Quick Guide to Prototype PCB Quotes: Get the Best Price

In today's rapidly evolving tech landscape, getting a precise prototype PCB quote is crucial for turning innovative ideas into tangible products. Whether you're a hobbyist or an established firm, understanding the factors influencing your quote is the key to budget-friendly and effective prototype development. This guide breaks down everything you need to know about obtaining a prototype PCB quote, connecting the complex world of PCB fabrication to your project's success, while highlighting the ease of access now available.
Understanding the Factors Affecting Your Prototype PCB Quote

The cost of a prototype Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is not fixed; it is a function of several key parameters related to the board's design, materials, and manufacturing process. These elements interact to determine the final quote, making it essential to understand their influence for effective cost management.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | The base material of the PCB, such as FR-4, aluminum, or polyimide. | Higher performance materials typically increase cost. |
| Board Size | The dimensions of the PCB, often measured in square inches or millimeters. | Larger boards require more material and processing, increasing cost. |
| Layer Count | The number of conductive layers within the PCB. | More layers add complexity and cost due to additional processing and materials. |
| Surface Finish | The final coating applied to the PCB, like ENIG, HASL, or OSP. | Precious metal finishes (ENIG) are more expensive than other options (HASL). |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Features like via size, trace width, and component density. | Finer features require more precise and expensive manufacturing processes, increasing costs. |
| Production Time | The turnaround time for production, from order placement to delivery. | Faster turnarounds may incur extra fees due to expedited production and shipping. |
Online PCB Quote Calculators: An In-Depth Comparison

Online PCB quote calculators are indispensable tools for obtaining rapid pricing estimates for prototype printed circuit boards. These platforms, offered by numerous PCB manufacturers, allow users to input their design specifications and receive instant quotes, streamlining the procurement process. This section provides a comparative analysis of these calculators, focusing on their features, usability, and effectiveness in generating accurate pricing.
| Feature | Platform A | Platform B | Platform C |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ease of Use | Intuitive, clear interface | Slightly complex, requires some navigation | Simple, streamlined design |
| Specification Options | Comprehensive, allows many customizations | Limited options, may not suit complex designs | Good selection, covers most standard specs |
| Quote Accuracy | Highly accurate, transparent breakdown | Reasonably accurate, some deviations noted | Generally accurate, within acceptable ranges |
| Real-time Adjustments | Allows for on-the-fly changes, real time updates | Requires recalculating after every change | Offers limited real-time adjustment |
| Supported File Formats | Gerber, Eagle, KiCAD | Gerber only | Gerber, Altium |
| Additional Services (e.g., Assembly) | Provides instant quotes for assembly | Limited or no assembly quotes | Assembly quotes available but not instant |
| Customer Support | Responsive and helpful, detailed documentation | Moderate response time, limited FAQs | Good support via chat and email |
The effective use of online PCB quote calculators hinges on the precise input of design specifications. Ensure that you have finalized all key parameters such as board dimensions, layer count, material type, copper thickness, solder mask color, and surface finish before using the calculator to obtain the most accurate quote. The ability to directly upload design files (such as Gerber files) significantly enhances accuracy, minimizes errors, and reduces the need for manual data entry.
Key Specifications That Impact PCB Pricing
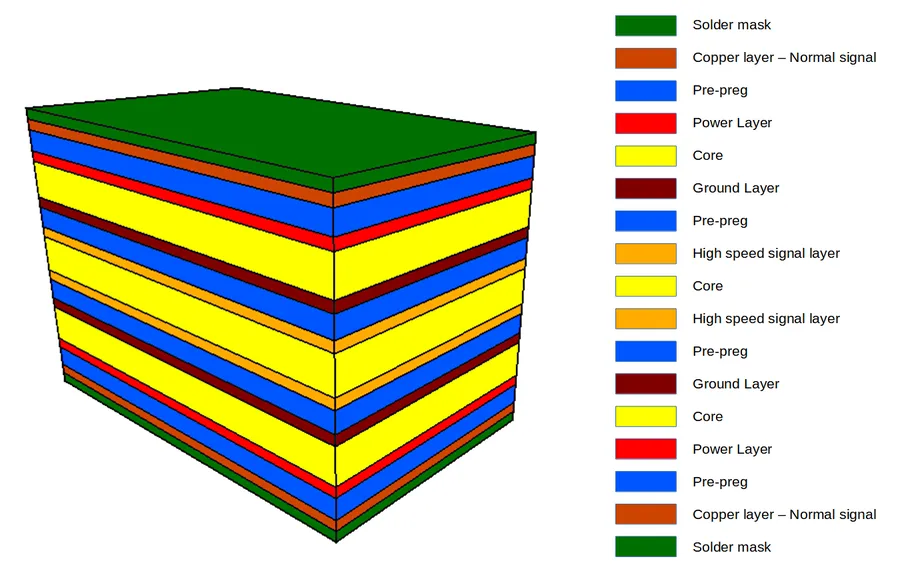
The cost of a prototype PCB is not fixed; it fluctuates based on several design and manufacturing specifications. Understanding how these parameters affect pricing allows for more informed decisions, helping to control costs effectively during the prototyping phase. This section details the critical specifications influencing the final quote.
| Specification | Impact on Cost | Example of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Board Dimensions | Directly proportional; larger boards require more material and processing. | Increasing board size from 50mm x 50mm to 100mm x 100mm could double the material cost. |
| Number of Layers | Increased complexity and cost with more layers due to additional processing and material. | A two-layer board is significantly cheaper than a four-layer or six-layer board. |
| Material Type (e.g., FR-4, Aluminum) | Varies by material cost and its specific performance properties. | FR-4 is cost-effective; aluminum PCBs for thermal management are more expensive. |
| Copper Thickness | Thicker copper increases cost due to more material usage. | Moving from 1oz copper to 2oz copper can add a small percentage to the cost. |
| Solder Mask Color | Standard colors like green are usually cheaper, while custom colors increase costs due to setup time. | Choosing a non-standard color like yellow or blue will likely increase the price. |
| Surface Finish (e.g., HASL, ENIG) | ENIG is more expensive than HASL due to the use of gold and more complex processing. | Upgrading from HASL to ENIG can increase cost by 10-20%. |
| Drill Hole Size and Number | Smaller drill holes and higher density drilling increase costs due to greater precision requirements. | Many small vias versus fewer large through-hole can be more expensive |
Navigating Lead Times and Production Speed for Prototype PCBs

Lead time, the duration between placing an order and receiving the finished PCBs, significantly influences the cost of prototype PCB fabrication. Understanding the trade-offs between standard production and expedited services is crucial for effective project management and cost control.
| Production Type | Typical Lead Time | Cost Implications | Appropriate Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Production | 1-2 weeks | Lower cost per unit, more economical for larger prototype runs and non-urgent projects. | Projects with flexible deadlines, initial prototypes for concept validation. |
| Quick-Turn Production | 2-5 business days | Higher cost per unit, faster turnaround for time-sensitive projects. | Projects with tight deadlines, iterative design changes, urgent testing needs. |
| Expedited Services | 24-48 hours | Highest cost per unit, extremely rapid turnaround for critical projects. | Projects encountering critical delays, urgent troubleshooting, and immediate validation requirements |
Choosing the appropriate lead time depends on your project’s specific needs. Standard production is suitable for projects with flexible timelines and a need for cost-effectiveness. Quick-turn services are essential when time is of the essence, enabling rapid design iterations and shorter feedback loops. Expedited services offer the fastest turnaround, crucial for projects facing critical delays and requiring immediate validation or testing.
The cost implications of production speed are straightforward: faster turnaround times necessitate higher costs. This is due to manufacturers allocating resources and prioritizing specific orders, thereby increasing production expenses. When deciding on a production speed, it’s crucial to evaluate the budget and schedule constraints carefully to optimize project outcomes and manage costs efficiently. Remember that cost savings with standard lead times may come at the expense of project timelines, while faster lead times require a financial trade-off. Therefore, consider both your budget and deadlines when deciding on your production speed.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Prototype Quotes
Understanding the costs associated with prototype PCB fabrication is crucial for effective project planning and budget allocation. This section addresses common queries regarding PCB prototyping costs, providing clarity and estimated pricing ranges to assist in your decision-making process.
- How much does it cost to prototype a PCB?
The cost of prototyping a PCB varies widely based on several factors, including the board's complexity (layer count, size), material, finish, and the manufacturer chosen. Simple, single- or double-layer PCBs might start at a few dollars per board for small quantities, while more complex multi-layer boards with specific requirements can cost significantly more, possibly ranging from tens to hundreds of dollars per board, especially when ordering small batches. Prices also depend on the chosen turnaround time and whether assembly is included. It’s important to get quotes from multiple manufacturers for accurate pricing, and to understand your boards’ specific requirements before requesting a quote. - How much should I charge for PCB design?
Charging for PCB design involves considering factors like complexity, time investment, and experience level. For simple designs, hourly rates may range from $30 to $75, while complex multi-layer designs could command rates from $75 to $150+ per hour. Flat-fee pricing is also used, especially for large, more predictable projects, ranging from a few hundred to several thousand dollars. The final cost depends on the specific requirements of the project, the PCB’s complexity, and the designer's expertise. - What is a PCB prototype?
A PCB prototype is a preliminary version of a printed circuit board created to validate a design before mass production. It serves as a testing platform to identify and resolve any design flaws, ensuring the final product functions correctly and meets performance criteria. Prototypes are typically produced in small quantities and may be subject to adjustments based on testing results, with the aim of optimizing the design before committing to larger manufacturing runs. - How much does it cost to get a PCB assembled?
The cost to assemble a PCB depends on the number of components, the complexity of the assembly, the type of components (surface mount vs. through-hole), and whether the components are provided by the client or the assembler. Surface mount assembly is generally more cost-effective for large quantities, while through-hole assembly might be preferred for prototypes or low volume runs. Costs can range from a few cents to several dollars per component, adding up to a total cost that can vary from a few dollars to hundreds of dollars per assembled board. It's crucial to consider labor costs, setup fees, and testing charges when evaluating assembly quotes. - What factors most influence the cost of a PCB prototype?
The primary cost drivers for PCB prototyping are the number of layers, board size, material type, copper thickness, surface finish, solder mask color, and production turnaround time. More layers mean more complexity and higher material costs. Larger boards require more material, also increasing costs. Using materials other than standard FR-4, such as aluminum or high-Tg laminates, can also impact costs. Expedited turnaround times, or quick-turn services, often come with a premium charge. Thus, to optimize cost, it’s critical to carefully select and balance these specifications while meeting functional requirements. - Are there ways to reduce prototype PCB costs without sacrificing quality?
Yes, there are several methods to reduce costs without compromising quality. Standardizing PCB sizes and using common materials can help. Optimizing the design for manufacturability (DFM) can reduce production costs. Choosing cost-effective surface finishes and solder mask colors can also lower costs. Consolidating orders with the same manufacturer and planning in advance to avoid quick-turn services can further reduce expenses. Consider these options alongside your requirements to optimize your budget while maintaining the required performance and durability.
Choosing the Right PCB Manufacturer: A Checklist

Selecting the ideal PCB manufacturer is crucial for ensuring the quality, cost-effectiveness, and timely delivery of your prototype PCBs. A thorough evaluation of potential partners is essential, focusing on several key criteria beyond just the lowest price.
- Experience and Expertise
Evaluate the manufacturer's track record in producing prototype PCBs. Look for experience with the specific technologies and materials relevant to your project. An experienced manufacturer is more likely to anticipate potential issues and provide effective solutions. - Manufacturing Capabilities
Confirm that the manufacturer has the necessary equipment and processes to meet your project's requirements. This includes the ability to handle your desired board size, layer count, material types, and tolerances. - Customer Service and Support
Assess the responsiveness and helpfulness of the manufacturer's customer service team. Prompt and effective communication is crucial throughout the prototyping process, particularly when unexpected issues or questions arise. - Pricing Structure
While price is a significant factor, don't solely prioritize the cheapest option. Compare quotes while accounting for the quality of materials, manufacturing precision, and lead times offered. A balance between cost and quality is paramount. - Quality Assurance Processes
Inquire about the manufacturer’s quality control procedures. Do they conduct inspections at various stages of the production process? Look for ISO certifications or similar quality standards compliance. - Lead Times and Production Speed
Evaluate the manufacturer's typical lead times for prototype production. Consider whether they offer expedited services or quick-turn options if your project has stringent timelines. However, ensure quick turnarounds are balanced with quality assurance. - Reviews and Testimonials
Seek out customer reviews and testimonials to gain insight into the manufacturer's reputation and service quality. Real-world experiences can help you make a well-informed decision. Pay attention to feedback concerning both manufacturing quality and customer interactions.
Tips for Reducing Your Prototype PCB Costs
Reducing the cost of prototype PCBs is crucial for project feasibility and budget management. Strategic design choices, material selection, and vendor negotiation can significantly lower your expenses. By carefully considering these factors, you can achieve cost-effective prototyping without compromising quality.
- Optimize Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Adhering to DFM principles during the design phase is critical. This includes using standard component sizes and spacing, minimizing the number of unique parts, avoiding complex geometries, and ensuring sufficient clearance for automated assembly. These changes reduce manufacturing time and increase yield, decreasing the final cost. - Panelization Strategies
Whenever possible, panelize multiple PCBs into one manufacturing array. This method reduces handling costs and overall material use, which can significantly impact the price per board for smaller prototypes. - Standard Material Selection
Opting for standard materials like FR-4 instead of more exotic alternatives reduces costs significantly. Unless you have a specific requirement, using common laminate materials can lower material expenses and simplify the manufacturing process. - Layer Count Optimization
Reducing the number of layers in your PCB design directly impacts cost. Each layer adds to the manufacturing complexity and material use. Carefully assess your design requirements to determine the minimum number of layers necessary to fulfill your functional requirements. - Surface Finish Selection
Choosing the appropriate surface finish can also affect costs. ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) is a high-end finish, while HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling) is more cost-effective. Evaluate your application requirements to determine if a more economical finish can be used. - Negotiate with Vendors
Don't hesitate to negotiate with PCB manufacturers, especially if you are ordering in larger quantities or have a repeat project in the works. Vendors often provide discounts for larger orders or long-term partnerships. Establish a good working relationship to explore cost-saving opportunities. - Avoid Rush Orders
Expedited manufacturing always carries a premium. Plan your project timeline to avoid needing quick-turn services, allowing manufacturers more time to process your order efficiently and economically. - Leverage Bundle Packages
Many PCB manufacturers offer discounted bundles or packages that include assembly or stencil production. If applicable to your project, look into utilizing these to reduce the combined cost of PCB fabrication and assembly. - Early Vendor Engagement
Involving your chosen PCB manufacturer early in the design process can prevent costly mistakes and enable them to suggest cost-saving measures specific to their capabilities. Their expertise can help you refine your design to be both effective and inexpensive.
The Future of PCB Prototyping: Emerging Trends and Innovations

The landscape of PCB prototyping is continuously evolving, driven by the demand for faster, more efficient, and cost-effective solutions. Emerging trends are focused on advanced materials and innovative fabrication techniques, promising significant improvements in both performance and production timelines, which will reshape how we approach PCB design and manufacturing in the near future.
- Advanced Materials
The development of new materials, such as flexible substrates, ceramic composites, and enhanced polymers, is enabling PCBs to achieve higher thermal conductivity, improved signal integrity, and greater mechanical flexibility. These materials are expanding the possibilities for applications in diverse sectors, including aerospace, automotive, and wearable electronics. - Additive Manufacturing
3D printing techniques are revolutionizing PCB prototyping by allowing for the direct fabrication of circuit boards. This approach bypasses traditional subtractive methods, offering faster turnaround times, reduced waste, and the ability to create complex three-dimensional circuit structures. 3D printing technology is gradually becoming more precise and affordable, presenting an alternative for small-batch and highly customized PCB fabrication. - AI and Machine Learning in Design
Artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms are being applied to PCB design and layout optimization. AI-powered tools can automatically generate optimized layouts based on predefined constraints, ensuring maximum signal integrity and efficient use of space. This not only accelerates the design process but also helps to reduce errors and design flaws, leading to higher-quality PCB prototypes and, ultimately, lower costs. - Eco-Friendly Manufacturing Processes
Growing environmental concerns are driving a shift toward more sustainable PCB manufacturing practices. Innovations include the use of biodegradable materials, water-based and low-VOC coatings, and recycling techniques for recovered metals, minimizing the environmental impact of PCB fabrication and reducing waste. These sustainable approaches align with the goals of responsible engineering and circular economy principles. - Integration of Embedded Components
New methods are emerging for integrating active and passive components directly within the PCB structure, leading to smaller, more compact designs. The incorporation of passives, heatsinks, and other components directly into the PCB, results in higher performance, greater density, and more compact finished products. This trend towards integrated components allows for more efficient designs and reduces overall component count.
Obtaining a prototype PCB quote might seem daunting, but understanding the contributing factors and utilizing the available online tools can streamline the process. By focusing on clear specifications, considering both your project needs and vendor capabilities, you can secure a great prototype PCB quote. Ultimately, the cost-effective fabrication of your prototype PCB represents a significant step in your product development lifecycle, moving your concept from design to reality. Remember to use the tools and resources available, and you’ll be well on your way to seeing your innovative ideas take physical form.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA