenges upfront. A collaborative approach allows the supplier to offer expertise and identify potential issues early, reducing the risk of costly errors and delays. This includes early involvement in the design for manufacturability (DFM) process. - Understanding Supplier's Capabilities
Take the time to understand the capabilities, limitations, and core competencies of your chosen supplier. This helps ensure alignment between your requirements and their capacity. It facilitates realistic expectations and smoother project executions. - Long-Term Partnership Mindset
Focus on building a long-term relationship based on trust and mutual respect. View your supplier as a strategic partner, not just a source for assembly. This allows for better collaboration, resource planning, and improved efficiency over time. A long term relationship will enable them to anticipate future demands and support capacity planning better.
Selecting the right PCB assembly services supplier is crucial for the success of your electronic projects. By carefully evaluating your needs, understanding the capabilities of [pcb assembly services suppliers], and focusing on quality and communication, you can ensure a smooth, reliable, and cost-effective assembly process, ultimately bringing your innovative ideas to life. Remember to consider the long-term implications of your supplier choice, focusing on partners who can grow and adapt with your business needs, providing you a sustainable path to success in the ever evolving landscape of electronics manufacturing.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA