Shared Charging Cable / Wireless Charging Solution
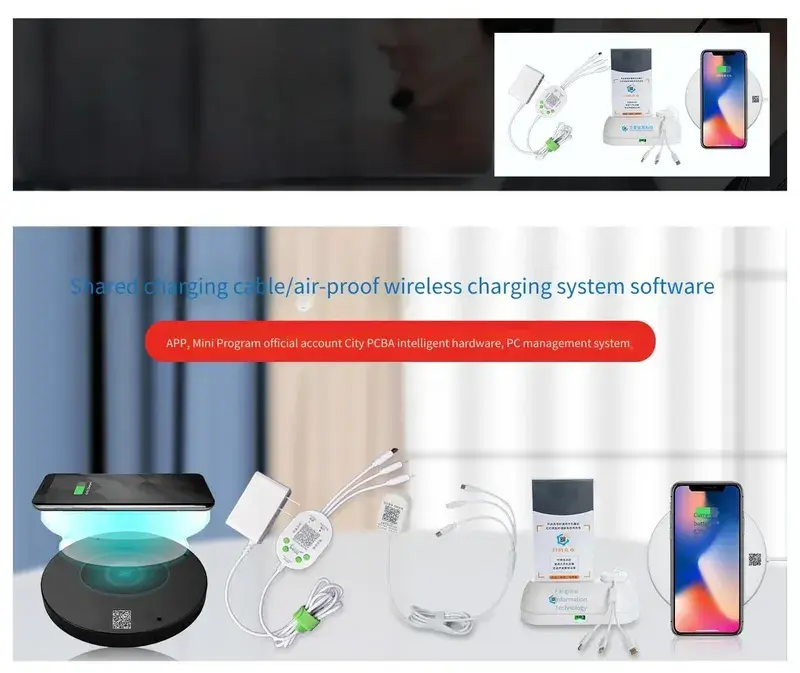
In our hyper-connected world, the ubiquitous demand for power presents a unique challenge: keeping devices charged on the go. From bustling cafes to public transport, the scramble for an available outlet or the right charging cable is a common scenario. This universal need has spurred significant innovation in shared charging, moving beyond simple power strips to sophisticated, user-friendly solutions. At Zero One Solution Limited, we are at the forefront of this evolution, leveraging our deep expertise in PCB design and rapid prototyping to develop robust and efficient shared charging cable and wireless charging solutions that meet the demands of modern life and the fast-paced electronics industry.
The Evolution of Shared Charging: From Cables to Wireless Freedom

The concept of shared charging has dramatically evolved, mirroring advancements in technology and the increasing demand for convenient power solutions. From the early days of simple, often tangled, multi-headed charging cables to the sophisticated wireless charging technologies of today, the journey reflects a continuous pursuit of efficiency and user-friendliness.
Initially, shared charging was synonymous with physical adapters – a single cable branching out into multiple connectors to accommodate various devices. These early solutions, while functional, presented challenges in terms of cable management, compatibility issues across different devices, and limitations in charging speed. The need for something more streamlined and universally adaptable paved the way for the exploration of wireless charging.
The emergence of wireless charging technologies marked a significant leap forward. Inductive charging, utilizing magnetic fields to transfer energy, offered a cleaner and more convenient alternative. Standards like Qi have become prevalent, enabling interoperability between various devices and charging pads. More recently, resonant charging and other advanced methods are being developed to extend the range and flexibility of wireless power transfer, further enhancing the shared charging experience.
This evolution is not just about technological advancement; it's also a response to changing user needs and environments. Shared charging solutions are now integral in public spaces like airports and cafes, in vehicles, and even in furniture design. The progression from basic cables to wireless freedom underscores a commitment to innovation and a vision of a future where power is readily and conveniently accessible.
Key Technologies Powering Shared Charging Cable Solutions
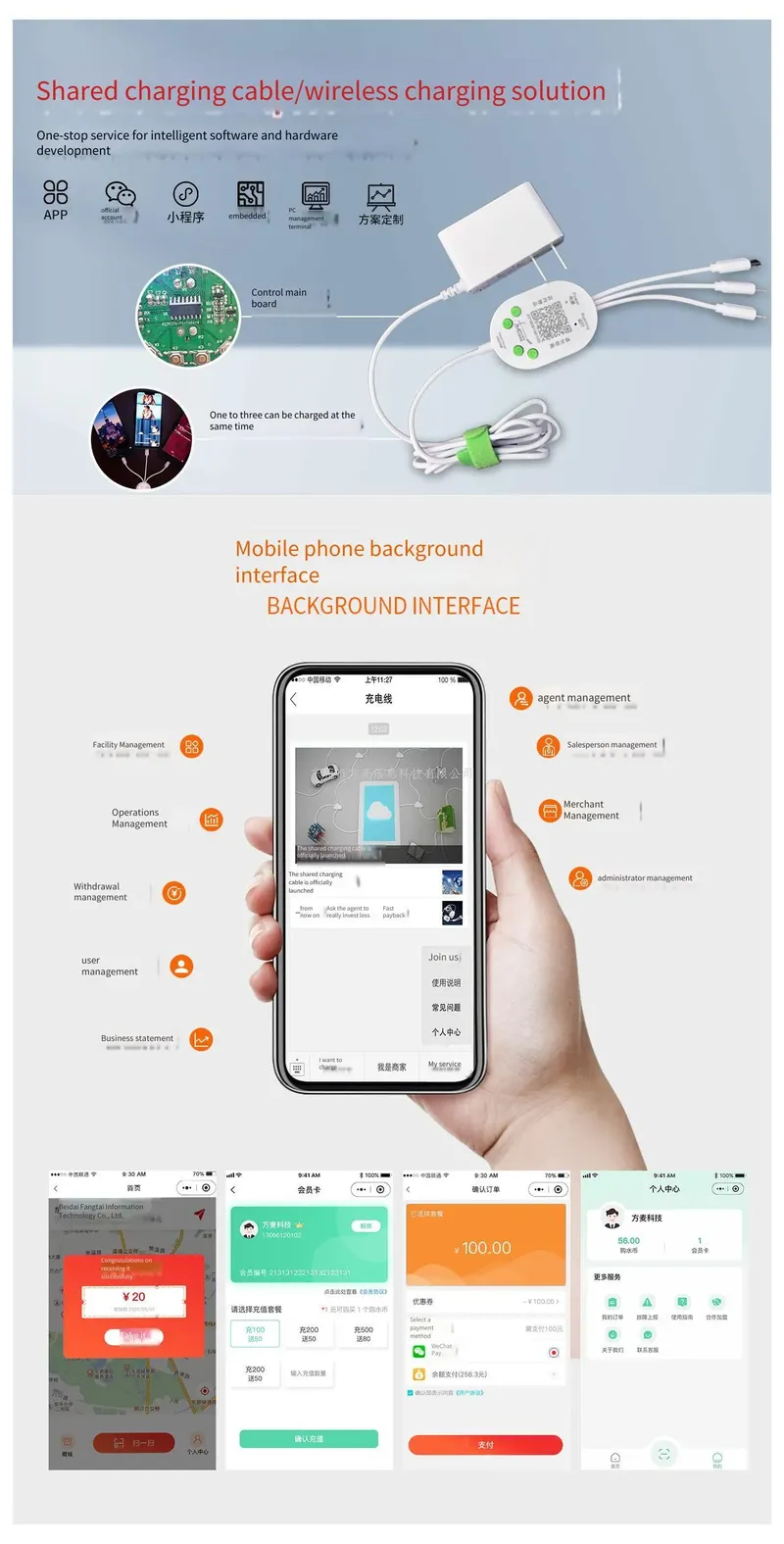
Shared charging cable solutions rely on a combination of key technologies to ensure robust power delivery, efficient data management, and user safety. These technologies encompass both the electronic components within the charging system and the PCB design strategies that bring them together. Understanding these elements is crucial for designing and implementing effective shared charging solutions.
- Power Delivery (PD) Chips
PD chips are the brains behind intelligent charging. They negotiate voltage and current levels with connected devices, optimizing power transfer while protecting against overcharging and voltage spikes. Compliance with USB-PD standards is essential for broad device compatibility and safety. - Multiplexer ICs
In multi-port charging solutions, multiplexer ICs intelligently switch power and data lines between multiple connected devices. This allows a single charging source to efficiently serve several devices without performance degradation. - Overcurrent and Overvoltage Protection Circuits
These circuits are essential for safeguarding connected devices and the charging system itself. They detect and interrupt excessive current flow or voltage spikes, preventing damage from faulty devices or power surges. Fuses, TVS diodes, and resettable fuses (PTCs) are common components in these circuits. - Data Management ICs
Shared charging solutions often need to handle data transfer in addition to power. Data management ICs ensure reliable data communication between devices and the charging system, supporting functionalities like device identification and charging status reporting. - High-Quality Connectors and Cables
The physical connectors and cables are a critical link in the charging chain. High-quality components minimize signal loss, ensure reliable power transfer, and withstand the wear and tear of frequent use in shared environments. Look for durable materials and robust construction. - Efficient Power Conversion Circuitry
AC-DC or DC-DC converters with high efficiency minimize energy waste during power conversion. This reduces heat generation, improves overall system efficiency, and lowers operating costs. - Microcontrollers (MCUs)
MCUs can add smart features to shared charging solutions. They can manage charging schedules, monitor system health, implement user authentication, and provide data logging capabilities.
PCB Design Considerations for Shared Charging Cable Solutions:
- Thermal Management
High power density in shared charging systems generates significant heat. Effective thermal management techniques, such as heat sinks, thermal vias, and strategic component placement, are crucial for maintaining reliable operation and preventing component failure. - Signal Integrity
Maintaining signal integrity is vital for reliable data transfer, especially with high-speed data protocols. Controlled impedance routing, proper grounding, and minimizing trace lengths are essential PCB design practices. - EMI/EMC Compliance
Shared charging systems must comply with electromagnetic interference (EMI) and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations. Shielding, filtering, and careful PCB layout are necessary to minimize emissions and ensure immunity to external interference. - Layer Stackup
The PCB layer stackup significantly impacts signal integrity, power distribution, and thermal management. A well-designed stackup with dedicated ground and power planes is essential for optimal performance. - Component Selection and Placement
Choosing components with appropriate power ratings and thermal characteristics is crucial. Strategic component placement minimizes heat concentration and optimizes signal routing. - Power Plane Design
Solid and properly sized power planes are crucial for delivering stable power to all components. Careful consideration should be given to current carrying capacity and voltage drop.
Unlocking Convenience: The Promise of Wireless Charging Solutions
Wireless charging is revolutionizing shared environments by offering a seamless and convenient power solution. Eliminating the need for physical cables, wireless charging technology enhances user experience and reduces cable clutter. This section explores the core principles and significant advantages of implementing wireless charging in shared spaces, with a particular focus on inductive and resonant charging technologies, alongside the challenges of their integration.
Wireless charging operates primarily through two methods:
- Inductive Charging
This method requires direct contact between the charging pad and the device. Energy is transferred via electromagnetic induction over a short distance. It's commonly used in smartphones and smaller devices. - Resonant Charging
Resonant charging allows for power transfer over a slightly greater distance and does not require precise alignment. This technology is beneficial in shared environments where devices may not be perfectly positioned on the charging surface.
Advantages of wireless charging solutions in shared environments:
- Enhanced User Experience
Users benefit from the simplicity of placing their devices on a charging surface without needing to plug in cables. - Reduced Cable Clutter
Wireless charging eliminates tangled cables, creating a cleaner and more organized environment. - Increased Durability
With no need to plug and unplug cables, the wear and tear on device charging ports is significantly reduced, prolonging the lifespan of devices. - Versatile Integration
Wireless charging can be integrated into various surfaces, such as tables, counters, and furniture, making it a versatile solution for diverse environments.
However, integrating wireless charging solutions is not without its challenges:
- Efficiency
Wireless charging can be less energy-efficient than wired charging, with some energy lost during the transfer. - Charging Speed
Depending on the technology, wireless charging may be slower than wired charging, although advancements are continually improving these speeds. - Compatibility
Not all devices support wireless charging, potentially requiring a mix of charging solutions in shared environments. - Cost
The initial investment for setting up wireless charging infrastructure can be higher compared to traditional wired solutions.
PCB Design Challenges and Innovations in Shared Charging
Shared charging solutions, while offering convenience, present unique PCB design challenges. These challenges stem from the need to handle varying power demands, ensure safety across multiple devices, and maintain signal integrity in complex electronic environments. Overcoming these hurdles requires innovative PCB design strategies focusing on thermal management, electromagnetic interference (EMI) mitigation, and versatile multi-device compatibility.
- Thermal Management Solutions in Shared Charging PCBs
High power throughput in shared charging systems generates significant heat. Effective thermal management is crucial to prevent component failure and ensure system longevity. Strategies include incorporating heat sinks, utilizing thermal vias to conduct heat away from critical components, and optimizing PCB layout to promote airflow. Advanced materials with enhanced thermal conductivity, such as metal core PCBs, can also significantly improve heat dissipation. - Mitigating EMI in Multi-Device Charging Environments
The close proximity of multiple devices and high-frequency switching circuits in shared charging setups can lead to increased EMI. To mitigate this, designers employ techniques such as ground plane optimization, shielding, and careful component placement. Implementing filtering circuits and adhering to strict EMC (Electromagnetic Compatibility) guidelines are also essential to minimize interference and ensure compliance with regulatory standards. - Addressing Multi-Device Compatibility and Power Delivery
Shared charging PCBs must accommodate a wide range of devices with varying power requirements. This necessitates intelligent power delivery systems capable of dynamically adjusting voltage and current levels to suit each connected device. Implementing USB Power Delivery (USB-PD) controllers and incorporating robust protection circuitry are vital for ensuring safe and efficient charging across different device types. - What PCB materials are best for thermal management in shared charging applications?
Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as metal core PCBs (MCPCBs) or those with integrated heat spreaders, are ideal for efficiently dissipating heat generated in high-power shared charging systems. Ceramic substrates also offer excellent thermal performance. - How can PCB layout minimize EMI in shared charging solutions?
Optimizing ground planes, using short trace lengths, strategically placing components to minimize loop areas, and incorporating shielding techniques are effective methods for reducing EMI. Following EMC design guidelines and best practices is crucial. - What design considerations ensure compatibility with various devices in a shared charging system?
Implementing intelligent power delivery controllers (e.g., USB-PD), incorporating robust over-voltage and over-current protection, and designing for a wide input voltage range are key considerations. Testing with a diverse range of devices is also essential. - Are there specific PCB stack-up strategies that improve signal integrity in shared charging applications?
Using a multi-layer PCB with dedicated ground and power planes can significantly improve signal integrity. Carefully controlling impedance and minimizing signal trace lengths also helps to reduce signal reflections and crosstalk.
Zero One Solution Limited: Your Partner in Rapid Prototyping and Production
Zero One Solution Limited stands at the forefront of accelerating shared charging innovation, providing comprehensive PCB solutions from initial design to final assembly. Our expertise in rapid prototyping empowers clients to quickly test and refine their shared charging concepts, significantly reducing time-to-market and development costs. We are dedicated to enabling our partners to lead the charge in this rapidly evolving sector, transforming ideas into tangible, market-ready products.
- Rapid PCB Prototyping for Shared Charging Solutions
We specialize in fast-turnaround PCB prototyping, allowing for quick iteration and validation of shared charging designs. This includes support for various wireless charging standards (Qi, AirFuel) and wired charging protocols (USB-PD, Quick Charge). - Comprehensive PCB Manufacturing Services
Our state-of-the-art manufacturing facilities are equipped to handle complex PCB designs required for shared charging applications, including multi-layer boards, HDI PCBs, and flexible circuits. We ensure high-quality production runs, adhering to stringent industry standards. - Expert PCB Assembly Services
Zero One Solution Limited offers full-service PCB assembly, including SMT, through-hole, and mixed technology assembly. We are adept at handling the precise component placement and soldering required for shared charging circuits, guaranteeing optimal performance and reliability. - Design for Excellence (DFX) Support
Our engineering team provides DFX support, optimizing designs for manufacturability, testability, and reliability. This ensures that shared charging solutions are not only innovative but also cost-effective and scalable for mass production. - Global Supply Chain Network
With headquarters in Shenzhen and a branch office in Dubai, we leverage a global PCBA supply chain network to provide seamless access to worldwide resources and support. This ensures timely delivery of components and efficient project management. - Customized Solutions
We understand that every shared charging project is unique. Zero One Solution Limited offers customized solutions tailored to meet specific requirements, whether it's a small-scale prototype or a large-volume production run. We work closely with our clients to ensure their vision is realized.
Applications and Future Trends of Shared Charging Technologies

Shared charging technologies are rapidly expanding beyond personal devices, finding applications across diverse industries and public spaces. From enhancing customer experiences in hospitality to streamlining operations in transportation and revolutionizing public amenities, shared charging solutions are poised for significant growth. Future trends point towards greater integration with smart city infrastructure, advancements in wireless charging efficiency, and a stronger emphasis on sustainability.
Here's a look at the applications and future trends:
- Hospitality:
Hotels, cafes, and restaurants are increasingly offering shared charging stations to attract and retain customers. These stations provide a convenient amenity, allowing guests to charge their devices while enjoying the establishment's services. Expect to see more sophisticated integrations, such as tabletop wireless chargers and charging built into furniture. - Transportation:
Shared charging is becoming essential in public transportation hubs like airports, train stations, and bus terminals. Charging kiosks and integrated charging ports in seats enable travelers to stay connected during their journeys. Electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure is also expanding, with shared charging stations becoming commonplace in parking garages and along highways. - Public Spaces:
Parks, libraries, and community centers are incorporating shared charging solutions to enhance public amenities. Solar-powered charging benches and kiosks offer sustainable charging options in outdoor settings. These initiatives promote connectivity and accessibility in public spaces. - Education:
Universities and schools are installing shared charging stations in classrooms, libraries, and common areas to support students' learning and research activities. This ensures students can keep their devices powered throughout the day for note-taking, accessing online resources, and collaborating on projects. - Healthcare:
Hospitals and clinics are providing charging solutions for patients and visitors in waiting areas and patient rooms. This helps individuals stay connected with family and work while undergoing treatment or waiting for appointments. Wireless charging pads embedded in furniture offer a hygienic and convenient option. - Smart City Integration:
Shared charging is becoming an integral part of smart city initiatives, with charging stations embedded in streetlights, bus shelters, and public furniture. This integrated approach provides convenient charging access throughout the city, promoting sustainable transportation and enhancing urban living. - Wireless Charging Advancements:
Advancements in wireless charging technology are driving greater efficiency and convenience. Resonant inductive charging allows for charging at a distance, while multi-device charging pads enable simultaneous charging of multiple devices. Future trends include faster charging speeds, improved energy efficiency, and greater compatibility across different devices. - Sustainability:
There's a growing emphasis on sustainable charging solutions, with solar-powered charging stations and energy-efficient charging technologies gaining popularity. These initiatives reduce the environmental impact of charging devices and promote a greener future. The use of eco-friendly materials in charging station construction is also becoming more prevalent.
Frequently Asked Questions About Shared Charging Solutions
Navigating the world of shared charging solutions can bring up various questions regarding their implementation, safety, and technology. Below are some frequently asked questions addressing these concerns to provide clarity and ensure a better understanding of both shared charging cable and wireless charging systems.
- Are shared charging cables safe for my devices?
Yes, shared charging cables are generally safe when designed with appropriate safety features. Reputable manufacturers incorporate over-voltage protection, over-current protection, and short-circuit protection to safeguard connected devices from potential electrical issues. However, the quality of the cable and the reputation of the manufacturer are critical factors to consider. Always opt for cables from trusted brands that comply with international safety standards. - How does wireless charging work in shared charging stations?
Wireless charging in shared stations typically uses inductive charging, where energy is transferred wirelessly from the charging pad to the device via electromagnetic fields. The device must be compatible with the Qi wireless charging standard, which is the most widely adopted. When a device is placed on the charging pad, a magnetic field is created between the charging pad and the device, enabling power transfer without needing a physical connection. - What are the benefits of using a shared charging solution?
Shared charging solutions offer several benefits, primarily convenience and cost-effectiveness. They eliminate the need for individuals to carry their own chargers, making them ideal for public spaces like airports, cafes, and hotels. For businesses, providing shared charging can enhance customer satisfaction and attract more visitors. Furthermore, they help reduce e-waste by promoting the reuse of charging infrastructure. - Can shared charging cables transmit data as well as power?
Yes, many shared charging cables are designed to transmit both data and power. This capability allows users to sync their devices or transfer files while charging. However, for security reasons, some shared charging stations may disable the data transfer function to prevent potential malware infections or data theft. Always check the specifications of the charging station if data transfer is a concern. - How secure is wireless charging in public shared charging stations?
Wireless charging is generally considered secure, as it does not involve a direct physical connection that could be exploited for data transfer. Unlike USB charging, which has potential vulnerabilities like 'juice jacking,' wireless charging primarily transfers power. However, users should still be cautious and ensure their devices have the latest security updates to protect against any unforeseen vulnerabilities. - What is the lifespan of shared charging cables and wireless charging pads?
The lifespan of shared charging cables and wireless charging pads depends on usage frequency, build quality, and environmental factors. High-quality cables with robust connectors and durable shielding can last for several years with proper care. Wireless charging pads, which have fewer mechanical parts, may last even longer. Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and avoiding excessive bending of cables, can extend their lifespan. - Are shared charging solutions energy efficient?
The energy efficiency of shared charging solutions varies depending on the technology used. Wireless charging, for example, is typically less energy-efficient than wired charging due to energy losses during wireless power transfer. However, advancements in wireless charging technology are continually improving efficiency. Shared charging stations often incorporate power management systems that optimize energy usage and reduce wastage when devices are fully charged or not in use.
The evolution of shared charging solutions, encompassing both traditional cables and advanced wireless technologies, is not just about convenience; it's about building a more connected and efficient ecosystem. At Zero One Solution Limited, our commitment to excellence in PCB design, rapid prototyping, and one-stop manufacturing empowers innovators to bring their shared charging visions to life with unparalleled speed and precision. We stand ready to transform your concepts into market-ready products, offering a seamless path from design to assembly, backed by our global supply chain network. Partner with us to power the future of shared connectivity and redefine accessibility in charging.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA