Your Guide to Buy Custom PCB: Options, Process & Best Practices
From the smartwatches on our wrists to the complex machinery in factories, custom PCBs are the unsung heroes of modern technology. If you're diving into electronics or launching a new project, understanding how to buy custom PCBs is crucial. In this article, we will guide you through every step, from selecting the right manufacturing partner to ensuring your design is ready for production. Let's explore how these intricate circuits enable our digital world, making sure you're prepared to buy custom PCBs with confidence.
Understanding Your Custom PCB Needs

Before initiating the procurement of custom Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs), a precise definition of project requirements is paramount. This foundational step dictates the selection of appropriate manufacturing processes and ensures that the final product meets all functional and performance criteria. Key considerations include the type of PCB, layer count, functional specifications, and the required quantity for prototyping or mass production.
- PCB Layer Count
Determine if your design requires a single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer PCB. This decision directly affects complexity, cost, and signal routing capabilities. Single-layer PCBs are simplest and cheapest, suitable for basic circuits. Double-layer PCBs provide increased routing flexibility, and multi-layer PCBs are necessary for complex designs needing multiple routing layers and advanced functionalities. - Functional Requirements
Clearly identify the PCB's intended functionality. Considerations include signal type (digital, analog, high-frequency), impedance control, power requirements, component density, and any specialized features like thermal management or high-voltage isolation. These will impact the materials selection, track widths, via sizes, and stack-up. - Prototyping vs. Production Quantities
Distinguish between prototyping needs (low quantity) and mass production (high quantity). Prototyping emphasizes fast turnaround times and is suited for design validation. Production runs must be balanced between quality, cost, and lead times. PCB manufacturers often provide different service options, lead times, and prices based on quantity and urgency.
Choosing the Right PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the ideal PCB manufacturer is a critical step in ensuring the success of your project. This decision hinges on various factors, including the manufacturer's reputation, service capabilities, pricing, lead times, and adherence to industry certifications. Thorough evaluation of these aspects is essential for identifying a partner that aligns with your specific project needs.
To aid in this process, consider the following key areas when evaluating potential PCB manufacturers:
- Reputation and Reviews
A manufacturer's reputation is often a strong indicator of its reliability and quality. Look for independent reviews, customer testimonials, and industry ratings to gauge their performance. Check for consistency in delivering quality products and meeting deadlines. - Service Offerings
Evaluate the range of services offered by the manufacturer. Do they specialize in single-layer, double-layer, or multilayer PCBs? Are they capable of producing the specific materials and finishes your project requires? Do they offer PCB assembly or only manufacturing? - Pricing Structure
Compare the pricing of different manufacturers. Understand how their pricing is structured, whether it's per square inch, number of layers, or a combination. Be cautious of manufacturers with unusually low prices as this may indicate lower quality or hidden costs. - Lead Times
Lead times, the time from ordering to receiving your PCBs, can significantly impact your project timeline. Inquire about standard lead times, and if expedited options are available for urgent projects. Ensure lead times are realistic. - Certifications and Standards
Verify that the manufacturer adheres to relevant industry standards and holds necessary certifications. Standards such as ISO 9001 for quality management are an indicator of commitment to best practices. Certifications may include IPC standards for PCB fabrication. - Online Quoting and Ordering Systems
Manufacturers with robust online quoting and ordering platforms can streamline your workflow. These systems typically allow you to upload design files (Gerber), obtain instant quotes, and manage your orders. Online capabilities for design rule checks can also save time and prevent errors. - Specialization
Some manufacturers specialize in specific types of boards or industries. If your project has unique requirements, it may be beneficial to choose a manufacturer with expertise in that area. For example, some manufacturers focus on high-frequency boards or high-reliability applications.
Online PCB Quote and Ordering Process
The online PCB quote and ordering process has streamlined custom PCB fabrication, enabling rapid prototyping and production. Typically, this process involves uploading Gerber files, the industry standard for PCB design, to a manufacturer's online platform. These platforms facilitate instant quoting based on design specifications and allow users to select various manufacturing and delivery options.
- Gerber File Upload
The initial step requires uploading your PCB design data in Gerber format. These files describe the layers, pads, traces, and other necessary attributes to manufacture the board. - Instant Quoting
Online platforms analyze the uploaded Gerber files and generate an instant quote. This quote considers factors like board dimensions, layer count, material type, and quantity. - Customization Options
Users can specify various customizations such as solder mask color, silkscreen requirements, surface finish, and the specific material type such as FR4, Aluminum, or Flexible. - Turn Time Selection
The platform allows users to select their preferred turnaround time, ranging from standard to express services, which affect the production timeline. - Shipping Selection
Users choose their shipping method, balancing cost and delivery speed to align with project deadlines. - Order Placement and Tracking
Once customizations are set and the quote is accepted, users can place the order. Most platforms provide tracking updates to monitor the progress of the production and shipment.
PCB Design Considerations for Manufacturing
Optimizing your PCB design for manufacturing is crucial to ensure the final product meets specifications and avoids costly errors. Adhering to the chosen manufacturer's guidelines, which are rooted in material properties, fabrication processes and machinery capabilities, is paramount.
| Design Parameter | Considerations | Impact of Incorrect Design |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum Trace Width and Spacing | Refer to the manufacturer's specifications. Ensure traces are wide enough to carry the intended current and have adequate spacing to prevent shorts. Typical values are from 4 mil to 8 mil. | Short circuits, open circuits, impedance mismatches, potential for trace damage during manufacturing, reduced signal integrity. |
| Via Sizes and Types | Choose appropriate via sizes based on board thickness and the manufacturer's capabilities. Select via types (through-hole, blind, buried) according to your design needs. | Difficulties in soldering, open circuit issues, delamination during lamination processes, reduced thermal performance. |
| Copper Weight | Specify the correct copper weight based on current carrying requirements. Higher current requires a higher copper weight. | Overheating, trace damage, unreliable performance, and reduced lifespan of components. |
| Solder Mask and Silkscreen | Ensure accurate alignment of solder mask to pads and adequate clearance for silkscreen. Improper solder mask may cause solder bridging, while incorrect silkscreen will result in confusing product or difficult troubleshooting. | Solder bridges, reduced reliability, difficult assembly, incorrect part placement and functionality issues. |
| Gerber Files | Use the correct Gerber format (RS-274X) and ensure all layers are exported accurately, including drill files and pick-and-place data. | Manufacturing errors, delayed production, need for re-spins of boards, increase costs and timelines. |
Utilizing Design Rule Checks (DRCs) within your PCB design software is essential before sending the files to fabrication. These automated checks verify the design parameters against the manufacturers' specifications, preventing common design errors.
Cost-Effective Strategies When Ordering Custom PCBs
Optimizing costs when ordering custom PCBs is crucial for any project, whether it's a prototype or a large production run. Strategic planning in board design, material selection, and order timing can significantly reduce expenses without sacrificing quality or functionality. This section will delve into actionable strategies to help you get the most value from your PCB order.
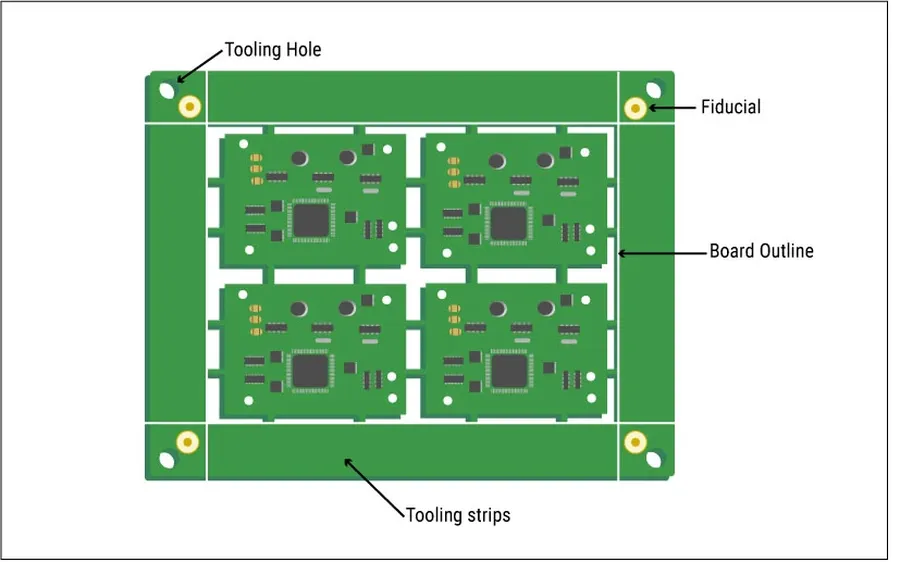
- Panelization for Efficiency
Panelizing, or combining multiple PCB designs onto a single larger board, can significantly cut down manufacturing costs. This is because the manufacturer can process more boards in a single run, reducing per-unit costs. When designing your panel, ensure that all boards are adequately separated and the panel layout aligns with the manufacturer’s guidelines. - Optimize Board Size and Shape
Smaller and simpler boards generally cost less to produce. Review your design and remove unnecessary space or complexity. Use the smallest dimensions needed to support the circuit’s functionality and optimize the board's shape to maximize material utilization. For rectangular boards, standard industry panel sizes often lead to less waste and lower costs. - Material Selection
While FR-4 is the most common and cost-effective base material, exploring alternatives might be worthwhile for specific applications. For example, if your design doesn’t require high-temperature resistance, using materials with lower thermal endurance may reduce costs. Additionally, consider the thickness and copper weight needed as thinner boards and less copper can sometimes result in lower pricing. - Lead Time Flexibility
Standard lead times are often more cost-effective than expedited options. If your project allows for some flexibility, opting for a longer lead time can reduce manufacturing costs. Plan your orders in advance to avoid rush fees and extra charges associated with fast turnaround. - Order Volume and Frequency
Ordering in higher volumes typically leads to lower per-unit costs. Consider combining multiple prototype orders into a larger production run or group orders to receive discounts and better pricing. Similarly, establishing consistent relationships with PCB manufacturers can sometimes result in loyalty discounts and improved terms. - Avoid Unnecessary Options
Analyze if specific features or manufacturing options add real value or if they are expendable. Gold plating, custom solder mask colors, and special surface finishes often carry extra costs. Carefully evaluate whether these features are essential for the performance of your board or can be eliminated to save expenses. - Leverage Manufacturer's Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Tools
Use the DFM tools provided by manufacturers to pinpoint potential design flaws that could cause manufacturing problems, and fix them early on. This prevents re-fabrication which is more time and money consuming. These tools check for common manufacturing issues like trace width, spacing, drill size, and proper board layer alignment that could affect costs.
| Cost-Saving Strategy | Description | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Panelization | Combining multiple PCBs into one larger board. | Reduces per-unit cost through efficient manufacturing. |
| Board Size Optimization | Reducing board size and complexity. | Decreases material usage and manufacturing time. |
| Material Selection | Choosing appropriate materials. | Can lower material and production costs. |
| Lead Time Flexibility | Opting for standard or longer lead times. | Avoids rush fees and extra charges. |
| Volume Ordering | Ordering in larger quantities. | Reduces per-unit price. |
| Eliminating Unnecessary Options | Avoiding optional features that add cost. | Minimizes additional charges. |
| DFM Tools | Using manufacturer's tools to identify and fix design flaws. | Reduces the risk of re-fabrication which is more time and money consuming. |
Payment Methods and Shipping Options

Selecting the appropriate payment and shipping methods is crucial for a smooth custom PCB purchasing experience. Understanding the options offered by PCB manufacturers ensures that transactions are secure and deliveries are timely, aligning with your project's timelines and financial preferences.
The following table summarizes common payment and shipping options, outlining their features and considerations to help you make informed decisions.
| Payment Method | Description | Pros | Cons | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PayPal | An online payment system allowing secure fund transfers. | Secure, widely accepted, buyer protection. | Potential fees, may require PayPal account. | Suitable for smaller transactions and when buyer protection is desired. |
| Credit Cards (Visa, Mastercard, etc.) | Standard payment method using credit cards. | Convenient, widely accepted, quick processing. | May incur processing fees, potential for fraud if not secure. | Ideal for users familiar with credit card transactions. |
| Telegraphic Transfer (TT) | Bank-to-bank transfer, often used for larger transactions. | Suitable for large amounts, traceable. | Slower processing, may incur bank fees, requires bank details. | Best for large orders or when direct bank transfers are required. |
| Western Union | Money transfer service. | Global reach, fast transfers. | Higher fees, less secure than other options. | Used when other electronic payment methods are not available. |
| Other Local Payment Methods | Various methods specific to regions or countries. | Caters to local preferences, lower transaction cost | Limited applicability to specific regions | Check for options specific to your location. |
Shipping options typically include standard, expedited, and express services. The delivery timeframe varies significantly depending on the service, destination and the manufacturer. For example, manufacturers like JLCPCB or PCBWay often provide various shipping options with detailed delivery timeframes.
Key considerations when selecting shipping method include cost, lead time, and reliability.
Quality Control and Testing of Custom PCBs
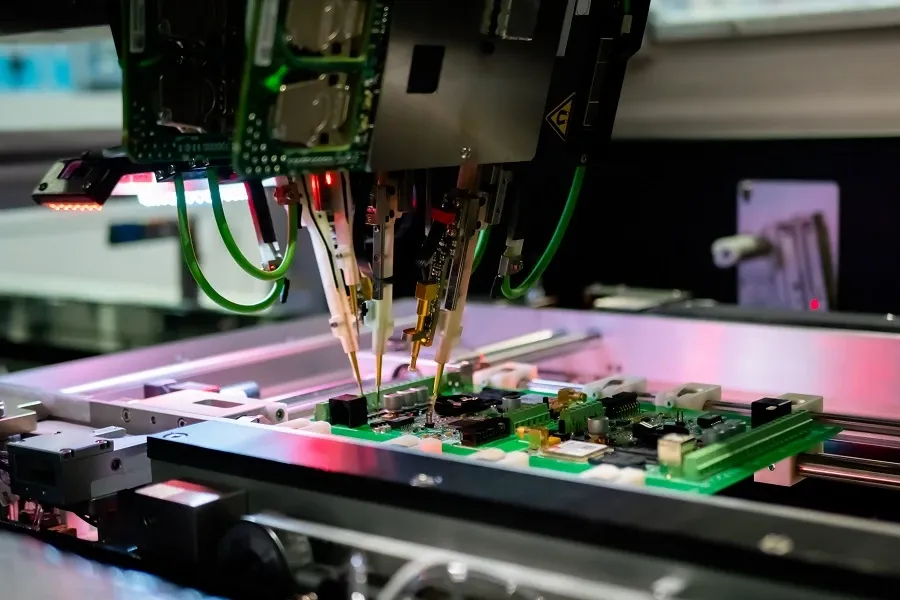
Rigorous quality control and comprehensive testing are paramount to ensuring that custom PCBs perform as intended and meet the required specifications for any application. Manufacturers implement various procedures to verify the integrity and functionality of each board, from initial production to final delivery.
- Importance of PCB Testing
PCB testing is crucial for identifying defects, ensuring circuit functionality, and validating that boards meet design specifications, thus minimizing the risk of failures and maintaining product reliability. Testing is an essential part of the manufacturing process; it can not be ignored. - Electrical Testing
This encompasses various tests such as: In-Circuit Testing (ICT) which verifies components are correctly mounted and that there is no shorts or open circuits. Flying probe testing uses probes to check for connectivity and continuity without needing special fixtures. Functional testing simulates real-world conditions to ensure the PCB functions as designed. These tests are critical in detecting manufacturing defects and ensuring proper functionality. - Visual Inspection
Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) uses high-resolution cameras to inspect for defects like misaligned components, solder bridges, or missing parts. Manual inspection with trained personnel to spot visual defects. This type of inspection is crucial to ensure that all the visual specifications are met. - Other Testing Methods
X-ray inspection can check solder joints in Ball Grid Array (BGA) packages which are difficult to inspect visually and is vital for verifying the structural integrity of these connections. Reliability testing and environmental stress testing are used to ensure the boards can withstand varying conditions such as temperature and humidity. These tests ensure the long term reliability of the boards.
Frequently Asked Questions about PCB Quality Control and Testing
- What are the primary types of tests conducted on custom PCBs?
Custom PCBs typically undergo electrical testing, including in-circuit testing (ICT) and flying probe tests, visual inspections using automated optical inspection (AOI), and sometimes X-ray inspection for complex components like BGAs. Additional tests such as functional and environmental tests may be performed to ensure the long-term reliability. - How does In-Circuit Testing (ICT) work?
ICT involves using a bed of nails fixture that aligns with specific test points on the PCB. It verifies components are correctly mounted, checks for shorts and open circuits, and tests the functionality of individual components on the assembled board. This ensures that the board was assembled as per specifications. - What defects does Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) identify?
AOI systems use high-resolution cameras to detect a wide range of defects including misaligned components, solder bridges, insufficient solder, missing components, and other surface-level anomalies. This ensures that every single PCB meets the required visual standard. - Why is X-ray inspection needed for PCBs?
X-ray inspection is crucial for inspecting solder joints under Ball Grid Array (BGA) components, which are difficult to inspect visually due to the nature of their connections. It helps to ensure that BGA solder joints are correctly formed and that there are no voids or other defects that could cause reliability issues. - What is the role of functional testing in PCB quality control?
Functional testing involves simulating real-world operating conditions to assess if the PCB performs its intended functions correctly. It verifies that the complete circuit and assembled board meets the required design specifications and performs its intended use case. - How does environmental stress testing contribute to PCB reliability?
Environmental stress testing subjects the PCB to various conditions such as high and low temperatures, humidity, and vibrations to verify the board's robustness and reliability under different environmental conditions. This test is important to ensure the PCB performs even in harsh and challenging environments.
Frequently Asked Questions About Buying Custom PCBs
Purchasing custom PCBs can be complex. This section addresses common queries to ensure a smooth process, helping you understand the nuances of file formats, lead times, design pitfalls, and quality control measures.
- What are the standard file formats required for PCB manufacturing?
The most common file format is Gerber, which contains information about each layer of your PCB design. These files are generated from your PCB design software and are crucial for manufacturers to accurately produce your board. In addition to Gerber files, manufacturers may also require drill files (Excellon format) for hole locations and a netlist for verifying connectivity. - How do lead times affect the cost of custom PCBs?
Shorter lead times typically incur higher costs due to expedited manufacturing processes and priority scheduling. Standard lead times usually offer the most cost-effective option, while extended lead times, such as those used in group buys, can reduce costs further due to optimized production scheduling. If you are flexible, it's advisable to choose longer lead times where possible to save money. - What are some common PCB design mistakes to avoid when ordering?
Several common mistakes can lead to manufacturing issues or functional failures. These include incorrect trace widths and spacing that can lead to shorts or opens, using vias that are too small for fabrication capabilities, errors in pad sizes, and insufficient clearance around components. Ensure all design rules are checked by running the Design Rule Check in your PCB layout software prior to submitting your design. - What are typical quality control processes used by PCB manufacturers?
Quality control processes usually begin with a design rule check (DRC) to ensure the design meets the manufacturer's capabilities. After fabrication, electrical testing is done to verify the board’s connectivity and identify any opens or shorts. Visual inspections are carried out for defects and flaws. Some manufactures provide impedance testing and micro sectioning to ensure quality. It is crucial to review the manufacturer's quality control methods to ensure they meet your board’s requirements. - What is the significance of panelization when buying PCBs?
Panelization refers to the process of grouping multiple PCBs onto a single production panel, which can reduce manufacturing costs for multiple boards. Panelization allows manufacturers to utilize production equipment and materials more efficiently, passing the saving on to you. If your design is small, requesting panelization can result in a lower price per PCB. - What factors should I consider when comparing PCB manufacturers?
When selecting a PCB manufacturer, consider several factors: reputation, based on reviews and industry reputation; the manufacturer's service offering including the range of PCB types they manufacture and if they offer full assembly; pricing, comparing pricing structures for small prototypes to large production runs; and lead times, to assess whether they fit your project timeline. It's also important to consider any available certifications or if the manufacturer specializes in certain types of PCBs. Lastly, look for manufacturers who provide clear communication channels with technical support, if needed. - How do different PCB materials affect the board's performance?
The material of your PCB significantly impacts performance. FR-4 is commonly used, its cost-effective and suitable for standard applications. However, for high-speed or high-frequency applications, materials like Rogers or Teflon-based laminates may be necessary due to their superior electrical properties and reduced signal loss. Therefore, carefully consider the thermal and electrical demands of your project when choosing materials.
Buying custom PCBs is a crucial step for any electronics project, be it for prototyping or full-scale production. From choosing the right manufacturer to ensuring your design is manufacturable, every detail counts. Understanding your specific needs and conducting thorough research are vital to ensuring the success of your projects. Don't hesitate to reach out for quotes, ask questions, and, once you're ready, buy custom PCB to bring your ideas to life. This will ensure your journey into electronics is both smooth and successful.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA