Understanding Mobile PCB Board Price: A Comprehensive Guide
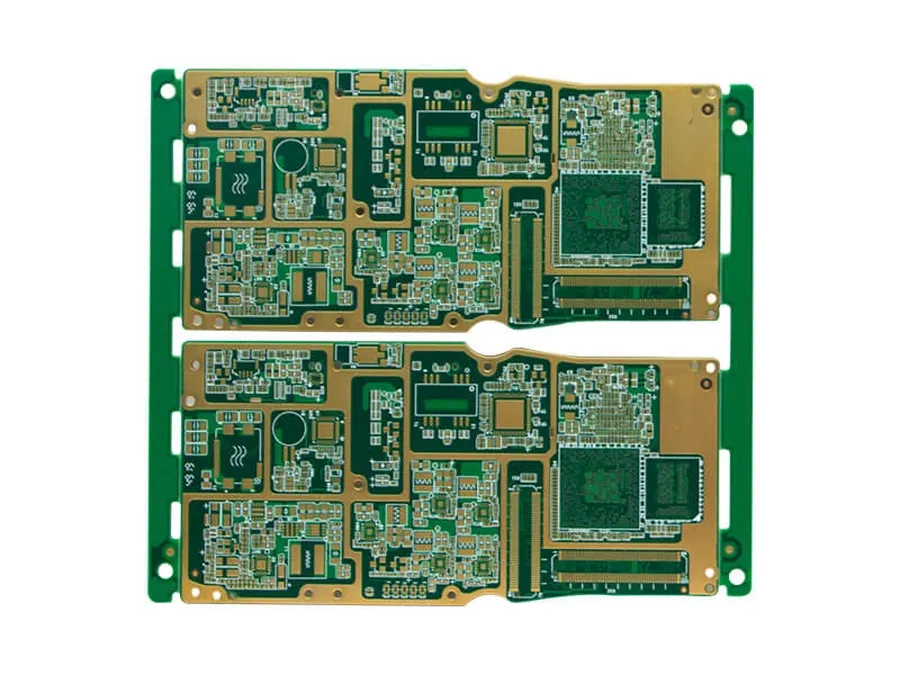
The mobile phone, a ubiquitous tool in modern life, relies on a complex Printed Circuit Board (PCB) at its core. Understanding the 'mobile pcb board price' is key to appreciating the technology behind our devices. This article delves into the various factors influencing this price, from the materials used to the complexity of the design and manufacturing processes, guiding both professionals and interested consumers.
What is a Mobile PCB Board?

A mobile Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is the foundational component of a mobile phone, serving as the physical platform that mechanically supports and electrically connects the electronic components. It is a complex, multi-layered structure comprised of conductive traces, pads, and vias, fabricated from insulating materials like FR-4, which facilitate the operation of all integrated circuits and passive components within the phone. The PCB's layers and materials determine its electrical characteristics, ensuring reliable signal transmission and power distribution throughout the device.
- Layers
Mobile PCBs are typically multi-layered, with alternating layers of conductive materials (copper) and insulating substrates. This structure allows for complex routing and increased component density. - Materials
Common materials include FR-4 (a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate), and more specialized materials like high-Tg (high glass transition temperature) laminates for improved thermal performance. - Key Circuits
The PCB houses several critical circuits including the power management circuit, CPU and memory interfaces, wireless communication circuits (Wi-Fi, Bluetooth), and sensor interfaces. - Function
The PCB board provides mechanical support and electrical interconnections, making mobile devices compact, efficient, and durable.
Key Factors Influencing Mobile PCB Board Prices
The price of a mobile PCB board is a complex interplay of several factors, each contributing significantly to the final cost. These factors range from the raw materials used in construction to the intricacies of the design and the precision of the manufacturing process. Understanding these factors is crucial for accurate cost estimation and effective decision-making in mobile device manufacturing.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Type of laminate, e.g., FR-4, High-Tg FR-4, Rogers, and their respective grades. | Higher-grade materials with superior electrical and thermal properties increase cost. |
| Number of Layers | Refers to the number of conductive copper layers in the PCB. | More layers mean more complex manufacturing, resulting in higher costs. |
| Design Complexity | The inclusion of features such as HDI, fine-pitch components, and complex routing. | Advanced features and intricate layouts drive up production costs. |
| Surface Finish | Finishes like ENIG, HASL, or Immersion Silver, impacting solderability and corrosion resistance. | High-performance finishes increase cost due to the materials and processes involved. |
| Tolerances | The required precision in dimensions, layer alignment, and other specifications. | Tighter tolerances need more precise and often slower processes, thus increasing costs. |
Material Costs: Impact on Mobile PCB Board Price

The selection of materials for a mobile PCB board is a pivotal factor that significantly influences its final cost. The performance, durability, and overall reliability of the PCB are intrinsically linked to the materials used, driving a direct correlation between material choice and price. This section delves into how different material types and their associated properties affect the cost of mobile PCB boards.
| Material Type | Description | Typical Applications | Cost Impact | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | Most common PCB material, composed of woven fiberglass cloth with epoxy resin binder. | Standard mobile PCBs, consumer electronics. | Low to moderate. Highly available and widely used, cost-effective. | Good balance of cost and performance; suitable for many applications. |
| High-Tg FR-4 | Enhanced version of FR-4 with higher glass transition temperature for better thermal performance. | High-temperature mobile environments, high-performance applications | Moderate. Higher performance comes at a slightly increased cost. | Improved reliability under heat; consider when thermal stress is high. |
| Rogers Materials | Specialized laminates with enhanced electrical properties and high-frequency performance. | Advanced mobile communication, RF circuits. | High. Premium materials for niche, high-performance applications. | Excellent electrical properties; needed for RF and high-speed designs. |
| High-Speed Laminates | Materials optimized for high-speed digital signal transmission. | Advanced data processing, high-speed memory. | Moderate to High. Necessary for higher-speed applications, increases cost. | Essential for designs where signal integrity is paramount. |
| Flex Materials(Polyimide, Polyester) | Flexible substrate material allowing boards to bend. | Complex folding mobile components and interconnects. | Moderate to High. Adds design and fabrication complexity. | Enables innovative designs and form factors. |
The grade of material further refines the cost structure. For instance, within the FR-4 category, variations exist in epoxy resin type and fiberglass weave quality, influencing thermal performance, mechanical strength, and price. High-grade FR-4 can command higher costs compared to its standard counterparts. Similarly, within Rogers materials, specific variants may possess particular dielectric constants and loss tangents, directly affecting pricing.
Material selection not only impacts the raw material cost but also influences manufacturing process parameters. For example, materials with higher thermal stability might enable faster and more efficient lamination processes, while certain high-performance laminates require specialized handling, affecting manufacturing costs. Therefore, a holistic analysis of material costs is crucial, encompassing both raw material expense and downstream manufacturing impacts.
Manufacturing Process and Mobile PCB Board Cost
The cost of a mobile PCB board is significantly influenced by the intricate manufacturing processes involved. Each step, from initial material preparation to final surface finishing, adds to the overall price, reflecting the precision and technology required to create these essential components for mobile devices.
| Manufacturing Step | Description | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Lamination | Layering and bonding of substrate materials with copper foil using heat and pressure. | High. Precision equipment and material costs drive up the price. |
| Drilling | Creating vias and through-holes for electrical connections between layers. | Medium to High. Cost increases with hole density, smaller sizes, and higher layer counts. |
| Plating | Depositing conductive materials (typically copper) in drilled holes and on the board surface to establish electrical paths. | Medium. Process and chemical costs contribute to the price. |
| Etching | Removal of unwanted copper from the surface to create circuit patterns. | Medium. Requires precise chemical controls and can be more costly with finer patterns. |
| Solder Mask Application | Applying a protective layer to prevent solder bridges during assembly, typically green. | Low to Medium. Cost depends on the number of layers and the surface area covered. |
| Surface Finishing | Applying a final coating (e.g., ENIG, HASL, OSP) to protect copper and ensure good solderability. | Medium to High. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) is more expensive than HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), for example. |
Complexity of Design and its Influence on Price
The complexity of a mobile PCB design significantly impacts its final price. Features such as High-Density Interconnects (HDI), fine-pitch components, and the number of layers all contribute to increased manufacturing costs. These advanced features require more precise and intricate manufacturing processes, driving up both material and labor expenses.
| Design Complexity Feature | Impact on Price | Manufacturing Process Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High-Density Interconnects (HDI) | Higher cost due to microvia technology and complex layering | Requires laser drilling, microvia plating, and precise alignment. |
| Fine Pitch Components | Increased price due to precision placement and advanced soldering techniques | Needs automated pick-and-place machines, advanced soldering, and high-resolution inspection. |
| Multi-Layer Boards | Elevated cost with each additional layer due to increased lamination, processing steps, and material | Involves multiple lamination cycles, precise via drilling and plating. |
| Impedance Control | Higher cost due to additional design constraints, material selection and testing | Requires controlled impedance materials, precision etching, and testing. |
| Buried and Blind Vias | Increased complexity, requiring additional drilling and plating steps, and more sophisticated manufacturing equipment and processes | Involves sequential layering and laser drilling, and is more expensive than through-hole vias |
Sourcing Mobile PCB Boards: Options and Cost Implications
Sourcing mobile PCB boards involves navigating a complex landscape of options, each with distinct cost, quality, and lead time implications. Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for making informed decisions that align with project requirements and budget constraints. Options range from direct engagement with manufacturers to leveraging online marketplaces, each presenting unique advantages and disadvantages.
| Sourcing Option | Advantages | Disadvantages | Cost Implications | Lead Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Direct Manufacturers | Customization capabilities, higher quality control, direct communication, potential for long-term partnerships. | Higher initial cost, longer lead times for small volumes, potentially less flexible in terms of volume fluctuations. | Generally higher for small and medium volumes but can decrease significantly with high order quantities. | Longer, may range from several weeks to months. |
| Online Marketplaces (e.g., Alibaba, AliExpress) | Lower initial costs, greater variety, flexible order quantities, faster lead times for standard designs. | Quality control challenges, potential for miscommunication, variable material quality, limited customization, higher risk of counterfeit parts. | Typically lower for small and medium quantities, may increase significantly with advanced designs. | Shorter, often within days or a few weeks, depending on the supplier. |
| Specialized PCB Brokers | Access to a network of manufacturers, expertise in sourcing and material selection, quality and compliance assurance | Higher cost compared to direct manufacturers and online marketplaces, intermediary delays | Typically moderate cost based on the supply network and services | Moderate to long based on their relationship with the supply network |
Mobile PCB Board Price Ranges and Market Variations
The price of mobile PCB boards exhibits considerable variation depending on several key factors, including the board's complexity, the volume of the order, the degree of customization required, and the geographical location of both the supplier and the demand. Understanding these variations is crucial for effective cost management and strategic sourcing.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | HDI, multi-layer, fine pitch | Higher |
| Materials | FR-4, Rogers, High-Tg | Higher for advanced materials |
| Order Volume | Small batch vs. mass production | Lower per unit for higher volumes |
| Customization | Specific design needs, unique layouts | Higher |
| Supplier Location | China, Europe, North America | Varies by labor, material costs, and proximity to end-user |
| Demand | High demand periods | Potential price increase |
Typical price ranges for mobile PCB boards can vary significantly. Basic, single-layer boards in high volume production can cost as little as a few cents per square inch. Conversely, complex multi-layer boards with HDI technology and stringent tolerances, manufactured in smaller batches, can cost several dollars per square inch. Additionally, boards that require specialized materials such as Rogers or high-Tg FR-4 will also command higher prices. Geographic location significantly impacts cost, with manufacturing in regions with lower labor costs often resulting in more competitive prices. Market conditions also play a role, with prices potentially fluctuating due to supply chain dynamics or demand surges.
Frequently Asked Questions about Mobile PCB Board Costs
This section addresses common questions regarding the costs associated with mobile PCB boards, providing clear and concise answers based on engineering principles and market realities.
- What is the typical cost range for a basic mobile PCB board?
The cost of a basic mobile PCB board can range significantly based on volume, materials, and complexity. Generally, for small batch production, a simple single or double-layer PCB could cost from a few dollars to around $10-$20 per board. However, large-scale manufacturing can significantly reduce the cost per unit. Prices are not fixed due to fluctuating material costs and production process requirements. - How much does a high-density interconnect (HDI) PCB for a smartphone cost?
HDI PCBs are more expensive due to their complex manufacturing process involving microvias and fine lines. For a single HDI PCB used in modern smartphones, the cost can range from $15 to $50 or more, depending on the specific technology, layer count, and manufacturing yield requirements. Mass production would result in lower unit costs. These figures are approximate and can vary based on technological advancements and material choices. - Is it cost-effective to replace a mobile phone's PCB board?
Replacing a mobile phone's PCB board is often not cost-effective. The cost of the PCB itself, along with the labor required for replacement (which is very technical and specialized), frequently exceeds the cost of a new or refurbished phone. Additionally, troubleshooting the exact fault on the existing board to ensure replacement is the right fix adds to the overall expenses. It's rarely a consumer-viable option. - What is a PCB board in a mobile phone and why is it critical?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in a mobile phone serves as the foundation for all the electronic components. It provides both mechanical support and electrical connections for components like the processor, memory, radio frequency modules, and power management circuits. It is critical because all these components need a substrate to be attached to, and complex interconnections so they can communicate with each other. A failure in the PCB typically means a non-functional device. - What factors influence the price of a mobile PCB board?
Several factors dictate the price of mobile PCB boards including material type (FR4, high Tg materials), number of layers, design complexity (HDI, fine pitch components), surface finish (ENIG, HASL), manufacturing tolerances, order volume, and the geographic location of manufacturing. - Can the price of a PCB board vary based on the manufacturer?
Yes, the price of PCB boards can vary significantly among manufacturers. This difference arises from their operational costs, the technology they employ, supply chain efficiency and their quality control procedures. Larger, more established manufacturers often have higher overhead but may offer better reliability. Smaller manufactures can offer a lower price, but there might be issues with the quality. Therefore a cost analysis is needed taking into account all trade-offs. - Does order volume have a significant impact on mobile PCB board prices?
Yes, order volume is a critical factor in determining PCB board prices. Larger production runs enable manufacturers to reduce their per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Setting up production lines for small orders involves high overhead, while mass production amortizes these costs over a larger number of units, dramatically reducing the cost per unit. This effect is most noticeable in high-volume industries like mobile devices.
Future Trends in Mobile PCB Manufacturing and Pricing
The mobile PCB industry is poised for significant transformation driven by technological advancements and shifting market demands. These changes are expected to influence both the manufacturing processes and the pricing of mobile PCB boards.
- Advanced Materials
The pursuit of higher performance and miniaturization is driving the adoption of advanced materials such as low-loss laminates and flexible substrates. These materials, while offering superior electrical and mechanical properties, initially may command higher prices. However, increased adoption and manufacturing process optimization are expected to eventually moderate their cost. - Miniaturization and Increased Density
The trend towards smaller and more powerful mobile devices necessitates increasingly dense and compact PCB designs. Techniques like High-Density Interconnect (HDI) and advanced microvia technologies are becoming more prevalent. These technologies require precision manufacturing processes, which will impact pricing. The benefits of smaller footprints and greater functionality, will ultimately justify the costs. - Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Processes
Environmental concerns are pushing the industry towards more sustainable manufacturing practices. This includes the use of lead-free solders, water-based inks, and recyclable materials. The initial adoption of these processes may add to the cost, but over time, it is anticipated to become more cost-effective and mandated by regulations. - AI and Automation
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and automation is revolutionizing PCB manufacturing. AI-powered design tools, automated assembly lines, and predictive maintenance can enhance production efficiency, reduce errors, and optimize resource utilization. This will lead to lower production costs and improved product quality. - 3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, hold immense potential for rapid prototyping and customization of PCB boards. As these technologies mature, they could enable the production of complex PCB designs with greater flexibility and reduced lead times. This may lead to more flexible supply chains and lower costs for low-volume or custom products.
Understanding the 'mobile pcb board price' involves evaluating multiple factors, from material choices to design complexity and sourcing strategies. By carefully considering these elements, manufacturers and consumers can make informed decisions that align with their needs and budgets. The market continues to evolve, with ongoing developments in material technology and manufacturing processes, that will impact the cost structure of these essential components in the future. Whether you're looking for a basic mobile pcb board or a complex multilayer design, a comprehensive understanding of these factors will help you navigate the market and find the best value for your needs.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA