Decoding BLDC Fan Circuit Board Prices: A Comprehensive Guide
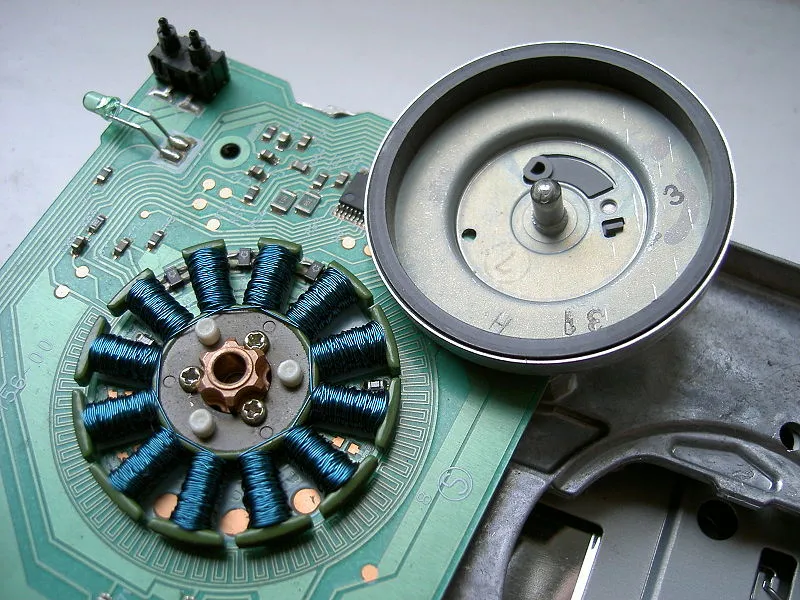
In an era where energy efficiency and technological advancements are paramount, BLDC (Brushless Direct Current) fans have surged in popularity. But what directly affects the bldc fan circuit board price? This article dives deep into the world of BLDC fan PCBs, unraveling the complexities of pricing, manufacturing, and key features. Understanding this will help both businesses and individuals to purchase and develop the appropriate products that meet their needs, just as the evolution of social science and technology has changed our world.
Understanding BLDC Fan Technology

Brushless Direct Current (BLDC) fans represent a significant advancement over traditional AC induction fans, primarily due to their higher energy efficiency and precise speed control capabilities. At the heart of this technology lies the BLDC motor, an electronically commutated motor that utilizes a permanent magnet rotor and a stator with electromagnetic coils. Unlike conventional brushed motors, BLDC motors do not rely on physical brushes for commutation, which leads to reduced friction, improved efficiency, and longer operational lifespan.
The BLDC fan circuit board acts as the brain of the system, playing a crucial role in the operation of a BLDC fan. It houses the electronic components and control circuitry necessary to convert incoming AC power into a form suitable for driving the BLDC motor. Its function includes controlling the timing and sequence of current flow through the stator coils to create a rotating magnetic field, which interacts with the rotor's permanent magnets, causing the motor to turn. The board regulates motor speed, manages power consumption, and implements safety features. Precise control of these functions allows for the efficient use of energy and enhanced performance. The components on this board influence the overall performance and cost, which directly affects the final bldc fan circuit board price.
- Key Functions of a BLDC Fan Circuit Board:
Convert AC power to DC for motor operation.
Generate the necessary signals to commutate the BLDC motor.
Control motor speed by adjusting voltage frequency.
Implement safety mechanisms to prevent overload and damage.
Key Components Influencing BLDC PCB Price
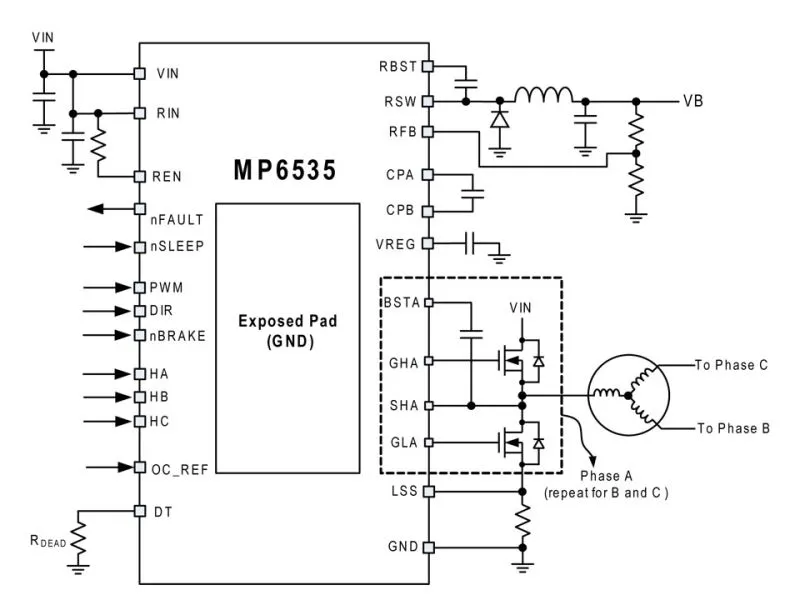
The price of a BLDC (Brushless DC) fan circuit board is significantly influenced by the cost of its constituent electronic components. These components, which perform essential functions like motor control, power management, and signal processing, directly affect the board's performance and overall cost.
The key components that directly impact the price of a BLDC fan PCB can be broken down as follows:
- Microcontroller (MCU)
The brain of the BLDC fan, responsible for executing the control algorithms, managing fan speed, and handling user interfaces. The complexity and performance of the MCU, including its processing power and memory capacity, have a significant impact on price. Higher-end MCUs with more advanced features (e.g., integrated Bluetooth, advanced motor control algorithms) come at a premium. - MOSFETs (Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistors)
These are power switching devices that control the current flow to the BLDC motor windings. The price of MOSFETs depends on their voltage and current handling capabilities and their on-resistance, which affects efficiency. High-performance MOSFETs with low on-resistance and higher current ratings are more costly. - Capacitors
Used for energy storage, filtering, and noise reduction. The type (e.g., ceramic, electrolytic) and rating of capacitors impact the overall cost. High-quality capacitors with better temperature stability and lower equivalent series resistance (ESR) will increase the component price. - Gate Driver ICs
These ICs interface between the MCU and the MOSFETs, providing the necessary drive signals. They ensure the MOSFETs switch efficiently and are protected. Integrated gate drivers with features like overcurrent protection and dead-time control are generally more expensive than simpler discrete implementations. - Current and Voltage Sensors
These devices measure the current flowing through the motor windings and the voltage across various points in the circuit. They are necessary for implementing accurate control algorithms and safety features. Higher-precision sensors are more expensive. - PCB Material and Manufacturing
The material used for the PCB substrate (e.g., FR4, Aluminum) impacts the cost, as well as the PCB layer count and trace width needed to handle high currents. Higher-grade PCB materials and complex layouts increase the manufacturing costs, therefore impact the final PCB price. - Connectors and Interface Components
Connectors, headers, and interface components for user controls and power supply also influence cost. More reliable or specialised connectors (e.g., waterproof) will impact cost.
| Component | Price Influence | Factors Affecting Price |
|---|---|---|
| Microcontroller (MCU) | High | Processing power, memory, features (Bluetooth, etc.) |
| MOSFETs | Medium to High | Voltage, current rating, on-resistance |
| Capacitors | Low to Medium | Type (ceramic, electrolytic), rating, temperature stability |
| Gate Driver ICs | Medium | Integration, protection features |
| Current/Voltage Sensors | Low to Medium | Precision and accuracy |
| PCB Material | Medium | Material type, layer count, and trace width |
| Connectors | Low | Reliability and type |
The selection of these components often involves a trade-off between performance, cost, and reliability. Manufacturers of BLDC fan circuit boards must carefully choose the components that best match the product's performance requirements, cost targets, and life span goals.
Types of BLDC Fan PCBs: Single vs. Multi-Speed, RF & IR Control
BLDC fan Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) are not created equal; they vary significantly in complexity and functionality, directly impacting their price. This section will explore the differences between single-speed, multi-speed, and advanced remote-controlled PCBs, highlighting how these variations influence cost.
| Feature | Single-Speed PCB | Multi-Speed PCB | RF/IR Control PCB |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed Control | Fixed Speed | Multiple Preset Speeds | Variable Speed with Remote |
| Control Method | Simple On/Off Switch | Button/Rotary Switch | Remote Control (RF/IR) |
| Components | Basic Microcontroller, Minimal Components | Enhanced Microcontroller, Additional Components | Complex Microcontroller, RF/IR Receiver, Memory |
| Complexity | Low | Medium | High |
| Cost | Lowest | Medium | Highest |
| Typical Application | Basic fans | General purpose fans | Premium/Smart fans |
Here's a breakdown of each type:
- Single-Speed BLDC Fan PCBs:
These are the most basic and cost-effective. They typically offer a fixed fan speed, controlled by a simple on/off switch. The circuitry is minimal, involving a basic microcontroller and essential components, resulting in a lower price. These are best suited for applications where speed control is not a requirement. - Multi-Speed BLDC Fan PCBs:
These PCBs allow users to select from a few pre-set speeds using buttons or a rotary switch. They feature a more advanced microcontroller and additional components, leading to a moderate increase in cost compared to single-speed boards. This type is common in general-purpose ceiling fans, where some level of speed variation is desired. - RF/IR Control BLDC Fan PCBs:
These represent the high-end of BLDC fan PCBs, enabling variable speed control via RF (radio frequency) or IR (infrared) remote controls. They incorporate sophisticated microcontrollers, RF/IR receiver modules, and often memory to store user settings and advanced features such as sleep timers and modes. The complexity of these boards results in the highest cost. These are generally found in premium or ‘smart’ fans.
The decision on the type of PCB to use depends on the requirements of the fan application and the targeted price point. Manufacturers must balance cost with functionality to satisfy different market segments. For instance, a low-cost fan for basic ventilation might use a single speed PCB, while a high-end fan with smart features might opt for a sophisticated RF/IR controlled PCB.
Factors Affecting BLDC Fan Circuit Board Price
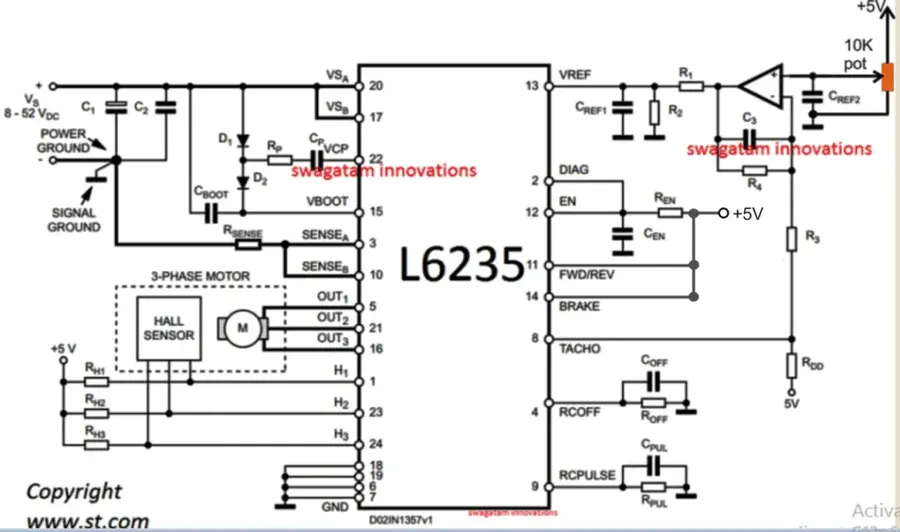
The price of a BLDC fan circuit board is not arbitrary; it's the result of several interacting factors. Understanding these influences provides crucial insight into the cost structure of these essential components and what drives the bldc fan circuit board price.
- Manufacturing Volume
The quantity of circuit boards produced significantly impacts the unit price. High-volume orders benefit from economies of scale, reducing per-unit costs due to optimized production runs and bulk purchasing of components. Lower production volumes, conversely, incur higher per-unit expenses. - PCB Material
The type of substrate material used for the circuit board directly affects the cost. Standard FR-4 material is cost-effective but may not be suitable for all applications. Advanced materials like high-Tg FR-4 or metal-core PCBs, offer better thermal and mechanical properties but come at a higher price. The choice of PCB material is usually a trade-off between cost, performance, and reliability - Design Complexity
The sophistication of the circuit design is a key factor. Simple, single-layer PCBs with minimal components are less expensive to manufacture than complex, multi-layer designs that include numerous components, intricate routing, and advanced functionalities such as multiple speed settings and RF/IR receiver for remote control. The design and implementation of additional features will increase the cost. - Component Quality and Brand
The quality of components used, such as microcontrollers, MOSFETs, capacitors, and sensors, impacts the overall cost. High-performance, branded components from reputable manufacturers generally cost more than generic components. The choice of components reflects a trade-off between cost, reliability and durability. - Testing Standards
Rigorous testing and quality control procedures add to the overall cost, but result in reliable circuit boards. Boards that undergo stringent electrical testing, burn-in tests and environmental tests are more expensive to manufacture, but offer better performance, durability and safety. - Assembly Process
The method of assembling the components onto the PCB board will affect the cost. Automated surface mount technology (SMT) assembly is generally more cost-effective for large production runs, while manual or thru-hole assembly methods are more expensive for lower quantities. SMT assembly generally provides higher reliability than manual assembly.
| Factor | Impact on Price | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Volume | High volume = Lower price | Economies of scale reduce per-unit costs in mass production. |
| PCB Material | Advanced Material = Higher price | FR-4 is cost effective, high performance materials like metal core are more expensive. |
| Design Complexity | Complex design = Higher price | Multi-layer boards with complex designs and advanced features are more expensive |
| Component Quality | Higher quality components = Higher price | Branded components from reputable manufacturers are more expensive, but offer higher performance. |
| Testing standards | Rigorous testing = Higher price | Comprehensive testing ensures higher reliability but increases cost. |
| Assembly Process | Automated SMT = Lower Price | Automated SMT assembly for higher volumes is more cost effective, while manual assembly is more expensive. |
The price of a BLDC circuit board is a function of multiple factors which must be considered in total. Each factor presents its own balance of cost, performance, reliability, durability and safety. Optimizing these tradeoffs is essential to selecting the best circuit board for the application. This makes it necessary to weigh performance, cost and reliability.
BLDC Fan PCB Price Comparison: Marketplace Insights
Navigating the BLDC fan circuit board market requires a keen understanding of pricing variations across different suppliers. This section provides a comparative analysis of BLDC fan PCB prices from various vendors, both domestic and international, highlighting potential trade-offs and considerations for buyers.
Prices for BLDC fan PCBs can vary significantly based on several factors such as the supplier's location, manufacturing capacity, and the specific features included on the board. This variation necessitates a careful evaluation of options.
| Supplier Type | Price Range (USD) | Typical Lead Time | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Domestic Manufacturers | $5 - $15 | 2-4 Weeks | Faster shipping, easier communication, local support | Potentially higher prices, limited customization options |
| International Suppliers (e.g., China) | $2 - $8 | 4-8 Weeks | Lower prices, wide range of customization | Longer shipping times, communication challenges, variable quality control |
| Specialized Distributors | $8 - $20 | 2-6 Weeks | High-quality boards, readily available inventory, specialized expertise | Higher costs, may not offer deep customization |
Note: The listed price ranges are approximate and can fluctuate due to volume orders, raw material costs, and currency exchange rates. Always request a formal quote from the supplier for an accurate price estimation.
- Key Considerations When Comparing Prices:
When comparing prices, it is crucial to consider the trade-offs in price versus quality, lead time, and customization. Here are important factors to examine: - PCB Material:
The type of substrate material used affects thermal performance, durability, and cost. FR4 is commonly used but other advanced materials are available at a premium. - Component Quality:
Lower-cost boards might use lower-grade components, potentially leading to reliability and performance issues. - Design Complexity:
Boards with advanced features such as RF control, multiple speed settings, or integrated protection circuits will typically cost more. - Testing and Certification:
Ensure the PCB meets necessary safety standards and certifications, adding to overall cost but ensuring safe use.
DIY vs. Purchased BLDC Fan PCBs: Cost and Feasibility Analysis

The decision between building a BLDC fan PCB from scratch and purchasing a pre-made one involves a careful assessment of cost, feasibility, and complexity. This section provides a detailed comparison to help you make an informed choice.
| Aspect | DIY BLDC Fan PCB | Purchased BLDC Fan PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Potentially lower for individual components but includes development costs; varies greatly based on design and component choice. | Higher upfront cost but can be more cost-effective for small quantities due to optimized production. |
| Feasibility | Requires expertise in PCB design, component selection, embedded programming, and electronics assembly. Success is contingent on technical skill and experience. | Easy to implement, requires only connecting the pre-made PCB to the BLDC motor and power source; user-friendly even for beginners. |
| Complexity | Very complex, involves designing the circuit, selecting components, creating layout, assembling PCB, and programming the microcontroller. | Low complexity; requires minimal effort beyond installation. |
| Time Commitment | Significant time investment in design, testing, and debugging. Multiple iterations might be necessary. | Minimal time commitment; ready to use out of the box. |
| Customization | Highly customizable; can be tailored to specific needs and feature requirements. | Limited customization; features are predetermined by the manufacturer. |
| Troubleshooting and Support | Requires in-depth knowledge to troubleshoot and fix any issues. No external support available. | Manufacturer provides support and warranty, making troubleshooting easier. |
| Component Sourcing | Requires sourcing individual components from various suppliers which may affect price and availability. | Sourcing and component management handled by the manufacturer. |
| Quality & Reliability | Quality is dependent on individual workmanship and may vary significantly. Requires thorough testing to ensure reliability. | Manufactured in controlled environments with quality control procedures, providing better reliability |
**Cost Analysis:** While DIY might seem cheaper initially due to lower component costs, the hidden costs of design, debugging, testing, and potential rework can quickly escalate. Pre-made boards benefit from economies of scale and optimized manufacturing processes. The total cost of DIY can vary greatly depending on the design and component selection, and a first timer might waste materials on incorrect assembly or design issues.
**Feasibility Analysis:** The feasibility of DIY depends heavily on your skill set. It's a project best suited for those with a strong background in electronics, PCB design, and embedded systems. Purchasing a pre-made PCB is significantly more feasible for those who lack such skills or who require a quick and reliable solution.
**Complexity and Time Investment:** Designing a BLDC fan PCB requires a solid understanding of analog and digital electronics, microcontrollers, and motor control algorithms. This is a time-consuming process, often involving multiple iterations and debugging. Pre-made boards offer a plug-and-play solution, saving valuable time and effort.
**Recommendation:** For hobbyists and educational projects with advanced users, building a BLDC fan PCB can be a great learning experience. However, for commercial applications or situations where reliability and time are crucial, purchasing pre-made boards is often the more practical and cost-effective option.
Frequently Asked Questions About BLDC Fan Circuit Boards
This section addresses common queries regarding BLDC fan circuit boards, providing clear and concise answers to help users understand key aspects of these components, including selection, lifespan, repair, malfunction troubleshooting and popular brands.
- How do I choose a suitable BLDC fan PCB?
Selecting the right BLDC fan PCB involves matching the board's specifications with your fan motor's requirements. Crucially, ensure that the voltage and current ratings of the PCB are compatible with your motor. Consider features like speed control options (single-speed, multi-speed, or remote control), and additional functionalities such as soft start or reverse polarity protection. Look for boards from reputable manufacturers, as this is a key factor in ensuring reliability and performance. - What is the average lifespan of a BLDC fan PCB?
The typical lifespan of a BLDC fan PCB is largely determined by the quality of the components and the operational conditions. High-quality PCBs, utilizing robust components and operating within specified parameters, can last for several years, often matching the lifespan of the fan motor itself. Factors like excessive heat, humidity, and voltage spikes can significantly reduce a board’s longevity. Therefore, ensuring proper ventilation and power conditioning is essential for extending its lifespan. - Can I repair a damaged BLDC fan PCB?
Repairing a BLDC fan PCB is feasible, but it requires advanced knowledge of electronics and appropriate tools. Common failures involve component issues like burnt MOSFETs, damaged capacitors, or faulty microcontrollers. If the damage is extensive, or if you are not experienced with SMD soldering and PCB repairs, it is more cost-effective to replace the entire PCB board. Diagnosing and sourcing replacement components can be time consuming and complex, making repair challenging for inexperienced users. - What should I do if my BLDC fan PCB malfunctions?
When a BLDC fan PCB malfunctions, it's important to first diagnose the specific issues. Check for any visible damage like burnt components or loose connections. If the fan doesn't respond to speed changes or exhibits erratic behavior, it may signal a fault with the microcontroller or power circuitry. If you have some electronics knowledge, you can use a multimeter to check voltage levels and continuity. Otherwise, consider consulting a qualified technician. For minor problems, you can first try powering down and then restarting the device before taking more advanced steps. - What are some popular BLDC fan PCB brands and their price ranges?
Several brands offer BLDC fan PCBs, each with varying specifications and pricing. Some well-known brands include Atomberg, which is known for high efficiency and reliability. Other notable brands include those by major fan manufacturers like Crompton, Havells, and Orient, which often produce boards specifically for their fan models. Prices can range from a few dollars for basic boards to upwards of $20-$30 for more advanced, feature-rich PCBs, with prices being highly variable and changing regularly. It’s recommended to check with authorized distributors for current prices. - How does a BLDC fan PCB with remote control differ in price?
BLDC fan PCBs with remote control functionality, either RF (Radio Frequency) or IR (Infrared), generally cost more than single-speed or basic multi-speed versions. These boards require additional components like receiver circuits and microcontrollers capable of handling remote commands. The added complexity in design and componentry accounts for the higher price tag. The difference can be as much as 20-40% higher than basic models. - Where can I source a BLDC fan PCB?
BLDC fan PCBs can be sourced from multiple channels. Online marketplaces like AliExpress, Amazon, and eBay often have a wide range of options, but you should verify the seller’s reputation. Authorized distributors of electronic components, as well as manufacturers who supply replacement parts for their products, are also good sources for obtaining BLDC fan PCBs. It is very important to consider only well known vendors with a good return policy, since performance variations and component counterfeits are common in this market.
Future Trends in BLDC Fan Circuit Board Technology and Pricing

The future of BLDC fan circuit board technology is poised for significant advancements, driven by the increasing demand for energy-efficient and smart home solutions. These innovations are expected to influence both the functionality and the pricing of BLDC fan PCBs.
Several key trends are emerging, with a significant focus on integrating advanced technologies.
- IoT Integration
The integration of Internet of Things (IoT) capabilities will enable users to remotely control and monitor their BLDC fans through smartphone apps and other connected devices. This includes features like scheduled operation, real-time energy consumption monitoring, and integration with smart home ecosystems. This enhanced connectivity will likely increase the complexity and, consequently, the cost of BLDC fan PCBs, at least initially. - AI-Powered Optimization
The use of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to optimize fan speed and airflow based on real-time environmental conditions, user preferences, and even predictive analysis of weather patterns. AI can dynamically adjust the fan speed to maximize comfort while minimizing energy consumption. This will lead to the development of more complex circuit boards with enhanced processing capabilities and increased memory. - Advanced Sensor Technologies
The incorporation of advanced sensors, including temperature, humidity, and air quality sensors, integrated directly onto the PCB. These sensors will allow for more precise control of the fan and potentially offer additional features such as air purification or allergen detection. The added functionality will likely increase the component cost for BLDC fan PCBs. - Miniaturization and Component Integration
A trend towards further miniaturization of components and increased levels of integration onto the PCB. This reduces the overall footprint of the board, potentially leading to more compact and aesthetically pleasing fan designs. This could lower costs through efficient design and reduced material usage. - Energy Harvesting
Exploring alternative power sources like solar energy or ambient kinetic energy for powering the fan's electronics. This trend could reduce reliance on the mains power supply and lead to more self-sustaining fan operation, thus making them more energy-efficient. This technology is in its early stages, thus it may increase the cost of the boards but offers great potential in the future.
Considering these trends, the pricing of BLDC fan circuit boards is anticipated to be dynamic. Initially, technologies like IoT integration and AI-powered optimization will likely increase the cost due to the need for more sophisticated components and design complexity. However, as manufacturing processes become more efficient and the technologies become more mainstream, prices are expected to stabilize or potentially decrease. It is crucial for manufacturers to balance the cost of new features against consumer demand to maintain a competitive edge.
| Trend | Impact on Price | Impact on Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| IoT Integration | Initially Increased, then potential stabilization | Remote Control, Monitoring, Smart Home Compatibility |
| AI-Powered Optimization | Initially Increased, then potential reduction with mainstream adoption | Dynamic speed and airflow adjustments for optimal comfort and efficiency |
| Advanced Sensor Technologies | Increase due to added component costs | Improved environmental monitoring and air quality control |
| Miniaturization & Integration | Potential Cost Reduction | Compact designs, improved aesthetics |
| Energy Harvesting | Increased Cost initially, Long-term savings in electricity. | Self-sustaining and energy-efficient operation |
The price of a BLDC fan circuit board hinges on several crucial factors, including the quality of components, the complexity of design, and market dynamics. Whether you're a DIY enthusiast or a manufacturer, understanding these factors can lead to more informed purchasing decisions, whether it is buying a circuit board for personal use, or understanding how it affects the final bldc fan circuit board price. Keep up with the latest technology for a better understanding of the future trends in BLDC fan technology and pricing.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA