Finding the Best PCB Maker: A Comprehensive Guide
In today's world of rapid technological advancement, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the backbone of almost every electronic device, powering everything from smartphones to complex industrial machinery. Choosing the right PCB maker is critical to ensuring the success of your project, impacting factors like quality, cost, and delivery time. This article guides you through selecting the best PCB maker by analyzing top manufacturers, offering a comprehensive comparison, and focusing on what matters most in a fabrication partner, ensuring you can bring your designs to life with the best PCB maker for your specific needs.
Understanding Your PCB Needs

Before embarking on the selection of a PCB manufacturer, a comprehensive understanding of your project's specific requirements is paramount. This initial step ensures that the chosen manufacturer possesses the necessary capabilities and resources to meet your needs efficiently and effectively. A well-defined set of requirements is crucial for successful PCB fabrication and project outcomes.
A clear understanding of your project needs translates to a more streamlined manufacturing process, reducing the risk of errors, delays, and unexpected costs. By addressing these elements upfront, you establish a strong foundation for effective communication with potential PCB makers and facilitate a smooth transition from design to final product.
- PCB Type
Determine whether your project requires single-sided, double-sided, or multi-layer PCBs. Each type has different complexity and manufacturing requirements, impacting cost and lead time. - Material Specifications
Specify the required materials (e.g., FR-4, aluminum, flex). Material choices influence performance characteristics, such as temperature resistance, mechanical strength, and signal integrity. - Dimensions and Size
Define the precise dimensions and size of the PCB. This specification is critical for production and ensures proper fit within your electronic device. - Complexity
Assess the complexity of the design, including the number of components, trace density, and via count. Highly complex designs require manufacturers with advanced technological capabilities. - Quantity Requirements
Determine whether you need prototypes, small batches, or high-volume production. Different manufacturers specialize in different production volumes, impacting costs and lead times. - Prototyping Needs
Identify if you need prototype PCBs for initial testing before large-scale production. Prototyping is critical to confirm design and functional specifications. - Specialized Requirements
Identify any specialized needs such as impedance control, blind/buried vias, or specific surface finishes. Specialized features increase the complexity and costs of the PCB.
Key Factors When Choosing a PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the right PCB manufacturer is crucial for the success of any electronics project. This decision hinges on several key factors that directly impact the quality, cost, and timeline of your project. A careful evaluation of these factors will ensure that your chosen manufacturer aligns with your specific needs and standards.
- Quality and Reliability
The quality of the manufactured PCB is paramount. It is not just about meeting the specifications, but also about the long term performance of the board. This can be gauged by adherence to industry standards, use of quality materials, and rigorous testing. Look for manufacturers with certifications like ISO 9001. - Cost Effectiveness
Cost is a significant factor, but should not be the sole determinant. Consider the overall value proposition – the balance between price and quality. Transparent pricing structures and a clear understanding of any additional fees is also crucial. Different manufacturers may be more suited to different budgets and project types - Turnaround Time
The time it takes to produce and deliver the boards is critical. Ensure the manufacturer's turnaround time matches your project schedule. This is specially true when multiple iterations or testing is needed. Consider manufacturers that can deliver boards quickly without sacrificing quality. - Customer Support
Good customer support ensures smooth communication and quick resolution of any issues. A responsive and knowledgeable support team can be invaluable, especially for complex designs. This includes the initial quotation, design support, order tracking, and any issue resolutions. - Technological Capabilities
Assess the manufacturer's technology to ensure they can meet the design requirements. This includes aspects such as layer count, via types, minimum trace width/spacing, materials supported and surface finish capabilities. Ensure their capabilities align with your project’s technical demands to ensure your design can be successfully manufactured. - Certifications and Standards
Certifications like ISO 9001 demonstrate a manufacturer's commitment to quality management. These are critical for ensuring reliability and adherence to industry best practices. Manufacturers with certifications can provide additional assurance of quality and consistency of their manufactured PCB's.
Top PCB Manufacturers: A Detailed Comparison
Selecting the right PCB manufacturer is crucial for the success of any electronics project. This section provides a detailed comparison of leading manufacturers, focusing on their pricing, capabilities, and special features. By evaluating these options, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your specific project requirements and budget, ensuring you get the best possible results from prototyping to high volume production. We will be focusing on some of the most popular manufacturers in the industry.
| PCB Maker | Price | Turnaround Time | Quality | Special Features | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JLCPCB | Low | Fast | Good | Wide range of options, cost-effective | Prototypes and small production runs |
| PCBWay | Mid | Medium | Good | Good support, advanced capabilities, more complex boards | Larger projects with more complexity |
| OSH Park | Higher | Longer | Great | Focus on high quality, smaller boards | Smaller, high-quality boards |
| Seeed Studio Fusion | Mid to High | Medium | Good | Strong prototyping capabilities, open-source friendly | Prototyping and small to medium batch production |
| Eurocircuits | High | Medium to Long | Excellent | High-reliability, specialized materials and technologies, advanced PCBs | Professional, high-reliability, industrial or aerospace projects |
PCB Maker Comparison Table
Selecting the right PCB manufacturer is crucial for the success of any electronics project. This section provides a detailed comparison of some of the top PCB makers, focusing on their pricing, turnaround time, quality, special features, and ideal use cases. The aim is to help users make informed decisions based on their specific project needs and constraints.
| PCB Maker | Price | Turnaround | Quality | Special Features | Best Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| JLCPCB | Low | Fast | Good | Wide range of options, SMT assembly service | Prototypes and small to medium-sized production runs, cost-sensitive projects. |
| PCBWay | Mid | Medium | Good | Good support, advanced capabilities, diverse material options. | More complex projects requiring advanced features, larger production runs, and a range of materials. |
| OSH Park | Higher | Longer | Great | Focus on high-quality small boards, purple solder mask. | Small, high-quality boards, projects where precision and quality are paramount |
| AllPCB | Competitive | Medium | Good to High | Assembly services available, various special material choices. | Projects that need assembly services and various types of PCB |
| Seeed Studio Fusion | Mid-Range | Medium | Good | Assembly and design services, one stop shop. | Projects that need design, assembly, and manufacturing |
PCB Manufacturing for Hobbyists vs. Professionals

The selection of a PCB manufacturer is heavily influenced by whether the intended application is for hobbyist projects or professional products. These two categories differ significantly in their needs, priorities, and acceptable trade-offs, which in turn dictate the optimal type of PCB maker. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for making informed decisions.
| Feature | Hobbyist Projects | Professional Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Primary concern; seeks affordable options | Important, but balanced with quality and reliability |
| Ease of Use | User-friendly interface and ordering process preferred | May prioritize technical capabilities over user experience |
| Quality | Good enough for prototyping and personal projects | High quality, precision, and adherence to standards essential |
| Turnaround Time | Often flexible; longer lead times acceptable | Fast turnaround times critical for production and deadlines |
| Advanced Capabilities | Basic features and capabilities are often sufficient | Advanced features, custom materials, and specialized finishes often required |
| Industry Standards | Less emphasis on certifications and industry standards | Strict adherence to ISO and other industry standards is mandatory |
| Volume | Typically low volume, often single prototypes or small runs | Ranges from small batch to high volume production depending on product needs |
Some PCB manufacturers cater primarily to one category, while others offer services suitable for both. For instance, manufacturers with budget-friendly pricing and easy-to-use platforms are popular among hobbyists, while those with advanced capabilities, stringent quality controls, and certifications are favored by professionals. It's important to select a PCB maker based on the specific requirements and goals of each project.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Makers
Selecting the right PCB manufacturer often raises several questions. This section addresses common inquiries to help you make informed decisions, drawing upon industry trends and best practices.
- Who is the Best PCB Manufacturer for My Needs?
The 'best' PCB manufacturer is subjective and depends heavily on your project's requirements. Factors such as budget, required quality, turnaround time, and the complexity of your design should all be considered. For example, JLCPCB is often favored for cost-effective prototyping, while PCBWay is preferred for more complex, medium-sized projects. OSH Park, while more expensive, caters to high-quality small-batch orders. Consider your specific project requirements to identify the best match. - Which PCB Manufacturer Offers the Best Value for Money?
Value is not just about low price but also quality and service. JLCPCB is frequently lauded for its cost-effectiveness, particularly for prototyping and small-batch orders. However, for more complex projects with specific needs, manufacturers such as PCBWay may offer a better overall value despite higher prices, due to their advanced capabilities and better support. Always compare the total cost, including shipping and potential extra charges, to find the best balance between price and value. - Who is the Largest PCB Manufacturer in the World?
Identifying the 'largest' PCB manufacturer can vary depending on the criteria used, such as revenue or manufacturing volume. However, companies such as Samsung Electro-Mechanics, Unimicron, and TTM Technologies are often cited as being among the largest in the global market, demonstrating significant production capabilities and global reach. - Which PCB Design Software is Recommended?
The 'best' PCB design software depends on your experience level and project needs. For beginners, software such as EasyEDA (web-based) or KiCad (open-source) can be excellent entry points due to their accessibility and ease of use. For professional use, software like Altium Designer or OrCAD may be more suitable due to their advanced features and capabilities, as they offer more control and features suitable for more complex projects. - What are the Key Certifications to look for in a PCB Manufacturer?
Key certifications indicate a manufacturer’s adherence to quality standards. ISO 9001 certification is crucial, demonstrating a company’s commitment to quality management. For certain industries, certifications such as ISO 13485 (medical devices) or IATF 16949 (automotive) might be necessary. Always review a manufacturer's certifications to confirm they meet industry requirements. - What are the typical lead times for PCB Manufacturing?
Lead times vary depending on the complexity of the board, the manufacturer, and the selected shipping method. For standard two-layer boards, a manufacturer like JLCPCB may offer quick turnaround times as short as a few days. More complex multilayer boards may take longer, and factors such as holidays or demand can cause delays. Always factor in an extra buffer for lead times, especially for tight deadlines. Confirm with the manufacturer about their specific timelines for a specific project. - How can I assess the quality of a PCB Manufacturer before placing an order?
Assessing a manufacturer’s quality before ordering is vital. Look for customer reviews and testimonials, and ask for sample boards if possible. Some manufacturers provide a photo or video of completed boards, which can offer a good indication of their quality standards. Always start with a small sample batch to properly evaluate their manufacturing process, quality, and the communication efficiency.
Optimizing Your PCB Design for Manufacturing
Optimizing a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) design for manufacturability (DFM) is crucial to prevent production issues, reduce costs, and ensure timely delivery. This involves adhering to specific design rules and guidelines that align with the capabilities of the chosen PCB manufacturer. Properly addressing DFM considerations from the outset will avoid potential redesigns and delays.
- Trace Width and Spacing
Ensure trace widths and spacing meet the manufacturer's minimum specifications. Inadequate spacing can lead to shorts, while overly thin traces can cause high resistance and potential failures. - Via Design
Appropriately sized and placed vias are essential for multilayer PCBs. Avoid placing vias too close together or too close to pads and traces. Consider using microvias when possible to minimize PCB area use. - Drill Sizes
Select drill sizes that are compatible with the manufacturer's tools, and are as large as possible to decrease manufacturing costs. Avoid using very small drill sizes whenever possible, as they can be more prone to breakage and require special tooling. - Component Placement
Position components to allow for easy assembly and soldering, this may require creating some distance between some components. Ensure sufficient clearance around components for automated pick-and-place machines and avoid placing components too close to the board's edge or fiducial markers. Follow your PCB manufacture's recommendations. - Solder Mask and Silk Screen
Verify that the solder mask clearance is appropriate and does not overlap with pads. Use clear, legible silkscreen markings, avoiding overlaps with pads, vias, or other board features. - Pad Design
Ensure pads have correct shapes and sizes according to the manufacturer's capabilities. Adhere to the datasheet for each component. Improper pads can lead to poor solder joints. - Panelization
If designing for panelization, verify if this service is needed. Plan the panel layout to maximize the number of PCBs per panel while following the manufacturer's rules, which should include the distance between boards and panel edges. - Board Outline
Define the board outline accurately and in the correct file format. Use clean lines, without overlaps or irregularities, while also taking into account the manufacturer's tolerances.
By adhering to these DFM principles, engineers can greatly reduce the risk of manufacturing defects, delays, and added costs. Consulting with the chosen PCB manufacturer early in the design process can also help identify potential issues before production begins.
The Future of PCB Manufacturing
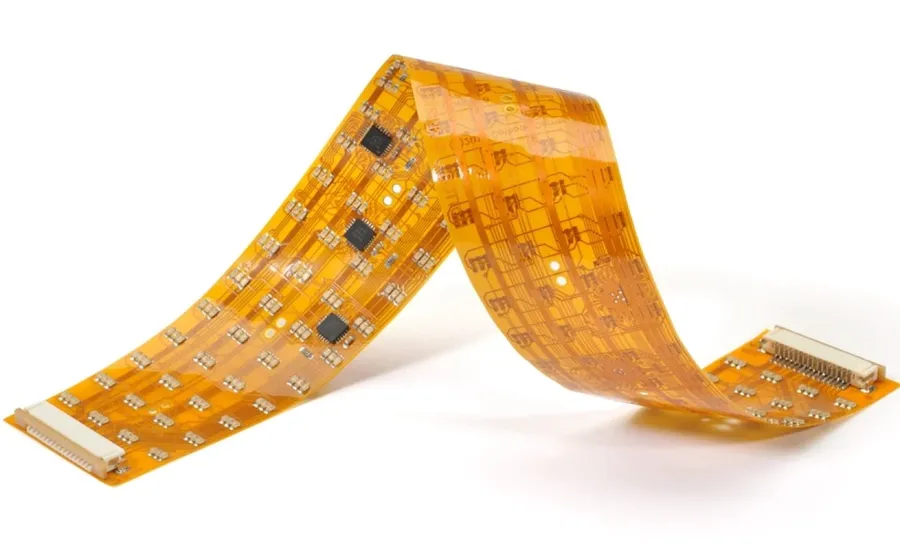

The printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing landscape is undergoing significant transformation driven by technological advancements and evolving market demands. Emerging trends promise to revolutionize how PCBs are designed, produced, and utilized, paving the way for more efficient, flexible, and environmentally conscious electronics.
- Flexible PCBs
Flexible PCBs, constructed from bendable substrates, are gaining traction due to their ability to conform to complex shapes and enable miniaturization. This technology is vital for applications such as wearable technology, automotive electronics, and medical devices, where space and flexibility are paramount. - Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
3D printing is beginning to play a role in PCB manufacturing, allowing for rapid prototyping and the creation of highly customized boards. This method offers the potential for more intricate designs, reduced material waste, and faster production cycles, moving beyond traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. - Eco-Friendly Practices
Sustainability is a growing focus in PCB manufacturing, with increasing emphasis on eco-friendly materials and production methods. This includes the use of biodegradable substrates, lead-free soldering, and closed-loop water systems, aiming to reduce the environmental impact of electronics manufacturing. - High-Density Interconnect (HDI) PCBs
The relentless push for smaller, more powerful electronic devices drives advancements in HDI PCB technology. These boards feature extremely fine lines, vias, and small component footprints, enabling higher densities and improved performance. The utilization of microvias, advanced materials, and precise manufacturing methods are key to this trend. - Embedded Components
Embedding components directly within the PCB layers offers increased miniaturization, improved signal integrity, and enhanced thermal management. This technique involves incorporating passive components, integrated circuits, and other functional elements into the substrate, leading to more compact and efficient electronic systems.
Real-World Case Studies and Examples
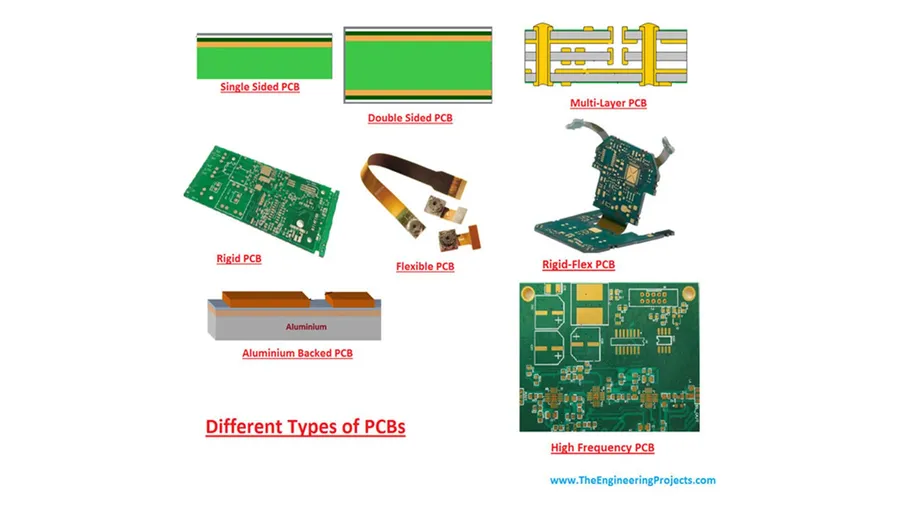
Examining real-world case studies provides invaluable insights into the practical implications of selecting a particular PCB manufacturer. These examples demonstrate how different PCB makers perform under diverse project requirements, highlighting both the benefits and potential drawbacks of each.
- Case Study 1: Rapid Prototyping with JLCPCB
A small electronics startup needed a quick turnaround for a prototype of a wearable device. JLCPCB's low cost and fast delivery times allowed them to iterate through multiple design revisions within a short timeframe. However, they noted that for their final high-volume production, they opted for a manufacturer that could offer more stringent quality control processes. - Case Study 2: Complex Multilayer Board with PCBWay
A research team required a highly complex, multilayer PCB for a medical device project. PCBWay's advanced capabilities and experienced support team were instrumental in navigating the design challenges. They benefited from PCBWay's ability to handle intricate trace patterns and specific material requirements, even though the cost was higher than some alternatives. - Case Study 3: High-Quality, Small Batch PCBs with OSH Park
An engineer working on high-precision audio equipment needed a small number of very high-quality PCBs. OSH Park's focus on quality control, although at a higher price and slower turnaround, resulted in a product that met their stringent requirements. The consistent quality provided by OSH Park was critical for the project's success. - Case Study 4: Cost-Effective Mass Production
A company producing consumer electronics required large quantities of a relatively simple double-sided PCB. They explored several manufacturers, balancing cost, lead time and quality, finally partnering with a large manufacturer in China capable of mass production, ultimately prioritizing cost reduction. While the quality was acceptable, they had to implement a rigorous in-house quality check. - Case Study 5: A Failure Example
A new business chose a very cheap manufacturer. The result was long delays, multiple boards arriving broken, and other not working at all due to poor quality control. This highlights the risk of prioritizing price over reliability. This company had to redo the entire manufacturing process, costing them valuable time and resources.
Selecting the best PCB maker is a critical step in bringing your electronic designs to life. By understanding your specific needs, carefully evaluating the top manufacturers, and optimizing your design for manufacturability, you can ensure high-quality, cost-effective production. The best PCB maker, whether JLCPCB or another provider, aligns with your project's unique demands, resulting in successful and efficient production, highlighting the importance of a strategic approach to PCB fabrication.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA