Choosing the Right PCB Provider: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's fast-paced tech world, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the unsung heroes powering our devices, from smartphones to complex medical equipment. Choosing the right PCB provider is paramount for any project that relies on these essential components. This article, drawing on years of experience in the PCB industry, offers a comprehensive guide to help you select the best PCB partner, ensuring quality, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Understanding Your PCB Needs

Before engaging a PCB provider, a precise understanding of your project requirements is paramount. This initial step ensures that the selected provider is well-equipped to meet the specific demands of your printed circuit board, thereby minimizing potential delays and additional costs. The critical parameters encompass board type, material specifications, quantity, and tolerances.
These parameters directly influence the selection of the most appropriate PCB provider and manufacturing processes. Consideration of each ensures that the end product aligns with the intended application.
- Board Type
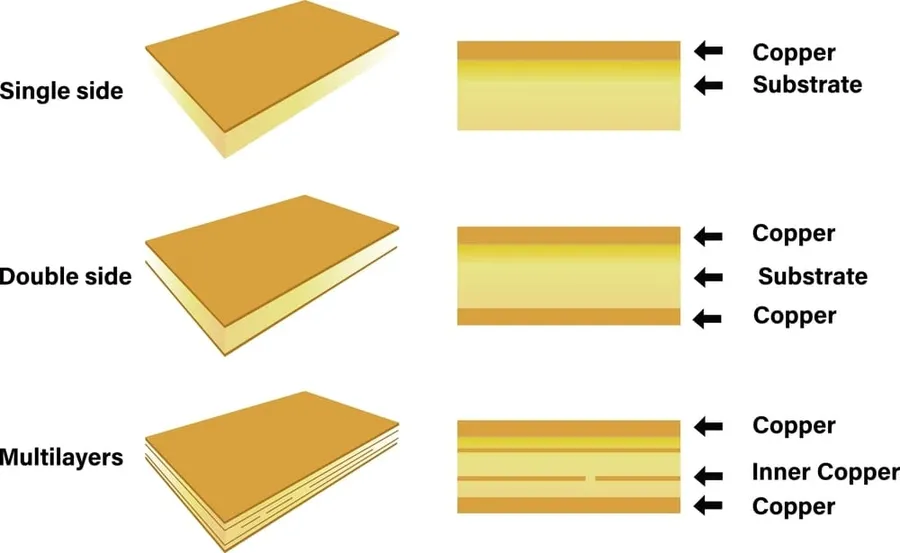
The selection of board type is a fundamental decision that impacts the complexity and cost of PCB manufacturing. Common board types include single-sided, double-sided, and multi-layer boards. Single-sided PCBs are often used for simpler circuits, while double-sided PCBs are common for intermediate complexity. Multi-layer boards are designed for highly complex circuitry, involving multiple layers of conductive material. The choice among these depends on the circuit complexity and component density. - Material Specifications
The base material of the PCB must be carefully selected to ensure it meets the performance demands of the application. FR4 is a common choice that provides a good balance between cost and performance for general use. Other materials include aluminum for enhanced thermal management, and flexible substrates for applications requiring physical flexibility. The selection of material should take into account the environmental and operational conditions, as well as the thermal and mechanical stresses the PCB is expected to endure. - Quantity
The number of PCBs needed for a production run has a significant impact on cost per board. Small-batch production typically has higher per-unit costs due to setup and overheads. Larger volumes reduce the per-unit cost due to economies of scale. PCB providers often offer pricing tiers based on volume, and understanding these tiers is crucial for accurate budgeting. - Tolerances
Tolerances specify the acceptable variations in the dimensions and properties of the PCB, ensuring its consistent performance. Tighter tolerances lead to more precise manufacturing, but may also increase costs and production time. Selecting appropriate tolerances that meet functional requirements without over-specifying is crucial for cost-effective production. These must be in accordance with both industry standards and specific project demands.
Key Factors to Consider When Choosing a PCB Provider
Selecting the right PCB provider is crucial for the success of any electronics project. A thorough evaluation based on several key factors ensures that the chosen provider meets the specific requirements of the project while also offering reliable service and support. These key factors include experience, manufacturing capabilities, certifications, pricing, turnaround time, customer support, and online resources.
- Experience
A provider with a proven track record and years of experience in the industry is more likely to deliver high-quality PCBs. Examine their portfolio and customer testimonials to gauge their reliability. - Manufacturing Capabilities
Assess the provider's ability to handle your specific PCB requirements. This includes technology (e.g., HDI, flex PCBs), material options (e.g., FR-4, Rogers), layer counts, trace widths, via types, and surface finishes (e.g., ENIG, HASL). Confirm their capabilities meet or exceed your design specifications. - Certifications
Certifications such as ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and UL demonstrate a provider's commitment to quality and environmental standards. These certifications ensure a consistent and reliable manufacturing process. - Pricing
Obtain detailed quotes and analyze the cost structure. Consider not just the per-unit price but also setup fees, tooling charges, and other potential costs. A lower price might compromise quality, so always balance cost against performance. - Turnaround Time
Evaluate the provider's turnaround times, especially for prototypes and urgent projects. Understand if they offer expedited services and ensure that their timelines match your project schedule without sacrificing quality. - Customer Support
Responsive and knowledgeable customer support can be invaluable, particularly when issues arise. Check if they offer dedicated support channels, technical assistance, and proactive communication throughout the process. - Online Resources
Evaluate the provider's online platform for ease of use. The availability of resources like design rule checks (DRC), online quoting tools, order tracking, and comprehensive documentation improves the overall user experience.
Comparing PCB Providers: A Detailed Look

Selecting the ideal PCB provider involves a thorough comparison of their capabilities, services, and specializations. This section provides an in-depth look at several leading PCB manufacturers, outlining their strengths and weaknesses to aid in your decision-making process. We will focus on key players like JLCPCB, PCBWay, and Advanced Circuits, examining what each offers to different types of projects and needs.
| Provider | Strengths | Weaknesses | Services Offered | Specializations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JLCPCB | Cost-effective, fast turnaround for prototypes, large-scale production capabilities | Limited material options, less customization flexibility, fewer advanced technology options | PCB prototyping, SMT assembly, stencil services | High-volume, low-cost production, quick-turn PCBs |
| PCBWay | Wide variety of materials and finishes, good customization options, comprehensive SMT assembly services, PCB design services | Can be slightly more expensive than JLCPCB, turnaround times vary based on complexity and quantity | PCB prototyping, SMT assembly, PCB design services, component sourcing, 3D printing, other manufacturing services | Complex designs, diverse materials, full service manufacturing |
| Advanced Circuits | High-reliability PCBs, excellent for high-technology, custom built boards, strong US based support | Higher pricing, can be costly for hobbyists and smaller projects, longer lead times | PCB prototyping, advanced manufacturing, quick turn, complex PCB builds, design for manufacturability. | High-reliability applications, defense, aerospace, complex designs. |
| Others (e.g., Allpcb, Eurocircuits) | Vary by provider, some specialize in unique niches like high-frequency or RF PCBs, good customer support, and quality. | Can vary widely based on provider, some may have higher prices or longer lead times, limited customization or technology. | Vary based on provider, focus on specialized PCBs, or value added design services | Varies widely, some may excel at specialized PCB types, or support specific markets. |
PCB Provider Capabilities: What to Look For
Selecting the right PCB provider hinges on their manufacturing capabilities, encompassing their processes, technology, material options, and customization potential. A thorough understanding of these capabilities is crucial to ensure the provider can meet the specific demands of your project.
Key aspects to evaluate include:
- Assembly Capabilities
Assess the provider's expertise in Surface Mount Technology (SMT) and Through-Hole assembly. SMT is used for small components mounted directly onto the board surface, while through-hole is used for components that have leads inserted through the board. Both are essential for a variety of projects, with some projects requiring both types of assembly. - Surface Finish Options
Providers should offer various surface finishes that protect the copper traces from corrosion and enhance solderability. Common options include Hot Air Solder Leveling (HASL), which is a cost-effective option; Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold (ENIG), which provides excellent corrosion resistance and solderability; and Immersion Silver (ImAg) offering good solderability and is lead-free. - PCB Material Options
Different materials offer varying performance characteristics. FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) is the most common and cost-effective option, while aluminum offers superior heat dissipation, and flexible materials are suitable for applications requiring bending. High frequency materials (e.g., Rogers) are also important when dealing with high-speed signals. Confirm that the provider can accommodate your required material. - Customization Options
Providers should allow customization in terms of board thickness, copper layer count, and trace widths. The ability to specify custom shapes, drill sizes, and via types can be crucial for particular applications. Check for capabilities to match your specific design requirements.
| Capability | Description | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| SMT Assembly | Mounting components on the board surface | Precision of component placement, solder quality, and component size compatibility |
| Through-Hole Assembly | Mounting components with leads through holes in the board | Hole size accuracy, solder joint strength, and component size compatibility |
| HASL Surface Finish | Solder applied to copper traces | Cost-effective, can have uneven surface |
| ENIG Surface Finish | Nickel layer followed by thin layer of gold | Excellent solderability and corrosion resistance, more expensive than HASL |
| FR4 Material | Standard fiberglass reinforced epoxy laminate | Cost-effective, suitable for most applications |
| Aluminum Material | Metal substrate with a dielectric layer | Good thermal performance, suitable for high power applications |
| Flexible Material | Polyimide or similar substrate | Good for flexible and curved applications, expensive |
Navigating PCB Manufacturing Pricing and Costs
Understanding the intricacies of PCB manufacturing pricing is crucial for effective project management. PCB costs are influenced by a multitude of factors, extending beyond just the size of the board. This section provides a deep dive into these cost drivers and offers practical advice on securing competitive quotes and optimizing your project budget without sacrificing quality.
| Cost Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Board Complexity | Number of layers, trace width/spacing, via type/size | Higher complexity results in increased cost due to more complex manufacturing processes. |
| Material | Type of substrate (FR4, Aluminum, Flexible, etc.), thickness, copper weight | Specialized materials and higher copper weights contribute to higher costs. |
| Quantity | Number of PCBs being manufactured in the order | Unit cost tends to decrease significantly with an increase in order volume. |
| Surface Finish | HASL, ENIG, Immersion Tin/Silver | ENIG and other advanced surface finishes typically increase the cost more than HASL. |
| Special Processes | Blind/buried vias, controlled impedance, gold fingers | These advanced processes drive up costs due to the need for precision manufacturing. |
| Testing & Inspection | Electrical tests, AOI, X-ray | The level of required testing will influence final project cost |
| Turnaround Time | Standard or expedited production. | Expedited production times often require a premium price. |
To effectively control PCB manufacturing costs, it's crucial to implement strategic approaches. Here are some practical tips for cost optimization:
- Optimize PCB Design:
Keep your design as simple as possible. Reduce the number of layers, vias, and unique features to lower manufacturing costs. Use standard component footprints when possible to avoid the need for custom component handling. - Standardize Materials:
Opt for commonly available materials like standard FR4, which is generally less expensive than specialized substrates. - Panelization Strategy:
Maximize panel utilization when ordering multiple boards. Proper panelization reduces material waste and lowers the cost per unit. It may require consulting with your PCB supplier to understand their panelization guidelines. - Plan for Batch Orders:
If possible, combine prototype orders with larger production runs. Ordering in bulk often significantly reduces the per-unit cost. - Request Multiple Quotes:
Do not settle for the first quote you receive. Gather quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure you're getting a competitive price for the same specifications. Verify the completeness of the quote to avoid hidden costs. - Clearly Define Requirements:
Ensure your design requirements and tolerances are clearly and accurately specified to the PCB provider to avoid costly misinterpretations or errors. Inaccuracies can result in rework or delays. - Use Standard Finishes:
Opt for cost-effective finishes like HASL, if your application allows it. Advanced finishes may not be necessary for all projects and can significantly raise manufacturing costs.
Securing precise quotes is another essential part of cost management. Provide detailed specifications to suppliers and double-check the quotes to include all expected charges. This proactive approach will help keep PCB costs under control and prevent budget overruns.
Turnaround Time: Balancing Speed and Quality
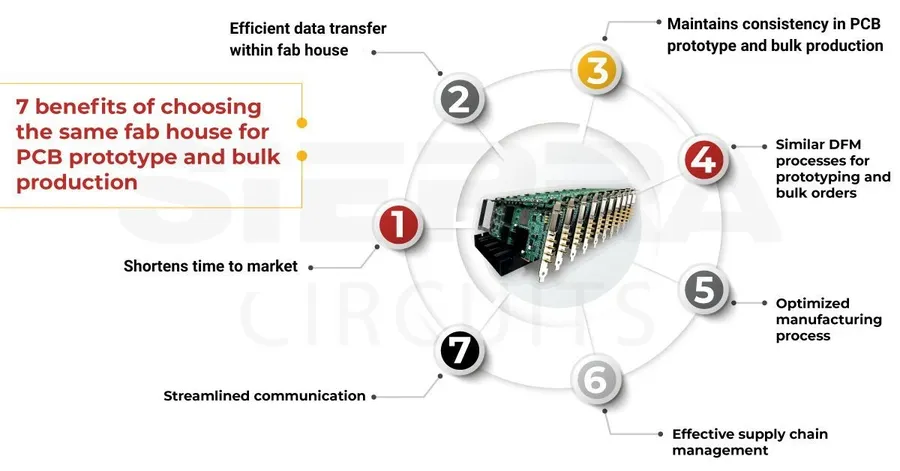
Turnaround time, the duration from order placement to delivery, is a crucial factor when selecting a PCB provider, particularly for projects with tight deadlines or when rapid prototyping is required. Balancing speed with the quality of the final product is essential to ensure project success, especially when dealing with complex PCBs that demand precision.
Understanding the trade-offs between faster turnaround times and potential impacts on quality allows for informed decisions that align with project requirements and acceptable cost levels. While some providers offer expedited services, it's crucial to assess their quality control standards and the capacity to consistently deliver reliable PCBs.
To manage expectations effectively, verify the provider's estimated lead times, understand their production process, and clarify any potential delays that may arise from unforeseen circumstances, such as component shortages, complex designs, or specific material requirements.
Frequently Asked Questions about PCB Providers
This section addresses common inquiries regarding PCB providers, offering clear and concise answers to guide both beginners and experienced users in making informed decisions. These FAQs cover a range of topics, from basic definitions to industry-specific queries, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the PCB manufacturing landscape.
- What does PCB stand for?
PCB stands for Printed Circuit Board. It's a foundational component in electronics, serving as a platform to connect electronic components and facilitate their operation. These boards provide both mechanical support and electrical pathways through conductive tracks and pads. - What is the role of a PCB provider?
A PCB provider is a company that manufactures printed circuit boards according to specific design requirements. Their services encompass everything from the fabrication of the bare board to, in many cases, component assembly and testing. They act as a critical link in bringing an electronic design into physical form. - What does PCB mean in the context of healthcare?
While 'PCB' primarily refers to 'Printed Circuit Board', in healthcare, it commonly represents 'Primary Care Body'. However, it's crucial to note that this meaning is entirely separate from the electronic context discussed in this article. Ensure you differentiate the context in which PCB is used. - Who are some of the largest PCB suppliers in the industry?
The PCB manufacturing industry is diverse, with several large players dominating the market. Some of the largest suppliers include companies like TTM Technologies, Unimicron, and Zhen Ding Technology. These companies have extensive manufacturing capabilities and serve a global client base. While not necessarily the absolute 'biggest' at all times, these represent significant players known for scale and consistent output. - What is the significance of PCB in a company?
For companies that design or utilize electronic products, PCBs are an essential part of their supply chain and operational workflow. For companies that manufacture and sell electronic products, the quality and reliability of PCBs directly affect the final product's performance, reliability, and overall success. - What are the common types of PCB materials?
Common PCB materials include FR-4 (a fiberglass-epoxy composite), aluminum, and flexible materials such as polyimide. The selection of a specific material depends on the application requirements, including thermal, mechanical, and electrical demands of the device. - How do I ensure the quality of PCBs from a provider?
To ensure the quality of PCBs, you should check for certifications such as ISO 9001 and IPC standards compliance. Also, request and examine samples, and check the provider's quality control documentation, and manufacturing process closely.
Making the Right PCB Provider Choice for Your Project

Selecting the ideal PCB provider hinges on a thorough understanding of your project's specific requirements and constraints. The market offers a plethora of options, each with unique strengths and weaknesses. A strategic evaluation process is paramount to ensuring a successful outcome. This section synthesizes the preceding discussions, offering a framework for informed decision-making based on industry best practices and decades of engineering expertise.
- Define Clear Project Specifications
Before engaging with any provider, meticulously document your PCB specifications. This includes layer count (single, double, or multi-layer), material type (FR4, aluminum, flexible, etc.), critical dimensions, impedance requirements, and any specific finishing needs. A well-defined specification minimizes ambiguity and ensures that quotes are accurate and comparable. - Prioritize Key Selection Factors
Based on your specifications, prioritize the selection criteria most relevant to your project. Consider factors such as manufacturing capabilities, certifications (ISO, UL), pricing, turnaround time, and the level of technical support offered. For instance, a prototype may prioritize speed, while a high-volume production run might emphasize cost-effectiveness. - Evaluate Provider Capabilities
Assess potential providers against your prioritized criteria. Examine their manufacturing processes, including SMT assembly, through-hole assembly, and surface finish options (HASL, ENIG, etc.). Special material handling and the provider's experience with different PCB designs can also prove important. Ensure the provider has experience with similar types of projects, and review their case studies or user testimonials. - Obtain and Compare Quotations
Request detailed quotes from multiple providers, ensuring each quote is based on identical specifications to facilitate an apples-to-apples comparison. Evaluate the total cost, including tooling, shipping, and any additional charges, and make sure to ask about potential cost increases when the order is changed during the manufacturing process. - Assess Turnaround Time and Lead times
Consider your project's timeline requirements and realistically assess the lead times for various providers. Some providers may offer accelerated or express services for rapid prototyping. Always confirm the lead time and production schedules. It is also important to review the provider’s history and ensure they are reliable in providing delivery on time. - Evaluate Support and Resources
Opt for providers that offer comprehensive customer support, and easy to use online resources and have established workflows for efficient order processing. This can include access to design rules, technical staff, dedicated project managers and direct engineering expertise. A provider with a client-oriented approach can offer better service quality, which helps to avoid delays and extra costs. - Make Informed Selection
Based on your comprehensive evaluation, select the provider that best meets your project's requirements while staying within your budgetary and timeline constraints. Document your rationale and maintain detailed communication with the selected provider throughout the production process. Maintain clear records of all your communication for future reference.
Selecting the right PCB provider is a critical step in ensuring your project's success. By carefully evaluating your needs and the provider's capabilities, you can ensure high-quality, cost-effective PCBs. As a leading [pcb provider], we understand the nuances of PCB design, manufacturing, and assembly, and we're committed to helping you achieve your goals, whether it's prototyping or full-scale production. Consider the factors discussed in this article and make an informed decision to partner with a [pcb provider] who is not only a manufacturer but also a trusted extension of your team.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA