Choosing the Right PCB Circuit Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide
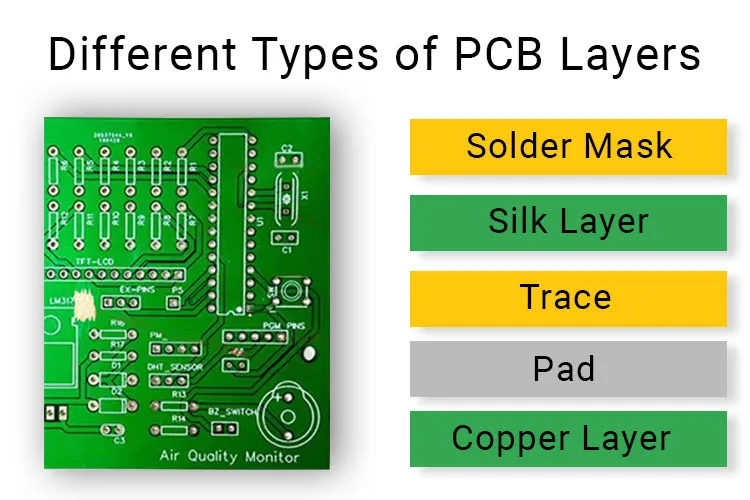
In our increasingly technology-dependent world, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of almost every electronic device. From the smartphones we use daily to complex industrial machinery, PCBs, made by various pcb circuit manufacturers, are indispensable. Selecting the right PCB circuit manufacturer is crucial to ensuring the quality and reliability of these vital components. This article aims to guide you through the process of choosing the ideal manufacturer, ensuring a smooth and successful journey from design to product.
Understanding Your PCB Needs

Before embarking on the selection of a PCB circuit manufacturer, a thorough assessment of your project's specific requirements is paramount. This initial step ensures that the chosen manufacturer aligns perfectly with the technical demands and scope of your project, ultimately leading to a successful and efficient production process. This section will guide you through the key considerations.
Accurately defining your PCB needs is crucial for several reasons. It allows you to effectively communicate your requirements to potential manufacturers, facilitates accurate quoting and avoids costly mistakes, and ensures that the final product meets the required performance criteria.
- Board Complexity:
Evaluate the complexity of your PCB design, whether it's a simple single-layer board or a complex multi-layer one with intricate routing patterns. - Layer Count:
Determine the number of layers your design requires, ranging from single-sided to multiple layers. The layer count directly impacts cost and complexity. - Materials Required:
Identify the specific materials needed for your board, such as FR-4, Rogers, or aluminum, considering electrical, thermal and mechanical requirements. - Production Volume:
Decide on your production volume, be it for prototyping, a small batch, or large-scale production. This will affect the manufacturing processes and cost. - Turnaround Time:
Establish your timeline, which will determine the lead time required from the manufacturer. This helps manage your project’s timeline. - Specialized Requirements:
Consider any specialized needs, such as controlled impedance, blind and buried vias, or specific finishes (e.g., ENIG, HASL).
By considering these factors, you can narrow down potential PCB manufacturers. This process ensures that the selected manufacturer has the capability, expertise and equipment to satisfy your specific project needs. The more precise your definition, the smoother the production process and the more satisfactory the outcome.
Types of PCB Manufacturers and Their Specializations
PCB manufacturers often specialize in distinct areas of production, each catering to different project requirements. Understanding these specializations is crucial for aligning your specific needs with the most suitable supplier. Manufacturers may focus on prototyping, mass production, or particular types of PCBs, which can significantly influence your project’s outcome.
These specializations often dictate the types of materials, production volumes, and technological expertise a manufacturer possesses. This section will explore common specializations to guide your selection process.
- Standard PCB Manufacturers
These manufacturers produce common single-layer, double-layer, and multi-layer PCBs. They are suitable for general electronic applications and often offer lower costs and faster turnaround times for simpler designs. - Flexible PCB (FPC) Manufacturers
Specializing in flexible circuit boards, these manufacturers utilize flexible substrates like polyimide. FPCs are ideal for applications requiring bending and flexing, such as wearable devices and automotive electronics. - Rigid-Flex PCB Manufacturers
These manufacturers produce boards that combine rigid and flexible sections within the same circuit. This technology is ideal for applications needing structural support combined with flexible interconnections, commonly used in aerospace, medical, and consumer electronics. - Metal Core PCB Manufacturers
These manufacturers specialize in PCBs with a metal core (usually aluminum or copper) for enhanced thermal management. Metal core PCBs are used in applications with high power requirements or sensitive components like LED lighting and power electronics. - High-Frequency PCB Manufacturers
These manufacturers focus on producing boards with materials that have specific electrical properties at high frequencies, such as low dielectric loss and controlled impedance. High-frequency PCBs are used in radar, communication, and high-speed data transmission applications. - Prototyping Focused Manufacturers
These manufacturers specialize in small-batch and rapid prototyping services, offering quick turnaround times and flexible design adjustments. They are ideal for initial development stages and smaller scale projects. - Mass Production Focused Manufacturers
These manufacturers are equipped for large-scale production runs, focusing on efficiency and cost reduction for large quantity orders. They generally have established processes for consistent quality and high-volume manufacturing.
| Specialization | Typical Application | Key Feature | Suitability |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard PCB | General electronics | Cost-effective, versatile | Low-complexity designs |
| Flexible PCB | Wearables, Automotive | Bendable, Lightweight | Dynamic, space-limited applications |
| Rigid-Flex PCB | Aerospace, Medical | Combined rigid and flexible | Complex interconnections |
| Metal Core PCB | LED Lighting, Power Electronics | Enhanced Thermal Management | High power applications |
| High-Frequency PCB | Radar, Communications | Low dielectric loss, controlled impedance | High-speed data, RF applications |
| Prototyping Focused | Initial development stages | Rapid turnaround, design flexibility | Small scale projects |
| Mass Production Focused | Large-scale production | Efficiency, cost reduction | Large quantity orders |
Evaluating PCB Manufacturer Capabilities
Selecting a PCB circuit manufacturer requires careful evaluation beyond just pricing. Assessing their capabilities, certifications, and technological proficiency ensures the delivery of high-quality, reliable printed circuit boards that meet your project's specific needs. A comprehensive evaluation minimizes the risk of production delays, quality issues, and ultimately, project failure.
- Certifications and Standards
Look for certifications like ISO 9001, ISO 13485 (for medical devices), or other relevant industry standards, which demonstrate the manufacturer's commitment to quality management and consistent processes. - Manufacturing Process Capabilities
Evaluate the manufacturer's capabilities in areas such as minimum trace width/spacing, via size, layer count, and maximum board size. Ensure these parameters align with your design specifications. - Material Stock Options
Check the availability of different PCB materials such as FR-4, Rogers, aluminum, and others. The manufacturer should offer a variety of materials to meet your specific application requirements (e.g., high temperature, high frequency, etc.). - Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Expertise
A manufacturer that offers DFM services can identify potential issues in your design early in the process. This prevents costly rework and delays, ensuring smooth production. DFM analysis includes checks for manufacturability, solderability, and testability of the design. - Technology and Equipment
Asses the type of equipment they use like drilling machines, etching equipment, AOI machines, testing equipment, etc, for production, and whether they use advanced technology to ensure a quality production, as well as if their equipment is up to date, and well maintained. - Technical Support
A strong technical support team can resolve design-related issues, provide guidance on material selection, and ensure effective communication between your team and the manufacturer.
| Capability | Importance | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Certifications (ISO 9001, etc.) | Ensures consistent quality and process control. | Look for certifications relevant to your industry. |
| Minimum Trace Width/Spacing | Affects the complexity and density of your design. | Match with your design requirements (e.g., higher density boards require finer features). |
| Layer Count | Determines board complexity and signal routing capability. | Choose a manufacturer capable of producing your required layer count. |
| Material Options | Impacts thermal and electrical performance. | Choose a material that meets your specific application needs. |
| DFM Services | Helps avoid manufacturing issues. | Check what DFM analyses the manufacturer can provide. |
| Equipment and Technology | Ensures high-quality production. | Confirm they have the right machinery and technology for your PCB type. |
| Technical Support | Facilitates good communication and problem-solving. | Ensure they have engineers to solve your problems quickly. |
The Importance of Quality Control and Testing
Rigorous quality control and comprehensive testing are not merely desirable, but absolutely essential in printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing. These processes directly impact the reliability, performance, and longevity of the final product. A robust quality management system ensures that each PCB meets stringent specifications and operates flawlessly in its intended application.
The absence of adequate quality control can lead to a multitude of issues, including functional failures, premature degradation, and safety hazards. These problems can result in costly recalls, damaged reputations, and project delays. Therefore, selecting a manufacturer that demonstrates a strong commitment to quality is paramount.
- Key Quality Control Elements
This includes incoming material inspection, in-process quality checks, and final product verification. Each stage is crucial for catching potential errors early in the process. - Testing and Inspection Techniques
Utilizing advanced techniques such as Automated Optical Inspection (AOI), In-Circuit Testing (ICT), and functional testing are crucial. AOI uses cameras to scan the board for visual defects such as shorts and opens. ICT tests the electrical performance of the individual components on the assembled PCB. Functional testing ensures that the assembled board performs to design specifications. - Compliance and Certification
Look for manufacturers that comply with recognized standards such as ISO 9001. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to consistent quality management processes.
| Testing Type | Description | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) | Automated visual inspection using cameras and image processing. | Detects surface defects, component placement issues, and solder joint quality. |
| In-Circuit Testing (ICT) | Electrical testing of individual components and connections. | Verifies the correct placement and functionality of components before board operation. |
| Functional Testing | Testing of the completed PCB within its target system environment. | Ensures that the complete assembly operates as intended. |
| X-Ray Inspection | Non-destructive testing using X-rays to see hidden defects. | Examines solder joints under components like BGAs and hidden layers. |
The combination of a well-defined quality control process and rigorous testing ensures a higher degree of product reliability and reduces the chance of failures once deployed in the field. It is essential that when selecting a PCB manufacturer, that these capabilities are robust and up to the task.
Cost Considerations and Budgeting for PCB Manufacturing
Cost is a pivotal factor in PCB manufacturing, extending beyond the initial quote to encompass long-term expenses like tooling, testing, and potential rework. A thorough evaluation of these factors is crucial for effective budgeting and avoiding unexpected costs.
Effective cost management in PCB manufacturing requires a holistic approach, considering not just the price per board, but also associated costs that can significantly impact the overall project budget. Transparent pricing from manufacturers is key, along with a willingness to negotiate based on project specifics.
| Cost Factor | Description | Impact on Budget |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Board Price | The cost per PCB unit, typically affected by quantity, complexity, and material type. | Directly impacts total cost, but should not be the only factor. |
| Tooling Costs | Charges for creating specific tools needed for manufacturing, such as stencils and fixtures. | Can be a substantial upfront expense, especially for unique board designs. |
| Testing Costs | Expenses associated with testing each board for functionality and quality. | Essential for reliability but adds to the overall cost. |
| Rework Costs | Expenses incurred when boards fail quality checks and need to be corrected. | Can significantly increase costs if quality is not assured. |
| Shipping Costs | Expenses for delivery of the final boards. | Can fluctuate based on supplier location and shipping method. |
| Material Costs | Cost of raw materials used in board production, such as substrates and laminates | Varies with materials type and market price changes |
| Set-up Fees | Initial costs for preparing the production line | Often applied to new orders and small production runs |
When comparing quotes from different manufacturers, it's important to ensure they include all potential costs. Be wary of quotes that seem unusually low, as they may exclude essential services or have hidden charges. A clear understanding of the pricing structure will facilitate accurate budget planning.
Negotiating with manufacturers is a normal and often necessary part of the process. Be transparent about your budget constraints and explore the possibility of price reductions for larger orders or long-term partnerships. Also, consider whether using standard material or reducing some tolerance or spec will help reduce the cost, without compromising product quality.
Turnaround Time and Lead Times
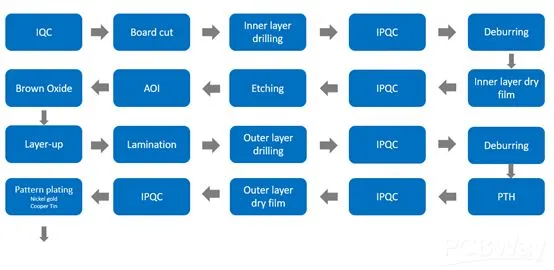
In today's rapidly evolving technological landscape, the time required to manufacture and deliver printed circuit boards (PCBs) is often a critical factor in project success. Understanding and managing turnaround time and lead times from PCB circuit manufacturers is essential for maintaining project timelines and avoiding costly delays.
Turnaround time refers to the duration from when a PCB manufacturer receives your design files to when the finished boards are ready to ship. Lead time, on the other hand, encompasses the entire duration from when an order is placed to when the product is received. Effective project management requires a clear understanding of both.
- Factors Affecting Turnaround Time:
Several factors influence how quickly a manufacturer can produce your PCBs. These include the complexity of the board design, the required layer count, the type of materials specified, the production volume (prototype, small batch, or mass production), and the current workload of the manufacturer. Unforeseen issues or a backlog can also extend turnaround times. - Factors Affecting Lead Time:
Lead time encompasses turnaround time as well as the duration required for any additional processes such as design review, tooling preparation, procurement of materials, and shipping. Transportation time is especially relevant when ordering from international manufacturers. It is essential to discuss all potential factors to understand the total lead time.
| Production Phase | Typical Turnaround Time | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| PCB Prototyping | 2-7 Days | Faster turnaround times are possible for simpler designs with common materials. May vary based on manufacturer's processes and capacity. |
| Small Batch Production | 1-3 Weeks | Lead times may increase with complexity and material availability. Requires proper planning. |
| Mass Production | 3-8 Weeks | Complex boards and high volume requires more planning. Lead times will depend on material supply and capacity. |
It's also crucial to understand how manufacturers handle expedited orders. Some manufacturers offer faster turnaround options for an additional fee. If speed is of the essence, confirm these capabilities upfront and understand any associated cost implications. Transparent communication with your manufacturer is key to setting realistic expectations and planning accordingly.
A common issue is a disconnect between quoted and actual lead times. To mitigate this, ensure that timelines are clearly defined in the quote. Regularly touch base with the manufacturer to receive updates and clarify any potential delays as soon as they are detected. Good communication practices will help ensure your project is delivered on time.
Location and Geographical Considerations for PCB Circuit Manufacturers

The geographical location of your PCB circuit manufacturer can significantly impact project timelines, communication, and overall cost. Choosing between domestic and international manufacturers involves evaluating several trade-offs to align with your project's specific needs.
| Factor | Domestic Manufacturer | International Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Often easier due to proximity and similar time zones. May involve face-to-face meetings. | Potentially more challenging due to language barriers, time zone differences, and less in-person interaction. |
| Lead Times | Generally shorter lead times due to reduced shipping distances and faster logistics. | Potentially longer lead times due to longer shipping distances and customs clearance. |
| Shipping Costs | Lower shipping costs due to shorter distances. | Higher shipping costs due to longer distances and potential tariffs. |
| Cost | May be higher due to domestic labor and operating costs. | May be lower due to lower labor and manufacturing costs. |
| Intellectual Property Protection | Potentially stronger due to domestic legal and business practices. | Requires careful due diligence to ensure compliance with international IP laws and agreements. |
| Quality Control | Easier to oversee and audit processes, with potentially greater oversight. | Requires more stringent due diligence and communication to maintain quality standards. |
Choosing a domestic manufacturer can be advantageous if you require quicker turnaround times, have stringent quality requirements, or prefer face-to-face interactions for design and development. Conversely, international manufacturers can provide more competitive pricing for larger-scale production runs or standard PCB designs, making them attractive for projects with tighter budgets. Some manufacturers have facilities in both domestic and international locations.
Ultimately, the optimal location of your PCB circuit manufacturer depends on the priorities and demands of each project. Careful consideration of communication, logistics, cost, quality, and intellectual property concerns is essential before making a decision. It may be beneficial to maintain relationships with both domestic and international vendors to leverage their specific advantages for different projects.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Circuit Manufacturers
Choosing the right PCB manufacturer involves many considerations beyond simply finding a list of suppliers. This section addresses common questions, offering a structured approach to evaluating manufacturers based on your specific needs, rather than providing a potentially biased list of 'best' options.
- Who is the best PCB manufacturer?
There is no single 'best' PCB manufacturer, as the ideal choice depends entirely on your project's unique requirements. Instead of seeking a general recommendation, focus on identifying manufacturers that specialize in the type of PCBs you need (e.g., high-layer count, flexible, etc.), can meet your volume and turnaround time needs, and have strong quality control processes. Evaluate their capabilities, certifications, and customer feedback before making a decision. - Who manufactures PCBs?
PCBs are manufactured by a diverse range of companies, from small local shops to large international corporations. The best way to find a suitable manufacturer is to first determine your PCB specifications, such as complexity, layer count, and materials, then research manufacturers specializing in those areas. - Who is the largest PCB manufacturer in the world?
Identifying the 'largest' PCB manufacturer can be misleading as rankings can vary based on revenue, volume produced, or geographical region. Instead, focus on identifying manufacturers that align with your specific production and technology needs and ensure they have adequate capacity to fulfill your orders. Market size does not guarantee quality or suitability for your project. - Which company's PCB is best?
The 'best' PCB is subjective and depends on the performance requirements of the application. The company that can meet all your specifications with proven quality and acceptable costs is the best choice. You should select companies based on their capability to meet your specific need, not based on generalized claims of superiority. - What is a typical turnaround time for PCB prototyping?
Typical turnaround times for PCB prototyping can vary significantly depending on the manufacturer, complexity of the design, and the quantity of boards. Express services might deliver prototypes in 1-2 days, while standard prototyping runs can take 1-2 weeks. - What is the approximate cost for PCB prototyping?
The cost of PCB prototyping is influenced by factors including board complexity (layer count, size, etc.), materials, technology (e.g., HDI), quantity, and turnaround time. Prices can range from tens to thousands of dollars per prototype. Request detailed quotations from potential manufacturers. - What certifications should a good PCB manufacturer possess?
Key certifications for a reliable PCB manufacturer include ISO 9001 (Quality Management System), ISO 14001 (Environmental Management), and industry-specific certifications like IATF 16949 for automotive applications or UL certifications for safety. Compliance with IPC standards for PCB design and manufacturing is also important.
| Question | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Turnaround Time | Compare lead times for prototypes, small batches, and mass production. Evaluate if expedited options are available. |
| Prototype Cost | Request quotes for specific design complexity. Understand tooling and setup costs. |
| Quality Control | Inquire about testing capabilities (AOI, X-ray), sampling plans, and certification procedures. |
| Manufacturing Capabilities | Assess technology (fine-pitch, blind/buried vias), material handling, and layer count limits. |
| Customer Support | Evaluate communication response times and technical support availability. |
| Minimum Order Quantity | Understand MOQ requirements for both prototyping and production. |
Steps Before Choosing Your Final PCB Manufacturer
Finalizing your PCB manufacturer requires a thorough evaluation beyond initial assessments. This involves practical testing of their capabilities and a deeper understanding of their operational practices. It's essential to validate your top candidates through tangible methods before committing to large-scale production.
- Sample Board Evaluation
Request sample boards from your shortlisted manufacturers. This provides a hands-on opportunity to evaluate the actual quality of their work. Check for dimensional accuracy, material quality, and finish consistency. Sample boards serve as a tangible representation of their manufacturing prowess. - Facility Tours (Physical or Virtual)
Whenever possible, conduct a site visit or a virtual tour. This allows for a firsthand observation of their production line, equipment quality, and organizational structure. This gives insight into their work environment and commitment to quality. It's a chance to assess their operational standards beyond what is shared in their marketing materials. - Reference Checks and Customer Reviews
Seek references from their past clients and scrutinize online reviews. Real feedback from previous users is valuable in understanding their strengths, weaknesses, and customer service. This peer review process helps uncover any hidden issues that are not immediately apparent.
Sample Board Testing: Key Evaluation Points
When testing your sample boards, consider these critical aspects:
- Dimensional Accuracy:
Verify that the board dimensions, drill hole diameters, and trace widths match the design specifications. - Material Quality:
Ensure the materials used, including the laminate, solder mask, and silkscreen, are of the agreed-upon type and quality. - Surface Finish:
Evaluate the quality of the surface finish, checking for uniform coating, smoothness, and absence of defects such as burrs. - Solder Mask Alignment and Quality:
Confirm that the solder mask is accurately aligned with the pads and that there are no unwanted solder mask on exposed pads. - Silkscreen Quality:
Ensure the silkscreen is legible, correctly placed, and resistant to smudging or fading. - Electrical Testing:
If possible, conduct basic electrical tests to ensure the continuity and isolation of traces.
Facility Visit: What to Observe
A physical or virtual tour of the manufacturer’s facility should focus on these elements:
- Cleanliness and Organization:
Assess the facility's overall cleanliness and organization, which reflects their attention to detail. - Equipment Quality:
Examine the type and condition of their machinery, checking for modern, well-maintained equipment. - Production Flow:
Observe the flow of materials and products through the production process, looking for efficiency and control points. - Quality Control Processes:
Verify the presence of well-defined quality control checkpoints and testing stations. - Technical Staff:
Note the expertise of the technical personnel and their responsiveness to questions and concerns. - Environmental Conditions:
Confirm that the manufacturing area has the necessary controls (temperature, humidity, etc.)
Reference Checks: Key Questions to Ask
When contacting references, focus on asking relevant questions such as:
- Quality of PCB:
Were the PCBs consistently delivered to the required specifications and quality? - Adherence to Lead Times:
Did the manufacturer consistently meet the agreed-upon delivery schedules? - Problem Resolution:
How effectively did the manufacturer handle any issues or problems that arose? - Customer Service:
How responsive and helpful was the manufacturer's customer service team? - Pricing Transparency:
Was the manufacturer transparent with their pricing and billing practices? - Overall Satisfaction:
Would the customer recommend this manufacturer based on their experiences?
Choosing the right pcb circuit manufacturer is a crucial step in ensuring the success of any electronics project. By carefully considering factors such as your project's needs, manufacturer's capabilities, cost, turnaround time, and quality standards, you can select a partner that not only meets but exceeds your expectations. Remember to conduct thorough research, evaluate your options, and choose a pcb circuit manufacturer that aligns with your goals. This approach will contribute to the overall quality, reliability, and success of your final product, ensuring satisfaction with your electronic product while also enhancing the performance of your business. Ultimately, building a strong relationship with the right PCB circuit manufacturer can benefit your business for years to come.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA