Finding the Right Aluminum PCB Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide
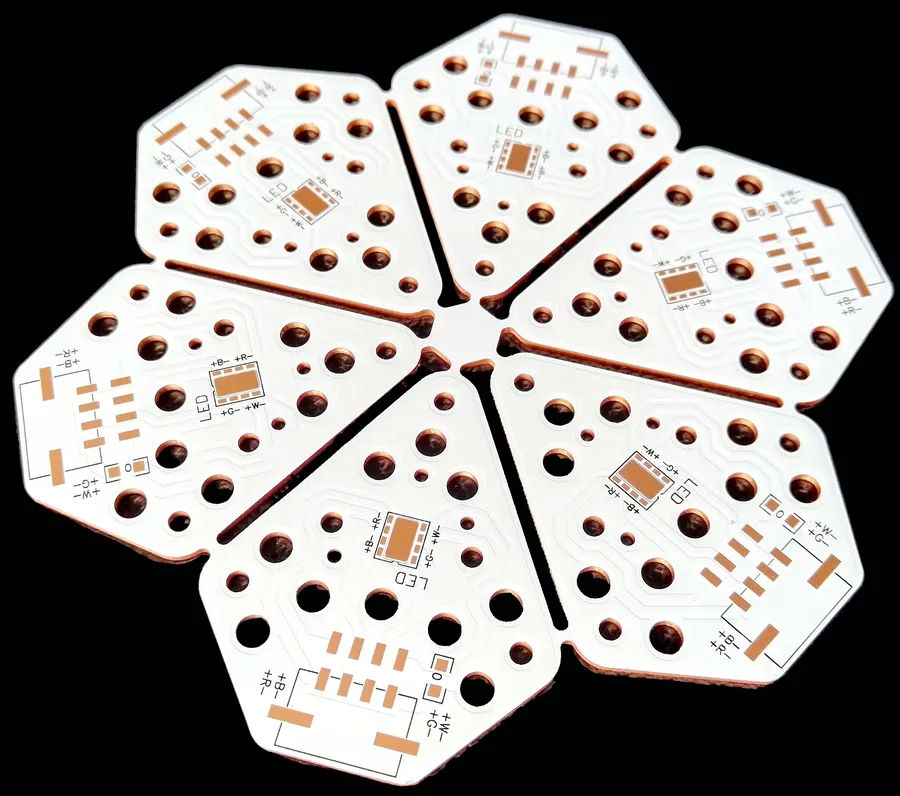
In today's fast-paced electronics industry, effective thermal management is crucial. Aluminum PCBs, known for their superior heat dissipation capabilities, have become a go-to solution. This guide will help you navigate the world of aluminum PCB manufacturers, providing essential information for making the best choice for your project, and highlighting why working with a reliable aluminum PCB manufacturer is critical for success. We'll explore the benefits, considerations, and key aspects to evaluate when selecting a manufacturer.
Understanding Aluminum PCBs: Why Choose Metal Core?

Aluminum PCBs, distinguished by their metal core, offer significant advantages over traditional FR4 (Flame Retardant 4) boards, primarily in thermal management, durability, and operational longevity. The choice of aluminum stems from its superior ability to dissipate heat, which is crucial in high-power and high-temperature applications where maintaining optimal operating temperatures is paramount for performance and reliability.
- Superior Thermal Dissipation
Aluminum boasts a thermal conductivity significantly higher than FR4, enabling efficient heat transfer away from components, preventing overheating and ensuring stable performance. - Enhanced Durability
The robustness of aluminum provides excellent mechanical strength, making it less prone to damage from vibrations, shocks, and thermal cycling, extending the operational life of the PCB. - Effective Heat Spreading
Aluminum's ability to spread heat across its surface is vital for even heat distribution, avoiding hot spots and improving the overall thermal efficiency of the assembly. - Extended Component Lifespan
By effectively managing heat, aluminum PCBs help prevent thermal stress on components, leading to increased reliability and a prolonged lifespan. - Dimensional Stability
Aluminum's low coefficient of thermal expansion ensures better dimensional stability, reducing the risk of warping and mechanical stress during temperature fluctuations.
Key Factors When Selecting an Aluminum PCB Manufacturer
Selecting the right aluminum PCB manufacturer is critical for ensuring the quality, reliability, and performance of your electronic devices. This section details the essential factors to consider when evaluating potential partners, focusing on their experience, certifications, production capabilities, and quality control processes to ensure you choose a manufacturer who can consistently meet your specific requirements.
- Experience and Expertise
A manufacturer's experience in producing aluminum PCBs is paramount. Look for a company with a proven track record and a portfolio demonstrating their capabilities in handling diverse projects. Evaluate their longevity in the industry, which often reflects their accumulated knowledge and reliability. - Certifications and Compliance
Ensure the manufacturer holds relevant certifications like ISO 9001, ISO 14001, and IATF 16949 (for automotive applications), indicating adherence to international standards for quality management, environmental responsibility, and automotive quality systems. These certifications ensure the manufacturer's commitment to consistent process control and continuous improvement. - Production Capabilities
Assess the manufacturer’s technological capabilities. They should possess advanced equipment for precision manufacturing, including capabilities for various processes such as etching, drilling, surface finishing and multilayer PCB fabrication. The manufacturer should also offer a range of material options to suit different thermal and mechanical requirements. - Quality Control Processes
Robust quality control measures are essential to guarantee the reliability and consistency of aluminum PCBs. The manufacturer should have stringent testing protocols, including in-process inspections, electrical tests, and final quality checks. This will ensure that your PCB will meet the required design specifications. - Material Selection
A key indicator of a capable manufacturer is their material sourcing and handling process. They should offer a variety of core thicknesses, insulation materials, and copper weights with full transparency about the materials used and their properties, allowing you to select the optimum materials for your application. - Lead Times and Delivery
Efficient production planning and delivery are crucial, especially for time-sensitive projects. Evaluate a manufacturer's ability to provide realistic lead times and their adherence to delivery schedules. This capability reflects the manufacturer’s resource management and operational effectiveness. - Communication and Support
Effective communication and responsiveness are essential for smooth project management. The manufacturer should have a dedicated support team to address queries, provide technical assistance and offer design for manufacturing feedback. Good communication prevents misunderstandings and allows for quick resolution of any challenges.
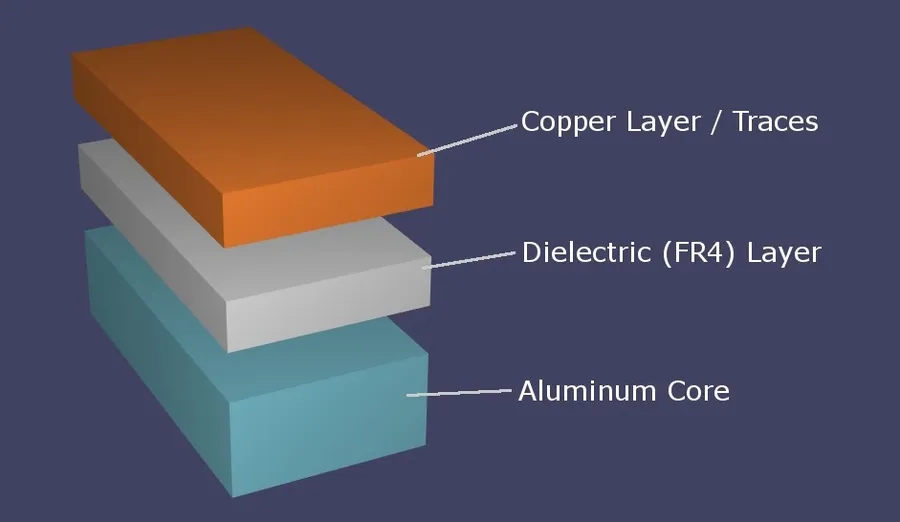
Aluminum PCB Materials and Stack-up
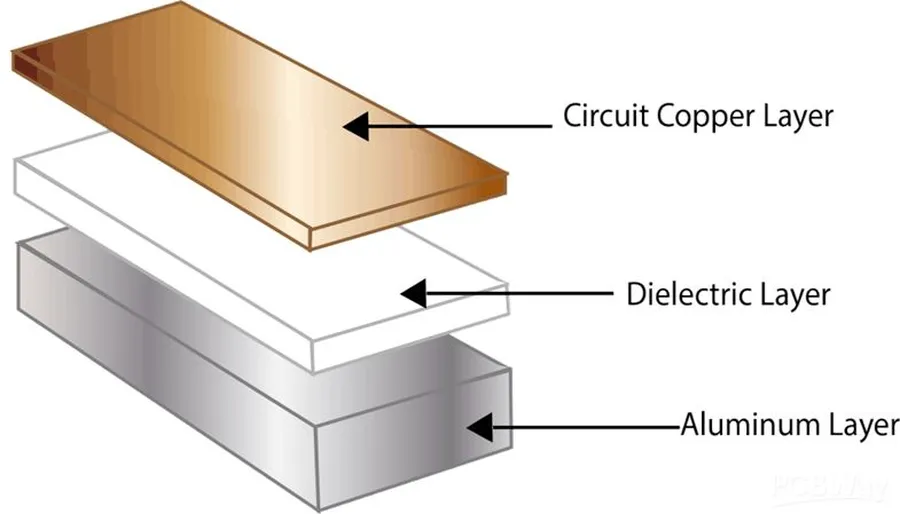
The performance and reliability of an aluminum PCB are significantly influenced by the materials and their stack-up. This section delves into the critical components, including the aluminum substrate, insulation layers, and copper foil, and examines how their arrangement affects the overall functionality and thermal management capabilities of the PCB.
Understanding these aspects is crucial for designing and selecting the appropriate PCB for your specific application.
| Material | Description | Typical Thickness | Key Property |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Substrate | The core layer providing structural support and primary heat dissipation. | 0.5mm - 3mm | High thermal conductivity, mechanical strength |
| Dielectric Layer | An electrically insulating layer between the aluminum base and the copper layer. It ensures electrical isolation while also enabling thermal transfer. | 50µm - 200µm | Electrical insulation, thermal conductivity |
| Copper Foil | Conductive layer used for circuitry. Typically laminated onto the dielectric layer. | 18µm - 70µm | Electrical conductivity, signal integrity |
Single-layer aluminum PCBs have a straightforward construction, consisting of a single conductive layer on top of the dielectric and aluminum substrate. Multilayer aluminum PCBs feature multiple copper layers separated by dielectric layers, providing more complex circuit designs and increased component density. The choice between single or multilayer depends on the complexity and performance requirements of the application.
The key parameters are:
- Substrate Thickness
The thickness of the aluminum base significantly impacts the PCB's mechanical rigidity and heat dissipation capability. Thicker substrates provide better thermal performance but also add weight and cost. - Insulation Layer Material
The material of the dielectric layer should have a high thermal conductivity and good electrical insulation properties. Materials like thermally conductive epoxies and ceramics are common choices. - Copper Layer Thickness
Copper foil thickness determines the current carrying capacity of the traces. Higher current applications require thicker copper to prevent overheating and voltage drops. - Thermal Conductivity
The overall thermal conductivity of the stack-up is critical for effective heat transfer. The choice of materials and the thickness of each layer will affect the overall thermal conductivity of the PCB.
Manufacturing Process Overview: From Design to Delivery

The manufacturing of aluminum PCBs is a multi-stage process that transforms a digital design into a physical product. This process requires precision and adherence to strict quality control measures to ensure the final product meets the design specifications and performance requirements. The journey encompasses design review, material preparation, fabrication, testing, and final delivery.
- Design Review and Preparation
The initial stage involves a comprehensive review of the PCB design files (Gerber files, etc.) to ensure manufacturability and identify potential issues. This includes checking for minimum trace widths, clearances, and via sizes, which are critical for aluminum PCBs due to their unique material properties. Adjustments may be necessary to optimize the design for aluminum substrates. Key factors in design review include thermal management considerations which are often prioritized due to the nature of aluminum PCB applications. - Material Selection and Preparation
Aluminum PCB manufacturing begins with the careful selection of the base materials. This consists of an aluminum core, typically an aluminum alloy, insulation layer (dielectric material), and copper foil. The chosen materials are prepared with precision and cut to size based on the required design. The aluminum core thickness is carefully determined by thermal management requirements. The chosen dielectric material needs to ensure the appropriate electrical isolation while facilitating heat dissipation and it has to be compatible with the subsequent processes. - Circuit Imaging and Etching
The copper foil is laminated onto the prepared aluminum substrate and dielectric layer. The circuit pattern is then transferred onto the copper layer using a photoresist process. The PCB is then exposed to UV light to harden the desired pattern. Following this, the unprotected copper is removed through chemical etching, leaving the desired circuit paths. - Drilling and Plating
Holes for vias and component mounting are precision drilled using high-accuracy equipment. To ensure electrical connections between layers, especially in multi-layer designs, the drilled holes are then plated with a conductive material, typically copper. - Solder Mask and Silkscreen Application
The solder mask is applied to protect the circuit traces and prevent solder bridging during the assembly process. Following this, a silkscreen layer is applied, providing component identification and polarity markings. The solder mask is a critical step for ensuring long-term reliability of the PCB. - Surface Finishing
A surface finish is applied to the exposed copper pads. Common surface finishes include HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and others. The choice of finish depends on factors such as cost, performance requirements, and application specifics. ENIG offers excellent solderability and protection against oxidation but comes at a higher cost compared to HASL. - Electrical Testing and Quality Control
Completed PCBs undergo rigorous electrical testing using automated testing equipment. This involves continuity testing, insulation resistance testing, and other tests to ensure the circuits are working correctly and meet design specifications. Visual inspection and mechanical checks are carried out to identify any physical defects. Quality control is a critical step in aluminum PCB manufacturing due to the complex interactions between materials and processes. - Profiling and Final Inspection
The final step involves profiling the board, this involves cutting the PCB from the panel, typically using CNC routing or laser cutting, to achieve the final shape and dimensions. After profiling the board, final inspection is performed to ensure that each PCB meets the quality standards before shipping. - Packaging and Delivery
The finished PCBs are carefully packed using protective materials to prevent damage during shipping. Proper packaging and handling are necessary to maintain the product's integrity during transportation and storage. Attention is paid to ESD protection, and moisture barriers. PCBs are shipped in accordance with customer requirements
Cost Considerations for Aluminum PCB Manufacturing
The cost of aluminum PCB manufacturing is influenced by several key factors, including the complexity of the design, material selection, production volume, and any additional services required. Understanding these cost drivers is crucial for effective budget planning and achieving cost-efficient PCB production.
| Cost Factor | Description | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type & Thickness | The type and thickness of the aluminum substrate, insulation layer, and copper foil. | Higher thermal conductivity materials and thicker substrates increase cost. |
| PCB Layer Count | The number of copper layers in the PCB design. | Multi-layer PCBs are significantly more expensive than single-layer. |
| PCB Size & Complexity | The overall dimensions of the PCB and the complexity of the circuit design. | Larger and more complex designs demand more materials and processing time, resulting in higher cost. |
| Production Volume | The quantity of PCBs ordered. | Higher production volumes generally lead to lower unit costs due to economies of scale. |
| Surface Finish | The type of surface finish applied (e.g., HASL, ENIG, OSP). | More advanced finishes such as ENIG are more expensive. |
| Drilling and Routing | The number and complexity of holes and the routing pattern. | Complex drilling and routing patterns increase processing time and costs. |
| Testing & Inspection | The level of testing and inspection required. | Comprehensive testing adds cost but ensures quality and reliability. |
| Lead Time | The time required to manufacture and deliver the PCBs. | Shorter lead times may incur additional charges for expedited manufacturing. |
| Additional Services | Services such as design assistance, impedance control, and special packaging. | Additional services increase the total cost. |
Aluminum PCB Applications in Different Industries
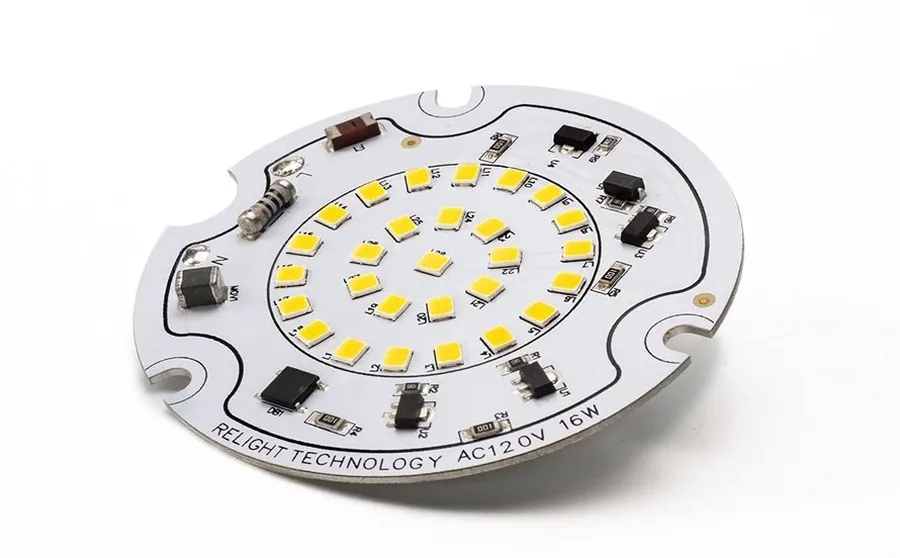

Aluminum PCBs, with their superior thermal management capabilities and durability, have found widespread use across diverse industries. Their ability to effectively dissipate heat makes them ideal for applications where thermal control is critical, leading to increased reliability and performance of electronic devices.
- LED Lighting
Aluminum PCBs are extensively used in LED lighting due to their excellent heat dissipation, which is crucial for the longevity and efficiency of LEDs. They help maintain a lower operating temperature, preventing premature failure and ensuring consistent light output. The thermal conductivity of aluminum allows for the efficient transfer of heat away from the LEDs, which can generate significant heat during operation, increasing lifespan and performance. This is why they are widely used in applications like street lighting, automotive lighting, and display backlights. - Automotive
In the automotive industry, aluminum PCBs are favored for their robustness and ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions. They are used in various applications such as engine control units (ECUs), power steering systems, and lighting systems. The ability of aluminum PCBs to withstand vibrations and thermal cycling makes them suitable for challenging automotive environments. They provide a stable platform for the electronic components, enhancing reliability and performance in demanding driving conditions. - Power Electronics
Power electronics applications, such as power converters, inverters, and motor drives, benefit from the high thermal conductivity of aluminum PCBs. These devices generate significant heat during operation, and effective heat management is essential to prevent overheating and maintain reliability. Aluminum PCBs help dissipate the heat efficiently, allowing these power electronics devices to operate at optimal temperatures. This helps to improve the efficiency and reliability of the systems. - Medical Devices
Medical devices also benefit from the properties of aluminum PCBs. Their use in medical equipment that requires precision and reliability such as imaging equipment, diagnostic tools, and patient monitoring systems, is important. The thermal stability of aluminum PCBs ensures the accuracy of the sensitive electronic components within the equipment, while the robust nature of the board material ensures a long lifespan and reliability. Aluminum PCBs offer a stable, reliable and thermally robust solution for complex medical electronic needs. - Other Industries
Beyond these major sectors, aluminum PCBs are also employed in aerospace, telecommunications, and industrial control systems, where their thermal properties and durability offer significant advantages. In aerospace, they are chosen due to the light weight of aluminum and the need for robust thermal management. In telecommunications, aluminum PCBs are used in high-powered network equipment, and in industrial control, they provide reliable operation in harsh environments. This versatility highlights the diverse benefits of aluminum PCBs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Aluminum PCBs
This section addresses common questions regarding aluminum PCBs, providing clarity on their applications, advantages over FR4, thermal management strategies, and supplier selection.
- What are the primary advantages of using aluminum PCBs?
Aluminum PCBs excel in thermal management due to aluminum's high thermal conductivity, effectively dissipating heat and improving component reliability. They also offer superior mechanical stability and durability compared to FR4 boards, making them suitable for harsh operating environments. - In what applications are aluminum PCBs most effective?
Aluminum PCBs are particularly beneficial in applications with high power densities or significant heat generation, such as LED lighting, power electronics, automotive systems, and medical devices. Their thermal management capabilities ensure long-term performance and reliability of the circuit. - How does thermal management in aluminum PCBs compare to traditional FR4 PCBs?
Aluminum PCBs offer significantly better thermal management because of the high thermal conductivity of aluminum. FR4, a common PCB substrate, is an insulator and has a much lower thermal conductivity. Aluminum's ability to dissipate heat efficiently reduces component operating temperatures, enhancing lifespan and performance. This advantage can eliminate the need for external heat sinks in some applications. - What is the difference between single-layer and multi-layer aluminum PCBs?
Single-layer aluminum PCBs feature a single conductive layer on an aluminum substrate, ideal for simpler designs with lower circuit density, often used in lighting and low-power applications. Multi-layer aluminum PCBs are more complex and provide multiple copper layers separated by insulating materials, suitable for high-density circuits with advanced functions. Multi-layer PCBs benefit from the same improved thermal properties as single-layer boards. The specific requirements of an application should drive the choice between a single-layer or multi-layer design. - Are there any limitations to using aluminum PCBs?
While aluminum PCBs offer numerous advantages, they typically have a higher cost compared to FR4 boards, particularly for complex designs. They may also not be suitable for high-frequency applications because of limitations of their dielectric properties in high-frequency ranges. Additionally, the design considerations for aluminum PCBs may be more specialized, necessitating expert knowledge in PCB design and fabrication. - What considerations should I have when selecting an aluminum PCB manufacturer?
When choosing a manufacturer for aluminum PCBs, key factors include their experience with aluminum substrates, certification, manufacturing capabilities, and quality control processes. It is essential to assess their capacity to handle the required thermal management and design complexities. Also, checking for references and customer reviews is highly recommended before making a decision. - How does the cost of aluminum PCBs compare to FR4 PCBs?
Aluminum PCBs are generally more expensive than FR4 PCBs due to the cost of materials and the specialized manufacturing processes required. However, in applications where thermal management is critical, the higher cost is justified by the improved reliability and performance of aluminum PCBs and may result in cost savings due to improved product life.
Aluminum PCB vs. FR4: A Comparative Analysis
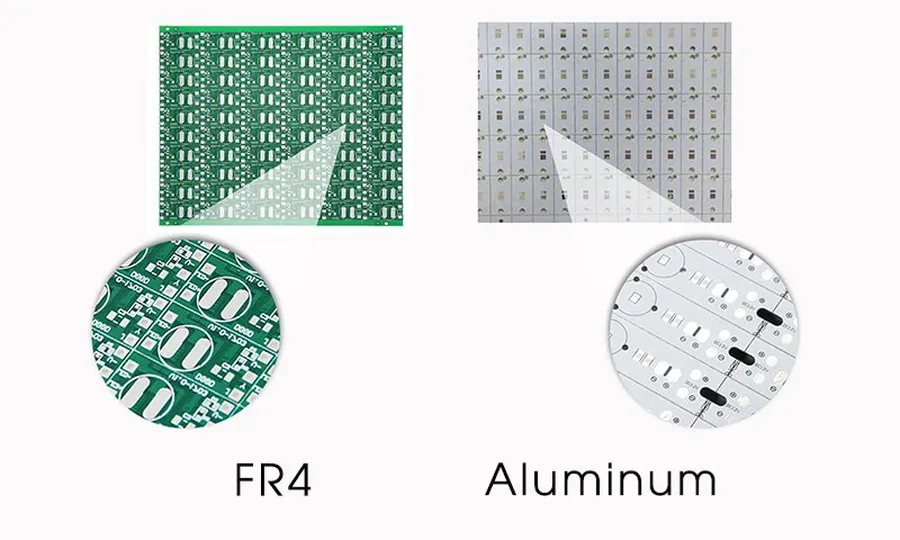
This section provides a direct comparison between aluminum PCBs and traditional FR4 PCBs, highlighting the key performance metrics and differentiating factors to aid in material selection. Aluminum PCBs excel in thermal management, while FR4 remains a cost-effective standard for general-purpose applications. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for engineers to choose the appropriate material for specific requirements.
| Feature | Aluminum PCB | FR4 PCB |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity | High (typically 1-2 W/m·K for dielectric layer, 200 W/m·K for Aluminum Base) | Low (0.2-0.3 W/m·K) |
| Heat Dissipation | Excellent | Poor |
| Operating Temperature | Up to 150°C | Up to 130°C |
| Mechanical Strength | Good (Rigid) | Moderate (Rigid to Flexible) |
| Durability | High, but Aluminum layer can be more susceptible to damage if exposed. | Moderate |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Weight | Moderate to high | Moderate |
| Layer Count | Primarily Single-sided to Double sided | Multilayer |
| Applications | LED lighting, Power electronics, High thermal applications | General Electronics, Consumer products |
| Machinability | Good, but requires specific tooling. | Excellent |
Working with an Aluminum PCB Manufacturer: Key Questions to Ask
Selecting the right aluminum PCB manufacturer is crucial for ensuring the quality and success of your project. This section provides a list of key questions to ask potential manufacturers to assess their capabilities and suitability for your specific needs. Proactive questioning can help avoid common pitfalls and ensure a smooth production process.
- What is your experience with aluminum PCB manufacturing?
Inquire about the manufacturer's track record with aluminum PCBs, specifically focusing on the types of projects they've handled and their history with similar applications. Experience indicates a better understanding of the unique challenges of aluminum PCB production. - Can you provide details on your material sourcing and supply chain?
Understanding the manufacturer's material sourcing helps determine the quality of raw materials used, such as aluminum substrates and dielectric materials. A robust and reliable supply chain minimizes delays and ensures consistent material quality. - What are your quality control and testing procedures?
Ask about the quality control measures implemented at different stages of the manufacturing process. Thorough testing procedures such as impedance testing, thermal stress testing, and AOI (Automated Optical Inspection) are crucial to identify and mitigate potential defects. - What is your standard lead time for aluminum PCB production?
Inquire about the typical turnaround time for manufacturing aluminum PCBs, considering factors like material availability and production capacity. Understanding lead times is essential for project planning and avoiding costly delays. - Can you provide samples of previously manufactured aluminum PCBs?
Requesting samples allows you to physically inspect the manufacturer's work, assessing the quality of the finished product, precision of fabrication, and adherence to specifications. Samples provide tangible evidence of capability. - What are your capabilities for various aluminum PCB stack-ups and finishes?
Confirm their proficiency with the specific stack-up you require (single-layer, multi-layer), as well as capabilities for different surface finishes, such as HASL, ENIG, and others. This ensures they can meet the design specifications of your project. - What is your approach to communication and project management?
A clear and reliable approach to project management and communication is crucial. Understand how they handle project updates, address issues, and ensure they are responsive to your inquiries, to minimize the risk of misunderstanding and delays.
Future Trends in Aluminum PCB Technology
The aluminum PCB industry is in constant evolution, driven by the need for higher performance, better thermal management, and cost-effectiveness. Several trends are emerging that promise to significantly impact the design and manufacturing of aluminum PCBs. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of what's possible, opening up new applications and improving existing ones.
- Novel Materials and Substrates
Research into new aluminum alloys and composite materials is ongoing to improve thermal conductivity, mechanical strength, and overall performance. These new materials aim to achieve better heat transfer and durability at higher operating temperatures. - Advanced Thermal Designs
Beyond material improvements, advanced thermal designs such as embedded heat pipes, integrated heatsinks, and micro-channel cooling are being explored. These designs focus on localized heat removal, allowing for more efficient and compact solutions. - Innovative Manufacturing Methods
New manufacturing technologies like 3D printing, laser direct structuring (LDS), and advanced surface treatment are gaining traction. These techniques promise reduced lead times, better precision, and the ability to create complex geometries for customized thermal solutions. - Integration of Smart Functionality
The integration of sensors and other intelligent components directly into the aluminum PCB is a rising trend. This enables real-time monitoring of temperature, stress, and other parameters, which can enhance reliability and predictive maintenance capabilities. - Miniaturization and High-Density Designs
The push towards miniaturized electronic devices is driving the need for higher density designs in aluminum PCBs. This includes finer trace widths, closer spacing of components, and increased layer counts, all while maintaining effective thermal management. - Eco-Friendly Manufacturing
Sustainability is becoming a priority, leading to increased interest in eco-friendly manufacturing methods and materials. This includes reducing waste, minimizing the use of hazardous chemicals, and optimizing energy consumption during production.
Choosing the right aluminum PCB manufacturer is crucial for the success of any project requiring superior thermal management. By understanding the key considerations discussed in this guide, you can confidently select a partner that will deliver high-quality, reliable aluminum PCBs tailored to your specific needs. When selecting an aluminum PCB manufacturer, remember that experience, certifications, and customization options are the key factors that will guarantee high quality PCBs for your business, and will lead to project success. Working with a reliable aluminum PCB manufacturer is an investment in the success of your electronic applications.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA