Rogers PCB Price Guide: Understanding Costs & Factors
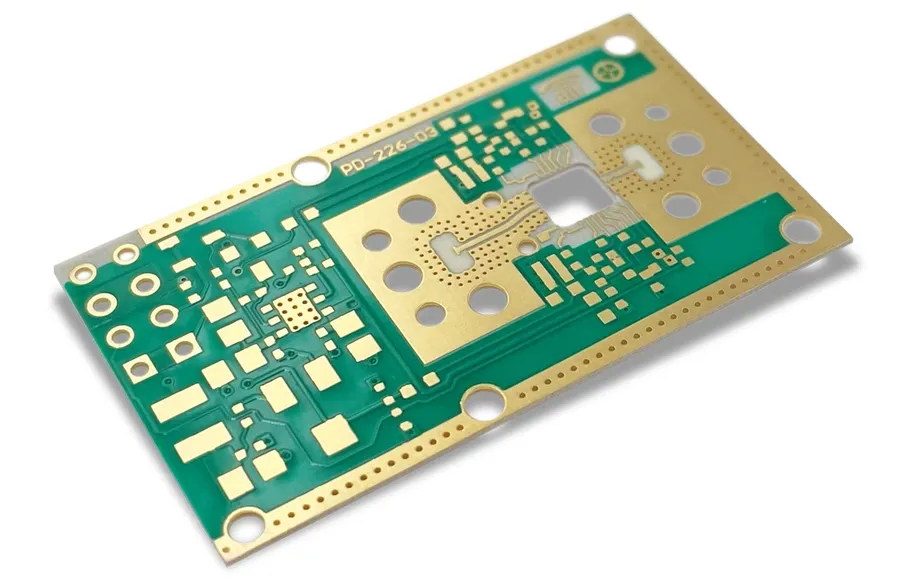
In today's world, advanced electronics often rely on high-frequency PCBs, and among the material options, Rogers PCBs stand out for their exceptional performance. But what exactly determines the final Rogers PCB price? Like a tailored suit, the cost is not uniform; it fluctuates with various factors, from material type to design complexity. This article dives deep into Rogers PCB pricing, giving you a comprehensive guide to making informed decisions, whether you’re building a cutting-edge communication device or a high-speed radar system.
Understanding Rogers PCB Materials

Rogers PCBs are renowned for their superior high-frequency performance, a characteristic directly attributable to the specialized materials used in their construction. Unlike standard FR-4 boards, Rogers materials offer tailored dielectric properties, resulting in lower signal loss, improved impedance control, and enhanced thermal management, which are crucial for demanding applications. This section will delve into the distinct attributes of several popular Rogers materials and their influence on the overall PCB cost.
| Material | Dielectric Constant (εr) | Dissipation Factor (tan δ) | Key Applications | Price Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RO4003C | 3.38 | 0.0027 | RF/Microwave, Automotive Radar, Wireless Infrastructure | Moderate |
| RO4350B | 3.48 | 0.0037 | Power Amplifiers, Antennas, High-Speed Digital | Moderate |
| RO3003 | 3.00 | 0.0013 | High-Frequency RF, Millimeter Wave, Aerospace | High |
| 5880 | 2.20 | 0.0004 | High-End RF/Microwave, Aerospace, Satellite Communications | Very High |
The dielectric constant (εr) determines the speed of signal propagation and impedance, while the dissipation factor (tan δ) indicates signal loss. Lower values of tan δ translate to better signal integrity. As illustrated in the table, RO3003 and 5880 have the lowest dissipation factors which explains their application in extremely high-frequency applications. The unique combination of these electrical properties, thermal stability, and mechanical robustness of each material impact their manufacturability, supply chain dynamics, and ultimately, the cost of the PCB. For example, materials like RO3003 and 5880 are significantly more costly due to their specialized formulations and performance characteristics.
Key Factors Affecting Rogers PCB Price
The price of a Rogers PCB is influenced by a multitude of factors, each contributing to the overall cost. Understanding these factors is crucial for effective budget planning and design optimization. These factors include the specific Rogers material used, the complexity of the PCB's construction (layer count), the dimensions of the board, its thickness, and the overall design complexity. Each of these will be discussed in detail.
| Factor | Impact on Price | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | High | Different Rogers materials (e.g., RO4003C, RO4350B, RO3003, 5880) have varying costs due to their unique dielectric properties and performance characteristics. Higher-performance materials typically cost more. |
| Layer Count | High | The number of conductive layers in a PCB significantly affects the cost. More layers require more material and complex manufacturing processes, increasing the price. |
| Board Size | Medium | Larger PCBs require more material, directly increasing cost. Manufacturing time may also increase slightly for large boards. |
| Board Thickness | Medium | Thicker PCBs require more material and may necessitate adjustments to manufacturing processes, which affects cost, especially for boards exceeding standard thicknesses. |
| Design Complexity | Medium to High | Complex designs with fine traces, vias, and intricate layouts demand advanced manufacturing techniques and may have higher reject rates, thus raising the overall cost. |
Each of these factors is interdependent; changes to one can influence others and consequently, the overall cost. For instance, increasing the layer count may also require adjustments to thickness, impacting material costs and manufacturing time. The selection of material is paramount because it dictates the underlying performance of the PCB. Rogers materials such as RO4003C, RO4350B and RO3003, which are designed for RF applications, are more expensive than FR-4 materials. Similarly, moving from a simple 2-layer design to a 6-layer design significantly increases cost due to material consumption and process complexity.
Rogers PCB Price Range: What to Expect

Determining the cost of Rogers PCBs requires understanding that pricing is not fixed and depends on a confluence of factors. While it's challenging to pinpoint an exact price without specific design details, we can provide a typical price range to set realistic budget expectations. This section offers insights into cost benchmarks per square foot and per board, supplemented by examples from different suppliers.
Generally, Rogers PCBs are more expensive than standard FR-4 PCBs due to the superior performance characteristics of their materials. These characteristics include low dielectric loss and excellent thermal and electrical properties, which are crucial for high-frequency applications.
| Metric | Typical Price Range (USD) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Price per Square Foot (Small Quantity) | $50 - $200+ | Varies based on material, layer count, complexity, and manufacturer. |
| Price per Square Foot (Large Quantity) | $20 - $100+ | Economies of scale result in reduced cost per unit. |
| Price per Board (Small Standard PCB) | $10 - $100+ | Simple designs with a few layers are on the lower end of this range. |
| Price per Board (Complex Multilayer PCB) | $100 - $1000+ | Complex designs with multiple layers are on the higher end of this range. |
To illustrate, let's consider some examples: * **Small Quantity Prototype Boards:** A small batch of prototype Rogers PCBs, such as 10 boards with a moderate layer count (4-6 layers), might cost between $50-$200 per board, while a similar board with FR-4 may be around $10 to $30 per board. * **Mid-Volume Production Run:** For a mid-volume production run (100-500 boards) of a relatively complex design, the price per board could be significantly lower, ranging from $25 to $100. This is due to the reduced setup cost per board at higher volumes. * **High-Volume Production Run:** For high-volume production runs of thousands of boards, the cost per board will further reduce significantly. However, high-volume productions are beyond the scope of the average consumer.
It's essential to obtain quotes from multiple suppliers as pricing can vary significantly based on the manufacturer's expertise, location, and material sourcing. Be prepared to provide detailed design specifications to get the most accurate pricing.
Comparing Rogers PCB Costs vs. FR-4
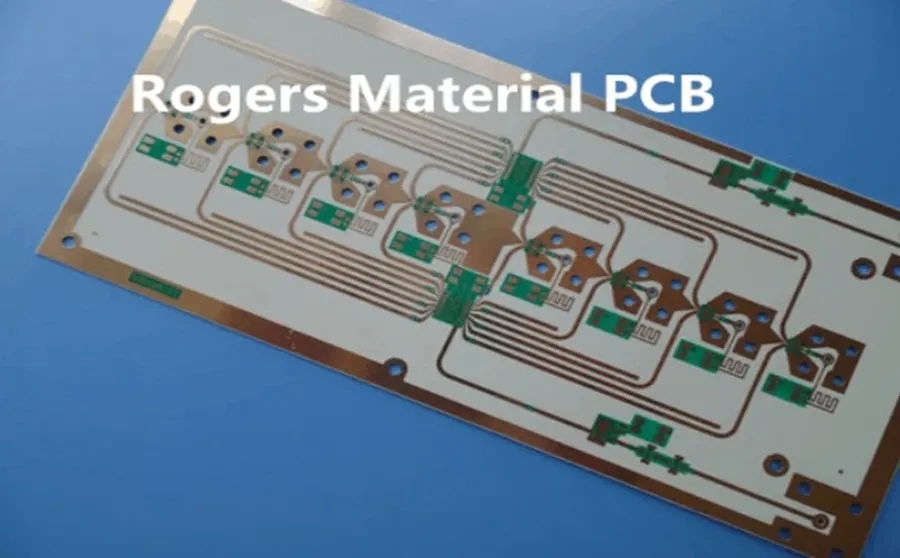
While FR-4 remains the industry standard for many PCB applications due to its cost-effectiveness and versatility, Rogers materials offer superior performance for high-frequency and specialized applications. The cost difference between FR-4 and Rogers PCBs is a key consideration, reflecting the performance advantages and manufacturing complexities associated with Rogers materials. This section provides a clear comparison of the cost implications of choosing Rogers over FR-4.
This table provides a general comparison and the exact prices can fluctuate significantly based on vendor, quantity and design complexity. Note that while the upfront cost of Rogers PCBs may be higher, their performance in high-frequency applications can result in overall system cost savings, reduced energy consumption, improved signal performance and better reliability.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rogers PCB Pricing
Understanding the cost of Rogers PCBs is crucial for project budgeting. This section addresses common questions about Rogers PCB pricing, providing clarity on what influences costs and what to expect.
- How much does a Rogers PCB cost?
The cost of a Rogers PCB varies significantly based on factors like material type, layer count, size, and complexity. It's generally higher than standard FR-4 PCBs, ranging from a few dollars per square inch for basic boards to tens of dollars for complex, multi-layered designs. A more accurate estimate requires specific design parameters. - What factors most influence Rogers PCB price?
The primary factors influencing Rogers PCB price include: the specific Rogers material used (e.g., RO4350B vs. RO3003), the number of layers, the overall board size, the copper thickness, the complexity of the design, and the order volume. Tighter tolerances or specialized treatments will also increase costs. - Why are Rogers PCBs more expensive than FR-4 PCBs?
Rogers materials are specialized high-performance laminates engineered for high-frequency applications. They exhibit superior electrical and thermal properties compared to standard FR-4, leading to a higher raw material cost. Manufacturing processes for these materials can also be more intricate and require specialized equipment, further contributing to higher prices. - Can I get an accurate price quote for a Rogers PCB?
To get an accurate quote, you'll need to provide your PCB manufacturer with precise specifications, including Gerber files, material type, layer count, board dimensions, and any special requirements. Incomplete specifications can lead to inaccurate pricing and potential project delays. - How does the order quantity affect the price of Rogers PCBs?
Like most manufactured goods, Rogers PCB pricing benefits from economies of scale. Larger production runs typically result in a lower per-unit cost. Consider aggregating your needs to minimize expenses if possible. - Are there ways to reduce Rogers PCB costs without sacrificing performance?
Yes. Careful design optimization is key. Reducing layer count, using standard board shapes, minimizing the overall board size, avoiding unnecessary features, and relaxing non-critical tolerances can all significantly impact the total cost of your Rogers PCB. - What is the typical lead time for Rogers PCBs?
Lead times for Rogers PCBs depend on the complexity of the design and the manufacturer's capabilities. Standard boards can typically be produced in 1-2 weeks, while complex, multi-layered designs might take longer. Factor this into your project timelines.
Tips for Reducing Rogers PCB Costs
Optimizing Rogers PCB costs requires a strategic approach to design and manufacturing. While Rogers materials offer superior high-frequency performance, their cost can be a concern. By focusing on key areas, it's possible to reduce expenses without sacrificing critical performance requirements. This section provides practical advice on achieving cost-effectiveness in Rogers PCB projects.
- Minimize Layer Count
Reducing the number of layers in your PCB design directly lowers material and processing costs. Carefully assess your design requirements to determine if a reduced layer count is feasible without compromising signal integrity or performance. Simplified designs are also faster to manufacture, which can further reduce overall costs. - Optimize Board Size
The overall PCB size significantly impacts cost. Larger boards require more material and incur higher processing expenses. Try to minimize the size of the board and panel effectively using layout software capabilities and considering panelization during manufacturing. The optimization of space not only affects material consumption but also reduces waste. - Standardize Board Thickness
Standard thickness options for Rogers laminates are generally more cost-effective compared to custom thicknesses. Specifying commonly available thicknesses can streamline manufacturing processes and reduce costs. Always double-check with the manufacturer about their standard options before locking in your board design. - Simplify Design Complexity
Complex board layouts with intricate routing and numerous vias contribute to higher production costs and manufacturing difficulties, so it is vital to make the design as simple and efficient as possible. Simpler designs also tend to be more reliable, which may reduce the chance of needing a redesign, thus reducing overall expenses and time. - Panelization Strategies
Utilizing efficient panelization techniques can optimize the utilization of material during manufacturing. Careful planning on panel size and number can significantly reduce raw material costs, thus reducing the cost per unit. - Early Supplier Engagement
Engage with PCB manufacturers early in the design process. Their expert advice can help you identify cost-saving opportunities and ensure your design aligns with standard manufacturing practices. Early communication can prevent costly design revisions and ensure production efficiency.
Working with PCB Manufacturers: Getting Accurate Quotes

Selecting the right PCB manufacturer is crucial for obtaining accurate cost estimates for Rogers PCBs. This process involves evaluating a manufacturer's capabilities, understanding their pricing models, and ensuring clear communication regarding your design specifications. A thorough approach ensures that the quote accurately reflects the complexity and requirements of your Rogers PCB, preventing unforeseen costs and delays.
- Evaluate Manufacturer Capabilities
Assess if the manufacturer has experience working with Rogers materials, particularly the specific materials you require (e.g., RO4003C, RO4350B, RO3003, 5880). Verify their equipment is suitable for handling these materials, which often require specialized processing techniques due to their unique electrical and mechanical properties. Check for certifications relevant to PCB manufacturing to ensure quality and reliability. - Understand Pricing Models
Inquire about the manufacturer's pricing structure. Do they charge per square inch, per board, or on a project basis? Confirm if there are additional costs for specific parameters such as layer count, thickness, or unique processing requirements related to Rogers materials. Also, check for setup fees, and understand how these charges apply to prototypes versus volume orders. - Ensure Clear Communication
Provide comprehensive design documentation, including Gerber files, detailed stack-up information, material specifications, and any specific requirements for impedance control, via structure, or surface finishes. Ensure that both your design team and the manufacturer’s team are on the same page and communicate proactively to mitigate design and manufacturing issues. Be very specific on your tolerancing and performance requirements as they influence pricing. - Request Detailed Quotes
Obtain a line-item breakdown of the costs, including materials, labor, fabrication processes, testing, and any other relevant charges. This transparency allows you to fully understand the final cost and how adjustments can impact the price. When necessary, ask for different quotes with small changes in design and see how the price changes. - Review Turnaround Times and Lead Time
Understand the time the manufacturer needs to provide the parts from your initial submission of the design files. Turnaround times can drastically impact project timelines and scheduling. Also, confirm if the manufacturer has processes to streamline and manage rush orders to ensure on-time delivery. If time is a sensitive variable, confirm that you are aware of all the delivery times and potential supply chain issues that may create longer lead times.
The Impact of Order Volume on Rogers PCB Price
The quantity of Rogers PCBs ordered significantly influences the unit price due to economies of scale inherent in manufacturing processes. Larger production runs allow manufacturers to distribute fixed costs across more units, resulting in a lower cost per PCB.
- Reduced Setup Costs
The initial setup costs for PCB manufacturing, including tooling and programming, are relatively fixed. When producing larger quantities, these costs are spread over more units, decreasing the per-unit cost. - Material Procurement
Manufacturers often receive bulk discounts from suppliers when purchasing larger quantities of materials like Rogers laminates. These savings are then passed on to the customer, leading to lower prices for larger orders. - Production Efficiency
Larger production runs streamline the manufacturing process. Fewer changeovers and interruptions increase efficiency, reducing labor costs per PCB, which can significantly impact the final price. - Increased Automation
For large orders, manufacturers can leverage automated processes and equipment more effectively, decreasing production time and reducing the likelihood of errors. This increased efficiency translates to cost savings for the customer.
| Order Quantity | Relative Unit Price | Impact on Per-Unit Cost |
|---|---|---|
| 1-10 | High | Setup costs dominate, lower material discount |
| 10-100 | Medium | Economies of scale begin to reduce cost |
| 100-1000 | Lower | Material discounts and production efficiency reduce cost further |
| 1000+ | Lowest | Maximum impact from economies of scale and material procurement |
The Rogers PCB price, while potentially higher than standard FR-4, is an investment in superior performance, especially for high-frequency applications. Understanding the factors that drive these costs, from materials to manufacturing complexity, empowers you to make informed decisions. Ultimately, choosing a Rogers PCB involves balancing performance needs with budget constraints, with careful planning ensuring you get the best value for your design. Knowing these parameters will help you get accurate quotes from manufacturers and ensure that your product performs exceptionally without breaking the bank. When planning your next project, remember that transparency around Rogers PCB price is key.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA