Choosing the Right LED Bulb PCB Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide
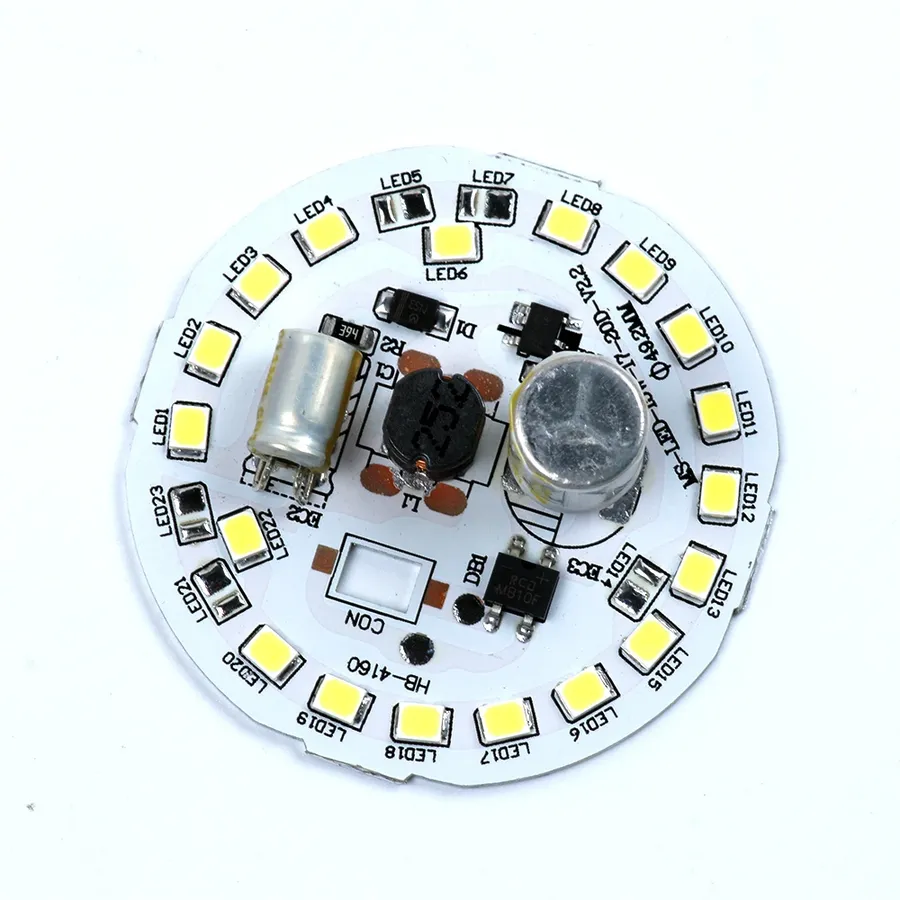
In our modern world, LED bulbs have become indispensable for lighting homes, businesses, and streets, and the key component enabling this revolution is the LED bulb PCB. Choosing the right LED bulb PCB manufacturer is crucial for the performance and reliability of these ubiquitous lights. This article will guide you through the intricacies of selecting a suitable manufacturer, covering essential aspects from design considerations to quality checks.
Understanding the Importance of a Quality LED Bulb PCB

The Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is the foundational element of an LED bulb, serving as the mechanical base and electrical pathway for all components. A high-quality PCB is not merely a structural component; it is critical to achieving optimal light performance, efficient heat dissipation, and the overall longevity of the LED bulb. Compromising on PCB quality can lead to significant issues, such as reduced lifespan, inconsistent light output, and premature failure.
A well-designed and manufactured PCB ensures that LEDs receive the precise electrical current and voltage required for optimal operation. Poor PCB design or manufacturing defects can cause uneven current distribution, leading to some LEDs being underdriven while others are overdriven. This discrepancy results in variations in light intensity and color temperature, ultimately impacting the overall performance of the LED bulb. Moreover, a substandard PCB can impede heat dissipation, causing overheating, which significantly reduces the lifespan of LEDs.
Furthermore, the material composition of the PCB directly affects its thermal conductivity and resistance to environmental stressors. High-quality PCBs use materials with excellent thermal properties, allowing heat generated by the LEDs to be efficiently transferred away, preventing overheating and ensuring the stable operation of the bulb. The selection of appropriate substrate materials (e.g., aluminum, FR-4) and the correct copper thickness are essential factors in ensuring robust performance over time, contributing significantly to the reliability and longevity of the final product.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing an LED PCB Manufacturer

Selecting the right LED PCB manufacturer is crucial for ensuring the quality, reliability, and performance of your LED lighting products. Several key factors should be meticulously evaluated to make an informed decision. These factors encompass not only the manufacturer's capabilities but also their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- Manufacturing Experience and Expertise
A manufacturer's track record and experience in producing LED PCBs are paramount. Assess their portfolio, focusing on the complexity and scale of projects they've handled. Years of experience often translate to a deeper understanding of best practices and potential issues, allowing them to anticipate problems and provide effective solutions. - Technological Capabilities
Evaluate the technology and equipment used by the manufacturer. Modern, automated machinery and advanced techniques in PCB fabrication result in higher precision, quality, and throughput. Look for manufacturers that offer a range of technologies to meet diverse project needs, from standard single-layer PCBs to advanced multi-layer boards. - Certifications and Standards Compliance
Ensure the manufacturer adheres to industry-recognized certifications and standards, such as ISO 9001 for quality management and UL certifications for safety. These certifications serve as evidence of the manufacturer’s commitment to producing reliable, safe, and high-quality PCBs. Compliance with environmental standards, like RoHS, is also critical. - Material Selection and Quality
The materials used in the construction of PCBs directly impact their durability and thermal performance. A manufacturer should have stringent material quality control processes and offer a variety of options that meet the specific needs of the intended LED application. Factors to consider are substrate material (e.g., FR-4, aluminum), copper thickness, and surface finishes. - Design and Engineering Support
A manufacturer that offers robust design and engineering support can make a big difference in the success of a project. This includes assistance with PCB layout, design-for-manufacturability (DFM) analysis, and guidance on material selection. Effective design support can prevent costly errors and reduce development time. - Quality Control Processes
Detailed quality control processes are critical for ensuring the reliability of PCBs. A good manufacturer will employ several testing methods, including automated optical inspection (AOI), electrical testing, and functional testing. Transparency and comprehensive quality reporting provide additional assurance. - Customer Service and Communication
Clear communication and responsive customer support is paramount. Evaluate a manufacturer's responsiveness to questions, problem-solving capabilities, and their ability to provide regular updates on order status. Strong customer service facilitates a smooth and efficient working relationship.
Types of LED PCBs Offered by Manufacturers
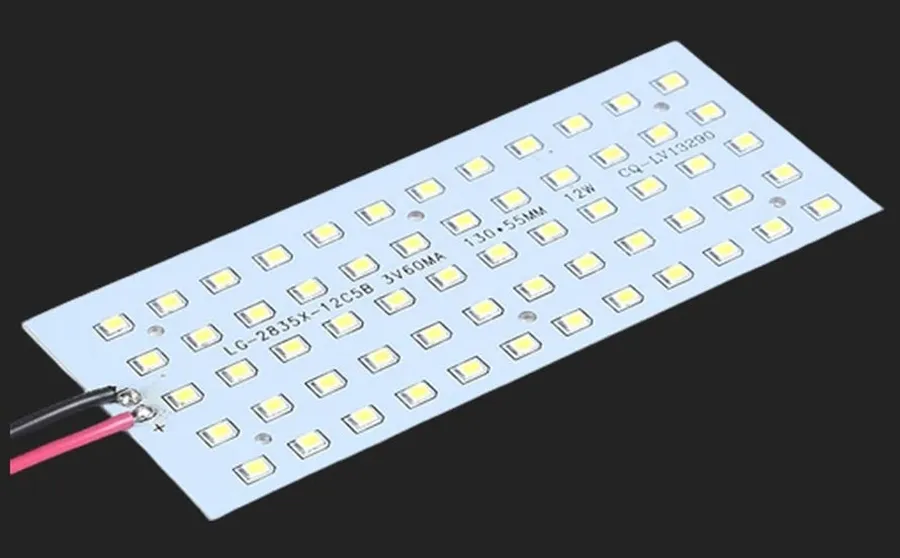
The selection of Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs) for LED bulbs is diverse, each type offering specific advantages and catering to different application needs. Manufacturers provide a range of PCB options, including single-sided, double-sided, multi-layer, aluminum-based, and flexible PCBs, each distinguished by its construction, performance, and cost.
| PCB Type | Description | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided PCB | Copper traces on one side of the board, simplest and least expensive PCB type. | Simple LED lighting fixtures, low-power indicator lights. | Cost-effective, easy to manufacture. | Limited circuit complexity and heat dissipation. |
| Double-Sided PCB | Copper traces on both sides of the board with vias connecting the layers. | Standard LED bulbs, moderately complex lighting systems. | Increased circuit density, better routing flexibility. | More expensive than single-sided PCBs. |
| Multi-Layer PCB | Three or more layers of copper traces, bonded together. | High-density LED arrays, advanced lighting control systems. | Very high circuit density, excellent heat dissipation potential. | Most complex and expensive to manufacture. |
| Aluminum-Based PCB | Dielectric layer on an aluminum substrate, designed for enhanced thermal management. | High-power LED lighting, applications requiring efficient heat dissipation. | Excellent heat dissipation, increased lifespan of LEDs. | Higher cost than standard PCBs, may be heavier. |
| Flexible PCB | Flexible substrate, can be bent into complex shapes, commonly made with polyimide or polyester. | Specialized lighting applications, curved or irregular lighting surfaces. | Flexibility in design, lightweight. | Less robust than rigid PCBs, more expensive for complex designs. |
Custom LED PCB Design and Manufacturing
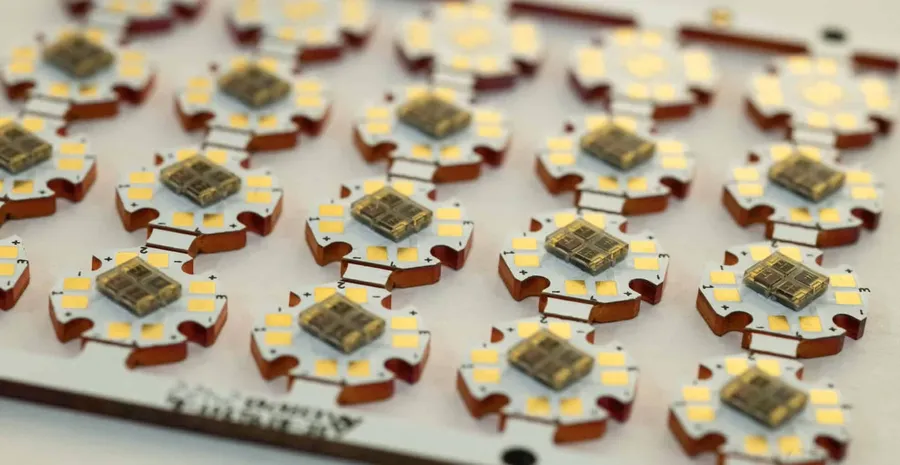
Custom LED PCB design and manufacturing involves tailoring a printed circuit board to meet the specific requirements of an LED lighting application. This process goes beyond off-the-shelf solutions, offering optimized performance, unique form factors, and specific features that can enhance a product's competitiveness and functionality.
When initiating a custom LED PCB project, consider the following aspects:
- Design Requirements
Defining precise design parameters including board dimensions, layer count, component placement, thermal management needs, electrical performance characteristics, and any special mechanical specifications. Detailed specifications are critical in the initial stage to reduce the likelihood of costly design changes during production. - CAD File Compatibility
Ensuring that your design files, usually in formats like Gerber, ODB++, or IPC-2581, are compatible with the manufacturer's systems. Adhering to standard file formats minimizes interpretation errors, and the use of proper design for manufacturing (DFM) principles is paramount during the design phase to avoid issues in production. - Customization Options
Exploring available options for material selection such as substrate type (e.g., FR-4, aluminum, flexible substrate), copper thickness, solder mask colors, surface finishes, and other tailored requirements that match the performance and longevity requirements of the LED product. - Prototyping
Requesting a prototype run, which allows for validation of the custom PCB design and the ability to test under the targeted environmental conditions to verify heat dissipation, circuit functionality, and mechanical stability. This prototyping phase is vital before mass production to iron out unforeseen issues. - Component Selection
Selecting the right components like LEDs, resistors, and connectors that align with your performance expectations and sourcing them from reliable vendors to prevent issues arising from substandard materials. The choice of components will impact overall performance, reliability, and lifespan of the PCB.
A close collaboration with the chosen LED bulb PCB manufacturer is vital. This engagement enables the smooth translation of design requirements into a tangible product that satisfies specific application demands.
Materials and Technologies Used in LED PCBs
The performance and longevity of LED PCBs are critically dependent on the materials and technologies employed in their construction. This section delves into the key components, including the substrate, copper layers, and surface finish, and how each affects the thermal management, durability, and overall reliability of the PCB.
The selection of appropriate materials and technologies during PCB manufacturing is crucial for ensuring optimal performance in LED lighting applications. These components not only impact the functionality of the LED bulb but also its lifespan and efficiency. By understanding the intricate relationships between these materials, engineers can design LED lighting solutions that are both reliable and cost effective.
| Component | Material/Technology | Impact on LED PCB Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Substrate | FR-4 (Fiberglass Reinforced Epoxy), Aluminum, Ceramic | Impacts thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and cost; Aluminum or ceramic substrates are superior for thermal dissipation compared to FR-4. |
| Copper Layer | Varying thicknesses, typically 1oz to 3oz per square foot | Determines current carrying capacity and heat dissipation; thicker copper provides better heat dissipation and lower resistance, but increases cost. |
| Surface Finish | HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), Immersion Tin, OSP (Organic Solderability Preservative) | Protects copper from oxidation and ensures good solderability, ENIG offers superior solderability and corrosion resistance compared to HASL but is more expensive. |
| Solder Mask | Epoxy based resin | Protects the copper layer from oxidation, solder bridging, and environmental contaminants. Choose the correct color based on need. |
| Dielectric Material | Epoxy resin, polyimide, or other materials based on the substrate material | Determines the insulation properties between layers, dielectric strength, and impacts thermal properties. |
Quality Control and Testing Procedures for LED Bulb PCBs
Rigorous quality control and testing procedures are essential in LED bulb PCB manufacturing to ensure reliability, performance, and longevity of the final product. These processes identify and rectify potential defects before PCBs are integrated into LED bulbs.
Effective quality control encompasses several stages, from material inspection to final product testing. These stages are designed to catch errors early in the production process, reducing the risk of costly failures in the field.
- Incoming Material Inspection
Verification of raw materials such as substrate, copper foil, and solder resist for compliance with specifications before manufacturing. - Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
AOI is a critical step involving cameras that scan the PCB for defects like missing components, incorrect placement, or solder joint issues. AOI can detect defects that are easily missed by human inspection, leading to higher quality PCBs. - Electrical Testing
Electrical testing includes in-circuit testing (ICT) and functional testing to verify the electrical performance of the PCB. This includes testing for shorts, opens, and continuity, ensuring the PCB meets the required electrical standards. - X-ray Inspection
Used for multi-layer PCBs or those with complex designs, X-ray inspection can reveal hidden defects like voids in solder joints or misalignments in the internal layers. - Environmental Stress Testing
Testing PCBs under extreme environmental conditions, including temperature and humidity variations, to check their durability and reliability in adverse conditions. - Final Visual Inspection
A final manual visual check for any physical defects that may have been missed by the automated systems. This is the last line of defense before PCBs are cleared for assembly into LED bulbs.
Frequently Asked Questions about LED Bulb PCBs
This section addresses common questions regarding LED bulb PCBs, providing clear and concise answers to help clarify the role, manufacturing, and sourcing of these essential components in LED lighting.
- What exactly is a PCB in an LED bulb?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) in an LED bulb is a substrate that provides mechanical support and electrical connections for the LED chips and other electronic components. It serves as the foundation for the LED lighting system, facilitating power delivery and heat dissipation. - Who are the major manufacturers of LED bulb PCBs?
While the specific manufacturer can vary, major PCB manufacturers often have divisions or subsidiaries specializing in LED lighting applications. The industry leaders often include companies that have a wide range of production capabilities and can produce high volumes of quality PCBs and also the best customer service. Many are located in China, but manufacturers are also found in other countries, such as the USA, South Korea and Germany. Identifying specific manufacturers would require a separate market research and is subject to change. - How do I locate the biggest PCB suppliers for LED applications?
Finding the biggest PCB supplier involves looking at metrics like production volume, revenue, and global reach. You would need to research the leading companies through industry reports, financial databases, and trade publications. Large distributors who source from the major manufacturers can also provide information. Focus on suppliers with a strong presence in the LED lighting sector. - What kind of PCB is best for LED bulbs?
The ideal PCB for an LED bulb depends on several factors including the bulb's power rating, size, and application. Aluminum-backed PCBs are often preferred for their excellent heat dissipation capabilities. Double-sided or multi-layer PCBs can also be used, depending on the circuit complexity. The best type of PCB is often a balance of performance, cost, and manufacturing efficiency. - Can I get a custom-designed LED PCB for my specific bulb?
Yes, many manufacturers offer custom design services. This process usually involves submitting detailed design specifications, including dimensions, component placement, and electrical requirements. Manufacturers will then create prototypes, before proceeding with the volume order. Ensure you provide all design details including gerber files, layer stacks, drill data, copper thickness requirements and BOM. - How important is thermal management in LED PCB design?
Thermal management is critical. LEDs generate heat, and inadequate heat dissipation can lead to reduced light output, color shift, and premature failure. PCB design must incorporate materials and design strategies to effectively draw heat away from the LEDs, such as metal core substrates, thermal vias, and heat sinks. - What certifications should a LED PCB manufacturer have?
A reliable manufacturer will have certifications such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and IPC standards. These certifications ensure adherence to quality and environmental standards. Other specific certifications can vary based on geographic location and customer requirements.
Comparative Analysis: Global vs. Local LED PCB Manufacturers

Selecting the right LED PCB manufacturer is critical, and the decision often involves weighing the benefits of global versus local suppliers. Each option presents distinct advantages and disadvantages regarding cost, turnaround time, quality, and communication. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision that aligns with your project's specific needs and constraints.
| Factor | Global Manufacturer | Local Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Generally lower due to economies of scale and lower labor costs. | Generally higher due to higher labor and operating expenses. |
| Turnaround Time | Potentially longer lead times due to shipping and customs processes. | Faster turnaround times due to proximity and simplified logistics. |
| Quality Control | May vary; requires thorough vetting and clear communication protocols. | Potentially easier to audit and monitor quality with closer access. |
| Communication | Can be challenging due to language barriers and time zone differences. | Generally easier due to shared language and time zone. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | Often higher, suitable for large production runs. | Potentially lower MOQ, suitable for small to medium projects. |
| Logistics and Shipping | Involves international shipping, customs clearance and potentially higher costs. | Simpler, faster and less expensive shipping and logistics. |
| Intellectual Property Protection | May require stronger legal framework to protect IP rights. | Generally easier to manage and enforce IP protection. |
| Support & Flexibility | Less flexible on design changes, and communication can be slow. | More flexibility on custom design and fast communication & support. |
Cost Optimization Strategies with Your LED PCB Manufacturer
Optimizing costs when working with an LED PCB manufacturer involves strategic planning and a deep understanding of the manufacturing process. Implementing effective cost optimization techniques can significantly reduce expenses without compromising the quality and performance of the final LED bulb product. These strategies range from initial design considerations to volume negotiations and material selection.
Here are some key strategies to consider:
- Design for Manufacturing (DFM)
Implementing DFM principles from the outset of the PCB design process is paramount. This includes considerations such as standardizing component sizes, minimizing the number of layers, optimizing panel utilization to reduce waste, and ensuring adequate spacing for manufacturability. Identifying and addressing potential manufacturing challenges early in the design phase can drastically reduce production costs and time. DFM analysis can significantly decrease the risk of production delays, material wastage, and defects. This leads to cost savings by avoiding rework and higher yields. - Material Selection
Careful material selection can significantly impact cost. For instance, opting for standard substrate materials over specialized ones can be a cost-effective approach. It is crucial to balance performance requirements with cost. Furthermore, exploring alternative materials that meet the electrical and thermal needs of the LED bulb without excessive performance margins could further reduce costs without sacrificing quality or longevity. - Negotiating Order Volumes
Engage with the manufacturer to explore volume-based pricing structures. Larger production runs generally reduce the per-unit cost due to economies of scale. Negotiating favorable payment terms and delivery schedules also can help manage costs effectively, ensuring a balance between production needs and cash flow. Forecasting accurate production needs can ensure that neither unnecessary stock nor production delays are incurred, therefore reducing overall operational costs. Long-term planning and consistent orders can allow manufacturers to amortize fixed costs over larger production volumes which often results in lower pricing. - Utilize Standard Components
Opting for standard, off-the-shelf components over custom-designed ones can often reduce both the material and manufacturing costs. Standard parts are typically less expensive and have shorter lead times, helping to decrease production costs. This standardization also streamlines assembly and reduces the likelihood of errors. - Panelization Strategy
Optimize panelization (arranging multiple PCBs on a single production panel) to minimize waste and maximize material utilization. Efficient panelization reduces material consumption per PCB, reducing the overall manufacturing cost. Careful analysis of board size and shape can make sure no excess materials are unnecessarily used which in turn will lower costs per unit. - Regularly Review and Audit
Conduct regular reviews of your manufacturing process and costs with your chosen manufacturer. Auditing practices ensure you are getting the best possible price. By continuously examining the production methods and identifying areas for improvement, further cost optimizations can be identified.
Future Trends and Innovations in LED Bulb PCB Manufacturing

The LED bulb PCB manufacturing industry is in constant evolution, driven by the demand for more efficient, reliable, and cost-effective lighting solutions. Future trends are centered around advancements in materials, designs, and manufacturing processes that aim to improve thermal management, reduce energy consumption, and enhance the overall performance of LED bulbs.
- Advanced Substrate Materials
The development of new substrate materials with higher thermal conductivity and lower dielectric constants is crucial for improving heat dissipation and reducing signal loss. Materials like ceramic composites and advanced polymers are being explored as alternatives to traditional FR-4. - Integrated Circuit (IC) Embedding
Embedding ICs directly into the PCB substrate, also known as embedded die technology, offers benefits such as miniaturization, improved thermal performance, and reduced electromagnetic interference. This approach is gaining traction for complex LED driver circuits. - Flexible and Stretchable PCBs
Flexible and stretchable PCBs are enabling the development of LED lighting for curved and unconventional surfaces. These designs can be incorporated into various applications, offering design freedom and flexibility for LED lighting. - Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
The adoption of additive manufacturing techniques for PCB fabrication is allowing for more complex and customized designs, which can reduce waste and the cost of rapid prototyping. Direct digital fabrication can also enable faster turnaround times for LED PCB designs. - Miniaturization and High-Density Interconnect (HDI)
Ongoing miniaturization efforts are leading to higher component densities on PCBs, enabling smaller and more compact LED bulb designs. HDI technologies play an important role in achieving these higher densities. - Smart PCBs with Integrated Sensors
Integrating sensors directly into the PCB allows for intelligent lighting control and monitoring, enabling features such as adaptive brightness, color temperature adjustment, and predictive maintenance of LED bulbs.
Selecting the right LED bulb PCB manufacturer is a critical decision for the success of any lighting product. By understanding the key factors discussed, from design to quality, you can confidently choose an LED bulb PCB manufacturer to ensure your products' performance, reliability, and longevity. Remember that the choice of manufacturer directly affects the quality and reliability of the final product. As the industry continues to innovate, staying informed about the latest advancements in LED PCB technology is crucial. Partnering with a trusted and experienced LED bulb PCB manufacturer will pave the way for success in this ever-evolving market.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA