Decoding UPS PCB Board Prices: A Comprehensive Guide for Buyers
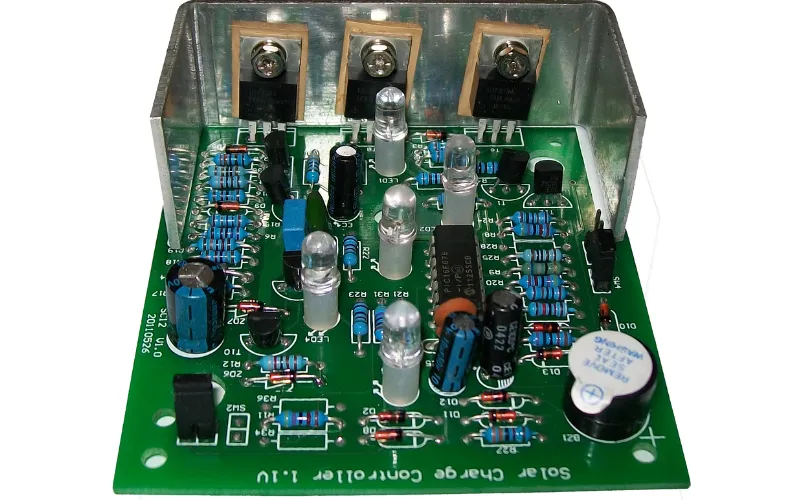

In our tech-driven world, Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) are crucial for maintaining consistent power, safeguarding electronics from unexpected outages. At the heart of every UPS lies a Printed Circuit Board (PCB), the unsung hero ensuring stable power delivery. Understanding the factors influencing the ups pcb board price, from raw materials to technology, is vital for both manufacturers and consumers. This article demystifies the often-opaque world of UPS PCB pricing, helping you make informed purchasing decisions and grasp the complexities behind this essential piece of technology.
Key Factors Influencing UPS PCB Board Prices

The price of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) PCB (Printed Circuit Board) is determined by a confluence of factors, including raw material costs, the complexity of the board's design, the manufacturing processes employed, and the overall production volume. These elements interact to establish the final cost, making a nuanced understanding of each essential for accurate price assessment.
- Raw Material Costs
The choice of substrate materials, such as FR-4 or specialized high-performance laminates, profoundly impacts the PCB's price. Additionally, the cost of copper, solder, and other conductive materials varies based on market conditions and purity requirements. - Board Complexity
The intricacy of the PCB design, including the number of layers, trace density, and component density, directly affects the manufacturing difficulty and cost. Multi-layer boards with fine-pitch components command higher prices compared to simpler single-layer designs. - Manufacturing Processes
Automated assembly lines, surface mount technology (SMT), and through-hole technology all come with different production costs. Stringent quality control measures, although essential for reliability, also contribute to the final price of the board. - Production Volume
The quantity of PCBs ordered significantly influences the per-unit cost. Larger production runs allow manufacturers to distribute fixed costs over more units, resulting in lower prices. This is a key factor in price negotiation.
The Role of PCB Complexity in Pricing
The complexity of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a primary driver of its cost, directly impacting the final price of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) system. This complexity is not just about the number of components but also the intricacy of the board's design, layering, and component density.
| PCB Complexity Factor | Impact on Cost | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Layers | Directly Proportional | Single-layer PCBs are the least expensive, while multi-layer PCBs, which incorporate more conductive layers for complex signal routing, are considerably more expensive. Each additional layer involves increased manufacturing steps and material costs. |
| Component Density | Directly Proportional | Higher component density, meaning more components placed in a smaller area, requires precise manufacturing techniques, thus increasing the cost. It also necessitates finer traces and vias. |
| Board Size | Directly Proportional | Larger PCBs require more material, have higher manufacturing costs, and can have lower production yields. Especially for multi-layer boards, the cost increases substantially with area. |
| Routing Complexity | Directly Proportional | Complex trace routing with many signal paths, especially for high-speed circuits, increases the difficulty of design and manufacturing. This complexity requires more advanced manufacturing equipment. |
| Use of Advanced Components | Directly Proportional | Use of surface mount components (SMT), fine pitch components, or Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages, which have higher manufacturing costs than through hole technology, also adds complexity and cost to the PCB design. |
Manufacturing Process Impact on Cost

The manufacturing process significantly influences the final cost of a UPS PCB board. The choice between automated and manual assembly, as well as the implementation of surface mount technology (SMT) versus through-hole technology, directly affects production expenses. Furthermore, stringent quality control measures, while increasing initial costs, are crucial for ensuring the long-term reliability of the board.
| Manufacturing Process Aspect | Impact on Cost | Impact on Quality |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Assembly | Generally lower per-unit cost for high volume production due to efficiency and speed. | High consistency and precision, leading to fewer errors. |
| Manual Assembly | Higher per-unit cost, especially for high volume production, labor intensive. | Potentially variable quality, dependent on operator skill, may lead to defects. |
| Surface Mount Technology (SMT) | Cost-effective for small components and high-density boards, good for automated process. | Excellent electrical performance and reliability; good for automated process. |
| Through-Hole Technology | Higher assembly cost due to manual insertion and soldering, particularly for complex boards. | Strong mechanical bond but can be less precise than SMT, more susceptible to human error. |
| Strict Quality Control | Increases the initial costs due to testing, inspections, and rework. | Improved reliability, reduced failure rates, and increased product lifespan; also reduces long term cost. |
Material Sourcing and Its Effect on Pricing
The selection and origin of materials are pivotal factors determining the cost of a UPS PCB. The price is significantly influenced by the types of materials used—such as copper, solder, and substrate—with premium options and environmentally conscious choices typically leading to higher expenses. Fluctuations in raw material market conditions also exert a considerable impact on the final PCB cost.
| Material | Impact on Cost | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Copper | High | Purity and thickness affect conductivity and cost; sourcing from reputable suppliers ensures quality. |
| Solder | Medium | Lead-free solder is often more expensive but environmentally compliant; alloy composition influences joint strength and reliability. |
| Substrate (e.g., FR-4) | High | The type of substrate (e.g., FR-4, aluminum-backed, high-frequency) affects thermal and electrical performance; specialized materials drive up cost. |
| Component Materials | Variable | Quality, origin, and specific requirements of integrated circuits, capacitors, resistors, and other components directly impact price. |
| Gold Plating | High | Used for high reliability or high frequency signals; gold plating adds significantly to cost |
Furthermore, sourcing decisions impact cost, with local and long-term suppliers often offering more competitive pricing compared to spot purchases from different suppliers. The selection of raw materials is a complex process where performance needs, cost constraints, and sustainability concerns must be carefully balanced.
Understanding Market Prices: From Basic to Advanced Boards
The pricing landscape for UPS PCB boards is broad, influenced by factors such as complexity, functionality, and quantity. Basic, single-layer boards are at the lower end of the price spectrum, while high-end, complex multi-layer boards command significantly higher prices. Bulk purchasing can lead to substantial discounts, further impacting the per-unit cost.
| PCB Type | Description | Typical Price Range (USD per board) |
|---|---|---|
| Low-end | Basic single-layer PCB with minimal functionality. | $1 - $10 |
| Mid-range | Multi-layer PCB with basic to moderate functionality. | $10 - $50 |
| High-end | Advanced, complex multi-layer PCB with high component density. | $50 - $500+ |
It's important to note that these price ranges are approximate and can fluctuate based on market conditions, specific design requirements, and the chosen manufacturer or supplier. Additionally, factors such as component sourcing, lead times, and quality control standards will also influence the overall cost.
Where to Buy UPS PCB Boards: A Comparison of Suppliers

Procuring UPS PCB boards involves navigating various supply channels, each with its own implications for cost, lead time, and quality. Understanding these differences is critical for making informed purchasing decisions that align with project requirements and budget constraints.
| Supplier Type | Pricing | Lead Time | Quality | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Online Platforms (e.g., Alibaba, Amazon) | Variable, often competitive for standard boards; can fluctuate significantly. | Moderate to long, especially for overseas suppliers; can vary with seller and location. | Variable; quality control depends on the individual seller; requires careful vetting. | Good for initial sourcing and exploring options. Suitable for smaller orders, but due diligence is needed to avoid counterfeit or substandard products. |
| Specialized Component Suppliers | Moderate to high, typically offering better consistency in pricing within their range. | Generally moderate; may depend on supplier stock and order complexity. | High; often provides certification and detailed technical specifications. | Ideal for higher-quality components and designs. Offers better support and expertise, but at a premium. |
| Direct Manufacturers | Potentially competitive for large volumes; negotiation and volume discounts may be available. | Variable but often the longest, including production and delivery; can be reduced with prior agreements and scheduling. | High; can be customized to specific quality standards; may involve extensive quality control processes. | Best for large-scale projects, enabling customization and direct technical support, but usually requires volume commitments. |
Frequently Asked Questions about UPS PCB Boards
Understanding the nuances of UPS PCB boards is crucial for ensuring system reliability and cost-effectiveness. This section addresses common inquiries regarding their lifespan, failure indicators, efficiency optimization, and repair considerations, providing essential insights for informed decision-making.
- What is the typical lifespan of a UPS PCB?
The typical lifespan of a UPS PCB board is heavily influenced by operating conditions, component quality, and environmental factors such as temperature and humidity. Generally, a well-designed and properly maintained board can last anywhere from 5 to 10 years. However, constant exposure to high temperatures or frequent power surges can significantly reduce its lifespan. Regular inspections and preventative maintenance are crucial for extending the service life. - What are the main signs of a failing UPS PCB?
Signs of a failing UPS PCB can manifest in various forms. These include the UPS failing to switch to battery power during an outage, frequent alarms or error messages, the UPS not holding a charge, or complete failure to power on. Physical indicators such as burnt components, bulging capacitors, or discoloration of the board are also strong signs of potential failure. Early detection of these symptoms can prevent more extensive damage and costly repairs. If any of these occur, a thorough inspection by a professional is advised. - How can I optimize the efficiency of my UPS PCB?
Optimizing the efficiency of a UPS PCB involves several key strategies. Firstly, ensuring that the UPS is appropriately sized for the connected load prevents unnecessary energy consumption. Secondly, employing energy-efficient components in the PCB design can significantly reduce power loss and heat generation. Implementing an intelligent cooling system, such as properly sized heatsinks and fans, to maintain optimal operating temperatures also enhances efficiency and reliability. Regular maintenance, like cleaning dust and debris, helps prevent overheating and improves overall performance. It also makes sense to explore newer UPS topologies or PCB designs known for higher efficiency. - Can I repair a damaged UPS PCB myself, or should I seek professional help?
While some minor issues, such as loose connections, can be safely addressed by individuals with basic electronics knowledge, repairing a damaged UPS PCB is generally not advisable without proper training and equipment. Complex repairs involving component replacement or troubleshooting intricate circuits should always be handled by qualified professionals. Attempting such repairs without expertise can lead to further damage, create safety hazards, and void any existing warranty. A professional service will have a higher level of expertise and the tools to carry out a safe and effective repair. - What are the implications of using lower-grade materials in UPS PCB manufacturing?
Using lower-grade materials in UPS PCB manufacturing can have severe implications on the board's performance, reliability, and lifespan. Cheaper materials might exhibit higher resistance, leading to increased heat generation and energy loss. They may also be more susceptible to corrosion and degradation, especially in harsh environmental conditions. Furthermore, inferior materials may lack the required thermal stability to withstand demanding operational conditions, resulting in premature failures. Utilizing quality components and materials is critical for producing high-performing, dependable, and long-lasting UPS PCB boards. - How does the operating environment affect UPS PCB lifespan?
The operating environment is a critical factor influencing the lifespan of a UPS PCB. High ambient temperatures can accelerate component degradation, while excessive humidity can cause corrosion and electrical shorts. Dust accumulation can lead to overheating, and significant vibrations can loosen connections or damage sensitive components. A stable, temperature-controlled, and clean environment is ideal for ensuring that a UPS PCB performs optimally over an extended period of time. Following best practices for UPS placement, such as avoiding direct sunlight and ensuring adequate ventilation, will help to extend the longevity of a board.
Trends and Future of UPS PCB Board Pricing
The pricing landscape for UPS PCB boards is not static; it is shaped by technological advancements, raw material costs, and shifts in global demand. Understanding these dynamics is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Expect to see continued evolution in pricing due to these factors, with a particular emphasis on energy efficiency and miniaturization.
- Technological Advancements
The continuous development of new materials, manufacturing techniques, and more efficient circuit designs directly impacts the cost of PCBs. For example, improvements in surface mount technology (SMT) and the adoption of advanced PCB substrates can lower production costs, while also enabling more functionality. - Raw Material Cost Fluctuations
The prices of raw materials like copper, solder, and specialized substrates are subject to market volatility. Price increases in these essential components can cause corresponding increases in the cost of PCB manufacturing. Monitoring these fluctuations can help predict future cost changes. - Global Demand Shifts
Changes in global demand for electronics, particularly in sectors that rely heavily on UPS systems, affect PCB prices. Increased demand typically leads to higher prices due to supply chain pressures, while reduced demand can lead to price reductions, especially from competitive suppliers. - Energy Efficiency and Miniaturization
The trend toward more energy-efficient and compact electronic designs is driving the development of smaller and more sophisticated PCB boards. This shift may lead to cost reductions through lower material usage and increased integration, along with new performance standards, driving up prices for specialized, high-density boards.
| Trend | Potential Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Adoption of Advanced Materials | Potential for both price increases (for high-performance materials) and decreases (due to increased efficiency) based on the specific material. |
| Increased Automation | Likely to decrease production costs and potentially lower prices over time. |
| Focus on Green PCBs | Higher initial costs due to special materials and processes, but potential for long-term savings and compliance with environmental standards. |
| Miniaturization of Components | Potential price reduction due to less material used, and increased production efficiency, but specialized component prices may be higher. |
Practical Tips for Cost-Effective UPS PCB Procurement
Optimizing UPS PCB procurement requires a strategic approach that encompasses planning, negotiation, and design considerations. By adopting these practical tips, businesses can achieve significant cost reductions without compromising the quality or reliability of their UPS systems.
- Plan Your Production Cycles
Accurately forecasting demand and aligning production cycles with these forecasts allows you to secure better pricing through bulk orders and reduces the need for expedited production, which often incurs higher costs. Efficient planning minimizes waste and reduces the likelihood of overstocking or emergency orders. - Negotiate with Suppliers
Do not accept the first quote you receive. Explore multiple suppliers and compare their offers, using your planned production volume as leverage for better pricing and payment terms. Establishing long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can yield consistent savings over time. Be sure to review contracts thoroughly to understand the full cost implications, including any potential fees or hidden charges. - Optimize PCB Designs
Carefully consider the design specifications of your UPS PCB. Simplifying designs by reducing the number of layers and components, or using alternative but equivalent parts, can significantly lower costs without impacting functionality. Thorough testing will identify where you can make substitutions without sacrificing quality or performance. Consider design for manufacturability (DFM) principles to streamline production and reduce costs. - Avoid Unnecessary Complexity
Over-engineering PCBs adds unnecessary costs. Strive for designs that meet the functional requirements without adding non-essential features that increase the complexity. Focus on the essential features that deliver the desired performance and reliability, and remove any unnecessary complexity which can drive up the cost unnecessarily and prolong the development process. Avoid custom layouts unless absolutely necessary. Utilize standardized components and layouts when possible to reduce costs. - Regularly Review and Refine
Continuously monitor your UPS PCB procurement processes and identify areas for improvement. Market conditions and technology can change which means what might have been the best option last year may not be the best this year. By tracking key performance indicators (KPIs), such as cost per unit, delivery times, and defect rates, businesses can ensure the entire process remains efficient, and identify opportunities for further optimization
Navigating the world of UPS PCB board prices requires an understanding of the factors that influence cost, from raw materials to manufacturing. The ups pcb board price can vary widely based on these factors, and it’s crucial to balance cost with quality and performance. Whether you're purchasing for manufacturing or repair, this guide equips you with the knowledge to make informed decisions, ensuring you get the best value for your investment. Remember to evaluate your needs, compare different options, and always prioritize quality and reliability for the smooth operation of your electronic systems, always considering the total cost of ownership, not just the upfront purchase price.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA