Top PCB Assembly Companies: Choosing the Right Partner for Your Electronics
In today's fast-paced world of technology, where electronic devices are indispensable, the crucial role of PCB assembly companies cannot be overstated. These companies bridge the gap between design and functionality, assembling the vital components that power our everyday technology. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the top PCB assembly companies, offering insights into their services, specializations, and helping you navigate the selection process, ensuring your project's success from concept to completion. We will delve into crucial aspects that influence the selection process, from capabilities to cost considerations, providing you with the knowledge you need to make the best choice for your electronic project.
Understanding PCB Assembly Processes

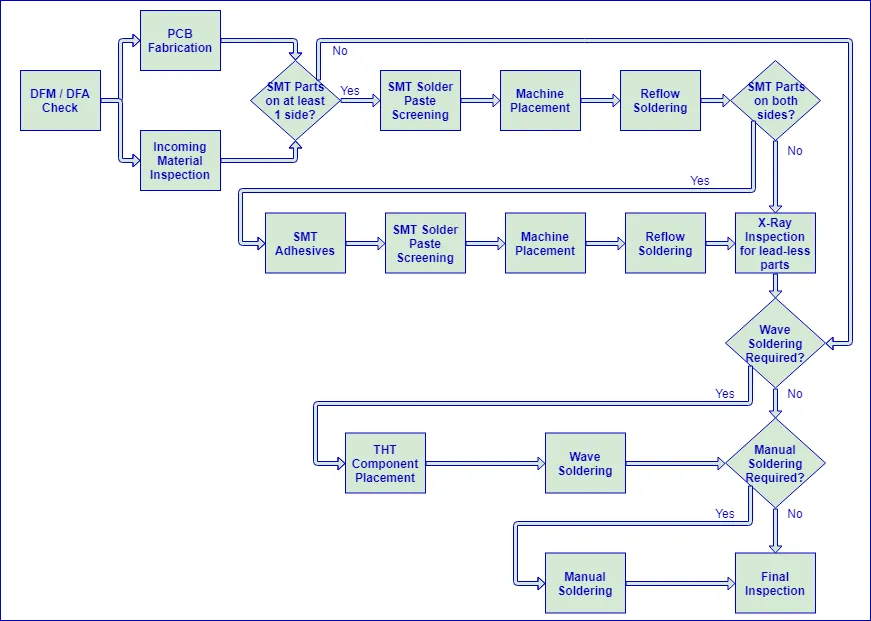
PCB assembly is the crucial process of mounting electronic components onto a printed circuit board (PCB) to create a functional electronic module. This process involves various techniques, each suited for specific component types and project requirements, with Surface Mount Technology (SMT), Through-Hole, and Mixed Technology assembly being the most prevalent.
| Assembly Method | Description | Best Use Cases | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Mount Technology (SMT) | Components are placed directly onto the surface of the PCB and soldered in place. | High-volume production, miniaturized devices, high-density boards. | High component density, excellent for small devices, automated assembly. | Requires specialized equipment, less robust for mechanical stress, difficult for manual rework. |
| Through-Hole Technology (THT) | Components are inserted into holes drilled in the PCB and soldered on the opposite side. | Prototypes, robust mechanical connections, larger components. | Stronger mechanical connections, better for larger components, easier for manual rework. | Lower component density, not suitable for miniaturized devices, less efficient for high volume production. |
| Mixed Technology | Combines both SMT and through-hole techniques on a single board. | Boards with both large and small components, varying performance requirements. | Flexibility in component selection, optimal performance, adaptable for complex designs. | Requires more complex assembly processes, higher cost for assembly and rework. |
Key Capabilities to Look for in PCB Assembly Companies

Selecting the right PCB assembly company hinges on a thorough evaluation of their capabilities. These capabilities should align with your project's specific needs, encompassing aspects from prototyping to high-volume production and specialized assembly techniques. A robust quality control process is also a crucial indicator of a reliable assembly partner.
| Capability | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Prototype Assembly | Ability to produce small batches of PCBs for testing and design validation. | Essential for iterative design processes and identifying potential issues early. |
| Low-Volume Production | Production of a limited number of PCBs, often for specialized or initial product launches. | Ideal for pilot programs and small-scale projects. |
| High-Volume Production | Large-scale manufacturing capacity to meet the demands of mass-market products. | Crucial for cost-effective production of commercial quantities. |
| Surface Mount Technology (SMT) | Automated assembly technique for mounting components directly onto the PCB surface. | The most common method for modern electronics assembly, ensuring efficient and reliable production. |
| Through-Hole Assembly | Assembly technique for components with leads that pass through holes in the PCB. | Still relevant for larger, more robust components and applications requiring strong mechanical connections. |
| Mixed Technology Assembly | The use of both SMT and through-hole techniques in a single assembly process. | Allows flexibility in component selection and optimization of performance. |
| Fine-Pitch Assembly | Precise placement of components with very small lead spacing. | Necessary for high-density designs, such as BGA and micro-BGA packages. |
| Ball Grid Array (BGA) Assembly | Specialized technique for mounting BGA packages, requiring precise handling and reflow processes. | Critical for complex integrated circuits and applications requiring high-density interconnectivity. |
| Testing and Quality Control | Rigorous testing procedures including visual inspection, functional testing, and in-circuit testing (ICT). | Ensures the reliability and functionality of the assembled PCBs before delivery. |
Geographical Considerations: USA Based PCB Assembly Companies

Choosing a PCB assembly company involves several critical factors, and geographical location, particularly within the USA, presents distinct advantages. Opting for a US-based partner can significantly impact project timelines, communication efficiency, and compliance with rigorous quality standards.
The benefits of partnering with USA-based PCB assembly companies are multifaceted. Shorter lead times, a direct result of reduced shipping distances and streamlined logistics, are a major draw for projects with tight deadlines. Furthermore, domestic production fosters better communication, allowing for easier engagement and quicker resolution of any production-related issues. Finally, adherence to stringent US quality control standards and regulatory compliances ensures a higher quality final product.
When selecting a US-based PCB assembly partner, it's crucial to match their expertise with specific project requirements. Some companies may specialize in rapid prototyping, while others excel in high-volume manufacturing. Additionally, certain companies may have particular strengths in advanced assembly techniques, such as fine-pitch BGA assembly or mixed-technology integration. Evaluating these factors ensures that the chosen partner aligns with your needs for optimal efficiency.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Shorter Lead Times | Reduced shipping distances and streamlined logistics result in faster turnaround times. |
| Improved Communication | Real-time engagement and quicker resolution of any production issues due to fewer time zone barriers and closer proximity. |
| Compliance with US Standards | Adherence to stringent US quality control standards and regulatory compliance ensure a higher quality final product. |
| Intellectual Property Protection | Working with a domestic partner can reduce concerns related to intellectual property and information security. |
| Economic Benefits | Supporting domestic manufacturing contributes to local job creation and economic growth. |
Evaluating Cost Factors in PCB Assembly
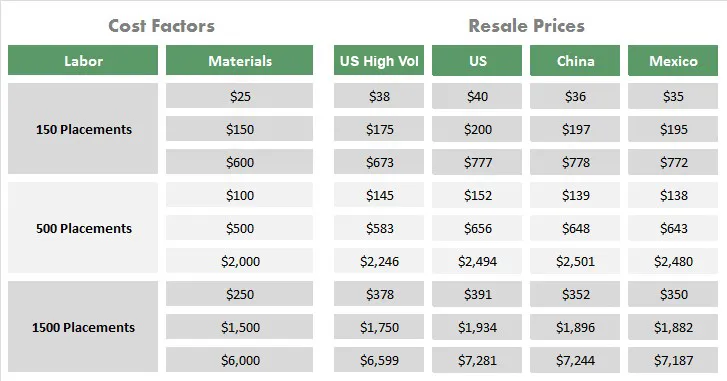
Understanding the cost drivers in PCB assembly is crucial for effective project budgeting and vendor selection. Several factors contribute to the overall cost, and a comprehensive analysis is essential to optimize expenses without sacrificing the quality or functionality of the final product. This section provides insights into these factors to help you navigate the complexities of PCB assembly pricing.
| Cost Factor | Description | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Material Costs | The price of raw materials like substrates (FR-4, etc.), solder, and components (resistors, capacitors, ICs, etc.) | Directly impacts cost; higher-grade materials and specialized components increase cost. |
| Labor Costs | Expenses related to personnel involved in assembly processes, including manual assembly, machine operation, and quality checks. | Varies based on location, complexity of work, automation level, and the company's operational efficiency; higher for manual assembly and highly skilled operations. |
| Assembly Complexity | The difficulty and intricacy of the PCB design which requires specialized machinery, techniques, and handling, including the number of layers, components size (fine-pitch), and number of through-hole parts. | Complex designs with more layers, fine-pitch components, and a mix of SMT and through-hole parts increase both time and labor costs. |
| Order Quantity | The volume of PCBs to be assembled in a single order or over a certain time. Includes considerations of batch sizes and economies of scale | Higher volumes often yield lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale, including reduced material purchasing costs and production setup costs. |
| Testing Requirements | The type and extent of testing needed, including functional, ICT (In-Circuit Testing), and AOI (Automated Optical Inspection). | More rigorous and comprehensive testing protocols will increase the cost but reduce the risk of product defects. |
| Lead Time | The time required to complete an order; shorter lead times may involve higher priority and expedited production. | Shorter lead times, especially rush orders, can significantly raise costs to accommodate fast turnaround demands. |
| Technology | Specific assembly technologies used, such as BGA, fine-pitch, and mixed technology. | Advanced assembly techniques will impact the cost of specialized equipment, labor, and process parameters. |
| Location | Geographic location of the PCB assembler, factoring in import/export expenses, and local regulations, as well as shipping costs and logistics. | Varies due to material sourcing, labor rates, and regional or national regulations. |
Balancing cost with quality requires a strategic approach. Engaging with a PCB assembly company early in the design phase can provide valuable insights into cost-effective design choices. Some options to consider include design for manufacturability (DFM) analysis to optimize component placement and layout, and choosing standard or commonly available parts to lower material costs. By understanding the interplay of these factors, companies can make informed decisions, ensuring cost-effective and high-quality PCB assemblies.
How to Choose a PCB Assembly Partner: Key Criteria
Selecting the right PCB assembly partner is crucial for the success of any electronics project. It's a decision that impacts not only the quality and reliability of the final product but also the project timeline and budget. Therefore, a systematic evaluation based on key criteria is essential to ensure a successful partnership.
- Expertise and Experience
Evaluate the company's experience with similar projects, including the types of PCBs they have assembled and the industries they serve. Look for a partner with a track record of success in handling projects of comparable complexity and scale. - Technological Capabilities
Assess whether the assembly company possesses the necessary technology to meet your project's specifications. This includes their equipment for SMT, through-hole, and mixed-technology assembly, as well as advanced capabilities like fine-pitch and BGA assembly. Confirm that their equipment is regularly maintained and calibrated. - Customer Support and Communication
Effective communication is key to a smooth working relationship. Determine the level of customer support the company offers. Can you easily reach their project managers? How quickly do they respond to inquiries? Consistent, clear communication is critical for troubleshooting and project management. - Quality Management System
Verify that the PCB assembly company has a robust quality management system in place. This should include rigorous testing procedures, inspection processes, and adherence to industry standards like ISO 9001 or IPC standards. Detailed testing, such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) and In-Circuit Testing (ICT), is essential. - Certifications and Compliance
Confirm that the assembly company has the necessary certifications for the specific industry and region. Certifications validate the company's commitment to quality and their ability to meet specific industry regulations, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices or AS9100 for aerospace. - Turnaround Times
Evaluate the company's lead times for both prototype and production runs. Ensure they can meet your project schedule without compromising on quality. Discuss their production capacity and capabilities to handle your expected volumes. - References and Customer Reviews
Before making a final decision, check references and read customer reviews. This provides insight into other clients' experiences with the company. Contacting past clients directly can provide valuable information about the company's performance.
Supply Chain and Material Management by PCB Assembly Companies

A robust supply chain and meticulous material management are critical for PCB assembly companies to ensure timely project completion and high-quality output. Effective management in this area directly translates to reliability, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to meet stringent project deadlines.
Key aspects of supply chain and material management include:
- Component Sourcing:
Identifying and selecting reliable suppliers for electronic components. This involves assessing supplier quality, lead times, and pricing, ensuring availability of both standard and specialized components. Companies that maintain strong relationships with a diverse supplier base can better navigate component shortages and price fluctuations. - Procurement Processes:
Implementing efficient and transparent procurement practices. This involves a clear understanding of project requirements, accurate demand forecasting, and effective order placement. Sophisticated ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) systems often play a vital role in this, helping to streamline the entire procurement lifecycle. - Inventory Control:
Maintaining optimal inventory levels to balance cost and availability. Effective inventory control minimizes storage costs, reduces the risk of component obsolescence, and ensures components are readily accessible for production. Techniques such as Just-In-Time (JIT) inventory management can be beneficial, provided supply lines are reliable. - Quality Assurance of Materials:
Implementing stringent quality control measures at the point of receiving materials. This includes visual inspections and functional testing, ensuring all parts meet specified requirements. Companies that maintain a high level of material quality assurance are better equipped to produce high quality finished products. - Risk Management:
Identifying and mitigating potential supply chain risks, including geopolitical instability, transportation disruptions, and natural disasters. Diversifying supplier base and maintaining backup supply channels are crucial risk management strategies for ensuring continuity of supply.
Assessing a PCB Assembly Partner's Supply Chain Capabilities:
- Supplier Network:
Evaluate the diversity and reliability of their supplier network. Check if they have a backup supplier for critical components. - Procurement Systems:
Inquire about the tools and systems they use to manage procurement and material planning. Look for sophisticated software and processes that streamline procurement and reduce the risk of delays and errors. - Inventory Management Practices:
Assess their inventory management techniques. Seek companies that minimize inventory costs without compromising on component availability. - Material Traceability:
Ensure their material traceability processes are transparent, robust, and comply with industry standards. Proper traceability ensures components can be easily tracked, providing quality assurance. - Lead time management:
Understand their strategies for mitigating delays, especially for components with long lead times. A good PCB assembly partner will provide realistic timelines for each phase of the process.
Advanced PCB Assembly Techniques and Their Applications
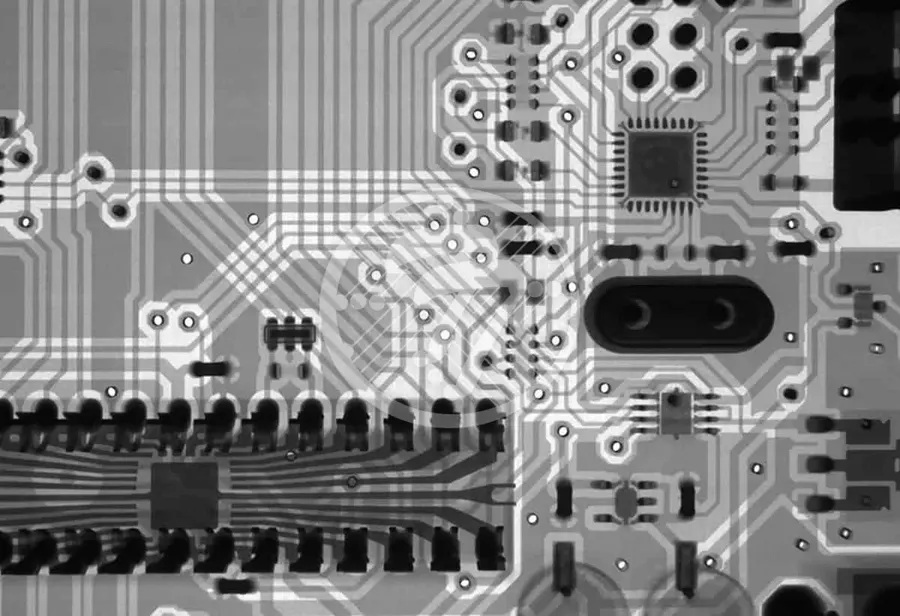
Advanced PCB assembly techniques are crucial for producing sophisticated electronic devices, addressing the increasing demand for miniaturization and enhanced performance. These methods go beyond standard surface mount (SMT) and through-hole technologies, incorporating complex processes to handle delicate and intricate components. This section will delve into several of these advanced techniques, highlighting their applications and the specific advantages they offer for specialized electronics projects.
| Technique | Description | Typical Applications | Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fine-Pitch BGA Assembly | Assembly of Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages with very small ball spacing (pitch), requiring precise placement and soldering. | High-density circuits, mobile devices, advanced processors, network equipment | Increased component density, improved signal integrity, reduced board size |
| Micro-BGA Assembly | Assembly of BGA packages with extremely small ball sizes and pitch, requiring highly specialized equipment and processes. | Miniaturized devices, wearable technology, medical devices, advanced sensor systems | Extremely high component density, enabling ultra-compact designs, reduced weight |
| Mixed-Technology Assembly | Integration of both surface mount (SMT) and through-hole components on the same PCB, requiring careful planning and processing. | Industrial controls, power supplies, high-reliability applications, legacy systems integration | Flexibility in design, support for a wider range of components, cost-effectiveness |
| System in Package (SiP) Assembly | Integration of multiple active and passive components into a single package, requiring specialized bonding and assembly techniques. | High-performance computing, advanced mobile devices, compact sensors and actuators | Reduced form factor, enhanced system performance, improved reliability |
These advanced assembly techniques enable the creation of highly sophisticated and compact electronic devices that would be impossible with standard assembly processes. Selecting a PCB assembly partner with expertise in these techniques is critical for projects requiring cutting-edge technology.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Assembly
This section addresses common questions regarding PCB assembly, providing clear and concise answers to guide you in your selection process. Understanding these frequently asked questions can help clarify key considerations when choosing the right PCB assembly partner.
- What is the best PCB assembly company for my project?
The 'best' company is subjective and depends on your project's specific needs, such as volume, complexity, technology requirements, and budget. It's crucial to evaluate companies based on their capabilities, certifications, customer reviews, and alignment with your project specifications. - How much does PCB assembly cost?
PCB assembly costs vary significantly depending on factors such as the number of layers, component types (including the quantity of each), assembly complexity (fine-pitch, BGA, etc.), volume of boards to be assembled, and required turnaround time. It's best to get quotes from several companies to compare pricing. - Who are the largest PCB assembly suppliers?
Large PCB assembly suppliers often handle high-volume production and may have a global presence. The largest companies will vary by source but will typically include organizations known for their advanced technology and capacity, such as Jabil, Foxconn, and Sanmina. It is important to ensure the company's capabilities align with your needs. - Who actually manufactures PCBs?
PCB manufacturing is done by specialized companies that focus on creating the bare boards. These bare PCBs are then populated with components by PCB assembly companies. Some companies offer both manufacturing and assembly services, while others specialize in one or the other. - What certifications should a PCB assembly company have?
Key certifications to look for include ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 13485 (medical devices), AS9100 (aerospace), and IPC standards compliance (industry-specific standards for electronics manufacturing). Certifications signify a company’s adherence to quality and industry best practices. - What is the typical turnaround time for PCB assembly?
Turnaround times vary depending on the complexity of the assembly, order volume, and the company's workload. Standard times can range from a few days for simple prototypes to several weeks for large, complex orders. Rush services are often available at an additional cost. - How can I ensure the quality of my PCB assembly?
Quality can be ensured through a combination of factors, including stringent testing procedures (such as Automated Optical Inspection, In-Circuit Testing, and Functional Testing), selecting a company with appropriate certifications, ensuring they have documented processes, and carefully reviewing their customer references.
Emerging Trends and Innovations in PCB Assembly
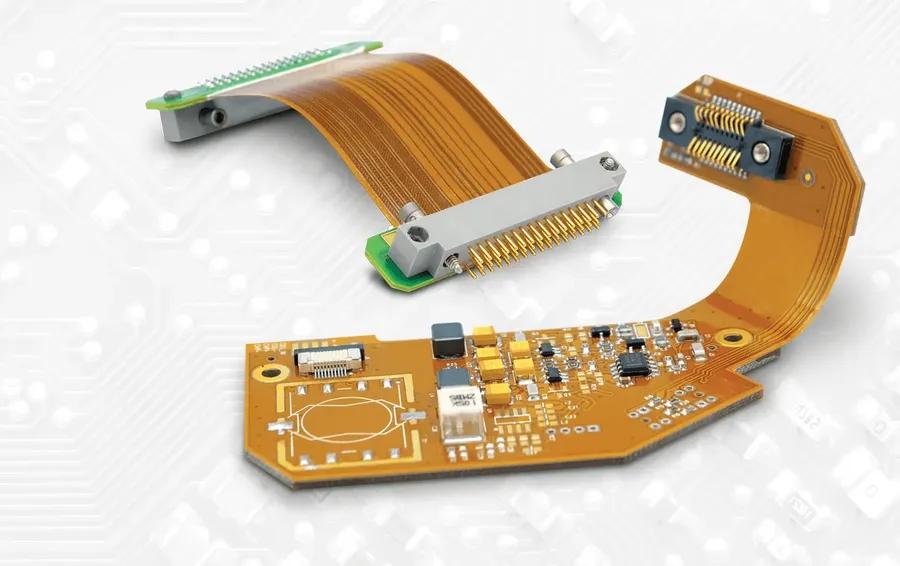
The PCB assembly landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements that are reshaping manufacturing processes and influencing the selection of suitable assembly partners. Key trends include increased automation, miniaturization, and a growing focus on sustainable manufacturing practices, all of which aim to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and meet the demands of increasingly complex electronic devices.
- Automation in PCB Assembly
Robotics and automated systems are increasingly prevalent in PCB assembly, enhancing precision, speed, and repeatability while reducing manual labor costs. Advanced pick-and-place machines, automated optical inspection (AOI) systems, and automated soldering processes contribute to a highly efficient and reliable assembly line. This trend is especially critical for high-volume production and complex assemblies, ensuring consistent quality and faster turnaround times. - Miniaturization
The push towards smaller and more powerful electronic devices necessitates advanced miniaturization techniques in PCB assembly. Fine-pitch components, micro-BGAs, and stacked vias require precise assembly processes and sophisticated equipment. As components become smaller, the need for high-precision assembly and advanced inspection technologies also increases, necessitating the adoption of newer, more precise assembly equipment and inspection methods. - Sustainable Manufacturing
Environmental concerns are driving a demand for sustainable manufacturing practices in PCB assembly. This includes the use of lead-free materials, the implementation of eco-friendly manufacturing processes, and efforts to minimize waste and energy consumption. Companies that are at the forefront of these sustainability initiatives are gaining a competitive edge by reducing their environmental footprint and appealing to environmentally conscious clients. This trend is not just about compliance; it is about adopting a responsible manufacturing ethos.
These trends are interconnected and collectively demand a more strategic approach when selecting a PCB assembly partner. Companies must evaluate not only the current capabilities of potential partners but also their readiness to adopt and integrate emerging technologies. Selecting a forward-thinking partner with a commitment to automation, miniaturization and sustainability will enable them to adapt to the future of the PCB assembly industry.
Selecting the right PCB assembly company is pivotal for the success of any electronics project. This guide has explored key aspects of PCB assembly from process understanding to cost evaluation, emphasizing the significance of capabilities, location, and technology. By considering all these factors, you are equipped to make an informed decision and partner with a reputable PCB assembly company that will bring your designs to life with efficiency and quality. As technology continues to evolve, choosing the right partner will be more critical than ever, ensuring continued innovation in electronics. Partnering with the right pcb assembly company ensures your projects' success from prototype to full-scale production, propelling your business in the competitive electronics industry.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA