Choosing the Right OEM Circuit Board Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide

In today's technology-driven world, circuit boards are the unsung heroes powering nearly every electronic device we use. For businesses looking to bring their innovative products to life, choosing the right OEM circuit board manufacturer is a critical decision. This article will explore the vital aspects of selecting a reliable partner, highlighting the different types of circuit boards, manufacturing processes, and key considerations to ensure your product's success, and how an experienced oem circuit board manufacturer can make all the difference.
Understanding OEM Circuit Boards

OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) circuit boards are custom-designed and manufactured PCBs (Printed Circuit Boards) tailored to a specific product or device, playing a crucial role in modern electronics manufacturing. Unlike standard or off-the-shelf PCBs, OEM boards are designed to meet the unique requirements of a particular application, ensuring optimal performance and integration.
The critical distinction between OEM and standard PCBs lies in their purpose and customization. Standard PCBs are general-purpose boards, while OEM PCBs are precisely engineered for a single product or a family of products, offering advantages such as specific form factors, component layouts, and performance characteristics.
Selecting an OEM circuit board manufacturer is crucial for companies seeking differentiated products with specific performance and integration requirements. This approach avoids the limitations of standard boards and leads to improved product efficiency, reliability, and optimized size and form factor for a given application. Ultimately, OEM circuit boards enable greater control over product development and contribute to a superior final product.
Types of Circuit Boards Offered by OEM Manufacturers
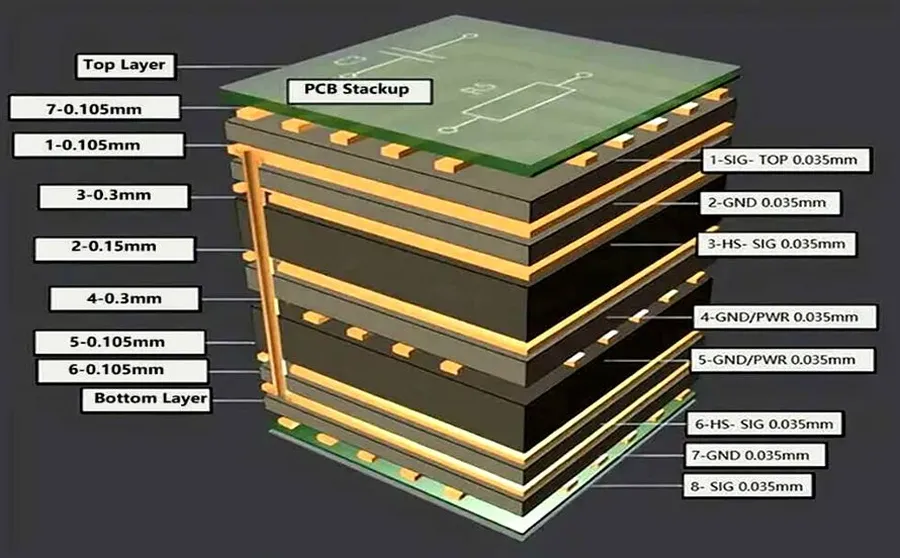
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) circuit board manufacturers offer a diverse range of PCBs tailored to specific application needs. These boards vary significantly in complexity, materials, and construction, allowing for precise customization in electronic product design. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the right board for your project, optimizing performance and cost-effectiveness.
| PCB Type | Description | Typical Applications | Advantages | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Layer PCB | Simplest type with conductive layer on one side. | Basic electronics, simple devices, LEDs. | Cost-effective, easy to manufacture. | Limited functionality, not suitable for complex circuits. |
| Double-Layer PCB | Conductive layers on both sides, allowing for more complex interconnections. | Power supplies, control circuits, audio equipment. | Increased circuit density, better for medium complexity designs. | More expensive than single-layer, but more versatile. |
| Multi-Layer PCB | Three or more layers of conductive material, interconnected with vias. | High-speed digital electronics, communication devices, computers. | High density, high complexity, improved performance. | Most expensive, requires more precise manufacturing process. |
| Rigid PCB | Made with a solid, inflexible substrate. | Most electronic devices, computers, consumer electronics. | Durable, reliable, cost-effective for many applications. | Not flexible, not suitable for dynamic mechanical designs. |
| Flexible PCB | Built on a flexible substrate, can bend and conform to curved surfaces. | Wearable electronics, automotive, aerospace. | Lightweight, space-saving, flexible design options. | More expensive than rigid, may require special handling. |
| Rigid-Flex PCB | Combination of rigid and flexible layers, provides both structural integrity and flexibility. | Medical devices, aerospace, advanced robotics. | Complex designs, high reliability, versatile. | Most expensive, complex manufacturing. |
Key Considerations When Selecting an OEM Circuit Board Manufacturer
Selecting the right OEM circuit board manufacturer is a critical decision that directly impacts product quality, time-to-market, and overall cost. This section details essential factors to evaluate when choosing a manufacturing partner, ensuring a robust and reliable supply chain for your electronic products.
- Manufacturing Capabilities
Assess the manufacturer's capacity to handle your project's specific requirements. This includes the complexity of the board (single-layer, multi-layer, flexible, rigid-flex), the size and volume of production runs, and their ability to manage surface mount technology (SMT) and through-hole assembly, including fine-pitch components and advanced packaging techniques. A capable manufacturer should also have a track record of producing boards with similar complexity to your needs. Evaluate if they use automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT) or other testing methodologies. - Quality Certifications
Verify that the manufacturer possesses essential quality certifications such as ISO 9001 (Quality Management System), ISO 13485 (Medical Devices), and UL certification (safety standards). These certifications are indicators of the manufacturer’s commitment to maintaining high standards in their production processes and product quality. Check if the manufacturer has third-party audit records or other proof of compliance. - Lead Times
Evaluate the manufacturer’s ability to meet your project deadlines, from prototyping to mass production. Realistic lead times, flexibility in scheduling, and transparency in communication are critical to achieving your time-to-market objectives. Verify average lead times for different types of orders (prototype, small batch, mass production) and whether expedited services are available. - Cost and Pricing Structure
Consider the overall cost structure, encompassing not only the per-unit price but also tooling costs, setup fees, and shipping expenses. A detailed cost breakdown allows for informed decision-making and financial planning. Inquire about payment terms and whether volume discounts are available. Be wary of manufacturers whose pricing is significantly lower than average, as this might be an indicator of lower quality. - Minimum Order Quantities (MOQ)
Understand the manufacturer’s minimum order quantity policies and whether they align with your project needs, particularly for prototype and small batch orders. An OEM partner that offers flexibility can avoid unnecessary inventory and costs. Check if there are penalties or additional charges for orders below MOQ. - Material Options
Confirm that the manufacturer is capable of handling the required PCB materials (e.g., FR-4, Rogers, CEM-1) and material specifications (e.g., thickness, copper weight, dielectric constant). The choice of materials affects the final performance and reliability of the board. It’s essential to know the range of options available, as well as cost impacts and material lead times. Also, check for material traceability and RoHS compliance.
The OEM PCB Manufacturing Process
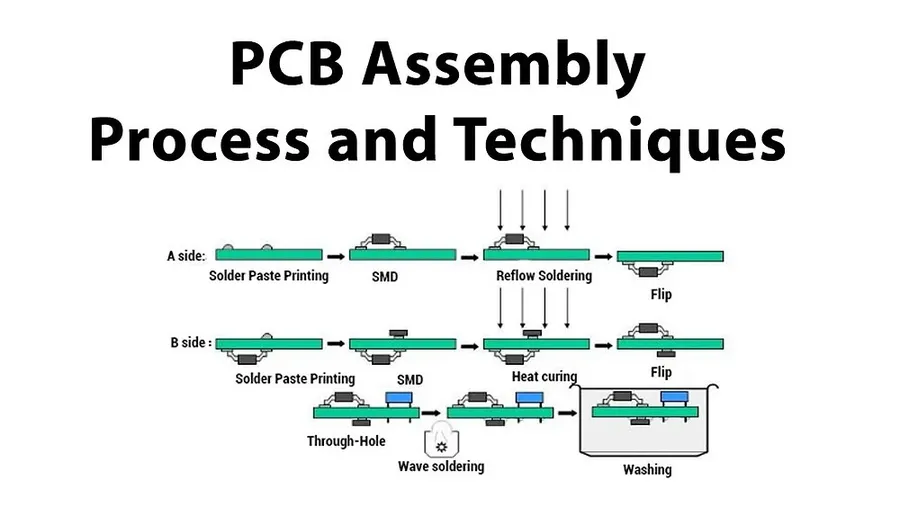
The OEM PCB manufacturing process is a complex series of steps, each critical to the final product's quality and performance. It begins with design and prototyping, moves through fabrication and assembly, and concludes with rigorous testing and quality control. A proficient OEM circuit board manufacturer must manage each phase efficiently to ensure that the PCBs meet the required specifications.
- Design and Prototyping
This initial stage involves translating circuit diagrams into digital PCB layouts. Sophisticated software tools are employed to design the board, considering factors like component placement, trace routing, and thermal management. Prototyping follows, where a small number of boards are produced for testing and design verification. This allows for identification and correction of any design flaws before large-scale production begins. - Fabrication
The fabrication stage is the physical creation of the PCB. It involves processes like layering, etching, drilling, and plating. This involves using specialized equipment and techniques to precisely create the conductive patterns and other necessary features on the board’s substrate (e.g., FR4, metal core). The accuracy of this process is critical for the functionality of the final product. - Assembly
Once the PCB is fabricated, electronic components are attached to it. Assembly may involve Surface Mount Technology (SMT) or Through-Hole Technology (THT). Precision and accuracy are necessary to ensure components are placed correctly and connections are secure. This stage can be automated or semi-automated, depending on volume requirements. The assembly process also includes soldering and inspection. - Testing
Rigorous testing is performed on the assembled PCBs to ensure they meet functional and quality standards. Various test methods are employed to verify electrical characteristics, signal integrity, and overall performance. Testing may include automated optical inspection (AOI), in-circuit testing (ICT), and functional testing. Any identified defects are addressed immediately. - Quality Control
Throughout the entire process, stringent quality control measures are implemented. This includes inspections at each stage and final checks before shipment to ensure the PCB meets all defined specifications and performance requirements. Traceability and compliance with relevant industry standards (e.g., IPC standards) are crucial elements of quality control.
Frequently Asked Questions About OEM Circuit Board Manufacturing
Navigating the world of OEM circuit board manufacturing can raise several questions. This section addresses some of the most common inquiries to provide clarity and assist in making informed decisions when choosing an OEM partner.
- What exactly is an OEM PCB?
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer) PCBs are circuit boards produced by a manufacturer to be used as a component in another company's final product. These PCBs are designed and built to the exact specifications of the purchasing company, allowing for customization and specific integration needs. This approach contrasts with off-the-shelf, standard PCBs which are not tailored to unique requirements. - Who are the primary manufacturers of circuit boards?
Circuit boards are manufactured by a wide range of companies, from large multinational corporations to smaller, specialized businesses. These manufacturers can be categorized as either dedicated PCB manufacturers or as OEM partners that provide both PCB production and other assembly services, Many companies, particularly in the electronics sector, produce their own PCBs as part of a vertical integration model. - How can I identify the best PCB manufacturer for my needs?
The 'best' PCB manufacturer is subjective and highly dependent on the specific requirements of your project. Key factors to consider include the manufacturer's production capabilities (e.g., complexity, volume, materials), quality certifications (e.g., ISO, UL), lead times, cost, and communication. Additionally, consider their track record and customer feedback to ensure they can reliably meet your requirements. There isn't a singular 'best' choice; it's about finding the most suitable partner. - What are the different standards for PCB quality?
PCB quality is assessed using several industry standards such as IPC standards which are globally recognized. These standards cover various aspects of PCB fabrication and assembly, including materials, design, and performance criteria. Certifications such as ISO 9001 and UL reinforce a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. The appropriate standard depends on the application and required reliability of the final product. - What factors impact the cost of OEM PCB manufacturing?
Several factors affect the cost of OEM PCB manufacturing, including the type of board (single-layer, multi-layer, etc.), material selection, design complexity, production volume, and lead times. Expedited lead times and high precision requirements will also impact costs, as will the cost of raw materials and the manufacturer’s overheads. These factors must be considered when assessing quotations. - What are the typical lead times for OEM PCB production?
Lead times for OEM PCB production can vary significantly based on the complexity of the design, the volume of the order, and the manufacturer’s current capacity. Simple designs with standard materials might have a lead time of a few days, while complex, multi-layer PCBs or large production runs can take several weeks. It is crucial to discuss timelines with potential manufacturers at the start of any project. - Is there a minimum order quantity for OEM PCB manufacturing?
Most OEM PCB manufacturers will have a minimum order quantity (MOQ), which can vary depending on the manufacturer and board type. For prototypes or small runs, the MOQ might be low, but it can increase considerably for large production volumes. Negotiating MOQs is often possible, especially when building long term relationships with your chosen manufacturing partner. It is important to factor this into project planning.
Comparing OEM Circuit Board Manufacturers: A Checklist

Selecting the right OEM circuit board manufacturer is critical for product success. This section provides a structured approach to comparing potential partners, focusing on key performance indicators such as pricing, quality, lead times, and customer support. A thorough evaluation using the checklist below will enable informed decision-making, ensuring that the chosen manufacturer aligns with your project's specific needs and constraints.
| Factor | Description | Evaluation Criteria | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Price | Cost per unit for circuit board production. | Compare quotes across multiple manufacturers, considering both unit price and tooling costs. Understand volume discounts. | Crucial for budget adherence. Balance cost with quality and other key factors. |
| Quality | Adherence to industry standards and product reliability. | Verify certifications (ISO, UL, etc.), examine sample products, assess process control and testing procedures. | Essential for product performance and longevity. Poor quality can lead to product failures. |
| Lead Time | Time required for production and delivery of circuit boards. | Inquire about typical lead times for prototyping and mass production. Verify production capacity and scheduling. | Impacts project timelines. Longer lead times may delay product launch. Shorter lead times may indicate superior process efficiency. |
| Customer Support | Responsiveness and support provided by the manufacturer. | Evaluate communication channels, technical support, design support, and the ability to resolve issues. Check response times and overall engagement. | Important for smooth collaboration. Poor customer support can cause delays and frustration. |
| Manufacturing Capabilities | Ability to handle specific board types and complexities. | Assess the manufacturer's experience with single-layer, double-layer, multilayer, flexible, and rigid-flex PCBs. Verify equipment capabilities and material handling. | Required for handling design requirements. Lack of suitable equipment can limit options for the customer. |
| Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ) | The minimum number of boards a manufacturer will produce. | Ensure MOQ matches project volumes, especially for prototyping and small-scale production. | Critical for cost efficiency. High MOQs may be unsuitable for prototypes. Low MOQs indicate flexibility. |
| Material Options | Variety of materials available for PCB substrate and finishes. | Inquire about a range of PCB materials (e.g., FR-4, aluminum, polyimide) and finishing options. Verify that these materials are of consistent quality. | Impacts performance and durability. Lack of choices may limit design options. |
| Certifications and Standards | Manufacturer's compliance with industry standards. | Verify compliance with ISO 9001, IPC standards, and other relevant standards. | Essential for regulatory compliance and quality assurance. |
The Role of OEM Circuit Board Manufacturer in Prototyping and Mass Production

An OEM circuit board manufacturer's capacity to support both prototyping and mass production is critical for a product's success. This capability ensures a seamless transition from initial design validation to large-scale manufacturing, optimizing both efficiency and cost-effectiveness. A capable OEM partner will provide crucial support at every stage, from design refinement to final product delivery.
- Prototyping Phase
During prototyping, the OEM manufacturer works closely with the client, utilizing their engineering expertise to optimize the design. This process involves rapid iterations and design adjustments to ensure performance and manufacturability. A good OEM will provide a range of low-volume production options to support this stage including DFM feedback. - Mass Production Phase
Once the prototype is validated, the OEM manufacturer scales up production to meet the required volumes. This involves optimizing the manufacturing process for efficiency, maintaining quality, and ensuring cost-effectiveness. A reliable manufacturer will have robust quality control processes in place to consistently deliver high-quality PCBs. - Design Verification
OEM manufacturers play a key role in design verification process by assisting in reviewing the initial design and suggesting necessary changes for efficient manufacturing. This helps to avoid costly mistakes in mass production. - Scalable Manufacturing
OEM Manufacturers should be capable of scaling production to meet the required volume. They should have the infrastructure and resources to smoothly transition from small batch prototyping to large-scale mass production.
Future Trends in OEM Circuit Board Manufacturing

The OEM circuit board manufacturing sector is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. Key trends include the rise of flexible PCBs, the relentless push towards miniaturization, and the increasing adoption of sustainable practices. These shifts are not just impacting the types of products OEM manufacturers produce, but also their operational strategies and long-term viability.
- Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs, using materials like polyimide, enable the creation of circuits that can conform to complex shapes, are more resilient in dynamic environments, and offer significant advantages for applications requiring small form factors and high reliability, often utilized in wearables, medical devices, and automotive technologies. - Miniaturization
The demand for smaller and more powerful electronic devices is driving the need for miniaturized PCBs. This involves technologies like high-density interconnects (HDI), microvias, and advanced packaging techniques, allowing more functionality to be packed into smaller spaces. OEM manufacturers must invest in precision manufacturing techniques and advanced materials to meet these demands. - Sustainable Practices
Growing environmental consciousness is compelling manufacturers to adopt sustainable practices, such as using eco-friendly materials, reducing waste, and implementing energy-efficient production processes. This focus is particularly crucial in response to directives aimed at minimizing the environmental footprint of electronics manufacturing. This includes implementing methods for recycling and the responsible disposal of electronic components and materials. - Advanced Materials
The performance of PCBs relies heavily on the materials used in their construction. Emerging trends include the use of materials with enhanced thermal and electrical properties as well as novel composites to further increase flexibility, strength, and durability. This can enhance reliability and longevity across a wide range of applications, including those in harsh or extreme environments. - Integration of Embedded Components
Embedding components directly into PCB layers reduces the overall size and complexity of the final product. This integration enhances functionality and can also improve the reliability and overall cost. Techniques such as system-in-package (SiP) and embedded passives are becoming more prevalent as device densities increase. This trend is seen across a variety of high-density product categories.
Choosing the right OEM circuit board manufacturer is a pivotal step in bringing your electronic product to market. By carefully assessing their capabilities, quality standards, and manufacturing processes, you can secure a reliable partner who can support your project from prototyping to mass production. An experienced oem circuit board manufacturer will not only deliver quality products, but also provide valuable expertise to ensure your product's success in the competitive electronics market. With an understanding of your needs and attention to detail, you can ensure a smooth and effective development process, leading to an efficient and successful launch.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA