Understanding PCB Plate Price: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's world, the intricate dance of electronics hinges on the unassuming yet vital component: the PCB (Printed Circuit Board). Just like a city's foundation, PCBs support and connect electronic components. Whether it's your smartphone or a complex industrial machine, they are crucial, and understanding the factors behind the PCB plate price is important for both DIY hobbyists and professional manufacturers. This article delves into what determines the cost of a PCB plate, exploring variables like materials, production complexities, and market trends, offering a thorough picture of PCB pricing. Get ready to unravel the details behind these critical components and make informed decisions based on your needs and budget.
Factors Influencing PCB Plate Prices

The price of a PCB (Printed Circuit Board) plate is not fixed; it fluctuates based on a confluence of factors. These elements range from the raw materials used in construction to the complexity of the board design and the sheer volume of the order. Understanding these variables is crucial for both designers and purchasers to optimize cost-effectiveness.
The key drivers affecting PCB plate pricing can be broadly categorized as follows:
- Material Selection
The type of material used, such as FR-4, aluminum, or specialized laminates, greatly influences the cost. FR-4 is typically the most cost-effective choice, whereas materials like aluminum offer enhanced heat dissipation but come at a higher price point. - Board Size and Dimensions
Larger PCBs require more material and processing, resulting in higher costs. Pricing is often calculated based on square area (e.g., square inches or square centimeters) of the board. - Layer Count
The number of layers in a PCB (single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layer) dramatically impacts cost. Multi-layer boards require more complex manufacturing processes and materials, escalating costs. - Design Complexity
Intricate designs with fine traces, small vias, and high component density demand more precise manufacturing, leading to increased costs. The complexity of the circuit design directly influences the time and resources required for fabrication. - Manufacturing Processes
Techniques used, like drilling, etching, and plating, contribute to the overall cost. The precision and sophistication of these processes directly affect the price. - Order Volume
Purchasing PCBs in bulk often reduces the unit cost due to economies of scale. Larger orders spread setup and tooling costs across a greater number of units. - Surface Finish
The type of finish applied (e.g., HASL, ENIG) affects both the performance and the cost. ENIG provides superior solderability and oxidation resistance, but it's more expensive than HASL. - Tolerances
Tighter tolerances required for specific applications also impact costs due to the increased precision and quality control measures needed.
Material Types and Their Impact on PCB Plate Price

The selection of materials for PCB construction is a crucial factor directly influencing the final price of the PCB plate. Different materials offer varying electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, which consequently affect manufacturing costs and performance. Understanding these impacts is essential for cost-effective design and procurement.
| Material | Description | Cost Impact | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | A fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate. It is the most common and cost-effective material. | Low to Moderate | Most general-purpose PCBs, including consumer electronics, computer motherboards. |
| Aluminum | Aluminum core PCBs offer superior heat dissipation. | Moderate to High | LED lighting, power electronics, high-temperature applications. |
| Copper | Copper is primarily used for the conductive layers in a PCB but sometimes forms the base for metal core boards. | Low to Moderate | Conductive traces, heatsink backings. |
| Rogers | High-frequency laminates known for their superior dielectric properties. | High | RF and microwave circuits, high-speed data transmission. |
| Polyimide | Flexible substrate with good temperature resistance. | High | Flexible circuits, aerospace applications. |
The cost implications extend beyond the raw material cost. For instance, materials requiring specialized processing or those with lower yields during manufacturing will increase the final PCB plate price.
Single-Sided vs. Double-Sided vs. Multi-Layer PCBs: Cost Comparison
The number of layers in a printed circuit board (PCB) directly impacts its cost, with single-sided PCBs being the most economical and multi-layer PCBs commanding a higher price due to their increased complexity and manufacturing requirements. This section will detail the cost implications of single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer PCBs.
| PCB Type | Complexity | Cost Factor | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided | Simplest | Lowest | Basic electronics, simple circuits, low-density devices |
| Double-Sided | Moderate | Medium | Intermediate complexity devices, some industrial and consumer applications |
| Multi-Layer (4-16 Layers) | Complex | High | Advanced electronics, high-density circuits, computer motherboards, medical devices |
| Multi-Layer (16+ Layers) | Highly Complex | Very High | Specialized applications, high-speed digital design, server hardware, aerospace applications |
The cost differential arises from several factors including the increased material usage (more copper layers and insulation), more intricate manufacturing processes (precision alignment and lamination), and the higher degree of process control required to ensure the reliability of multi-layer boards.
Choosing the appropriate number of layers is a trade-off between cost and performance requirements. Single-sided PCBs are sufficient for basic circuits but lack the design flexibility and density of multi-layer boards. Double-sided boards offer a good balance, while multi-layer PCBs enable complex routing and high-density component placement needed for advanced electronic systems.
Understanding PCB Size and Its Correlation with Price
The physical dimensions of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) directly influence its manufacturing cost. Larger PCBs generally require more raw materials and processing time, leading to higher prices. This section explores the relationship between PCB size and cost, focusing on how surface area calculations impact pricing.
The cost of a PCB isn't just about the surface area, it's also about how effectively the manufacturer can utilize the standard panel sizes they work with. For instance, if a PCB design is unusually sized, it can lead to greater material waste on the manufacturing floor, and thus increased costs. Standard PCB panel sizes are generally optimized for efficient production and reducing waste. Therefore, keeping your board design within standard dimensions can help reduce unnecessary expenses.
| Dimension | Impact on Price | Typical Unit | Cost Implication |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surface Area (Square Inches) | Directly Proportional | Square Inch | Larger area, higher cost due to more materials and processing. |
| Surface Area (Square Centimeters) | Directly Proportional | Square Centimeter | Larger area, higher cost due to more materials and processing. |
| Overall Dimensions | Indirectly Proportional | Inches or Millimeters | Non-standard sizes can increase cost due to material wastage and processing inefficiency. |
For a more accurate estimate of cost for a given PCB size, manufacturers often consider the number of PCBs that can be placed on a standard panel. Optimizing your design to fit within these panel parameters can help minimize the cost. It is also good practice to consider the utilization of the panel during the design phase. If you can reduce wasted area during manufacturing you can reduce the overall cost.
Manufacturing Processes and Their Influence on PCB Costs
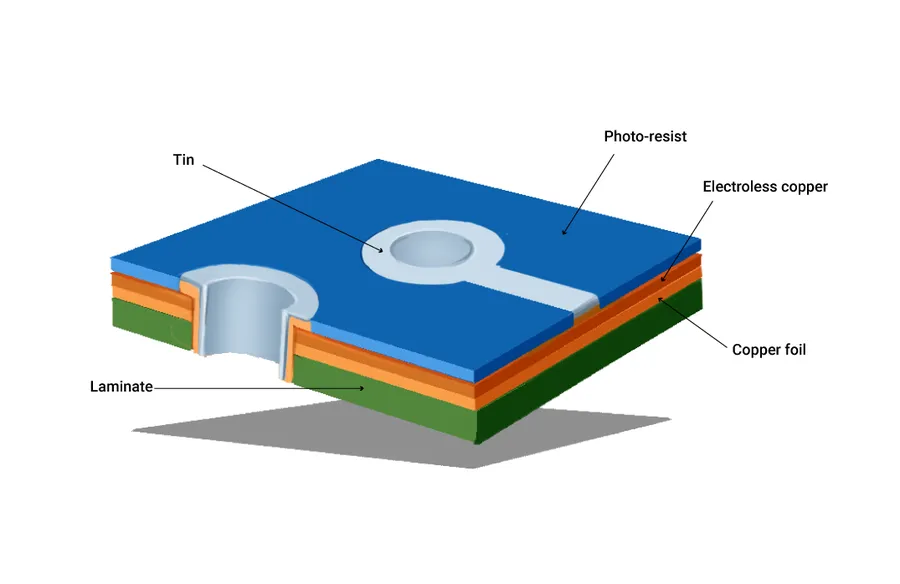
The cost of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is significantly impacted by the manufacturing processes involved, each contributing to the overall price. These processes include precision drilling for vias, chemical etching to define circuit traces, and surface plating to ensure connectivity and protection. Understanding these processes is crucial for comprehending the cost drivers of PCB production.
| Manufacturing Process | Description | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Drilling | Creating holes for vias and component leads, using mechanical or laser drilling. | Precision drilling, particularly for microvias, adds to cost due to equipment and process time. |
| Etching | Removing unwanted copper to define circuit traces using chemical etching. | Fine line etching requires more precise and expensive processes and chemicals, thus increasing cost. |
| Plating | Applying a thin layer of metal (e.g., copper, tin, gold) on board surfaces to enhance conductivity and solderability. | Specific plating materials like gold can increase costs, while selective plating may be more cost effective. |
| Solder Mask Application | Applying a protective layer to prevent solder bridging. | Solder mask application is standard, but custom colors or special masks might incur additional costs. |
| Silkscreen Printing | Printing component labels and reference designators using ink. | The addition of silkscreen can add some cost, particularly for multi-layered or complex designs. |
| Surface Finish | Applying a protective final layer to ensure solderability and prevent oxidation (e.g., HASL, ENIG). | Surface finishes like ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) are more expensive than HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling). |
Each of these processes has associated costs related to equipment, materials, and labor. The complexity of the design, the precision required, and the choice of materials will all influence the final price of the PCB.
Quantity vs. Price: How Order Volume Affects PCB Plate Costs
The correlation between order quantity and unit price in PCB manufacturing is a fundamental economic principle: larger order volumes typically result in a lower per-unit cost. This phenomenon arises from the distribution of fixed manufacturing costs across a greater number of units, allowing manufacturers to offer substantial discounts for bulk orders. Understanding this relationship is crucial for optimizing project budgets.
The cost reduction is not linear; it tends to follow a diminishing returns curve. Initially, the per-unit price drops dramatically as the quantity increases from small prototypes to small production runs. Beyond a certain point, however, while cost savings continue, the rate of savings slows as most of the fixed costs are already absorbed. Factors like raw material procurement discounts for high volume purchases and optimized production line setup for the specific design contribute to these economies of scale.
| Order Quantity | Approximate Unit Cost | Cost Reduction Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| 1-10 (Prototypes) | High | High Setup Cost, Minimal Volume Discount |
| 10 - 100 (Small Batch) | Medium-High | Some fixed costs are covered, slight discount on materials |
| 100 - 1000 (Medium Batch) | Medium | Significant per-unit cost reduction due to material cost discounts and production optimization. |
| 1000+ (Large Batch) | Low | Maximization of economies of scale, substantial discounts, reduced per-unit handling and setup cost |
To effectively optimize cost, consider the trade-offs between inventory holding costs and order quantities. Avoid ordering excessive quantities that could lead to storage costs or obsolescence issues. Efficient planning involves accurate forecasting of demand, which can allow for larger orders, maximizing the discounts while mitigating risks of overstocking. Explore strategies such as staged orders with contract manufacturers, where large volumes are produced over time, while minimizing the initial financial burden.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Plate Prices
This section addresses common queries regarding PCB plate pricing, providing clarity on factors influencing cost and strategies for obtaining better deals. We aim to demystify the pricing complexities associated with PCB manufacturing.
- What is the average price of a PCB plate?
The average price of a PCB plate varies significantly based on several factors including material, complexity (number of layers), size, and quantity. Simple single-sided boards can cost a few dollars, while complex multi-layer PCBs can range from tens to hundreds of dollars per unit. It's essential to get a quote specific to your design from a manufacturer. - How much does a basic PCB cost?
A basic PCB, typically a single- or double-sided board with standard FR-4 material, can cost as little as a few dollars for small quantities. However, prices increase with board size and higher quantities. For example, a 10cm x 10cm single-sided board might cost around $2-$5 per piece in small batches, but this will decrease with larger order sizes. Prices are also highly influenced by material selection and board thickness. - Why are some PCBs so much more expensive than others?
The primary drivers of PCB cost are complexity and material. Multi-layer PCBs require significantly more processing steps and are hence more costly than single or double-sided boards. Material choice is also critical: specialized substrates like aluminum or high-frequency laminates dramatically increase price. Other factors are the precision of manufacturing, the specific design constraints and quantity. Larger boards will also have higher costs. - How does the number of layers affect PCB price?
Each additional layer on a PCB requires extra manufacturing steps, increasing the complexity and material cost. A four-layer PCB will be more expensive than a two-layer one, and an eight-layer PCB will be more expensive than a four-layer one, and so on. This is because the process requires additional etching, plating, and lamination steps, directly impacting manufacturing costs. - What is the impact of PCB size on price?
Larger PCBs require more materials and often have a longer processing time, leading to higher prices. The price usually scales in relation to the surface area of the board, whether measured in square inches or square centimeters. The precise relationship may vary among different manufacturers. - How can I get a better deal on PCB plates?
To get a better deal on PCB plates, consider the following: Optimize your design for manufacturability to reduce material waste and processing complexity. Bulk ordering significantly reduces unit costs. Use standard materials and board thicknesses where appropriate. Select a manufacturer offering the most cost-effective options for your desired quantities and required performance. Lastly, get multiple quotes from various manufacturers to compare prices. Consider using online PCB fabrication services, which may offer more competitive rates compared to local options. - Are online PCB suppliers more cost-effective?
Online PCB suppliers often offer competitive pricing due to their streamlined production processes and lower overheads. However, it is crucial to evaluate the supplier's reputation, manufacturing quality, lead times, and customer service. While online options may be more cost-effective for many standard PCB fabrication requirements, for very high precision or specialized production, local or dedicated facilities may be more suited and offer better quality.
Comparative Analysis of PCB Plate Prices from Different Suppliers
Navigating the PCB market requires understanding price variations among different suppliers. This section analyzes pricing and offerings from various sources, including major online retailers and specialized manufacturers, to pinpoint where cost-effective solutions can be found, enabling informed purchasing decisions.
| Supplier | Typical Price Range (USD) for Standard FR-4 | Lead Time | Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Additional Services |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alibaba | Variable, $5 - $500+ per batch | 2-8 weeks | Variable, Often 10+ | Wide range of customization options, assembly services available |
| Amazon | $10 - $100 per board, often for small quantities | 2-7 days | 1+ | Limited customization, often pre-made boards |
| Specialized PCB Suppliers (e.g., JLCPCB, PCBWay) | $5 - $200+ per batch, dependent on complexity | 1-4 weeks | 1-5+ | Full customization, assembly, and advanced PCB options |
| Local PCB Manufacturers | Higher end, can vary from $20-$500+ per batch | 1-3 weeks | Variable, from 1+ | Proximity, easier communication, potentially faster turnarounds |
The price ranges provided in the table are approximations. The specific price will depend on many factors, including size, complexity, layer count, materials used and order quantity. It's imperative that buyers obtain detailed quotations before making purchasing decisions, especially for larger orders or specialized requirements.
Tips for Reducing PCB Plate Costs
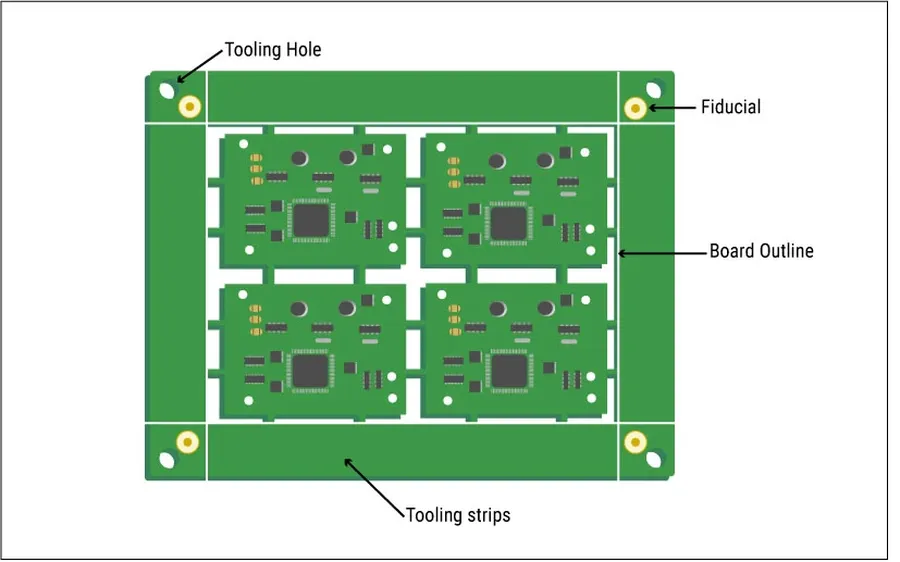
Reducing PCB plate costs requires a strategic approach that balances design choices, material selection, and efficient manufacturing practices, without sacrificing the required performance and reliability of the final product. By carefully considering these factors, it's possible to significantly lower expenses.
- Optimize PCB Design Complexity
Simplify your PCB design by minimizing the number of layers, vias, and intricate traces. This reduces manufacturing time and material usage, leading to lower costs. For instance, opting for a double-sided PCB over a multilayer one when feasible. - Standardize Component Footprints
Using standard component footprints simplifies the assembly process and reduces the potential for errors, which can increase costs, Also, it helps avoid unique assembly jigs and fixtures which will drive up the cost. - Choose Cost-Effective Materials
Selecting the right PCB material is crucial. While FR-4 is a common choice, consider cheaper alternatives if your application allows. For example, if thermal performance is not a critical factor, you might consider materials with slightly lower thermal ratings. - Panelize Efficiently
Proper panelization allows manufacturers to produce multiple PCBs on a single panel, reducing material waste and increasing production efficiency. Ensure that panel dimensions are optimized based on the manufacturing capabilities of your selected PCB vendor. - Optimize PCB Size
Design your PCB to be as compact as possible while still meeting performance requirements. Smaller PCBs require less material and less processing time, resulting in a lower overall cost. - Order in Bulk
Large volume orders generally come with a reduced per-unit price. Whenever possible, order the quantity needed for both current production and foreseeable future demand to gain economies of scale and reduce your overall PCB Plate Costs. - Select the Right PCB Manufacturer
Different PCB manufacturers have varying cost structures. Obtain multiple quotes from different vendors, not only focusing on price but also considering their production capabilities, quality control processes, and delivery timeframes. - Minimize Special Processes
Avoid unnecessary specialized processes like blind vias or impedance control if they are not critical to the performance of the board. Each special process adds costs to the final price of the board. - Use Standard Drill Sizes
Using a standard drill size available in the shop can lower costs by eliminating the need to change tooling on the manufacturing line. - Thoroughly Review Design Files
Before submitting your design for manufacturing, ensure a thorough review to eliminate errors and avoid rework. Error-free design files can streamline manufacturing and prevent costly delays.
Understanding the intricacies behind PCB plate price involves a deep dive into various material, manufacturing process, and order volume factors. By understanding these critical cost drivers, whether you're a hobbyist or a professional, you can make informed decisions. The cost of a PCB plate can vary widely, from a few dollars for basic boards to hundreds for complex ones. So, by understanding these key factors, you're equipped to optimize your budget and ensure you get the best possible value for your electronic projects. Considering a balance between your budget and project requirements helps navigate the PCB market effectively. Always comparing quotes and suppliers to secure the best possible PCB plate price is a key to your success.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA