Choosing the Right Domestic PCB Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide
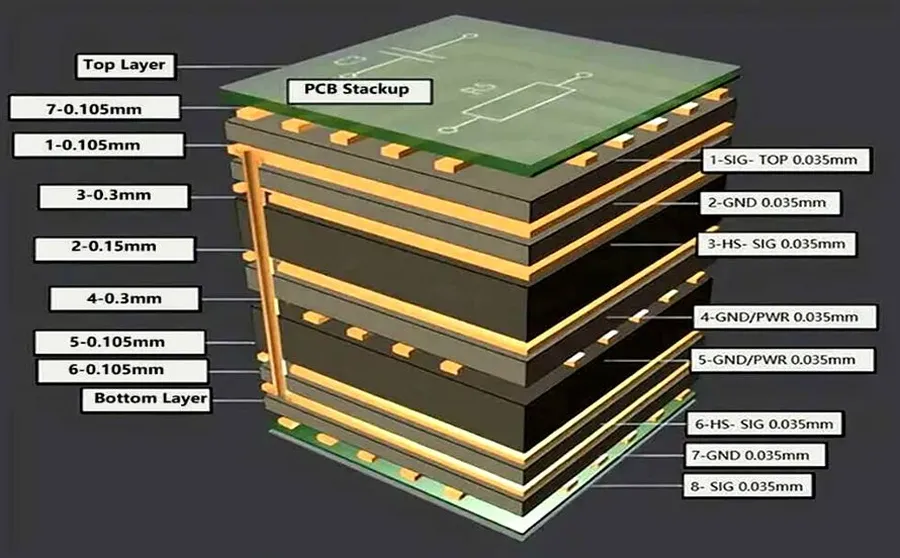
In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of nearly every electronic device. From smartphones to medical equipment, the quality and reliability of PCBs are paramount. Choosing a domestic PCB manufacturer not only supports local economies but also often ensures higher quality control and faster turnaround times. This article will delve into the crucial factors to consider when selecting a domestic PCB manufacturer, helping you make informed decisions that align with your project requirements and budget. We'll also explore some key manufacturers and their strengths, offering practical guidance for both informational and transactional users.
Understanding Your PCB Manufacturing Needs

Before embarking on a PCB manufacturing project, a thorough understanding of your specific needs is paramount. This initial step ensures the selection of a domestic PCB manufacturer that can effectively meet your requirements. Precise definition of these needs will streamline the selection process, ensuring a smoother and more efficient manufacturing experience.
- Board Complexity
Determine the number of layers required for your circuit board. Options include single-layer for simple circuits, double-layer for increased routing complexity, and multi-layer for highly complex designs. The layer count directly impacts the manufacturing process and cost. - Material Requirements
Specify the base material suitable for your PCB. Common choices include FR4 (most common and cost-effective), flex materials (for flexible circuits), and specialized materials for high-frequency applications or unique environmental conditions. The material affects electrical performance and reliability. - Surface Finish
Choose the appropriate surface finish based on your project's needs. Options range from HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) and ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) to others like Immersion Silver or Tin. This finish affects solderability, shelf life, and contact resistance. - Required Tolerances
Clearly define the dimensional tolerances required for your PCB design. These tolerances affect the precision of the manufacturing process, impacting the electrical performance and fit of the board. Tighter tolerances often increase manufacturing cost, so carefully consider the requirements.
Key Considerations When Selecting a Domestic PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the right domestic PCB manufacturer is critical for the success of any electronics project. Beyond simply finding a vendor, you need a partner whose expertise, capabilities, and operational standards align with your specific needs. This section outlines the crucial factors to evaluate when making this important decision.
- Experience and Expertise
A manufacturer's track record is a strong indicator of their ability to deliver quality PCBs. Consider the number of years they've been in operation, the types of projects they've handled, and their specialized expertise (e.g., high-speed, RF, or flexible PCBs). Deep expertise in your specific area is crucial. - Certifications and Standards
Look for manufacturers that adhere to industry standards and certifications, particularly ISO 9001 for quality management and IPC standards for PCB manufacturing. These certifications provide assurance of their commitment to quality and process control. Specifically, look for IPC-A-600 and IPC-6012 standards compliance. - Manufacturing Capabilities
Evaluate the range of services they offer. Do they specialize in prototyping, low-volume, or high-volume production? Ensure they have the technology to handle your desired board complexity (single-layer, double-layer, multi-layer), materials, and surface finishes. Also, consider if they offer in-house assembly or if that needs to be outsourced. - Lead Time
Turnaround time is often a significant factor. Inquire about their standard lead times for different types of orders and their ability to accommodate rush orders if needed. Verify their estimated shipping times and factor those into your project schedule. - Pricing Structures
Understand their pricing model. Do they charge per board, per panel, or using a different method? Are there additional fees for tooling, testing, or specific material types? Get a clear, itemized quote before making a commitment. Seek clarity on volume discounts and if those are applicable to your requirements. - Customer Support
Assess the responsiveness and helpfulness of their customer support. A dedicated point of contact can streamline communication and prevent delays. Inquire about communication channels, and their typical response times. Clear communication is key.
Prototyping vs. Production: Finding the Right Fit
The selection of a domestic PCB manufacturer hinges on whether your project necessitates prototyping or large-scale production. Prototyping is essential for initial design verification and testing, while mass production focuses on efficient replication of a finalized design. Therefore, it's critical to align a manufacturer's core competencies with your current project phase and future production volume needs.
Understanding the nuances of prototyping and mass production is essential for optimal PCB manufacturing. Each stage requires different capabilities and expertise. Selecting the right manufacturer, whether for rapid prototyping or high-volume production, is a strategic decision that affects cost, time, and overall success.
- Prototyping
Focuses on small batches, rapid turnaround, and design flexibility. It’s ideal for testing new designs and making quick modifications. Manufacturers specializing in prototyping often prioritize speed and adaptability, making them suitable for initial development phases. The emphasis is on verifying the functionality and design before moving to production. - Production
Emphasizes high-volume, cost-effective manufacturing. Here, efficiency, consistency, and economies of scale are paramount. Manufacturers adept at mass production have optimized their processes for high throughput and may have limited flexibility for design changes. This is ideal for products that are finalized and ready for large-scale manufacturing.
| Characteristic | Prototyping | Production |
|---|---|---|
| Volume | Low | High |
| Turnaround Time | Rapid | Longer |
| Design Flexibility | High | Lower |
| Cost per Unit | Higher | Lower |
| Purpose | Design Verification, Testing | Large-Scale Manufacturing |
Material Selection and Its Impact
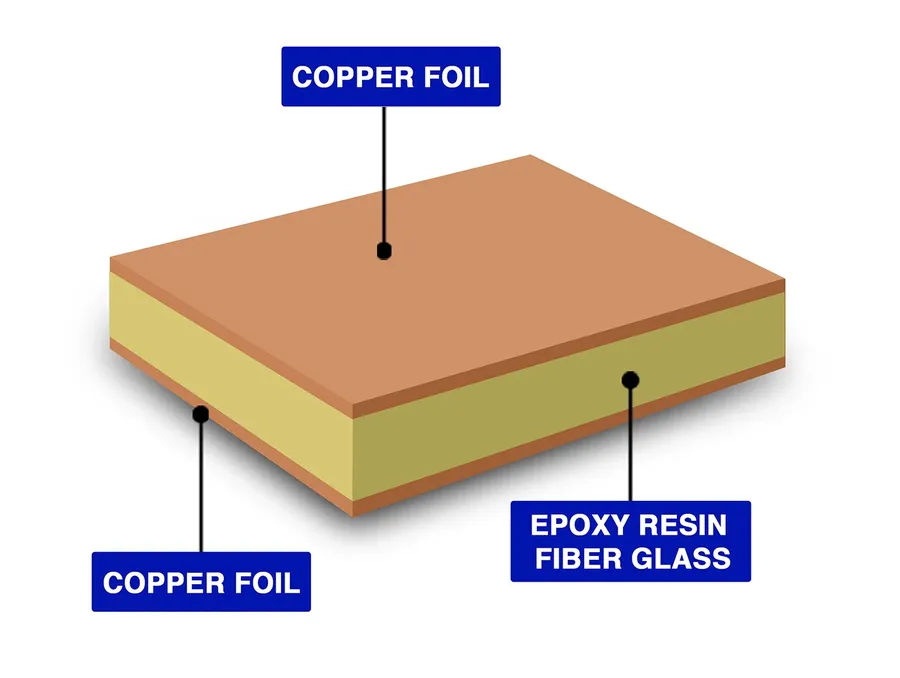
The selection of PCB material is a critical decision that significantly affects the performance, reliability, and longevity of the final product. Understanding the properties of various materials is crucial for aligning design requirements with manufacturing capabilities, ensuring optimal board functionality and suitability for its intended application. This choice extends beyond simple cost considerations and directly impacts signal integrity, thermal management, and mechanical robustness.
| Material | Description | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | Most common PCB material; a glass-reinforced epoxy laminate. | General electronics, consumer products. | Cost-effective, good mechanical and electrical properties, widely available. | Limited thermal conductivity, not suitable for high-frequency applications, can be brittle. |
| Polyimide | High-performance polymer offering excellent thermal and chemical resistance. | Aerospace, medical devices, high-temperature applications. | High thermal resistance, flexible, excellent chemical resistance. | More expensive than FR-4, can be more difficult to process. |
| Metal Core (Aluminum/Copper) | A metal base (typically aluminum or copper) bonded to a dielectric layer. | LED lighting, power electronics, thermal management applications. | Excellent thermal conductivity, good mechanical strength. | Higher cost, can be heavier than FR-4, requires specific manufacturing processes. |
| Rogers Materials | Specialty PTFE-based laminates. | RF/Microwave applications, high-frequency circuits. | Excellent high-frequency performance, low signal loss, stable dielectric constant. | High cost, requires specialized manufacturing, sensitive to processing conditions. |
| Flex PCB Materials (Polyimide, Polyester) | Flexible substrates that can be bent and folded. | Wearable electronics, automotive applications, small spaces. | Flexible, lightweight, space-saving. | Higher cost, specialized manufacturing, can have limited mechanical stability. |
Exploring Domestic PCB Manufacturer Capabilities and Technologies

A thorough evaluation of a domestic PCB manufacturer's capabilities and technologies is paramount to ensuring they can meet the specific demands of your project. This involves not only assessing their existing equipment and processes but also their ability to handle the complexity and technological requirements of your circuit board design. Understanding the types of advanced technologies they offer will help determine if they are the right fit for your needs.
- High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs
HDI PCBs feature finer lines and spacing, microvias, and higher layer counts, allowing for more compact designs and increased functionality. Evaluate if the manufacturer has experience and equipment for HDI processing if your design demands it. - Heavy Copper PCBs
These PCBs use thicker copper layers, enhancing their ability to carry high current and improve thermal management. Heavy copper PCBs are essential in power electronics. Verify that the manufacturer has the specialized plating and etching processes for this technology. - Radio Frequency (RF) and Microwave PCBs
RF/Microwave boards require specific materials and manufacturing techniques to minimize signal loss and maintain signal integrity at high frequencies. Confirm the manufacturer's expertise in fabricating these specialized PCBs. - Flex and Rigid-Flex PCBs
Flex and rigid-flex PCBs can be bent and folded to fit in unique form factors, providing greater design flexibility. Check if the manufacturer has the capability to handle flexible materials and complex layering for flex and rigid-flex designs. - Specialized Surface Finishes
Different finishes like ENIG, HASL, or Immersion Silver have varying electrical and mechanical properties. Ensure the manufacturer can provide the finish suitable for your application. - Advanced Drilling and Routing
Look for manufacturers with precision drilling and routing capabilities to handle fine features and complex board shapes to ensure your design requirements are accurately met.
When choosing a domestic PCB manufacturer, consider not only the types of advanced technologies they offer, but also their quality control processes related to these advanced technologies. Confirm if they have the necessary testing equipment and processes in place to ensure your PCBs meet the desired quality requirements. This includes but not limited to electrical testing, impedance control measurements and dimensional accuracy checks.
Domestic PCB Manufacturer Comparison: Key Players

Selecting the right domestic PCB manufacturer involves careful evaluation of their capabilities and alignment with your project needs. While specific endorsements are not provided, this section presents a comparison of hypothetical manufacturers based on key factors to illustrate the typical landscape. This comparison should serve as a starting point for more detailed research of individual manufacturers.
| Manufacturer Name | Specialization | Technology Focus | Lead Time | Minimum Order | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Manufacturer A | Prototyping | High-speed | 3-5 days | 5 pieces | Development, Testing |
| Manufacturer B | Mid-Volume | Flex PCBs | 10-15 days | 100 pieces | Aerospace, Medical |
| Manufacturer C | High-Volume | Heavy Copper | 20-30 days | 1000+ pieces | Industrial, Automotive |
This table highlights the diverse landscape of PCB manufacturers. Note that the lead times, minimum order quantities, and specializations are indicative and can vary significantly between real-world manufacturers. It is imperative to verify specific capabilities, certifications (like ISO 9001 and IPC standards), and pricing with each manufacturer to ascertain their fitness for your project.
Frequently Asked Questions About Domestic PCB Manufacturing
This section addresses common questions regarding domestic PCB manufacturing, providing clarity on factors influencing pricing, selection criteria, typical lead times, quality control standards, design file requirements, minimum order quantities (MOQ), and payment terms.
- What factors influence the cost of PCB manufacturing?
PCB cost is determined by several factors including board complexity (number of layers, via count, trace width), material selection (FR4, flex, etc.), surface finish (ENIG, HASL, etc.), quantity ordered, lead time requirements, and any special processing needs like impedance control or blind/buried vias. The manufacturing process complexity directly correlates with the cost. Larger quantities and less strict deadlines reduce per-unit costs due to economies of scale and better resource allocation. - How do I choose the best domestic PCB manufacturer for my project?
Selecting the right manufacturer involves matching your project requirements with the manufacturer's capabilities. Consider their experience, certifications (ISO 9001, IPC standards), technology focus (e.g., HDI, flex, RF), capacity (prototype, mid-volume, mass production), lead times, pricing structure, and customer support. It is vital to ensure that the manufacturer can handle your specific needs in terms of board complexity, materials, and tolerances, and that the company's values align with your long-term vision. Request samples and conduct thorough reviews to verify quality before committing to production. - What are typical turnaround times for PCB manufacturing?
Turnaround times vary depending on the complexity of the board, the manufacturer's workload, and the required lead time option. Prototyping can take as little as a few days to a week, while standard production runs can range from one to several weeks. Expedited services are often available at a premium for faster turnaround when necessary. A detailed discussion about timelines during your quotation process can help you choose the right company for your specific needs. - What quality control standards should I expect from a manufacturer?
Reputable manufacturers adhere to IPC standards (like IPC-A-600 for acceptability) and often have ISO 9001 certification. They conduct rigorous quality checks throughout the manufacturing process, including visual inspection, electrical testing (e.g., flying probe, bed of nails), and impedance testing, when required. They also have well-defined procedures for handling defects and ensuring that boards meet the design specifications. The level of testing should always be confirmed during the quoting phase and should meet your testing requirements. - What design files are required to submit to a PCB manufacturer?
Typically, manufacturers require Gerber files (RS-274X or X2 format), along with an Excellon drill file and any other files relating to the board stackup details, netlist, and assembly drawings (if needed). Ensure that all layers are correctly named, the drill files are in the correct format, and the board outline is clearly defined and closed. Also clarify if they have software or version preferences, or use a specific CAD software. - What are typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and payment terms?
MOQs vary depending on the manufacturer and the board complexity. Some may offer low MOQs for prototypes (e.g., 5-10 pieces), while others require higher minimums for production runs (100+). Payment terms typically involve an upfront deposit (often 50%) before production, with the remaining balance due upon completion or shipment. Payment terms are often tailored to each specific project, and is important to discuss this in the quotation process. Payment schedules can also be impacted by your credit and relationship with the manufacturing company. - How does material selection affect the PCB's performance and price?
The material used in a PCB impacts its electrical performance, thermal properties, and cost. FR4 is a standard material suitable for most applications, while materials like polyimide are used for flex boards and high-temperature applications. Higher performance materials, such as those with higher dielectric constants or better thermal conductivity, generally have increased costs. Therefore, the choice of material is an important tradeoff between cost and performance requirements.
Cost Analysis and Budgeting for Domestic PCB Manufacturing
Accurate cost analysis and budgeting are crucial for successful PCB manufacturing. Moving beyond the per-unit cost, a thorough evaluation must include all associated expenses to achieve a realistic estimate. This approach ensures you avoid financial surprises and select the best-suited domestic PCB manufacturer for your needs.
- Fabrication Costs
This is the base cost for manufacturing the bare PCB, including material and production. It is typically determined by board size, layer count, and material selection. More complex designs will increase the fabrication costs. - Assembly Costs
If assembly services are also required, factor in the cost of component placement, soldering, and testing. Assembly costs are influenced by the number of components, their package types, and the complexity of the assembly process (e.g., surface mount vs. through-hole). - Tooling Costs
Tooling may include setup costs for specific manufacturing processes like panelization, solder paste stencils, and custom fixtures. These costs tend to be fixed, so they can be amortized over larger production runs. This cost is highly dependent on the specific requirements of the board. - Additional Fees
Be aware of potential additional fees such as testing costs (e.g., flying probe tests, in-circuit tests), shipping costs, and expedited service fees. It's best to get all of these costs in writing and clearly defined before agreeing to production. - Payment Schedule
Payment terms should be carefully considered, some manufacturers require full or partial payment upfront, others may offer net terms. Understanding the payment schedule enables accurate cash flow forecasting and helps to avoid delays caused by lack of upfront funds.
It is critical to note that the overall cost is affected by several factors, including order quantities, material types, and lead times. Higher quantities usually lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Premium materials will increase the board cost, and expedited lead times might incur additional fees. Therefore, a balanced view considering all factors is essential for cost-effective PCB manufacturing.
Ensuring Quality and Reliability in PCB Manufacturing
Quality and reliability are paramount in PCB manufacturing, directly impacting the performance and longevity of electronic devices. Rigorous quality assurance measures are necessary to minimize defects, ensure consistent performance, and ultimately avoid costly failures. When selecting a domestic PCB manufacturer, a thorough evaluation of their quality control processes is essential to safeguard your investment.
- Importance of Quality Assurance
Quality assurance ensures that PCBs meet specified performance requirements and that defects are minimized, reducing the risk of product failures. It encompasses all stages of production, from raw material inspection to final product testing. - Key Quality Control Checks
Manufacturers should perform regular inspections, such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) to detect surface defects, and electrical testing to confirm circuit functionality, during the production process. - Testing Procedures
Thorough testing, including in-circuit testing (ICT), flying probe testing, and functional testing, are crucial to validating the performance of the manufactured PCBs. - Industry Certifications
Certifications like ISO 9001 demonstrate a manufacturer's commitment to quality management. Compliance with IPC standards ensures adherence to industry best practices for PCB manufacturing. - Traceability
A robust traceability system is critical, as it allows for tracking of individual boards through the production and delivery process, and allows for root cause analysis in the event of failure, further enhancing quality.
| Quality Control Measure | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Uses cameras to visually scan the PCB for defects like shorts, opens, and missing components | Ensures accurate pattern transfer and defect detection early in the process |
| Electrical Testing | Checks the electrical connectivity and functionality of the circuits | Verifies that the circuit design is properly implemented and functional |
| In-Circuit Testing (ICT) | Tests individual components and their connections on the board. | Detects component-level issues and solder joint problems |
| Flying Probe Testing | Uses moving probes to test different points on the PCB | Flexible and efficient for testing prototypes and low-volume production |
| Functional Testing | Verifies if the PCB operates as intended in its end application | Assesses overall PCB functionality |
Building a Strong Partnership with Your Domestic PCB Manufacturer
A robust partnership with your chosen domestic PCB manufacturer is paramount for consistent success and streamlined production. This collaborative relationship, built on mutual understanding and effective communication, ensures that your project's specific needs are met efficiently and accurately from design to delivery.
- Establish Clear Communication Channels
Designate specific points of contact on both sides to streamline discussions and promptly address any queries or concerns. This ensures that information flows seamlessly and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings. - Share Detailed Design Specifications
Provide manufacturers with comprehensive design files, including Gerber files, BOM (Bill of Materials), and assembly drawings. Accuracy and completeness here minimize delays and errors during the manufacturing process. - Regularly Communicate Feedback and Project Changes
Maintain an open dialogue throughout the project, providing timely updates on any modifications or issues. This proactive approach enables the manufacturer to adjust accordingly and prevents costly rework. - Foster a Collaborative Environment
View the manufacturer as a vital partner, not just a vendor. Encourage collaboration in problem-solving and process optimization. This synergistic approach leads to more efficient and cost-effective outcomes. Sharing project goals and expectations will create a shared objective between your team and the manufacturer. - Understand the Manufacturer's Capabilities and Constraints
Familiarize yourself with the manufacturer's expertise and limitations. A deeper understanding of their processes allows you to design your PCBs with manufacturability in mind, preventing delays due to design-related issues. This also allows you to select a manufacturer that is the most suitable.
Choosing the right domestic PCB manufacturer is a critical decision that can impact the success of your electronics project. By carefully assessing your needs, researching potential manufacturers, considering cost, and focusing on quality, you can find a partner that meets your needs and enables you to create a high quality and reliable product. Domestic PCB manufacturers offer a variety of capabilities and it is critical to find one that meets your specific needs. By following the steps in this guide, you will find the right PCB manufacturer for your project.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA