Understanding 94V-0 Circuit Boards: Safety & Applications

In our increasingly technology-dependent world, the safety of electronic devices is paramount. A crucial element contributing to this safety is the 94V-0 circuit board. But what exactly is it? These boards, often found in everyday gadgets and complex machinery, are designed with a flame-retardant material meeting stringent UL94V-0 standards. This article will delve into the specifics of 94V-0 circuit boards, explaining their importance, construction, applications and addressing frequently asked questions, bridging the gap between safety and practical technology.
What is a 94V-0 Circuit Board?

A 94V-0 circuit board is a printed circuit board (PCB) constructed using materials that adhere to the UL 94V-0 flammability standard, signifying a high degree of flame resistance. This standard ensures that the board will self-extinguish quickly after ignition, enhancing the safety and reliability of electronic devices.
Understanding the UL94V-0 Standard
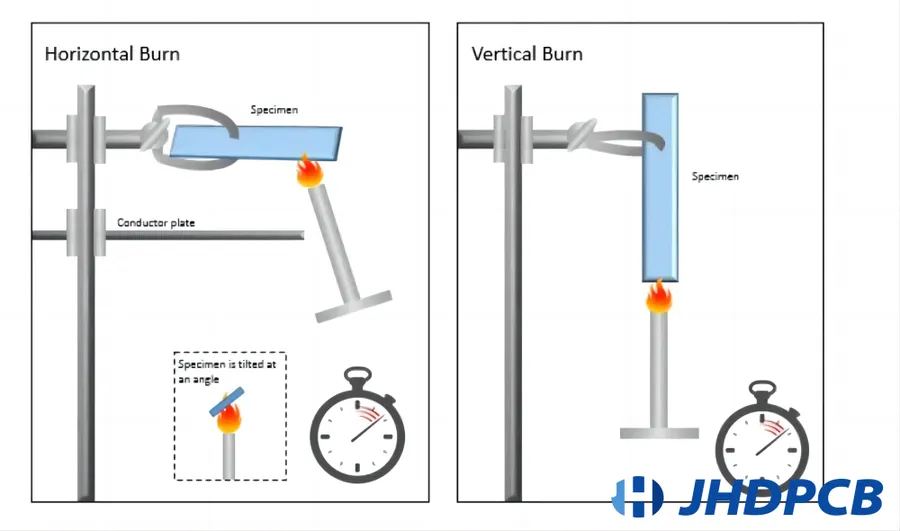
The UL94V-0 standard, established by Underwriters Laboratories (UL), is a critical benchmark for assessing the flammability of plastic materials used in electronic components, including printed circuit boards (PCBs). This standard specifically addresses the material's ability to resist ignition and to self-extinguish quickly once ignited, minimizing the potential for fire propagation. Achieving the UL94V-0 rating is a key requirement for products intended for use in environments where fire safety is paramount.
The UL94 standard has different levels of flammability ratings. The ‘V’ in ‘94V-0’ indicates that the standard applies to materials tested in a vertical position and the ‘0’ is the highest rating within the standard that denotes the material’s fire retardant capability. During testing, a flame is applied to a vertically held sample for 10 seconds. The material must self-extinguish within 10 seconds after the flame is removed, and there should be no dripping of flaming particles.
| Rating | Self-Extinguishing Time (seconds) | Dripping Allowed? | Flaming Particles Allowed? |
|---|---|---|---|
| UL94V-0 | ≤ 10 | No | No |
| UL94V-1 | ≤ 30 | No | Yes |
| UL94V-2 | ≤ 30 | Yes | Yes |
Materials Used in 94V-0 Circuit Boards

The selection of materials for 94V-0 circuit boards is paramount to achieving the required flame retardancy and performance characteristics. FR-4 glass epoxy laminate is the predominant choice due to its balanced properties.
While FR-4 is the most common, other materials can be used, depending on the specific application requirements. These materials are chosen to ensure the circuit board meets the UL 94V-0 standard while providing adequate electrical and mechanical performance. The following table highlights key aspects of FR-4 and other materials used in 94V-0 PCBs:
| Material | Description | Flame Retardancy | Electrical Insulation | Mechanical Strength | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | Glass epoxy laminate, most common PCB material | Meets UL 94V-0 standards | Excellent | Good | General-purpose PCBs, widely used |
| High-Tg FR-4 | FR-4 with higher glass transition temperature | Meets UL 94V-0 standards | Excellent | Improved at higher temperatures | High-temperature applications, automotive |
| CEM-1 | Paper-based composite, lower cost alternative | Can be formulated to meet UL 94V-0 standards | Good | Fair | Less demanding applications, consumer electronics |
| Polyimide | High-performance polymer | Meets UL 94V-0 standards | Excellent | Excellent | High-reliability applications, aerospace |
| PTFE (Teflon) | Fluoropolymer | Meets UL 94V-0 standards | Exceptional | Good | High-frequency applications, RF circuits |
Key Characteristics of 94V-0 PCBs
Beyond their defining flame-retardant properties, 94V-0 printed circuit boards exhibit a suite of characteristics critical for reliable electronic applications. These include robust electrical performance, substantial mechanical integrity, and the capacity to endure standard soldering procedures without compromising functionality.
| Characteristic | Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Flame Retardancy | Self-extinguishes within 10 seconds after ignition; no flaming drips. | Crucial for safety; minimizes fire spread. |
| Electrical Properties | Maintains stable dielectric constant and insulation resistance. | Ensures reliable signal transmission and prevents short circuits. |
| Mechanical Strength | High flexural strength and impact resistance. | Provides durability against physical stress and vibrations. |
| Solderability | Compatible with standard soldering processes and temperatures. | Facilitates reliable component assembly. |
| Dimensional Stability | Maintains precise dimensions and prevents warping. | Ensures accurate circuit alignment and proper fit within enclosures. |
Applications of 94V-0 Circuit Boards
94V-0 circuit boards are essential components across diverse sectors due to their superior flame-retardant properties. Their reliability and safety make them indispensable in applications where fire risk and operational integrity are paramount. This section details these critical applications, highlighting the significance of UL 94V-0 rated PCBs.
- Power Supplies and Chargers
Used extensively in power supplies and chargers for devices, ranging from mobile phones to industrial equipment, 94V-0 boards ensure fire safety in power conversion processes where heat generation is common. - Inverters
Inverters, which convert DC to AC power, frequently rely on 94V-0 PCBs to mitigate the risk of fire, especially in applications like solar power systems and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). - Consumer Electronics
From computers and TVs to smaller handheld devices, the widespread use of 94V-0 PCBs in consumer electronics underscores the industry's focus on consumer safety and compliance with stringent safety regulations. These boards offer a critical layer of protection against fire hazards, particularly in devices that generate heat during normal operation. - Automotive Electronics
In automotive systems, where reliability under demanding conditions is crucial, 94V-0 circuit boards are used in various control systems, ensuring that these electronic components can withstand potential high temperature and vibration environments while minimizing fire hazards. This includes engine management systems, safety control modules, and infotainment systems. - Industrial Equipment
Industrial machinery, control panels, and automation systems incorporate 94V-0 PCBs due to their durability and enhanced safety. The flame-retardant properties of these boards are particularly important in industrial environments where equipment is often exposed to high temperatures, demanding conditions, and potential electrical faults. - Telecommunications Devices
Telecommunication equipment, including routers, switches, and base stations, use 94V-0 PCBs to maintain consistent functionality and safety. The high performance requirements of telecommunication networks require high durability and fire resistance, ensuring reliable data transmission. - LED Lighting
LED lighting systems, especially those designed for high-power applications, often integrate 94V-0 circuit boards to prevent fire hazards resulting from electrical shorts or overheating, which is a common concern in lighting design.
The Manufacturing Process of a 94V-0 PCB
The fabrication of a 94V-0 printed circuit board (PCB) is a multi-stage process requiring strict adherence to quality control, beginning with material selection and concluding with component placement. It's not just about assembling a circuit, but also ensuring that the final product complies with the UL 94V-0 flammability standard, a crucial aspect for safety-critical applications.
- Material Selection
The cornerstone of a 94V-0 PCB lies in using base materials that meet the stringent UL 94V-0 flammability rating. FR-4, a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate, is predominantly utilized due to its excellent electrical insulation, mechanical strength, and inherent flame-retardant properties. Other materials with UL 94V-0 compliance may be employed based on specific application needs. - Circuit Design and Layout
The circuit design is translated into a physical layout using CAD tools. This layout dictates the conductive pathways and component placement on the PCB. Optimization of this layout is critical for signal integrity, power distribution, and efficient manufacturability. Considerations for thermal management are also addressed during this stage. - Patterning and Etching
The designed circuit pattern is transferred onto the copper-clad laminate using photo-lithographic processes. Unwanted copper is then etched away, leaving behind the intended conductive pathways. Precision is paramount during this stage to guarantee the correct electrical connections and prevent any short circuits or signal losses. - Drilling
Holes are precisely drilled into the board to accommodate component leads, vias, and mounting hardware. The accuracy of drilling is essential to ensure correct component placement and avoid damage to the board. Hole diameters must adhere to design specifications to facilitate secure connections. - Plating
Following drilling, the board undergoes a plating process. The drilled holes are plated with copper, creating conductive paths through the board, referred to as vias, especially in multilayer boards. This ensures reliable interconnections between the layers. Additional plating of materials such as gold or nickel may be used for contact surfaces. - Solder Mask Application
A solder mask, typically a polymer-based coating, is applied to the PCB to prevent solder bridges during the assembly process, ensuring that solder only adheres to the intended pads. This protective layer also guards against environmental factors such as moisture and dust. The solder mask is usually colored green, although different colors are used for various applications. - Silkscreen Printing
A silkscreen layer is applied on top of the solder mask to print component references, logos, and other necessary identification details. This helps in the ease of assembly, component identification, and in simplifying maintenance processes. - Surface Finish
A surface finish is applied to the exposed copper pads to enhance solderability and protect against corrosion. Common surface finishes include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative). The selection of the finish depends on the specific application and environmental requirements. - Component Assembly
Once the PCB fabrication is complete, components are carefully placed and soldered onto the board through automated assembly processes. Reflow soldering is a commonly used technique for surface mount components, while wave soldering is employed for through-hole components. - Testing and Inspection
Rigorous testing and inspection are crucial to ensure the proper functionality of the assembled circuit board. Electrical tests, functional tests, and visual inspection are conducted to identify defects or any non-conformance with the UL94V-0 standard. Boards that do not meet standards are rejected to maintain quality control.
94V-0 vs. Other Flammability Ratings
The UL 94 standard classifies the flammability of plastic materials used in device and appliance parts, with 94V-0, 94V-1, and 94V-2 being common ratings. The 94V-0 rating signifies the highest level of flame retardancy, indicating superior performance in preventing fire spread compared to other ratings. This makes 94V-0 a critical choice for applications where fire safety is paramount.
| Rating | Flame Extinguishing Time | Dripping Particles Allowed? | Application Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| 94V-0 | Self-extinguishes within 10 seconds | No flaming drips allowed | Highest safety applications, e.g. power supplies, critical electronics |
| 94V-1 | Self-extinguishes within 30 seconds | Dripping of flaming particles allowed | Medium safety applications, e.g. consumer electronics |
| 94V-2 | Self-extinguishes within 60 seconds | Dripping of flaming particles allowed | Lower safety applications, e.g. general purpose enclosures |
The primary differentiator between these ratings lies in the time it takes for the material to self-extinguish after being ignited and whether flaming drips are allowed. Materials rated 94V-0 offer the best resistance to fire propagation. When specifying materials for PCBs, understanding these differences is critical to achieving the desired level of safety for the end-product. The selection of the appropriate rating should align directly with the application's safety requirements and the potential fire risks.
Frequently Asked Questions About 94V-0 Circuit Boards
This section addresses common queries regarding 94V-0 circuit boards, providing clear and concise answers to enhance understanding of their properties, applications, and safety standards. These FAQs are designed to clarify key aspects for both technical and non-technical audiences.
- What does the 'V' in 94V-0 stand for?
In the UL94 flammability standard, the 'V' signifies 'Vertical burning test'. Materials with a 'V' rating are tested for flammability when positioned vertically, which more accurately simulates real-world applications and is a critical aspect of the material's safety certification. - What is the significance of the '0' in 94V-0?
The '0' in 94V-0 indicates the highest level of flame retardancy within the UL94V classification. Materials rated as 94V-0 must self-extinguish within 10 seconds after flame removal, without dripping flaming particles that could ignite surrounding materials. This is a key requirement for safety-critical applications. - Is there a UL94V-0 temperature rating?
The UL94V-0 standard is primarily a flammability rating and doesn't specify a maximum operating temperature. However, the materials used in 94V-0 PCBs, such as FR-4, do have temperature limits. Standard FR-4 typically has a maximum operating temperature around 130°C. The 94V-0 rating ensures flame retardancy at typical operating conditions, but specific temperature limits depend on the base materials used in the PCB. - Can all PCBs achieve a 94V-0 rating?
No, not all PCBs can achieve a 94V-0 rating. It depends on the materials used. The PCB substrate material must be inherently flame-retardant and tested according to the UL 94V-0 standard. Therefore, only those PCBs that are manufactured with materials meeting this flammability standard can achieve this rating. - How can I understand 94V-0 circuit board diagrams and datasheets?
94V-0 circuit board diagrams and datasheets primarily detail the electrical layout, component placements, and material specifications of the board, the UL94V-0 rating is normally mentioned in the material specification section of the datasheet, emphasizing the PCB's material's compliance with the flammability requirements. Such diagrams do not typically describe the 94V-0 properties. A datasheet will clearly state if the base material is compliant with the 94V-0 standard and other characteristics such as material thickness, heat resistance, and solderability. - What are the key advantages of using a 94V-0 rated PCB?
The primary advantage of using 94V-0 rated PCBs is enhanced safety due to their flame-retardant properties. They provide a significant reduction in fire risk, making them suitable for use in high-reliability electronic equipment. These PCBs also demonstrate good mechanical and electrical performance. - Are there any alternatives to 94V-0 rated PCBs?
While other UL94 ratings (such as 94V-1 or 94V-2) exist, they offer lower levels of flame retardancy. Depending on the application's requirements, 94V-0 rated PCBs may be necessary for applications with heightened fire safety concerns. For applications that don't require high-level flame retardancy, materials with lower UL94 ratings might be sufficient.
The 94V-0 circuit board stands as a silent guardian within our electronic world. Its flame-retardant properties, achieved through adherence to the stringent UL94V-0 standards, make it a critical component in ensuring the safety and reliability of countless devices. Understanding its specifications, applications, and the processes behind its construction allows us to appreciate the crucial role these boards play in our daily lives. As technology evolves, the importance of 94V-0 certified PCBs will only continue to grow, emphasizing the intersection of safety and innovation.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA