Selecting the Right MCPCB Manufacturer: A Comprehensive Guide
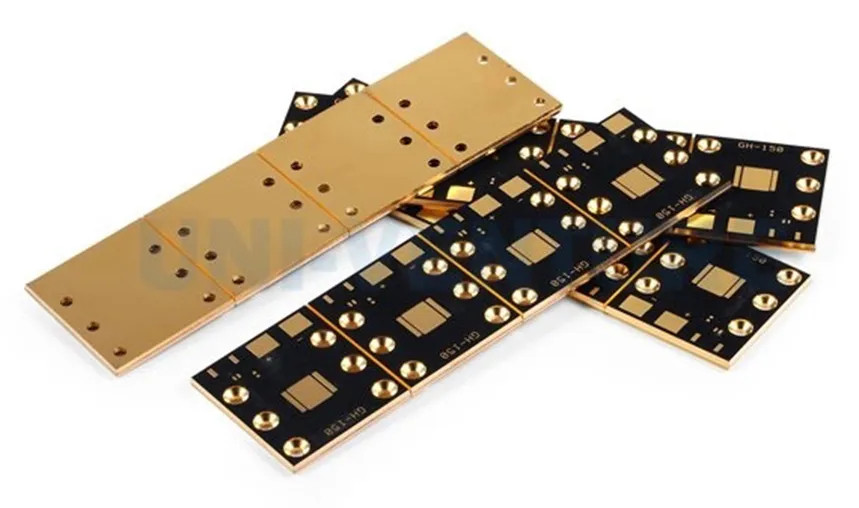
In today's electronic landscape, efficient thermal management is critical, and Metal Core PCBs (MCPCBs) play a vital role. These boards, often built by specialized mcpcb manufacturers, are crucial for applications needing high heat dissipation. From LEDs to power electronics, understanding how to choose the right MCPCB manufacturer can significantly impact performance and reliability. This article will guide you through selecting the ideal partner, focusing on key criteria and insights to ensure your project's success.
Understanding Metal Core PCBs (MCPCBs)

Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) are specialized PCBs designed to efficiently dissipate heat, a critical requirement for high-power electronic applications. Unlike standard PCBs constructed from fiberglass-reinforced epoxy (FR-4), MCPCBs utilize a metal base, typically aluminum or copper, to conduct heat away from sensitive components, thereby enhancing the reliability and longevity of electronic devices.
The fundamental distinction between MCPCBs and standard PCBs lies in their construction and thermal management capabilities. Standard PCBs, with their FR-4 substrate, offer good electrical insulation but poor thermal conductivity. In contrast, MCPCBs leverage the high thermal conductivity of metal to provide a pathway for heat to escape, preventing component overheating. This makes MCPCBs indispensable in applications where high power densities and heat generation are significant concerns.
- Key Structural Components
MCPCBs typically consist of three primary layers: a metal base (usually aluminum or copper), a dielectric layer, and a copper foil layer for circuitry. The metal base provides mechanical support and thermal conductivity; the dielectric layer insulates the circuitry from the metal base and the copper foil facilitates electrical connections. - Thermal Management Role
The primary function of MCPCBs is thermal management. By effectively dissipating heat, these boards prevent components from exceeding their maximum operating temperatures, ensuring optimal performance and preventing premature failure. This is particularly crucial in applications such as LED lighting, power supplies, and automotive electronics, where heat generation is significant. - Applications of MCPCBs
MCPCBs find applications across various sectors, including LED lighting (where they are crucial for maintaining light output and longevity), automotive electronics (for managing heat in high-power modules), power electronics (for efficiently dissipating heat from power transistors and other heat-generating components), and industrial applications (for robust thermal management in harsh environments). Their ability to handle high power densities makes them invaluable in these areas.
Key Materials Used by MCPCB Manufacturers

The performance and application of Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) are heavily influenced by the materials used in their construction. Primarily, aluminum and copper are favored for their excellent thermal conductivity, but their specific properties impact the final product's suitability for diverse applications. Selecting the appropriate material is a critical step in the MCPCB design process, directly impacting thermal management, cost, and weight.
| Property | Aluminum | Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) | Typically 200-240 (can be alloy dependent) | 385-400 |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Weight | Lighter | Heavier |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good (with proper surface treatment) | Excellent |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | Good |
| Typical Applications | General lighting, LED modules, power supplies | High-power LED lighting, high-frequency circuits, high heat dissipation applications |
While aluminum is cost-effective and lighter, offering a good balance of thermal performance for many applications, copper excels in thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for higher-performance MCPCBs. However, copper's increased weight and cost must be factored into design considerations.
MCPCB Manufacturing Capabilities and Technology

MCPCB manufacturing demands specialized processes and technology due to the unique nature of metal substrates. These processes significantly impact the thermal performance, reliability, and overall quality of the final product. A deep understanding of these capabilities is crucial for selecting a competent MCPCB manufacturer.
Key aspects of MCPCB manufacturing technology include:
- Layer Types
MCPCBs can be single-layer, double-layer, or multi-layer. Single-layer MCPCBs feature circuitry on one side of the metal core, while double-layer MCPCBs have circuitry on both sides, and multi-layer builds provide the most complex circuits. The choice depends on the application's thermal and electrical demands. - Lamination Techniques
Lamination is the process of bonding the dielectric material and copper foil to the metal core. Specialized techniques are required to ensure strong adhesion and consistent thermal performance. Key lamination methods include using pressure-sensitive adhesives or thermally conductive bonding films. - Surface Finish Options
Various surface finishes, such as HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling), ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold), and immersion tin, are available. The appropriate surface finish selection is critical for ensuring solderability and preventing corrosion. - Precision Requirements
MCPCB manufacturing requires high precision to accurately align and pattern layers, especially in multi-layer designs. This involves precision drilling, laser direct imaging, and etching processes to ensure high quality and precise circuit features. - Thermal Management Techniques
Manufacturers employ thermal management techniques such as thermal vias, which are drilled and plated holes that conduct heat from the components to the metal core, enhancing heat dissipation. Techniques to enhance heat transfer to the metal core include using thermally conductive materials and specialized design layouts. - Material Processing Technology
The technology used to process core materials is also very important, the metal core is difficult to handle, the manufacturer needs to have mature cutting, drilling and other technologies. - Automated Assembly
Automated assembly lines are used for efficient and precise placement of components, reducing manual errors and ensuring high throughput for MCPCB production.
It is essential for manufacturers to have a robust understanding of these aspects to deliver high-quality MCPCBs that meet the thermal and electrical demands of various applications. Furthermore, the adoption of advanced manufacturing methods can significantly enhance the reliability and performance of MCPCBs.
Evaluating MCPCB Manufacturer Quality Control
Rigorous quality control is paramount when selecting an MCPCB manufacturer, directly impacting the reliability and performance of the final product. This involves not only adherence to recognized industry standards but also implementation of thorough testing protocols throughout the manufacturing process.
A crucial aspect of quality control is the adoption of relevant certifications. ISO 9001 certification indicates that the manufacturer has implemented a robust quality management system that consistently meets customer and regulatory requirements. In addition, UL certification, particularly UL 796 for printed wiring boards, demonstrates compliance with stringent safety standards, which is often critical for products intended for electrical applications. Manufacturers should provide records of these certifications to demonstrate the reliability of their processes and products.
Testing should cover multiple areas, including material quality, layer adhesion, thermal performance and electrical properties. This can involve visual inspections, electrical testing with flying probe testers or bed-of-nails fixtures and thermal cycling tests to stress the MCPCB under extreme conditions. Manufacturers should also maintain statistical process control and conduct failure analysis as part of their ongoing quality improvement efforts. The consistency of the manufacturing process should also be documented, demonstrating stable fabrication techniques that yield products with minimal variation and high reliability.
The importance of robust testing procedures cannot be overstated; these procedures must encompass both individual MCPCB performance and adherence to specifications. The manufacturer should be able to provide comprehensive test reports as validation of their quality control efforts. This not only ensures the reliability of the product but also offers valuable insights into the manufacturer's quality culture.
Factors Influencing MCPCB Pricing
The cost of Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) is influenced by a combination of design, material, manufacturing, and logistical factors. Understanding these cost drivers is crucial for optimizing budgets and achieving cost-effective production.
- Design Complexity
Intricate designs with multiple layers, fine traces, and complex layouts demand advanced manufacturing processes, leading to higher costs. The number of vias, board size, and component density also contribute to design complexity. - Material Choices
The type of metal core (typically aluminum or copper), its thickness, and the dielectric material significantly impact the final price. Materials with higher thermal conductivity, such as copper, generally come with a premium. Similarly, specialized dielectric materials can increase the unit cost. - Manufacturing Volume
Economies of scale play a vital role in MCPCB pricing. Larger production runs typically reduce the per-unit cost due to optimized setups, reduced material waste, and efficient process utilization. Prototyping and small batch orders come at a higher relative price. - Turnaround Time
Rush orders or expedited turnaround times will result in increased production costs. The rapid scheduling and increased resource allocation required to meet expedited deadlines drives up per unit costs. - Surface Finish
The chosen surface finish has a major impact on the final product cost. Finishes like ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) or hard gold, while offering superior performance, will command a higher price than HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling). - Testing Requirements
Complex and extensive testing requirements that include specific electrical, thermal, or mechanical validations will increase the cost. Automated test equipment or specialized jigs and fixtures contribute to the total price.
To achieve cost-effective MCPCB manufacturing, consider the following:
- Optimize Design for Manufacturability
Simplify your design where possible to reduce production complexity. Opt for larger trace widths, standard via sizes, and streamlined layouts. - Choose Appropriate Materials
Select materials based on required thermal performance, balancing cost with application needs. Consider aluminum core MCPCBs as a more affordable alternative to copper core boards if feasible. - Plan for Sufficient Lead Time
Avoid rush orders by planning production well in advance. Longer lead times allow manufacturers to schedule production more efficiently, reducing your costs. - Bulk Orders
Consolidate orders, as large quantities are more cost-effective due to economies of scale and reduced setup expenses. - Consult with the Manufacturer
Engage with your chosen manufacturer early in the design phase. Their expertise and insight into manufacturing constraints can help you identify cost-saving design adjustments.
Choosing the Right MCPCB Manufacturer: Key Criteria

Selecting the ideal MCPCB manufacturer requires careful consideration of several crucial factors. These criteria encompass not only the manufacturer's technical capabilities but also their experience, capacity, and commitment to customer support. A thorough evaluation ensures the chosen partner can consistently deliver high-quality MCPCBs that meet specific application requirements.
- Experience in Specific Applications
Prioritize manufacturers with a proven track record in your target industry (e.g., LED lighting, power electronics, automotive). Experience translates to a deeper understanding of application-specific needs and challenges. - Production Capacity and Scalability
Assess the manufacturer's capacity to handle your current volume requirements and their ability to scale up for future needs. Look for consistent production capacity to minimize delays. - Lead Times and Turnaround
Evaluate the manufacturer's typical lead times for MCPCB production, especially for prototypes and urgent orders. Timely delivery is critical to the success of many projects, which has to be consistent with the manufacturer. - Customer Support and Communication
Choose a manufacturer offering reliable communication channels, clear technical support, and proactive problem-solving capabilities. Effective communication is the key to a successful collaboration. - Prototyping Capabilities
Confirm the manufacturer's ability to produce prototypes quickly and cost-effectively. Rapid prototyping is essential for design validation and iterative improvements. - Technical Expertise and Certifications
Evaluate the manufacturer's technical team expertise and the quality system certifications they hold (e.g. ISO 9001). This is crucial for the quality of the product. - Material and Process Capabilities
Ensure they have experience with the materials and manufacturing processes required for your application. Understand their options for materials and finishes.
Frequently Asked Questions about MCPCB Manufacturing
This section addresses common questions regarding Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs), providing clear and concise answers to help clarify their applications, design considerations, and manufacturing aspects.
- What is the primary difference between a standard PCB and an MCPCB?
The fundamental difference lies in the core material. Standard PCBs typically use a non-conductive substrate like FR-4, while MCPCBs incorporate a metal core, usually aluminum or copper, for enhanced thermal dissipation. This metal core allows MCPCBs to efficiently transfer heat away from components, which is critical in high-power electronics applications. - What are typical applications for MCPCBs?
MCPCBs are predominantly used in applications where thermal management is paramount. Common examples include LED lighting (both general and automotive), power electronics, automotive control systems, high-power amplifiers, and any device that generates significant heat during operation. Their ability to dissipate heat efficiently ensures reliability and prolongs the lifespan of electronic components. - How do I select the appropriate substrate material for an MCPCB?
The choice of substrate material depends on several factors, including the thermal performance requirements, mechanical demands, and cost constraints. Aluminum is generally favored for its cost-effectiveness and good thermal conductivity, while copper offers superior thermal performance but comes at a higher price. Consider the operating environment and the specific needs of your application when making your choice. - What are the key factors influencing the price of MCPCBs?
Several factors contribute to the overall cost of MCPCB production, including the type of metal core material, the complexity of the design (number of layers, via density), the quantity of boards required, the type of surface finish applied and any specific tolerance requirements, as well as the manufacturing volume and desired turnaround time. High precision, complex designs with copper substrates will lead to a higher cost compared to single sided aluminum boards. - What is the importance of thermal vias in MCPCB design?
Thermal vias are essential in MCPCB design as they provide a low resistance thermal pathway to transport heat from the surface components to the metal core. Proper via placement and design ensures efficient heat transfer and prevents the components from overheating. - What certifications should I look for when evaluating a MCPCB manufacturer?
When choosing an MCPCB manufacturer, ensure they hold relevant certifications such as ISO 9001 (quality management), ISO 14001 (environmental management) and UL certifications. These certifications demonstrate a commitment to quality, environmental responsibility and that the products meet established industry standards. - How can I ensure a smooth collaboration with the MCPCB manufacturer during the design process?
Effective collaboration starts with clear and concise communication. Sharing detailed design specifications, thermal performance requirements, and any specific application needs is crucial. It's beneficial to engage the manufacturer early in the design phase to leverage their expertise and ensure your design is manufacturable and cost-effective.
MCPCB Design Guidelines
Effective MCPCB design is crucial for optimal thermal performance and reliability. This section provides best practices for designing MCPCBs, emphasizing thermal management and collaboration with manufacturers. These guidelines ensure that the final product meets the required performance criteria and is manufacturable with minimal issues, while maximizing longevity.
- Thermal Via Placement
Strategically place thermal vias to conduct heat from the components to the metal core. Ensure vias are sufficiently large and plentiful, especially beneath high-power components. The via placement should be balanced and optimized based on heat generation analysis of the design. - Trace Design
Optimize trace widths and routing for both electrical and thermal performance. Wider traces can help dissipate heat. The thermal path must be designed to be as short as possible with minimal resistance. For high-current applications, appropriate trace widths are a must to prevent overheating and premature failure. - Material Selection
Choose materials with suitable thermal conductivity for the application. Consider the trade-offs between cost, thermal performance, and mechanical strength. The selection of appropriate dielectric material is also critical and depends on the operational frequency and voltage ratings of the circuit. - Component Placement
Place heat-generating components directly over the metal core for the most efficient heat transfer. Avoid clustering hot components together. The component layout must consider the airflow and heat sinks where applicable. - Layer Stack-Up
Proper layer stack-up is vital for minimizing thermal resistance. Ensure that the metal core is the primary heat conduction path, and that there are minimal dielectric layers to act as thermal insulators. Consider using thicker metal layers for added heat spreading, particularly for high power designs. - Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Collaborate closely with MCPCB manufacturers during the design process. Understand their capabilities and limitations to avoid design features that are difficult or expensive to manufacture. Consult with them on tolerances, material availability and optimal design rules.
Future Trends in MCPCB Technology
The field of Metal Core Printed Circuit Boards (MCPCBs) is rapidly evolving, driven by the increasing demands for higher power densities and improved thermal management in electronics. These advancements are pushing the boundaries of material science and manufacturing processes, leading to innovative solutions that enhance the performance and reliability of MCPCBs. MCPCB manufacturers play a critical role in adopting these emerging trends, enabling the next generation of electronic devices.
- Advanced Materials
The future of MCPCBs will see increased use of materials with higher thermal conductivities, such as ceramic-filled polymers, graphene-enhanced composites, and advanced metal alloys. These materials aim to reduce thermal impedance and improve overall heat dissipation, allowing for more efficient operation of high-power electronics. - Embedded Cooling Solutions
Emerging trends include integrating microfluidic cooling channels directly within the MCPCB structure. This approach allows for precise and efficient temperature control, particularly in applications with extreme thermal challenges. The use of liquid cooling is also being explored to achieve the best thermal performance. - Additive Manufacturing
Additive manufacturing, or 3D printing, presents a transformative way to produce complex MCPCB structures with improved thermal management capabilities. This technology enables the fabrication of custom heat sinks and other integrated thermal components, which is difficult to achieve with traditional methods. This flexibility is expected to push the limits of miniaturization and thermal efficiency. - Smart MCPCBs
The integration of sensors and actuators directly into MCPCBs is an emerging area. These smart MCPCBs can monitor thermal performance in real time and adjust operation to prevent overheating. This technology is especially useful in safety-critical applications. - Environmentally Sustainable Materials and Processes
The focus on environmentally friendly materials and manufacturing processes is growing. This includes using recyclable or biodegradable materials and reducing energy consumption and waste during manufacturing. Manufacturers are adopting lead-free solders and water-based chemicals, with a focus on improving the life cycle of MCPCBs.
Choosing the correct mcpcb manufacturer requires careful consideration of your specific needs, from the desired thermal performance and application, to budget and manufacturing capacity. By understanding MCPCB materials, manufacturing processes, and quality standards, you can confidently select a partner to build reliable and high-performing products. Partnering with a skilled MCPCB manufacturer ensures long-term reliability and success for your high-heat applications. As technology progresses, innovative materials and techniques promise even greater performance enhancements and increased applications of MCPCBs.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA