Understanding UPS PCB Price: Factors, Brands, and Trends
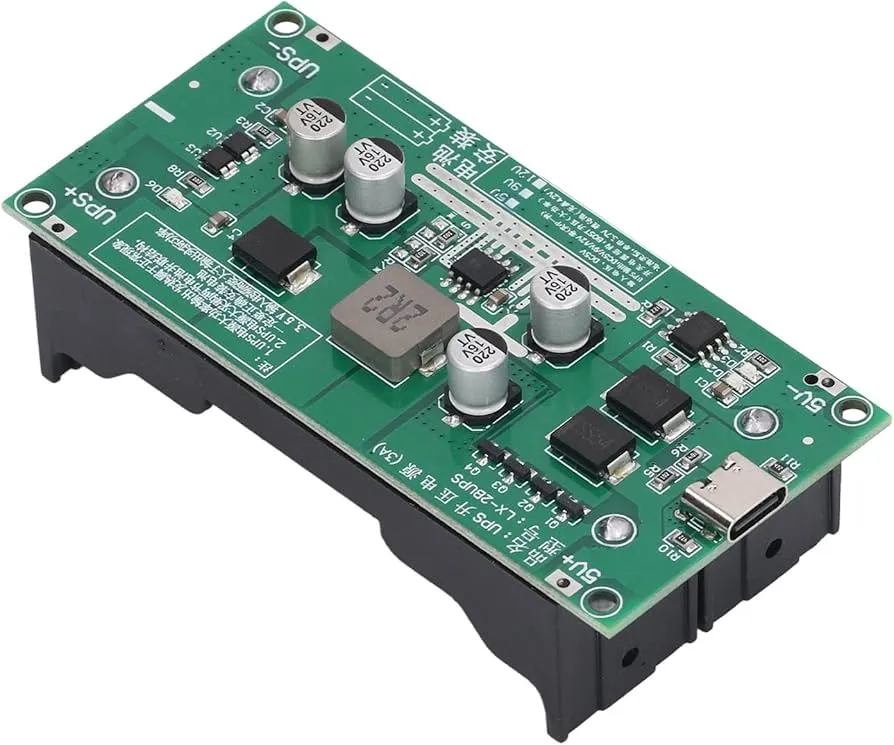

In our increasingly power-dependent world, Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS) are essential to keep our critical devices running. At the heart of every UPS is its printed circuit board (PCB), the unsung hero managing power flow, battery charging, and voltage regulation. As a core component, the price of UPS PCBs significantly impacts the final cost of these critical devices. This article delves into the factors influencing 'ups pcb price', providing you with a comprehensive understanding of how to navigate this market effectively.
Key Factors Influencing UPS PCB Price

The price of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is not arbitrary; it's a result of several interconnected factors. These factors range from the inherent complexity of the board itself to external market forces. Understanding these elements is crucial for effective cost management and strategic decision-making when sourcing UPS PCBs.
- PCB Complexity
The intricacy of the circuit design directly influences the cost. More complex designs, featuring a higher number of components, layers and sophisticated routing, necessitate advanced manufacturing processes, thereby driving up the price. For instance, boards with integrated microcontrollers or advanced power management circuits will inherently cost more to produce than simpler boards. - Material Quality
The type of materials used, such as the base substrate (e.g., FR-4, CEM-3), copper thickness, and surface finish, significantly impact cost. High-grade materials enhance performance and durability but come at a higher price point. For example, PCBs using high-frequency laminates for specialized UPS applications will incur greater expenses due to material cost. - Production Volume
Economies of scale play a vital role in determining PCB costs. Higher production volumes allow manufacturers to reduce per-unit costs, owing to the spreading of fixed costs over larger quantities. Conversely, low-volume orders typically carry higher unit costs due to setup fees and less efficient material usage. - Manufacturer's Reputation and Quality Standards
The brand reputation and quality control standards of a PCB manufacturer can significantly affect the price. Manufacturers with stringent quality controls, certifications, and advanced fabrication capabilities typically command higher prices. Reputable manufacturers often employ advanced testing methods and stringent material selection, adding to the overall cost but ensuring higher reliability and longevity of the PCB. - Design and Customization Requirements
Custom PCB designs tailored to specific UPS functionalities or form factors may result in higher costs, due to unique engineering, specialized equipment setup and the need for bespoke manufacturing processes, in contrast to standard or off-the-shelf board designs.
Types of UPS PCBs and Their Cost Implications
The architecture of a UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) Printed Circuit Board (PCB) directly impacts both its performance and cost. PCBs are categorized primarily by the number of conductive layers they incorporate: single-layer, double-layer, and multilayer, each of which carries distinct characteristics relating to functionality and price point. Understanding these differences is crucial for optimizing UPS design and cost management.
| PCB Type | Description | Complexity | Cost | Typical UPS Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer PCB | Consists of a single conductive layer of copper on one side of the board. | Low | Lowest | Simple, low-power UPS systems | Low cost, easy to manufacture | Limited routing density, susceptible to noise. |
| Double-Layer PCB | Features conductive layers on both sides of the board, allowing for connections through vias. | Medium | Moderate | Mid-range UPS systems. | Increased routing flexibility, better noise immunity compared to single-layer. | Limited routing density compared to multilayer. |
| Multilayer PCB | Includes three or more conductive layers, separated by insulating materials. Allows for complex interconnections and high density routing. | High | Highest | High-power and complex UPS systems. | High routing density, superior performance and noise immunity. | More expensive, complex manufacturing. |
Material Choices Impact on UPS PCB Price

The selection of materials for a UPS PCB directly influences both its performance and cost. Common materials like FR-4, CEM-3, and specialized high-frequency laminates exhibit varying electrical properties, thermal stability, and mechanical strength, leading to differences in price points. Understanding these material characteristics is crucial for optimizing the cost and performance balance of a UPS system.
| Material Type | Description | Typical Applications | Cost | Performance Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | A composite material made of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder. | Most common for standard UPS PCBs. | Moderate | Good balance of electrical and mechanical properties; widely available. |
| CEM-3 | Composite material with a paper core and fiberglass layers. | Cost-sensitive applications where performance is adequate. | Lower | Lower electrical and mechanical strength compared to FR-4, suitable for less demanding UPS systems. |
| High-Frequency Laminates (e.g., Rogers, Taconic) | Specialized materials with enhanced electrical properties for high-speed signal transmission. | High-performance UPS and specialized applications. | Higher | Superior electrical performance; typically required for advanced high-frequency switching and power control circuits. |
| Metal Core PCBs | PCBs with a metal base (e.g., aluminum or copper) to enhance thermal dissipation. | UPSs operating under high-power conditions and environments with heat management requirements. | Higher | Excellent thermal conductivity; ideal for higher-power applications where heat dissipation is critical. |
The choice of materials is not just about the cost but also about the reliability and lifespan of the UPS PCB. High-frequency laminates, while more expensive, are necessary for UPS designs requiring rapid switching and power control. Conversely, for lower power UPS systems where cost is a bigger constraint, CEM-3 can provide a viable option. The appropriate selection depends on performance requirements and budget limitations.
Brand Comparison of UPS PCB Prices
The price of UPS PCBs varies significantly across different brands due to factors such as brand reputation, manufacturing standards, component quality, and warranty provisions. This section will analyze and compare some of the leading brands in the UPS market to help you understand their pricing strategies, quality standards, and how they impact overall cost.
| Brand | Typical Application | Price Range (USD) | Quality Standard | Key Features | Warranty |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| APC | Consumer, Small Business | $$$ | High | Reliable, good support | 2 years |
| Schneider Electric | Enterprise, Industrial | $$$$ | Very High | Advanced features, Robust | 3-5 years |
| Eaton | Data centers, Industrial | $$$ | High | Energy efficient, scalable | 2-3 years |
| CyberPower | Consumer, Small Business | $$-$$$ | Medium to High | Cost-effective, good features | 1-3 years |
| Vertiv | Data centers, critical infrastructure | $$$$ | Very High | High performance, very reliable | 2-5 years |
| Local Manufacturers | Varies | $ | Variable | Economical, basic functionality | Varies, usually 1 year |
Note: Price ranges are indicative and can fluctuate based on specific models, features, and market conditions. Local manufacturers often provide cost-effective solutions but may have lower standards and less comprehensive warranty options. Brand reputation often correlates with the PCB's quality and the overall performance of the UPS.
Global Price Variations in UPS PCB Markets
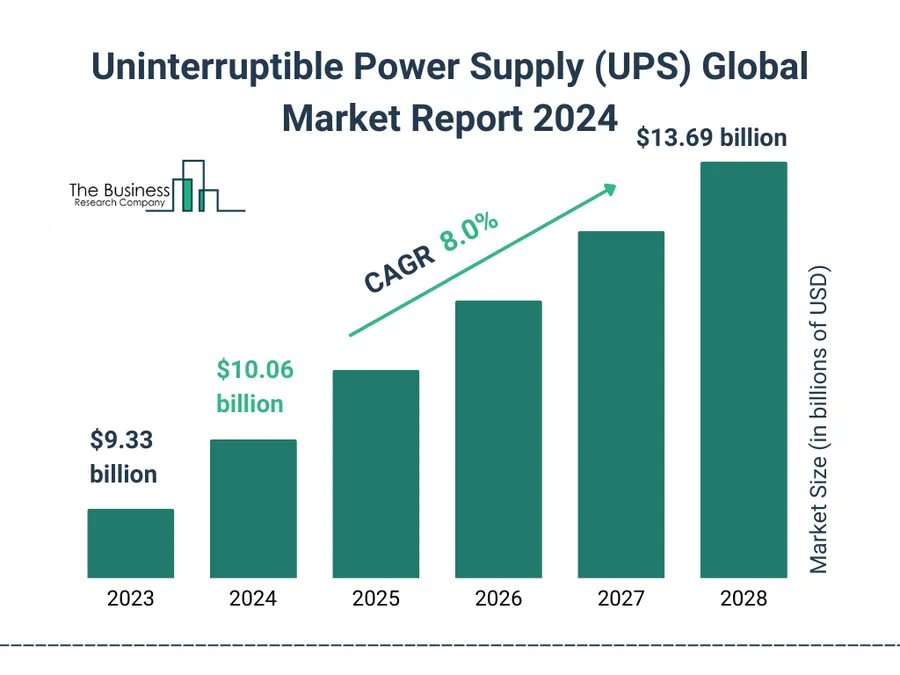
The global market for UPS PCBs exhibits significant price variations influenced by a complex interplay of factors, including regional labor costs, the availability of raw materials, and localized market demands and competitive landscapes. These variations can significantly impact sourcing and purchasing strategies for manufacturers and end-users.
| Region | Typical Labor Costs | Material Availability | Market Dynamics | Impact on PCB Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Asia (e.g., China, India) | Lower labor costs | Generally good availability, but may fluctuate based on global supply chains | Highly competitive market with a large number of manufacturers | Lower PCB prices due to competitive manufacturing costs |
| North America (e.g., USA, Canada) | Higher labor costs | Good availability, but some reliance on imported materials | Established market with a focus on high quality and advanced technology | Higher PCB prices due to higher labor and manufacturing costs |
| Europe (e.g., Germany, France) | Higher labor costs | Moderate availability, with a focus on eco-friendly and specialized materials | Technologically advanced market with strict environmental regulations | Higher prices driven by labor costs and environmental compliance |
| South America (e.g., Brazil, Argentina) | Moderate labor costs | Material availability can be inconsistent and reliant on imports | Growing market with varying levels of technological advancement | Prices vary based on material availability and local manufacturing capabilities |
| Other regions (e.g., Africa, Middle East) | Varying labor costs | Material availability is often limited and dependent on imports | Less developed market with limited local PCB manufacturing | Prices are generally higher due to limited local manufacturing and reliance on imports |
DIY UPS PCB Board Assembly vs. Purchasing Ready-Made Boards
The decision to assemble a UPS PCB board yourself or purchase a pre-assembled unit involves careful consideration of cost, time, skill, and risk. Each approach presents distinct advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed against project requirements and available resources.
| Factor | DIY Assembly | Purchasing Ready-Made |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | Potentially lower for components, but requires assembly tools, time and expertise. | Higher upfront cost due to labor and overhead, but includes assembly and testing. |
| Time Investment | Significant; requires time for design verification, component sourcing, assembly and troubleshooting. | Minimal; board is ready for installation after receiving. |
| Skill Level | Requires electronic engineering knowledge, soldering skills, and diagnostic experience. | Minimal; assumes user has basic installation knowledge. |
| Risk of Error | High, potential for assembly errors, component damage and functional failures. | Lower, typically factory tested to meet specifications. |
| Flexibility & Customization | High, offers opportunity for custom designs and component selection. | Limited to available models and features. |
| Repairability | Potentially easier for component-level repairs with good knowledge. | May be more difficult to repair if complex or if internal workings are less accessible. |
| Tools Required | Specialized soldering equipment, multimeter, and other testing instruments. | Minimal; requires basic installation tools (e.g., screwdriver). |
| Warranty & Support | No warranty, limited support. | Typically includes warranty and technical support by manufacturer. |
Frequently Asked Questions About UPS PCB Price
This section addresses common inquiries regarding UPS PCB costs, clarifying the role of PCBs in UPS systems and the factors influencing their price variations. Understanding these aspects can assist in making informed purchasing decisions.
- What is the role of a PCB in a UPS?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is the foundational component of a UPS, serving as the platform that electrically interconnects all electronic components. It manages power conversion, battery charging, inverter control, and overall system protection. In essence, the PCB is the brain and nervous system of the UPS, enabling its core functions. - How much does a basic UPS PCB cost?
The cost of a basic UPS PCB can vary significantly, typically ranging from a few dollars to several tens of dollars depending on its complexity, material, and production volume. Simple, single-layer PCBs for low-power UPS units are generally at the lower end of this range, while more complex multilayer boards for high-power or specialized units will be more expensive. - What factors contribute to the variation in UPS PCB prices?
Several factors influence the cost of a UPS PCB: PCB complexity (number of layers, component density), material type (e.g., FR-4, CEM-3), production volume (larger volumes reduce per-unit cost), manufacturer reputation and location, and specific functionalities implemented (e.g., advanced protection circuits, communication interfaces). Higher complexity and specialized materials often lead to increased cost. - What is the impact of PCB layer count on cost?
The number of layers in a PCB (single-layer, double-layer, multilayer) has a direct impact on cost. Single-layer PCBs are the simplest and least expensive. Double-layer PCBs offer more flexibility but cost more. Multilayer PCBs, with four or more layers, are the most complex and costly, providing increased circuit density and better performance for more advanced UPS systems. - Does the material of the PCB affect the price?
Yes, the choice of materials significantly impacts both the performance and price of a UPS PCB. FR-4 is a common and cost-effective choice, but more specialized materials like CEM-3, high-frequency laminates, and metal core PCBs offer enhanced thermal or electrical properties, which in turn increases the cost. - How does the manufacturer influence PCB price?
The manufacturer's reputation, quality standards, and production capabilities directly influence PCB price. Reputable manufacturers with advanced technologies and stringent quality control processes may charge more, but this reflects the enhanced reliability and performance. Less well-known manufacturers might offer lower prices, but the compromise may be on quality and longevity. The geographic location of the manufacturer also affects the cost due to variations in labor, material costs, and overheads. - Are there differences in pricing based on the application of the UPS?
Yes, the intended application of the UPS significantly influences the PCB design and price. PCBs for basic home UPS systems are less complex and therefore cheaper, whereas PCBs for industrial, data center, or medical UPS systems have stricter performance requirements, advanced protective measures, and higher component densities and thus, are more costly due to the need for high reliability, specific environmental specifications, and advanced features.
Future Trends in UPS PCB Technology and Pricing

The future of UPS PCB technology is poised for significant advancements, driven by innovations in material science, fabrication techniques, and sustainable practices. These advancements are expected to influence both the performance and the pricing of UPS PCBs, offering opportunities for more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective power solutions.
- Advanced Materials
The adoption of new materials with enhanced thermal and electrical properties is anticipated. For instance, materials with higher thermal conductivity could lead to more efficient heat dissipation, potentially allowing for smaller form factors and improved power densities. Nanomaterials, such as graphene, are also being explored for their superior electrical and mechanical characteristics. - Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Additive manufacturing is emerging as a viable technique for PCB fabrication. This approach enables the creation of highly complex circuit designs with reduced waste and potentially lower costs for prototypes and small production runs. It also facilitates on-demand manufacturing and customization. - Flexible and Stretchable PCBs
Flexible PCBs, which can conform to various shapes and sizes, are gaining popularity. In the future, stretchable PCBs may find use in UPS systems for applications where flexibility and adaptability are essential. These could potentially be integrated into unconventional spaces within UPS enclosures, reducing overall size. - Integration of Smart Features
The incorporation of smart technologies into UPS PCBs, such as integrated sensors for monitoring temperature, current, and voltage, will become more common. This will enable real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and improved overall UPS performance, potentially extending the lifespan of the equipment. - Eco-Friendly Practices
Sustainability is an increasingly important consideration. The industry is moving towards using more environmentally friendly materials and production processes that minimize waste and reduce the carbon footprint of PCB manufacturing. This includes the use of bio-based laminates and implementing recycling programs for end-of-life boards. - Miniaturization and High-Density Interconnects
Miniaturization of PCB components and the use of high-density interconnect technologies will allow for more functionality to be packed into smaller spaces. These advancements will be crucial for creating more compact and efficient UPS solutions.
Where to Buy UPS PCBs
Sourcing UPS PCBs requires careful consideration of factors such as brand reputation, customization needs, and purchasing volume. This section provides guidance on various avenues for acquiring UPS PCBs, ranging from established manufacturers to online marketplaces and specialized suppliers.
- Direct from Manufacturers
Purchasing directly from UPS PCB manufacturers, such as APC and Schneider Electric, ensures quality and compatibility, especially for proprietary designs. While this option may be more expensive, it often guarantees authentic products and access to technical support. It’s well-suited for large-scale deployments or where stringent quality control is critical. - Online Marketplaces
Platforms like Alibaba, Amazon, and eBay host a variety of suppliers and distributors offering UPS PCBs. While potentially offering competitive pricing, buyers should meticulously verify supplier credentials and product specifications. Be aware of quality inconsistencies, varying lead times and warranty conditions when sourcing from these channels. This approach is beneficial for smaller projects or where cost is a primary concern. - Specialized Electronic Component Distributors
Companies specializing in electronic components, like Digi-Key, Mouser Electronics, and Arrow Electronics, often stock a range of PCBs, including those used in UPS systems. These distributors provide detailed product specifications, data sheets and traceability which are important considerations. This is a strong option if high reliability is a priority, and is better suited for technically-proficient buyers. - Custom PCB Manufacturers
For specific requirements not met by off-the-shelf solutions, custom PCB manufacturers are ideal for tailored designs. These companies provide services from design to manufacturing, offering flexibility in material, layer count, and feature specifications. This route is ideal for specialized applications or innovative UPS designs that require specific board characteristics. - Regional or Local Suppliers
Local or regional suppliers are often a great choice for faster delivery times, reduced shipping costs, and potentially more direct support channels. Building a relationship with local suppliers may also facilitate easier communication and bespoke requests. Consider this if you prefer local support and wish to streamline your supply chain.
Understanding the cost of UPS PCBs is crucial, as it is directly correlated to the performance and reliability of your power backup system. This guide has explored the multiple facets influencing 'ups pcb price', from materials to manufacturing complexity and market trends. By considering these factors, you are better equipped to make informed decisions, ensuring you invest wisely in high-quality UPS components that meet your specific needs and budget requirements. As technology advances, the ‘ups pcb price’ landscape will continue to evolve, underscoring the importance of staying informed and adaptable in this dynamic market.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA