Where to Buy PCBs: A Comprehensive Guide for Every Project
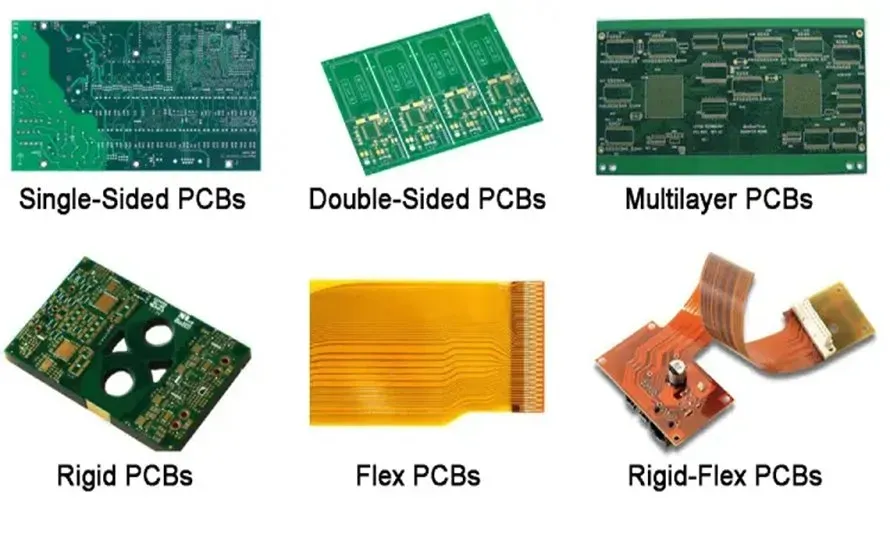
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of modern electronics, silently powering everything from smartphones to complex industrial machinery. Whether you're an electronics hobbyist prototyping a new design, or a professional bringing a product to market, the question is, where do you buy a PCB that meets your specific needs? This guide navigates the world of PCB manufacturing, helping you make informed decisions and showcasing how you can source high quality PCBs that are right for your project.
Understanding Your PCB Needs

Before initiating a PCB purchase, a thorough understanding of your project's specific requirements is crucial. This involves assessing several key parameters to ensure the final product meets your design criteria and functional needs. Accurate specifications streamline the selection process and lead to cost-effective purchasing.
- Layer Count
Determine if your design requires a single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer PCB. This is directly related to the complexity and routing density of your circuit. - PCB Dimensions
Specify the exact length and width of the board necessary for your project. Precise measurements are critical for proper fit and integration within your system. - Material Selection
Choose the appropriate substrate material, often FR-4, but consider materials like Aluminum, Rogers, or flexible substrates, depending on performance requirements and application environment. - Special Features
Identify any unique features such as impedance control for high-speed signals, controlled dielectric thickness, via type (blind/buried), or specific surface finish requirements.
Understanding these parameters early on will not only guide you in choosing the correct manufacturer and service but also reduce potential errors and ensure design manufacturability.
| Requirement | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Layer Count | Number of conductive layers | Complexity, cost, routing density |
| Dimensions | Length and width of PCB | Fit, space constraints |
| Material | Type of substrate used | Performance, cost, thermal properties |
| Special Features | Unique characteristics | Signal integrity, performance, environmental factors |
Top PCB Manufacturers: A Comparative Look

Selecting the right PCB manufacturer is crucial for the success of any electronics project. This section provides a comparative analysis of leading PCB manufacturers, focusing on their specializations, pricing structures, lead times, and manufacturing capabilities to guide you in making informed decisions when you buy a PCB.
| Manufacturer | Specializations | Pricing | Lead Times | Capabilities | Target Audience |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JLCPCB | Rapid prototyping, high-volume production, SMT assembly | Competitive, tiered pricing based on quantity and complexity | Fast, typically 2-7 days for standard PCBs | Multi-layer PCBs, various surface finishes, advanced technologies | Hobbyists, startups, small-to-medium enterprises |
| PCBWay | Prototyping, small batch production, advanced PCB technologies | Moderate, transparent pricing | Moderate, typically 3-10 days for standard PCBs | HDI PCBs, flexible PCBs, aluminum PCBs, advanced assembly | Professionals, research institutions, and high-tech companies |
| PCBBUY | High-quality production, complex multilayer boards, quick turn service | Moderate to high, focuses on premium quality | Moderate, typically 5-12 days for standard PCBs | Rigid-flex PCBs, impedance control, heavy copper boards, various material options | High-end engineering projects, aerospace, defense industries |
The table above offers a summarized comparison. When choosing a manufacturer to buy a pcb from, consider your specific needs in terms of design complexity, budget, timeline and order quantity.
Online PCB Ordering Platforms
Online PCB ordering platforms have revolutionized the way electronic engineers and hobbyists acquire custom printed circuit boards. These platforms provide a streamlined, efficient, and often more cost-effective alternative to traditional methods, offering a variety of tools and services to simplify the purchasing process.
The convenience of online platforms stems from their ability to provide instant quotes, handle file uploads seamlessly, and offer comprehensive order tracking features. This reduces the need for extensive back-and-forth communication, thus accelerating the entire process. Furthermore, these platforms often provide features that enhance user experience, improving design feedback and streamlining purchasing.
- Instant Quotation
Most platforms offer immediate price estimates based on your PCB specifications (size, layers, material, etc.). This feature helps in quick budgeting and decision-making. - File Uploads
Users can upload their Gerber files directly to the platform for automated processing. This eliminates potential errors during manual data transfer and speeds up the production process. - Order Tracking
Platforms provide a detailed tracking system, allowing users to monitor the production status of their PCBs in real time, from manufacturing to shipping, enhancing transparency and project management. - User Experience and Design Tools
Many platforms feature intuitive interfaces, design rule checks (DRC), and integrated design tools. These features ensure a smoother experience and aid in preventing design-related issues.
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Instant Quotes | Fast budgeting, immediate cost assessment |
| File Uploads | Eliminates manual errors, speeds up the process |
| Order Tracking | Real-time production updates, enhances transparency |
| User Experience | Streamlined workflow, reduced design errors |
When selecting an online platform, consider factors such as the platform’s ease of use, the range of services offered, customer support availability, and the specific tools it provides. By leveraging these platforms, you can improve the overall efficiency of the PCB purchasing process, enabling you to focus more on your design and project development.
Prototype vs. Production PCBs: What's the Difference?
When deciding to buy PCBs, it's crucial to distinguish between prototype and production PCBs. These two types cater to different stages of product development, each with distinct implications for cost, quantity, and lead time.
| Feature | Prototype PCBs | Production PCBs |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Testing and validation of design | Final product manufacturing |
| Quantity | Small batches, often a few units | Large quantities, potentially thousands or more |
| Cost | Higher per-unit cost | Lower per-unit cost due to economies of scale |
| Lead Time | Shorter lead times, often a few days | Longer lead times, often several weeks, dependent on order quantity |
| Design Adjustments | Design can be readily modified based on testing | Design typically finalized; changes may require rework. |
| Manufacturing Process | May involve less stringent processes and quality control | Requires robust and repeatable processes with strict quality control. |
Prototype PCBs are primarily used to validate a design before committing to mass production. The focus is on functionality and design verification, rather than cost or large-scale manufacturing. Production PCBs, on the other hand, are manufactured for end products, requiring stringent quality control, optimized manufacturing processes, and cost-effective pricing.
The decision to buy prototype PCBs versus production PCBs depends heavily on your project stage. For initial testing and iterative design adjustments, a prototype service is ideal. Once the design is finalized and the product is ready for market, a production run is more suitable.
Understanding these differences will allow you to effectively choose a pcb service and control your spending. When it comes to choosing a manufacturer, make sure that they offer both prototype and production services so that you can easily transition when the time is right.
Cost Factors: What Impacts PCB Pricing?
Understanding the various factors that influence PCB pricing is crucial for effective budgeting when planning to buy a pcb. These factors range from the physical characteristics of the board to the manufacturing processes involved. Awareness of these elements allows for more informed decision-making and cost optimization.
Several key elements affect the final cost of your PCBs:
- Board Dimensions and Area
The overall size of the PCB directly impacts the material usage and manufacturing time, leading to variations in cost. - Number of Layers
Single-layer PCBs are the most cost-effective, while multi-layer PCBs involve more complex fabrication processes and therefore higher costs. - Material Type
Different materials, such as FR-4, aluminum, or high-frequency laminates, have varying costs, with specialized materials typically commanding higher prices. - Surface Finish
Finishes like HASL, ENIG, and immersion silver each have different costs, performance characteristics, and environmental impacts. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), for instance, offers excellent solderability and is more expensive. - Solder Mask and Silkscreen
The colors and precision of solder mask and silkscreen layers can influence the price. Standard colors are generally less expensive compared to custom colors. - Drill hole size and quantity
Smaller drill holes and a greater number of holes will increase the cost of manufacturing due to the added manufacturing time and wear on the machinery - Special Requirements
Specific requirements, like impedance control, blind and buried vias, controlled depth drilling, and other special features, require more precise processes, resulting in increased cost.
| Cost Factor | Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Increased Board Size | Higher cost due to more material and processing time |
| More Layers | Higher cost due to more complex fabrication |
| Specialized Material (e.g., High-Frequency Laminate) | Higher cost due to increased material expense |
| ENIG Surface Finish | Higher cost for improved solderability and corrosion resistance |
| Custom Solder Mask Colors | Slightly higher cost than standard colors |
| Smaller and More Drill Holes | Higher cost due to increased processing time and machinery wear |
| Impedance Control | Higher cost due to precise manufacturing requirements |
Being informed about these cost determinants will enable more effective budget management and facilitate the purchase of pcb that meet both technical requirements and financial parameters. It is always wise to discuss any special requirements with your manufacturer, and to get cost estimates based on your exact requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Purchasing
This section addresses common questions related to purchasing PCBs, providing clear insights into cost factors and decision-making processes to help you make informed choices when buying PCBs.
- How much does a basic PCB cost?
The cost of a basic PCB can vary significantly depending on several factors. For simple, single-layer boards, prices can start as low as a few dollars per board, especially when ordering in larger quantities. However, factors like board size, material, and the complexity of the design can influence the final cost. - What factors contribute to the overall cost of PCBs?
Several factors affect PCB pricing. These include the number of layers, the type of material used (FR-4, aluminum, etc.), board size and thickness, the complexity of the design, surface finish requirements (HASL, ENIG, etc.), and any special features such as controlled impedance or via type. - Why are PCBs sometimes so expensive?
The expense of PCBs arises from the complex manufacturing process, which involves precision etching, drilling, plating, and lamination. Higher layer counts, special materials, and tight tolerances further increase costs. Low production volumes also lead to higher per-unit prices due to setup costs being spread across fewer units. - Does the quantity of PCBs ordered affect the price?
Yes, absolutely. PCB manufacturers often offer substantial discounts for larger orders. This is because the initial setup costs (preparing tooling, programming machines, etc.) are fixed, and these costs are distributed across the total number of boards. Therefore, ordering in larger volumes significantly reduces the per-unit cost. - What is the relationship between PCB complexity and cost?
There is a direct correlation between PCB complexity and cost. Complex designs, such as multi-layer boards with small features, high component density, and controlled impedance, require more advanced manufacturing processes and specialized equipment. This increases production costs, which are reflected in the final price of the PCB. - What is PCB in purchasing context?
In a purchasing context, PCB refers to the acquisition of printed circuit boards, a critical component in electronic devices. It involves determining requirements (layer count, material, dimensions), identifying suitable manufacturers or suppliers, managing costs and budgets, and handling the ordering and delivery process. The process aims to ensure timely acquisition of cost-effective and high-quality PCBs. - How can I reduce the cost of PCBs when buying?
To minimize PCB costs, consider simplifying your design to reduce the number of layers and component density if possible, choose a cost-effective material, and order in larger quantities. Furthermore, try to avoid complex features or custom requirements, and choose surface finishes such as HASL instead of more costly alternatives like ENIG when applicable. You can also ensure that your design files are fully optimized before production to avoid expensive revisions, and finally, plan well ahead to avoid express production surcharges.
DIY vs. Professional PCB Fabrication
Deciding between fabricating printed circuit boards (PCBs) in-house or using a professional service is a critical choice, especially when you buy a pcb for project needs. This section analyzes the trade-offs involved in DIY PCB production versus using professional services, particularly focusing on time, cost, and quality implications.
| Feature | DIY PCB Fabrication | Professional PCB Fabrication |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Initially lower for basic setups, but can escalate with complexity and failed attempts. | Higher initial cost, but potentially more economical for complex designs and large quantities. |
| Quality | Quality depends heavily on the user’s skill and equipment. Often suitable for simple circuits but may not meet high-precision standards. | Higher quality and precision with advanced manufacturing techniques and quality control processes. |
| Time | Time-consuming, especially with learning curves, manual processes, and potential for errors. | Faster turnaround times, especially with optimized manufacturing processes and advanced machinery. |
| Complexity | Limited to single-sided or simple double-sided boards with less precision. Difficult with multi-layer or complex designs. | Capable of handling single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer, complex, and high-density boards. Includes advanced options like impedance control. |
| Materials | Limited material selection. May be difficult to source special substrates or specific finishings. | Wider variety of substrates, finishes, and material options are available from specialized suppliers. |
| Equipment | Requires upfront investment in tools like etching equipment, UV exposure setups, drills, and software. | Uses advanced manufacturing equipment and machinery such as CNC machines, laser etching, and automated assembly lines. |
| Expertise | Requires in-depth understanding of etching, drilling, and chemical processes. Knowledge of PCB design software is needed. | Relies on professional design and manufacturing teams with years of experience and knowledge of industry standards and best practices. |
| Scalability | Difficult to scale production for large quantity requirements due to time, equipment and consistency issues | Can produce small and large quantities while maintaining consistency in quality and production. |
For hobbyists and straightforward projects, DIY methods may suffice when learning to buy a pcb. However, for projects requiring reliability, precision, and larger quantities, a professional service is usually the better choice. Furthermore, professional services can often accommodate special requirements such as controlled impedance, specialized materials, and fine-pitch components, which are exceptionally difficult to manage using DIY methods. The decision to buy a pcb using either method ultimately depends on the project’s requirements, budget, timeline, and your level of expertise. Consider the potential pitfalls in each case to ensure that the chosen method aligns with project goals.
Tips for Choosing the Right PCB Manufacturer

Selecting the right PCB manufacturer is critical for project success, affecting not only the quality of the final product but also the cost and timeline. This section provides a checklist to guide you through the evaluation process, ensuring you make an informed decision when you buy a PCB.
- Certifications and Standards
Verify the manufacturer's adherence to industry standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management and UL certifications for safety. These certifications guarantee that the PCBs meet specific quality and safety requirements, reducing the risk of defects and ensuring reliability. Authoritative sources include ISO and UL websites for verifying certification details. (Source: ISO.org, UL.com) - Quality Control Processes
Inquire about the manufacturer's quality control procedures, including automated optical inspection (AOI), electrical testing, and in-circuit testing. Robust quality control measures are essential to identify and rectify any defects before the PCBs are shipped, ensuring the final product functions as intended. This reduces the cost of potential rework and improves overall project efficiency. (Source: IPC standards for PCB manufacturing) - Turnaround Time
Evaluate the manufacturer's lead times for production and shipping. Check their stated lead times against your project timeline, considering both standard and expedited options. Accurate delivery times are critical to prevent project delays. A manufacturer that aligns with your timeline is invaluable. (Source: Industry benchmarks for PCB lead times) - Customer Reviews and Feedback
Look for reviews and testimonials from past clients to gauge customer satisfaction. Platforms like Google Reviews and industry forums can provide valuable insight. Positive customer experiences indicate consistent quality and service. (Source: Google Reviews, relevant industry forums) - Customer Support Services
Assess the availability and responsiveness of the manufacturer's customer support team. Ensure they provide technical assistance and order tracking. Responsive customer service helps to prevent potential issues and makes the ordering process smoother. (Source: Experience from engineers' reports) - Technological Capabilities
Consider the manufacturer's ability to handle various PCB technologies such as multi-layer boards, controlled impedance, blind and buried vias and specific material requirements. Align these capabilities with the specific requirements of your project. (Source: Manufacturers' specifications) - Pricing Structure and Transparency
Compare quotes and ensure the pricing is transparent without hidden costs. Understanding pricing and how it is affected by different specifications is key for budgeting for your project. (Source: Industry price comparisons and analysis)
By considering these critical factors, you are better equipped to choose a PCB manufacturer that best suits your project needs, ensuring high-quality, timely delivery of your PCBs when you buy a PCB.
Payment and Shipping Options for PCBs
Navigating payment and shipping is a crucial final step when you buy a PCB. Understanding available options and potential considerations, especially for international orders, ensures a smooth transaction and prevents unexpected delays. This section details the common payment methods and shipping options, along with advice for efficient international ordering.
When buying PCBs, payment methods typically include:
- Credit Cards
Major credit cards such as Visa, MasterCard, and American Express are widely accepted by most PCB manufacturers. - PayPal
A popular online payment system that offers an extra layer of security and buyer protection. - Bank Transfers
Sometimes an option for large orders or for customers in specific geographic locations. May have higher transaction fees. - Other Online Payment Gateways
Some manufacturers also support other payment gateways such as Stripe, or regional specific options, depending on location.
Shipping options vary based on speed and cost and include:
- Standard Shipping
Cost-effective but may have longer delivery times. Usually delivered by national postal services or similar. - Express Shipping
Faster delivery options, such as DHL, FedEx, or UPS, but with higher costs. Suitable for time-sensitive projects. - Specialized Logistics Providers
Some manufacturers use specialized logistics providers that are tailored to international shipping and local regulations.
When dealing with international PCB orders, consider the following:
- Customs and Duties
Be aware of import duties, taxes, and customs fees, which may vary by country and affect total cost when you buy a pcb. These costs are generally not included in the initial product price, and are the responsibility of the buyer. - Shipping Times
International shipping can take longer due to customs processes and distance. Plan lead times carefully to avoid delays when you buy a pcb. - Tracking
Select a shipping method that provides tracking information to monitor your package's journey. This can help prevent loss or delay when you buy a pcb. - Currency Exchange
If the payment currency differs from your local currency, be aware of exchange rates and potential bank fees. It's often best to pay in the currency the manufacturer requests.
To minimize issues related to payment and shipping, it is advisable to review manufacturer's policies thoroughly, confirm payment method prior to ordering, and always select a shipping option that best meets your project's needs. Doing so helps you to buy a pcb with confidence and certainty.
Choosing the right place to buy PCBs is vital for any electronic project. By understanding your project needs, comparing different manufacturers, and weighing factors like price and lead time, you can confidently buy a pcb that meets your requirements. With this guide, you’re now better equipped to navigate the PCB market effectively, ensuring you get the best value and quality for your needs.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA