Understanding Zero PCB Board Prices: A Comprehensive Guide
In the realm of electronics, prototyping is a critical step, and the zero PCB board is often the starting point. But what is a zero pcb board price, and what influences it? This article demystifies the pricing of these essential prototyping tools and will guide you through the essential aspects of zero PCB boards, from understanding their purpose to navigating the market for the best zero pcb board price.
What is a Zero PCB Board?

A zero PCB board, often referred to as a prototyping board or perfboard, serves as a foundational platform for electronics prototyping. Unlike standard printed circuit boards (PCBs) which have pre-defined conductive pathways, a zero PCB board features a grid of holes, typically spaced at 0.1-inch intervals, allowing for the flexible placement and interconnection of electronic components. This design facilitates rapid circuit assembly and testing without the need for custom-etched boards, making it ideal for experimenting with new circuit designs and verifying functionality before committing to a final PCB layout. The typical construction involves a substrate material like FR4 or phenolic, with a matrix of plated through-holes, and may or may not include conductive pads around each hole. Zero PCB boards are employed across various applications from hobbyist electronics projects to preliminary testing of complex embedded systems.
Factors Affecting Zero PCB Board Prices
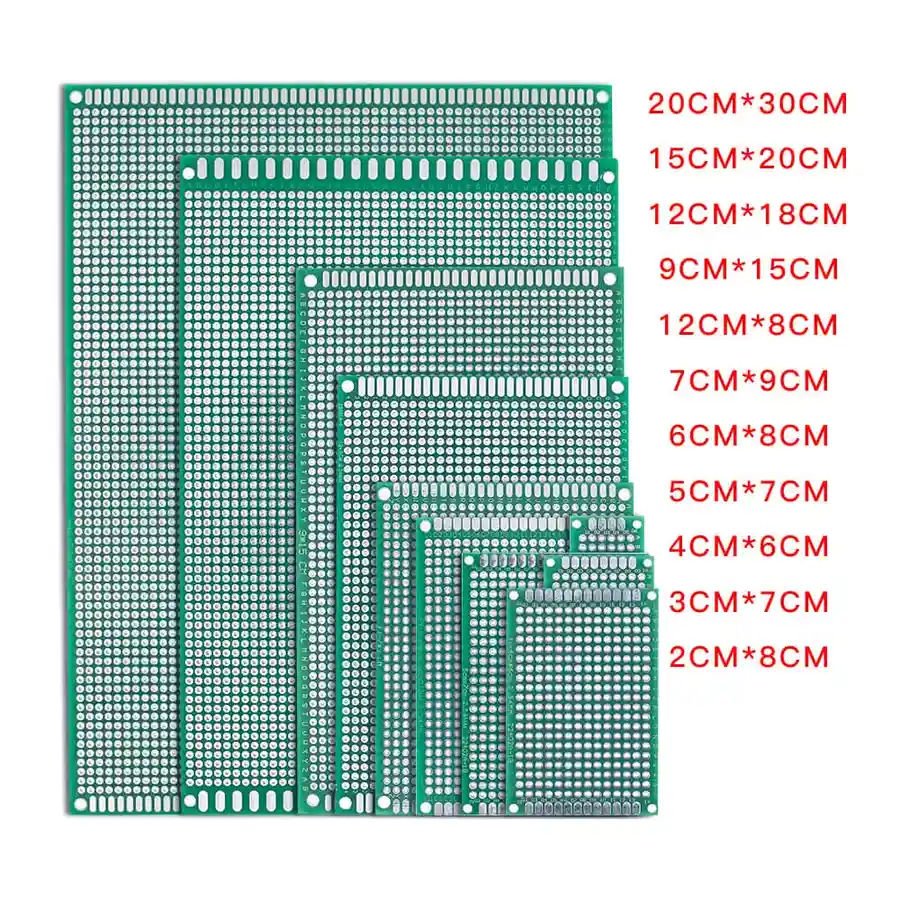
The price of zero PCB boards is not fixed and is influenced by a combination of design specifications, material choices, and market dynamics. Understanding these factors is crucial for cost-effective prototyping and project planning.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Board Size | The physical dimensions of the PCB. | Larger boards generally cost more due to increased material usage and processing requirements. |
| Material Type | The base material used for the board, typically FR4 or phenolic. | FR4 is more expensive than phenolic due to its superior electrical and mechanical properties. |
| Board Thickness | The thickness of the PCB material. | Thicker boards can be more expensive due to increased material and sometimes more complex processing requirements. |
| Number of Layers | Whether the board is single-sided or double-sided. | Double-sided boards are more expensive due to additional manufacturing steps and copper layering. |
| Surface Finish | The type of finish on the copper pads (e.g., tinned, bare copper, HASL, ENIG). | Tinned or HASL finishes are typically less expensive than ENIG, which provides superior solderability and corrosion resistance. |
| Quantity | The number of boards purchased. | Bulk orders usually result in lower per-unit prices due to economies of scale. |
| Vendor | The specific supplier or manufacturer. | Prices vary significantly between vendors, based on their overheads, location, and service level. |
The interplay of these factors determines the final cost, making it essential to evaluate project-specific needs and compare vendor offerings to achieve the optimal balance between cost and performance.
Typical Price Ranges for Zero PCB Boards

The price of zero PCB boards varies significantly based on size, material, and quantity. Understanding these price ranges is crucial for project budgeting, whether for hobbyist prototyping or larger-scale applications. Generally, smaller, single-sided boards made from basic materials will be the most cost-effective, while larger, double-sided boards with specialized finishes will command a higher price.
| Board Size (Approximate) | Material | Typical Price Range (USD) | Additional Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2x3 inch (5x7.5 cm) | FR4 (Single-sided) | $0.50 - $2.00 | Common for small circuits; often sold in bulk |
| 2x3 inch (5x7.5 cm) | Phenolic (Single-sided) | $0.30 - $1.50 | Lower cost than FR4 but less durable |
| 4x6 inch (10x15 cm) | FR4 (Single-sided) | $1.50 - $4.00 | Suitable for medium-sized projects; good balance of cost and area |
| 4x6 inch (10x15 cm) | FR4 (Double-sided) | $3.00 - $8.00 | More complex circuits; more robust |
| 10x15 cm | FR4 (Single-sided) | $3.00 - $7.00 | Larger area for more complex layouts; can be cut down |
| 10x15 cm | FR4 (Double-sided) | $6.00 - $15.00 | Complex projects requiring routing on both sides |
| Custom Size/Shape | FR4 | $5.00 and up (per board + Setup Cost) | Price is highly variable; depends on complexity and production volume |
Note that these are approximate ranges, and actual prices may vary due to factors such as the supplier, quantity ordered, and any additional services such as specific surface finishes or custom cuts. Buying in bulk from a manufacturer can significantly reduce the per-unit price, while purchasing from retail outlets may incur a higher cost per board.
Where to Buy Zero PCB Boards
Sourcing zero PCB boards effectively involves understanding the various options available, each with its own set of advantages and considerations. This section outlines popular online marketplaces, specialized electronics component stores, and local suppliers, evaluating their availability, price, shipping costs, and overall reliability to guide your purchasing decisions.
| Vendor Type | Availability | Price | Shipping Costs | Reliability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Online Marketplaces (e.g., Amazon, AliExpress) | High | Variable, often competitive | Variable, can be high for small orders | Variable, check seller ratings | Wide selection, convenient, but quality may vary |
| Specialized Electronic Component Stores (e.g., Digi-Key, Mouser) | High | Generally higher | Moderate to High | High | Good for quality and consistent supply, often caters to bulk orders |
| Local Electronics Suppliers | Variable, depends on location | Moderate to high | Low, often local pick-up | Moderate to High | Good for immediate needs, supports local businesses, may have limited selection |
Understanding Zero PCB Board Types and Sizes
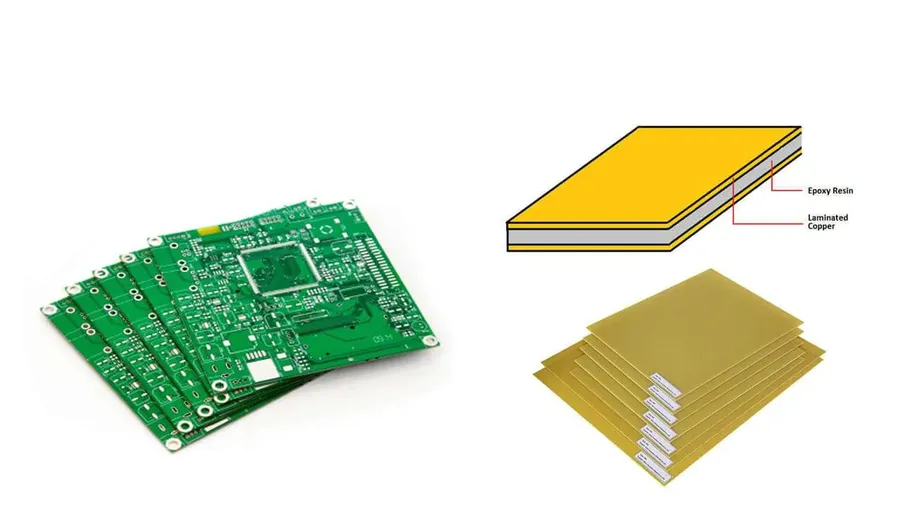
Zero PCB boards, fundamental to electronics prototyping, come in various types and sizes to accommodate different project requirements. The primary distinction lies between single-sided and double-sided boards, while sizes are standardized to facilitate ease of use and compatibility with common components.
| Feature | Single-Sided Zero PCB | Double-Sided Zero PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Copper Layers | One layer of conductive copper | Two layers of conductive copper |
| Complexity | Simpler designs, ideal for basic circuits | Allows for more complex circuit routing |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Slightly more expensive |
| Typical Usage | Simple prototype circuits, educational use | More intricate circuits requiring crossovers and multilayer components |
Common sizes for zero PCBs, often measured in inches or centimeters, include:
- 2x3 inch (50.8 x 76.2 mm)
Ideal for small, basic circuit tests and individual component testing. Compact and easily portable. - 4x6 inch (101.6 x 152.4 mm)
A versatile size for intermediate projects, offering a good balance between size and space for multiple components. Can accommodate more complex circuits. - 10x15 cm (approximately 3.94 x 5.91 inch)
Suitable for larger, more intricate circuit designs. Provides ample space for integrating various components and modules.
The practical use of a zero PCB board is highly dependent on its type and size, as larger sizes facilitate more complex layouts and double-sided boards offer routing flexibility and the capability to include more components. Selection should be based upon the complexity of the circuit to be prototyped, the number of components and specific space requirements, ensuring the correct board size is chosen for each project.
The Advantage of Using Zero PCB Boards for Prototyping
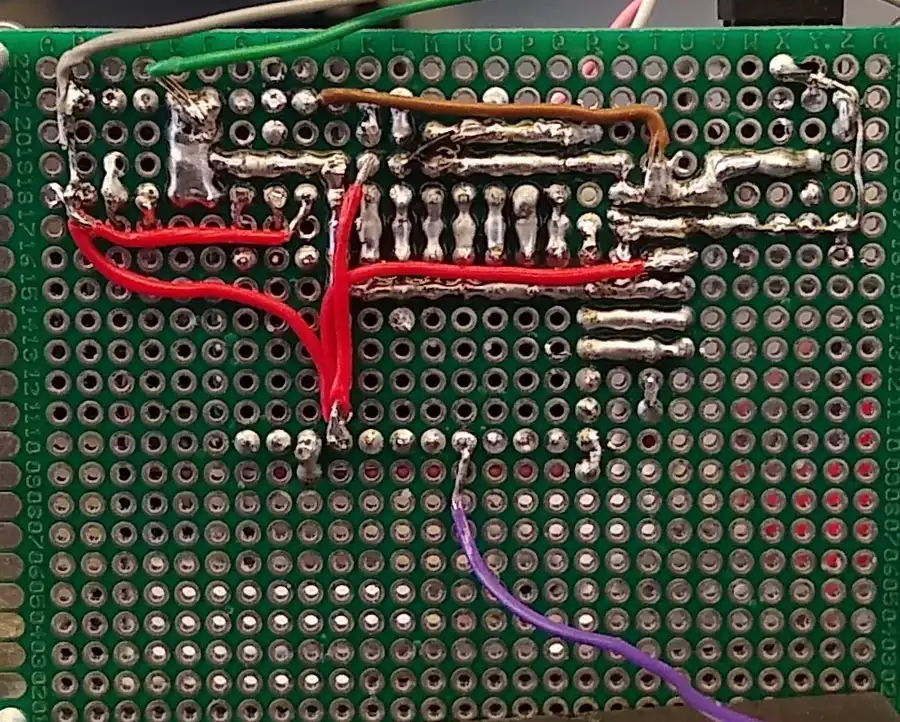
Zero PCB boards offer a compelling solution for electronics prototyping due to their inherent flexibility, cost-effectiveness, ease of use, and rapid circuit testing capabilities. These boards streamline the prototyping process by providing a versatile platform for building and testing various circuit designs.
The following details the advantages of zero PCB boards in prototyping:
- Flexibility
Zero PCBs allow for the free placement of components, without the constraints of pre-defined tracks or layouts. This makes them highly adaptable to diverse circuit designs and experimental configurations. - Cost-Effectiveness
Compared to custom-designed PCBs, zero PCBs are significantly less expensive, especially in the early stages of prototyping when design iterations are frequent. They minimize initial costs associated with fabricating circuit boards which is critical for hobbyists and students on a budget. - Ease of Use
The simplicity of zero PCBs enables even those with limited electronics experience to quickly build and test circuits. Soldering components directly onto the board is a straightforward process, allowing for fast design realization. - Rapid Circuit Testing
The ability to quickly assemble and modify circuits on zero PCBs accelerates the prototyping process. This fast turnaround facilitates experimentation and fine-tuning of designs before committing to a final layout. This allows iterative improvements rapidly. - Educational Value
Zero PCBs serve as a great educational tool for hands-on electronics learning. The direct manipulation and construction provide great insights and learning experiences for students.
By using zero PCB boards, you can quickly experiment with a large variety of designs at lower costs allowing for flexibility in your approach to product development.
Frequently Asked Questions About Zero PCB Boards
This section addresses common questions about zero PCB boards, providing concise and practical answers to assist users in their prototyping and project development endeavors.
- What are the key differences between single-sided and double-sided zero PCB boards?
Single-sided zero PCBs have conductive material on one side, limiting circuit complexity, while double-sided boards have conductive material on both sides, allowing for more intricate and compact designs. Double-sided boards also enable connections between different layers. - Is it cost-effective to use zero PCB boards for production runs?
Zero PCBs are primarily intended for prototyping due to their inherent flexibility and lack of plated through-holes or solder mask. For production runs, custom-designed PCBs are generally more cost-effective, offering better manufacturability and performance characteristics. - What tools do I need to work with zero PCB boards?
Essential tools include a soldering iron, solder, wire strippers, a multimeter, and a wire cutter. Depending on your project needs, you might also require a breadboard for component testing and prototyping, along with various electronic components and wires. - How do I choose the correct size of zero PCB board for my project?
Consider the physical space required by your components and circuit layout. Begin by creating a circuit diagram, then select a board size with ample area for all components, connections, and any desired modifications. It's advisable to have a bit of extra space for unforeseen needs during your prototyping phase. - Can I easily modify a zero PCB board?
Zero PCBs are designed for easy modification. Components can be added, removed, and rearranged to test various circuit configurations. This flexibility makes them ideal for rapid prototyping and experimentation. - How can I ensure good conductivity when working with zero PCBs?
Ensure secure solder joints and proper wire connections to maintain good electrical conductivity. Use a multimeter to check for continuity in your circuits and ensure that no cold solder joints exist, which would cause poor connectivity and circuit malfunction. Proper pre-tinning is a method to ensure consistent conductivity. - Are zero PCBs suitable for high-frequency circuits?
Zero PCBs are not generally recommended for high-frequency applications due to their lack of controlled impedance and grounding options. Custom PCBs offer better material selection and fabrication precision, thus are preferable for high-frequency circuits requiring stringent specifications.
Tips for Saving Money on Zero PCB Boards
Optimizing costs when purchasing zero PCB boards requires strategic planning, taking advantage of bulk discounts, careful vendor selection, and astute material choices aligned with project requirements. Prudent planning in these areas can yield substantial savings without compromising quality.
- Buy in Bulk
Purchasing larger quantities of zero PCB boards generally results in a lower per-unit cost. Manufacturers and distributors often offer tiered pricing, so consider consolidating your needs or anticipating future projects to leverage bulk discounts. - Compare Multiple Vendors
Prices for zero PCB boards can vary significantly between vendors. Obtain quotes from several suppliers, including both online marketplaces and specialized electronic component stores, to ensure you are getting the best possible price. Factor in shipping costs and lead times when comparing offers. - Monitor Sales and Promotions
Keep an eye out for sales, promotions, and clearance events offered by PCB suppliers. Subscribing to newsletters or following them on social media can alert you to special deals. - Optimize Board Size and Thickness
Choosing the correct board size and thickness directly influences cost. Select the smallest board size that meets the project's requirement to reduce material use. Similarly, opt for a thinner board if it does not compromise mechanical stability or performance for the intended application. - Material Selection
Where possible consider using phenolic material for low-cost applications. While FR4 is most commonly used it is more expensive. For prototyping and low power circuits phenolic can be a more cost effective choice. - Standardization
Adopting standardized board sizes across projects can allow bulk buying at lower prices and streamlined fabrication.
Understanding the zero pcb board price and the factors that influence it is essential for successful and cost effective electronics prototyping. This article has outlined the various aspects of zero PCBs, giving you a comprehensive overview from purchase to application. Remember, the key is to understand your project requirements, compare options, and choose the right type and size of zero pcb board at the best zero pcb board price for your needs. This will ensure your prototyping process is both successful and efficient.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA