Choosing the Right Single Layer PCB Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's tech-driven world, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the invisible backbone of countless devices, from everyday gadgets to sophisticated machinery. Among various PCB types, the single layer PCB stands out for its simplicity and cost-effectiveness, making it a popular choice for numerous applications. Choosing the right single layer pcb manufacturer is crucial for the success of any project. This guide will help you understand what to look for in a manufacturer, providing the insights needed to make an informed decision. We'll discuss manufacturing processes, cost considerations, and quality control to ensure your product’s success.
Understanding Single Layer PCBs: Basics and Applications

Single-layer PCBs, the foundational building blocks of electronics, are characterized by a single layer of conductive material, typically copper, affixed to one side of an insulating substrate. This design, the simplest form of printed circuit board, offers a cost-effective and efficient solution for less complex electronic devices, making them a popular choice when choosing a single layer pcb manufacturer. Their simplicity lends itself well to high-volume production and straightforward circuit layouts.
The primary advantage of single-layer PCBs lies in their straightforward manufacturing process and lower production costs when compared to their multi-layered counterparts. These attributes make them ideal for applications where cost-effectiveness and ease of manufacturing are paramount.
Single-layer PCBs find widespread applications in various sectors, including but not limited to:
- Consumer Electronics:
Simple calculators, basic remote controls, and LED lighting systems often utilize single-layer PCBs due to their cost-effectiveness and simplicity. - Power Supplies:
Many basic power supply circuits, including those for small appliances and chargers, are built on single-layer PCBs. - Sensor Boards:
Many sensor applications that do not require complex circuits, such as temperature or humidity sensors, are implemented using a single-layer PCB. - Simple Control Circuits:
Basic control systems like those for toys or small household devices are frequently based on single-layer PCBs. - Lighting Solutions:
LED lighting panels and simple light control circuits often use single-layer PCBs.
The selection of a single-layer PCB over a more complex multi-layer board is primarily driven by design requirements. When a circuit layout is straightforward and does not require the complexity of multiple conductive layers, single-layer PCBs offer a highly efficient and economical solution, therefore choosing the correct single layer pcb manufacturer can be critical to the success of a project.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Single Layer PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the right single layer PCB manufacturer is critical to ensure the quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery of your printed circuit boards. This section delves into the crucial factors that should guide your decision-making process, covering manufacturing capabilities, material choices, and lead times.
- Manufacturing Capabilities
Assess the manufacturer's equipment and processes for single-layer PCB production. This includes their ability to handle your specific design requirements, such as board size, trace width, and hole sizes. Check their capacity to meet your production volume needs, from small prototypes to large-scale orders. - Material Options
A reliable manufacturer should offer a range of suitable materials, most commonly FR-4, CEM-1, and aluminum. Understand each material's characteristics and how they align with your application requirements. The manufacturer should be able to advise on the best material selection based on performance needs, environmental conditions, and budget. - Lead Times
Evaluate the manufacturer's standard lead times for PCB production, from design verification to delivery. Confirm that their stated timelines align with your project schedule. Consider whether they offer expedited services for urgent projects. A manufacturer that provides transparent timelines is essential for effective project management. - Quality Standards and Certifications
Verify the manufacturer adheres to industry quality standards and has relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 or IPC standards. These certifications indicate commitment to quality and consistency in their manufacturing processes. - Design for Manufacturing (DFM) Support
A good manufacturer provides DFM feedback to ensure your design is manufacturable and to identify potential issues before production. This step can reduce risks and save costs by optimizing your design for their manufacturing processes. - Cost Transparency and Quotation
Request detailed quotations that break down all cost components, including fabrication, material costs, and other charges. A manufacturer that provides cost clarity is beneficial for making financial assessments and avoiding surprises. Compare quotes with other manufacturers to ensure you are receiving the most competitive offer. - Customer Support and Communication
Effective communication with the manufacturer is essential for project success. Ensure that they respond to inquiries promptly and provide technical support throughout the production process. A manufacturer that prioritizes customer service is crucial for a smooth collaboration.
Cost Factors in Single Layer PCB Manufacturing
Understanding the cost drivers in single-layer PCB manufacturing is crucial for making informed decisions and selecting a cost-effective manufacturer. This section will break down the various cost components, providing insights into how to balance quality and budget when choosing a single layer pcb manufacturer.
| Cost Component | Description | Influence on Overall Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Material Costs | The cost of the base substrate material (e.g., FR-4, CEM-1), copper foil, and other raw materials used. | Significant. Varies with material type and thickness. |
| Fabrication Charges | Covers the cost of manufacturing processes such as etching, drilling, and solder mask application. | Moderate. Depends on complexity and production volume. |
| Tooling Costs | One-time costs for creating the necessary tools like stencils and drill programs. | Can be significant for low-volume orders; amortized over larger quantities. |
| Surface Finish | The type of plating or finish applied to pads and vias, e.g. HASL, ENIG, Immersion Tin. | Moderate. Depends on the type of finish chosen. |
| Additional Services | Includes testing, electrical inspection, and specialized handling or packaging. | Can add to overall costs, especially with specific requirements. |
| Order Volume | The number of PCBs being produced. Often the most significant factor. | Typically lower per-unit costs at higher volumes, due to economies of scale. |
To optimize costs, consider the following: simplifying designs, using standard materials where possible, consolidating orders, and negotiating with manufacturers for bulk purchases.
Quality Control and Reliability in Single Layer PCB Production
Ensuring the quality and reliability of single-layer PCBs is paramount for the functionality and longevity of electronic devices. Rigorous quality control measures are implemented throughout the manufacturing process, adhering to industry standards to guarantee consistent performance and durability.
Quality control in single-layer PCB manufacturing encompasses several key stages and checks. These include:
- Incoming Material Inspection:
Verification of raw materials like substrates (FR-4, CEM-1), copper foil, and solder mask to ensure they meet the required specifications. This includes checking for thickness, composition, and any defects. - Fabrication Process Monitoring:
Continuous checks during etching, drilling, and plating processes to maintain precision and consistency. Dimensional accuracy of the board, hole sizes, and trace widths are critical parameters. Automated optical inspection (AOI) is often employed to detect any irregularities. - Solder Mask Application and Curing:
Inspection of the solder mask application for proper coverage, alignment, and thickness. The curing process is closely monitored to ensure the mask is fully hardened and adhered correctly to the PCB. - Silk Screen Verification:
Checking the accuracy and legibility of silk screen printing, which includes component designators and other markings crucial for assembly. Alignment with board features is also verified. - Final Electrical Testing:
Electrical tests, such as continuity and isolation tests, to ensure there are no shorts or open circuits. These tests are essential to guarantee that the final PCB is electrically sound and ready for use.
Industry standards such as IPC-A-600 (Acceptability of Printed Boards) are often used as a reference, as well as internal quality standards followed by the manufacturer. These standards provide a framework for acceptable quality levels. Reliability is further enhanced through material selection, precise manufacturing, and comprehensive testing, leading to single layer PCBs that meet stringent functional and durability requirements.
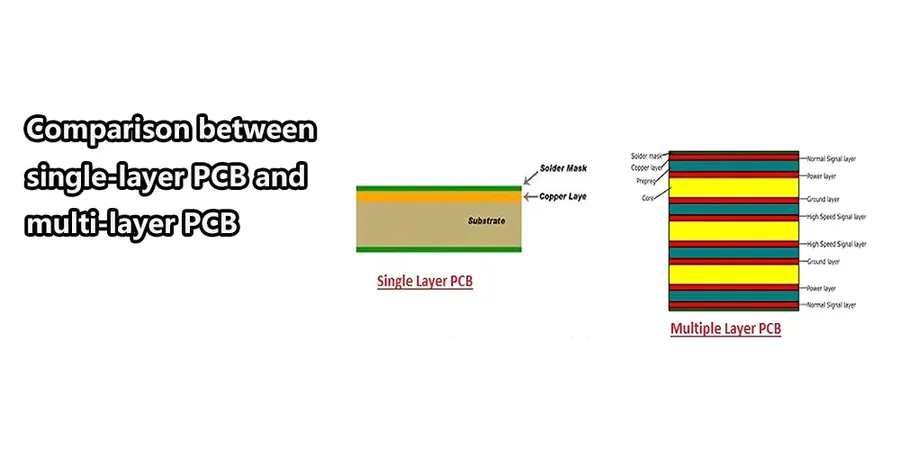
Single Layer PCB Materials: Selection Guide
The selection of materials for single-layer PCBs is crucial, impacting performance, cost, and application suitability. Key considerations include the material's dielectric constant, thermal properties, mechanical strength, and cost. Selecting the appropriate material is a fundamental step when choosing a single layer pcb manufacturer.
| Material | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FR-4 | Fiberglass-reinforced epoxy laminate, a common PCB substrate. | Good balance of mechanical strength, electrical properties, and cost-effectiveness; widely available. | Not suitable for high-temperature applications; relatively higher dielectric loss at high frequencies. | General-purpose electronics, consumer devices, low-frequency circuits. |
| CEM-1 | Composite material made of paper and epoxy resin, often less expensive than FR-4. | Cost-effective; good mechanical strength for basic applications. | Lower thermal resistance and higher moisture absorption compared to FR-4; less durable. | Cost-sensitive applications, non-critical electronics, simple circuits. |
| Aluminum | Aluminum substrate with a thin dielectric layer, suitable for thermal management. | Excellent thermal conductivity for heat dissipation; mechanically robust. | Electrically conductive; requires an insulating layer; more expensive than FR-4. | LED lighting, power electronics, applications requiring heat dissipation. |
| Flexible Substrates (e.g., Polyimide) | Flexible plastic substrates allowing the PCB to bend and flex. | Flexible and lightweight; ideal for dynamic or constrained spaces. | More expensive than rigid substrates; more susceptible to damage. | Wearable electronics, flexible displays, medical devices. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Single Layer PCB Manufacturing
This section addresses common queries regarding single layer PCB manufacturing, providing clear and concise answers to guide your understanding and decision-making process. We delve into aspects ranging from the manufacturing process to cost implications and quality considerations.
- What is the typical manufacturing process for a single layer PCB?
The manufacturing of a single layer PCB involves several key steps: First, a design is created using CAD software and transferred to a copper-clad laminate board. The copper is then etched to form the conductive pathways. After etching, solder mask is applied to protect the copper and finally the component markings are screen-printed. - Are single layer PCBs generally more cost-effective than double-layer PCBs?
Yes, single-layer PCBs are typically less expensive than double-layer PCBs due to their simpler design and fewer manufacturing steps. This translates to lower material costs, reduced processing time, and lower overall production expenses, making them a cost-effective solution for basic electronic applications. - How does the cost of single-layer PCBs compare to multi-layer PCBs?
Single-layer PCBs are significantly cheaper than multi-layer PCBs. Multi-layer PCBs require more complex manufacturing processes, including lamination of multiple layers, which leads to higher material and fabrication costs. Thus, single-layer PCBs are the most economical option for simple circuits. - Who are the largest PCB manufacturers globally, and do they specialize in single-layer PCBs?
While there are many large PCB manufacturers worldwide, many may not specialize primarily in single layer boards due to lower profits. Many specialize in high-density, multilayer boards. However, many regional manufacturers focus on single-layer boards to support local and international demand. It's more important to find a manufacturer with a proven history and experience with single-layer boards rather than focusing on the largest overall manufacturer. Focus your search on your location such as "single layer pcb manufacturer USA" if your products are located in the USA. - What are the best materials for single layer PCBs and which are the most commonly used?
FR-4 is the most common material for single-layer PCBs due to its good balance of cost, mechanical strength, and electrical insulation. Other materials like CEM-1 are sometimes used for cost considerations, while aluminum substrates are used for thermal management. The 'best' material depends on the application's specific requirements. - Are there any specific design rules that are more important for single layer boards than for multi-layer boards?
Yes, track and gap considerations are paramount in single-layer boards. Because there are no internal layers to route traces, you must be meticulous with your layout to reduce crosstalk, and to ensure there is sufficient copper width to carry required current, and sufficient clearance to ensure insulation and safety of the PCB, particularly on high voltage systems. Component placement is also more critical, due to routing being entirely on a single plane. It is also extremely important to perform a design rules check on your final PCB layout. - How do I find the most suitable single layer PCB manufacturer for my project?
To find the best manufacturer, evaluate their experience with single-layer PCBs, material options, manufacturing capabilities, quality assurance processes, lead times, and cost. Getting samples for evaluation and consulting with the manufacturer's team during design phase can significantly help avoid problems during manufacturing.
Comparing Single Layer PCB Manufacturers: A Practical Guide
Selecting the right single layer PCB manufacturer involves a thorough comparison of several critical factors to ensure your project’s success. This section provides a practical guide to help you effectively evaluate and compare potential manufacturers based on price, quality, delivery, and reliability.
| Factor | Description | Evaluation Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Price | Cost per unit, setup fees, and tooling costs. | Obtain detailed quotes, compare unit costs, consider quantity discounts, and identify any hidden charges. |
| Quality | Conformity to standards (IPC Class 2 or 3), material quality, and production accuracy. | Review manufacturer certifications, ask for sample boards, and check for quality control processes. |
| Delivery | Lead times, shipping options, and on-time delivery rate. | Assess lead times against project timelines, review shipping options and costs, and look for a manufacturer with a good track record for on-time delivery. |
| Reliability | Consistency in production quality and ability to meet agreed deadlines. | Check customer reviews, ask for references, and assess the manufacturer’s responsiveness to queries. |
| Manufacturing Capabilities | Range of services offered (e.g., surface finish options, assembly, testing). | Assess whether their capabilities align with your project needs and future scalability. |
| Communication | Clarity of communication and responsiveness of the manufacturer. | Gauge their responsiveness during the quoting process and look for clear communication channels. |
By systematically evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision, selecting a single layer PCB manufacturer that best fits your project's requirements for quality, cost, and time-to-market.
Future Trends and Innovations in Single Layer PCB Technology
The single layer PCB sector, while seemingly basic, is experiencing significant advancements driven by demands for enhanced performance, miniaturization, and sustainability. Innovations in materials, manufacturing techniques, and applications are shaping the future landscape of single-sided printed circuit boards, requiring single layer PCB manufacturers to adapt and innovate.
- Advanced Material Usage
Beyond traditional FR-4, manufacturers are exploring materials like flexible substrates, biodegradable options, and composites with enhanced thermal and electrical properties. These materials enable lighter, more robust, and environmentally friendly PCBs. - Additive Manufacturing Techniques
3D printing and other additive methods are emerging as alternatives to traditional subtractive processes, offering potential for rapid prototyping, customized designs, and reduced material waste in single layer PCB production. - Embedded Components
Integrating components directly into the substrate of the PCB allows for higher density designs and reduces the overall size of electronic devices. This also improves reliability and reduces the need for surface mounting - Smart PCBs
Adding sensors, microprocessors, and communication components to single-layer PCBs makes them suitable for a range of applications including IoT devices and environmental monitoring. - Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Processes
There is a growing emphasis on sustainable manufacturing, including the use of eco-friendly chemicals, water-based processes, and improved waste management systems. These advancements seek to lessen the environmental impact of PCB production. - High-Density Interconnect (HDI) Techniques
While typically associated with multilayer PCBs, HDI methods are being adapted for single-layer boards. This allows for greater circuit density and finer trace widths on a single layer.
Working with a Single Layer PCB Manufacturer: Tips for Success
Establishing a successful partnership with a single layer PCB manufacturer hinges on clear communication, meticulous planning, and a mutual understanding of project requirements. This section provides actionable tips to ensure a streamlined collaboration from initial design to final product delivery, emphasizing the importance of a strong working relationship.
- Clearly Define Project Specifications:
Provide detailed specifications including PCB dimensions, material requirements, component placement, and any specific performance criteria. Use standardized formats such as Gerber files to ensure accuracy and reduce interpretation errors. This upfront clarity will reduce misunderstandings and iterative design loops. - Engage in Open Communication:
Maintain open and frequent communication with the manufacturer throughout the production process. Regularly check in for updates and address any potential issues or concerns proactively. This constant feedback loop helps to make sure that any problems are dealt with before production is finalized. - Understand Manufacturing Capabilities:
Be sure the chosen manufacturer has the facilities and equipment to meet your needs and tolerances. This includes verifying the manufacturer’s minimum trace width and spacing, drill sizes, and material options to prevent costly re-design later. Confirm capabilities with sample boards or past projects. - Plan for Lead Times and Delivery Schedules:
Discuss and finalize production lead times and delivery schedules with the manufacturer early in the process. Account for potential delays in component sourcing or fabrication processes. Buffer times are crucial to mitigate project hold-ups. - Establish Quality Control Expectations:
Clearly outline quality control standards and testing protocols with the manufacturer. Ensure that the manufacturer adheres to industry standards such as IPC-A-600 for PCB quality. This minimizes product defects and enhances performance. - Review and Test Samples Thoroughly:
Request and test prototype samples from the manufacturer before proceeding to mass production. Thoroughly review these samples for compliance with design specifications and performance criteria. This step is imperative to correct any discrepancies before bulk orders. - Document All Agreements:
Formalize all agreements with the single layer PCB manufacturer including pricing, lead times, quality standards, and warranty terms in a written contract. Documented agreements will avoid any future ambiguity and make a more professional working environment.
Choosing the right single layer PCB manufacturer requires careful consideration of various factors including manufacturing capability, quality, cost, and communication. Armed with this comprehensive understanding, you'll be well-equipped to partner with a reliable single layer pcb manufacturer that can meet your project’s needs. Remember to prioritize communication, understand the manufacturing process, and select a manufacturer who can provide consistent, high-quality single layer PCBs. Consider future trends to ensure your chosen manufacturer is equipped to handle your ongoing project needs.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA