Top Copper Clad Board Manufacturers: A Comprehensive Guide

In the heart of every electronic device lies a printed circuit board (PCB), and at the core of that PCB is the copper clad board. These boards, created by laminating copper foil onto an insulating layer, form the foundation for all electronics. This article will delve into the world of copper clad board manufacturers, exploring what they offer, the materials they use, and how you can choose the best manufacturer for your projects. Just as the roots of a tree anchor it, the quality and selection of copper clad board determine the overall performance of any device, bridging the gap between fundamental materials and technological advancement.
Understanding Copper Clad Laminate (CCL)

Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) forms the foundational material for printed circuit boards (PCBs), acting as the structural base and electrical pathway facilitator. Its composite construction, typically consisting of copper foil, a resin matrix, and reinforcing materials, directly influences the performance and reliability of the final electronic product. The selection of specific materials for each component of the CCL is a critical design decision, impacting everything from signal integrity to thermal stability.
The core components and their functions are as follows:
- Copper Foil
Provides the conductive pathways for electrical signals within the PCB. The thickness and type of copper foil (e.g., rolled, electrodeposited) directly affect the current-carrying capacity and signal integrity. - Resin Matrix
The insulating material that bonds the copper foil and reinforcement, providing structural integrity to the CCL. Common resin types include epoxy, phenolic, polyimide, and Teflon, each offering distinct electrical, thermal, and mechanical characteristics. - Reinforcement Materials
Enhances the mechanical strength and dimensional stability of the CCL, preventing warping and breakage during manufacturing and operation. Examples include woven fiberglass cloth, paper, and aramid fibers. The choice of reinforcement material directly impacts the mechanical and thermal properties of the composite.
The strategic integration of these components in a CCL ensures reliable electrical functionality and structural integrity of the PCB, making it the cornerstone of modern electronics manufacturing.
Types of Copper Clad Boards
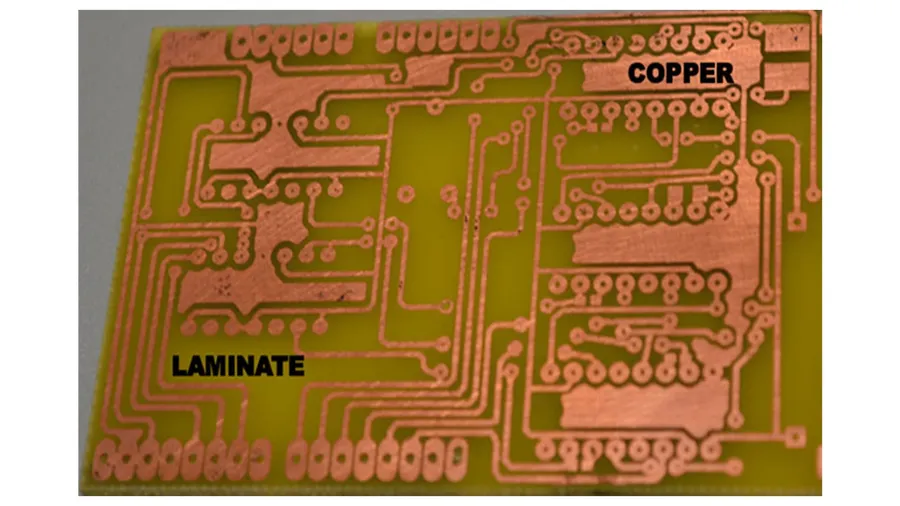
Copper clad boards, the foundational material for printed circuit boards (PCBs), are categorized primarily by their copper layering and the resin systems used. Understanding these types is essential for selecting the appropriate material for specific electronic applications. The most common classifications are based on the number of conductive copper layers and the type of insulating resin used.
| Board Type | Description | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Single-Sided | Copper layer on one side of the substrate. | Simple electronic devices, toys, low-density circuits. | Cost-effective, simple to manufacture. | Limited circuit complexity, single-layer routing. |
| Double-Sided | Copper layers on both sides of the substrate. | Intermediate complexity devices, simple logic circuits, some power electronics. | Increased routing capability compared to single-sided boards. | More complex than single-sided, limited layer density for complex circuits. |
| Multilayer | Multiple copper layers separated by insulating layers. | Complex electronics, high-speed digital circuits, high-density interconnects. | High routing density, complex circuit designs. | More expensive, complex manufacturing, requires specialized equipment. |
Resin type is another critical differentiator for copper clad boards. The resin system dictates the thermal, electrical, and mechanical properties of the final board. Common types include:
- Epoxy Resins (FR-4)
The most widely used resin due to its good balance of cost, electrical properties, and mechanical strength. It's suitable for a wide range of applications and is known for its flame retardant properties. - Phenolic Resins
Offers lower cost and good mechanical strength, but typically has poorer electrical and thermal properties compared to epoxy. It is often used in less demanding applications. - Polyimide Resins
Known for their exceptional thermal stability and high-temperature performance, making them suitable for demanding applications, such as aerospace and automotive electronics. They generally have higher costs. - Teflon/PTFE Resins
Exhibits excellent electrical properties, especially at high frequencies, with very low loss tangents. It's ideal for RF and microwave applications, but it's costly and may require special handling. - Other Resins
Other specialized resins are available including cyanate ester, bismaleimide triazine (BT), and others for specific performance requirements.
Key Considerations When Choosing a Copper Clad Board Manufacturer

Selecting the right copper clad board manufacturer is crucial for ensuring the quality, reliability, and performance of your printed circuit boards (PCBs). This decision requires a careful evaluation of several key factors that directly impact the final product's suitability for its intended application.
- Material Quality
The quality of raw materials directly impacts the final product's performance. Ensure that the manufacturer uses high-grade copper foil, resins, and reinforcement materials that meet industry standards and specific application requirements. For instance, high Tg (glass transition temperature) materials are essential for high-temperature environments. - Manufacturing Process
The manufacturer’s production methodology, including the precision of lamination, etching, and surface treatment processes, is paramount. Look for manufacturers employing advanced techniques to ensure consistent layer thickness, minimal defects, and adherence to tight tolerances. - Certifications and Compliance
Manufacturers should possess relevant industry certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 14001, UL certification) that demonstrate adherence to quality management systems and environmental standards. These certifications provide an assurance of product reliability and regulatory compliance. - Customization Options
Depending on your project's specific needs, assess the manufacturer's ability to provide custom board sizes, thicknesses, copper weights, and material options. The manufacturer should be capable of accommodating your unique design specifications, including specific resin types (e.g., epoxy, polyimide) for different applications. - Technical Support and Communication
A reliable manufacturer offers robust technical support to assist with material selection, design considerations, and troubleshooting. Clear and timely communication is vital for addressing issues promptly and ensuring a smooth manufacturing process. Verify that the manufacturer’s technical team is experienced and responsive. - Production Capacity and Lead Times
Evaluate the manufacturer's production capacity to ensure it can meet your volume requirements within the desired timeframe. Realistic lead times are crucial for project planning. A manufacturer with a well-organized supply chain will minimize delays and disruptions. - Geographical Reach and Logistics
Consider the manufacturer's location and supply chain capabilities to minimize shipping costs and ensure timely delivery, particularly for large orders or just-in-time manufacturing requirements. Local sourcing can be advantageous when time and logistics are critical.
Leading Copper Clad Board Manufacturers: A Comparison

The selection of a copper clad board manufacturer is critical for ensuring the performance and reliability of printed circuit boards (PCBs). This section provides a comparative analysis of leading manufacturers, highlighting their strengths, product offerings, and global presence. We aim to provide a detailed view of both general-purpose and specialized CCL solutions.
| Manufacturer | Strengths | Product Offerings | Geographical Reach | Specializations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Doosan | High-volume production, consistent quality | Standard FR-4, high-speed laminates | Global, with a strong presence in Asia | Large scale production capabilities |
| Isola | Advanced materials, high-frequency performance | RF and microwave laminates, high-speed digital materials | Global, with manufacturing and sales in multiple regions | High-performance laminates, specialized resin systems |
| AGC | Diverse material offerings, strong research and development | Fluoropolymer laminates, flexible CCL | Global, with a strong presence in Japan and Asia | Advanced materials, chemical expertise |
| Panasonic | Reliable and consistent materials | Standard FR-4, high-reliability laminates | Global, with a strong presence in Asia | Consumer electronics focused materials |
| Rogers Corporation | Specialized in high-performance materials | High-frequency laminates, PTFE-based materials | Global, with a strong presence in North America | High-frequency applications, demanding environment materials |
| Ventec International | Specializes in high-reliability materials | High-temperature laminates, halogen-free options | Global, with a strong presence in Europe and Asia | High reliability and advanced technology laminates |
Copper Clad Board Materials: Key Properties and Applications

The performance of a copper clad board (CCB) is significantly influenced by the materials used in its construction. The interplay between the copper foil, resin, and reinforcement materials dictates the board's electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties, making material selection crucial for specific applications. Understanding these material properties is vital for engineers to choose the correct board for optimal performance and reliability.
| Material | Key Properties | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Epoxy Resin (FR-4) | Good mechanical strength, moderate thermal performance, flame retardant | General-purpose PCBs, consumer electronics | Cost-effective, widely available | Lower thermal resistance compared to high-performance resins |
| Phenolic Resin | Low cost, moderate electrical performance | Single-sided PCBs, basic electronics | Economical | Lower mechanical strength, limited thermal performance |
| Polyimide Resin | Excellent thermal and electrical properties, high-temperature resistance | Aerospace, automotive, high-reliability applications | High temperature performance, good electrical properties | Expensive |
| Fluoropolymer (PTFE) | Superior high-frequency performance, low dielectric loss | High-speed digital circuits, microwave applications | Excellent high-frequency performance | High cost, can be mechanically challenging |
| Cyanate Ester Resin | Low dielectric constant, low dielectric loss, good thermal stability | High-speed communications, aerospace | Exceptional electrical and thermal stability | More expensive than epoxy, potential for higher moisture absorption |
| Metal Core Substrates (Aluminum, Copper) | Excellent thermal conductivity, good heat dissipation | LED lighting, power electronics | Effective heat dissipation | Can be heavier, more expensive |
- Thermal Properties:
The thermal conductivity and coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) of the materials impact the board's ability to dissipate heat and withstand temperature variations. For example, materials with high thermal conductivity are ideal for high-power applications where heat management is essential. - Electrical Properties:
The dielectric constant and loss tangent of the resin directly influence the signal integrity and performance of high-speed circuits. Materials with lower dielectric constants and loss tangents are preferred for applications requiring high-frequency signals. - Mechanical Properties:
Tensile strength, flexural strength, and impact resistance determine the board's durability and ability to withstand mechanical stress. The reinforcement materials, typically woven fiberglass, enhance the mechanical strength of the board. - Copper Foil:
The thickness and surface finish of copper foil affect its electrical conductivity and signal transmission characteristics. Thicker copper layers are suitable for high-current applications, while smooth surfaces ensure high signal integrity. - Reinforcement Materials:
Woven fiberglass is a common reinforcement material that enhances mechanical stability, but other materials such as paper or non-woven glass can be used for specific applications. The type of reinforcement material also affects the CTE and overall performance of the laminate.
The Manufacturing Process of Copper Clad Laminate
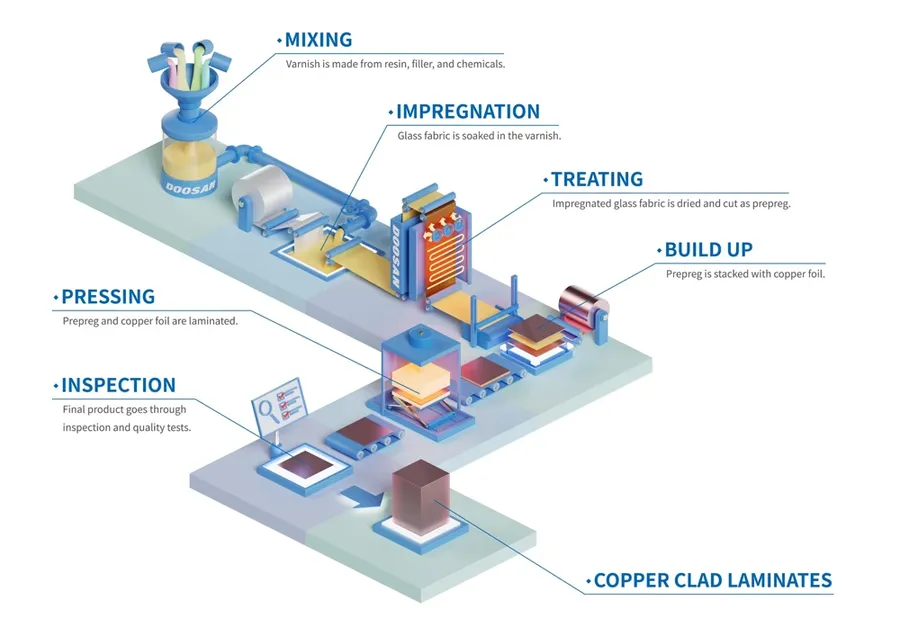
The manufacturing of copper clad laminate (CCL) is a multi-stage process that transforms raw materials into the foundational substrate for printed circuit boards (PCBs). This process is critical in determining the electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties of the final PCB.
The process can be broadly categorized into the following stages:
- Raw Material Selection
The process begins with the selection of appropriate raw materials. This includes the resin system (e.g., epoxy, phenolic, polyimide), reinforcement material (e.g., glass fiber, paper), and copper foil. The type and quality of these materials directly impact the final properties of the CCL. - Resin Preparation
The chosen resin is mixed with hardeners, catalysts, and other additives to achieve the desired viscosity, curing characteristics, and performance properties. This mixture, often referred to as 'varnish', is critical to ensuring the final performance of the CCL. - Reinforcement Material Impregnation
The reinforcement material, often in the form of a woven fabric or paper sheet, is impregnated with the prepared resin. This can be done through a variety of techniques including dipping and coating. The goal is to evenly distribute the resin throughout the reinforcement structure. - Lamination
The resin-impregnated reinforcement material is then placed between layers of copper foil. This 'sandwich' is subjected to heat and pressure in a lamination press. The heat cures the resin, bonding the copper foil to the reinforcement and forming a solid, composite sheet of CCL. - Quality Control
Throughout the entire process, various quality control checks are performed to ensure that the CCL meets specifications. This includes tests for thickness, copper adhesion, resin content, dimensional stability, and electrical properties. These checks are critical to maintaining the integrity and performance of the boards and also to make sure that there is no deviation from industry standards. The quality control data is often recorded and used to make necessary adjustments to maintain a consistent production output. - Finishing
After lamination, the CCL is typically trimmed, inspected again, and packaged for distribution to PCB manufacturers, either in sheet or roll form, ready to be used in the PCB manufacturing process.
Each stage of the manufacturing process involves critical parameters that impact the final CCL properties. Precise control of these parameters is crucial for producing high-quality, reliable materials.
Copper Clad Board Pricing Factors
The price of copper clad boards (CCBs) is determined by a multitude of factors, reflecting the complexity of their manufacturing and the diversity of their applications. These factors range from the raw materials used to the specific requirements of the end-product, encompassing both material costs and customization demands.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Material Costs | This includes the cost of copper foil, resin (epoxy, phenolic, etc.), and reinforcement materials (glass fiber, paper). | Higher cost materials, like fluoropolymers or high-performance resins, increase the overall cost. |
| Board Size and Thickness | Larger boards and increased thickness demand more material, impacting the cost. | Larger and thicker boards will be more expensive. |
| Number of Layers | Single-sided, double-sided, and multilayer boards have vastly different manufacturing complexities. | Multilayer boards are substantially more expensive due to added complexity in fabrication. |
| Resin Type | Different resin materials, such as epoxy, phenolic, polyimide, and PTFE, vary significantly in cost and performance. | High-performance resins such as Polyimide and PTFE lead to a higher price point. |
| Copper Thickness | The thickness of the copper layer affects material usage and performance. | Thicker copper layers tend to increase costs, particularly with heavy copper boards. |
| Custom Features | Specific requirements like custom shapes, sizes, special finishes, or impedance control. | These features, particularly impedance control, add to the production cost. |
| Manufacturing Volume | Quantity ordered affects the per-unit price due to economies of scale. | Larger orders typically benefit from a reduced per-unit cost. |
| Supplier Location | Geographical location influences costs (labor, transport) and duties/taxes. | Costs might vary greatly depending on supplier locations. |
| Quality Standards | Adherence to strict industrial standards and quality control measures. | High-quality boards can increase costs. |
| Certifications | Certifications such as UL or IPC affect manufacturing costs. | Boards with certifications incur additional testing and compliance costs. |
Frequently Asked Questions About Copper Clad Boards
This section addresses common queries regarding copper clad boards, providing concise answers to help clarify frequently asked questions and improve understanding of these essential PCB materials.
- How is copper clad laminate manufactured?
Copper clad laminate (CCL) is manufactured through a multi-stage process involving the application of heat and pressure to bond copper foil to a substrate material (such as resin-impregnated fiberglass or paper). The process typically begins with preparing the substrate material, followed by precise application of the copper foil. This assembly is then pressed under controlled temperature and pressure to achieve a uniform, bonded structure. Quality control checks are performed throughout the process to ensure consistency and performance. - What does Isola manufacture?
Isola is a well-known manufacturer specializing in high-performance copper clad laminates and dielectric materials used in printed circuit boards (PCBs). They produce a variety of materials, including those designed for high-frequency, high-speed, and thermally demanding applications. Their product range encompasses a broad selection of resin systems and reinforcement materials, catering to the diverse needs of the electronics industry. - Is copper clad the same as copper bonded?
The terms 'copper clad' and 'copper bonded' are often used interchangeably, but it is important to clarify that 'copper clad' refers specifically to a laminate material where a thin layer of copper foil is bonded to a substrate. 'Copper bonded' is a more general term that might include other methods of affixing copper to a material. Thus, a copper clad board is a type of copper-bonded material, but not all copper-bonded materials are copper clad laminates. The term ‘copper clad’ implies a specific manufacturing process where the copper layer is bonded to the substrate during the laminate manufacturing process. - What is the market report for copper clad laminate?
Market reports for copper clad laminates (CCLs) typically indicate significant growth driven by the increasing demand for electronic devices across various sectors, including consumer electronics, automotive, and telecommunications. Reports detail trends in material types, geographical market share, and competitive landscapes. The market is influenced by technological advancements, such as the need for higher performance, lower signal loss, and better thermal management in electronic devices, with the high-frequency material demand being of particular importance. Furthermore, sustainability and cost efficiency are prominent factors impacting market growth. - What are the common resin types used in copper clad laminates and their applications?
Common resin types in CCLs include epoxy, phenolic, and polyimide resins. Epoxy resins are versatile and cost-effective, suitable for general-purpose PCBs. Phenolic resins provide good electrical insulation and are often used in less demanding applications. Polyimide resins offer excellent high-temperature performance and are employed in applications requiring higher thermal stability, such as aerospace and automotive electronics. - What is the role of reinforcement materials in copper clad boards?
Reinforcement materials, such as fiberglass or woven glass fabric, are critical components of copper clad laminates. They provide mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and structural integrity to the composite material. The type and weave of the reinforcement directly impact the electrical and mechanical properties of the final board. For example, finer weaves and higher glass content can improve the board's stiffness and reduce thermal expansion, while also enhancing its electrical performance by reducing signal loss. - How does the thickness of copper foil affect PCB performance?
The thickness of the copper foil significantly impacts the current-carrying capacity of a PCB trace, along with signal integrity and thermal performance. Thicker copper foils can handle higher currents, making them suitable for power-intensive applications. They also improve heat dissipation, which helps in managing thermal issues. However, thicker foils may also make etching more challenging, require more precise control, and potentially impact impedance control in high-frequency circuits due to variations in etch profiles. In many applications, the copper foil thickness must be precisely specified to meet the desired performance requirements.
Future Trends in Copper Clad Board Manufacturing
The copper clad board (CCL) industry is undergoing significant transformations, driven by demands for higher performance, sustainability, and technological advancements. These trends will shape the future of PCB manufacturing and material science.
- Eco-Friendly Materials
The growing environmental consciousness is pushing the industry towards sustainable alternatives. This includes bio-based resins derived from renewable resources, and halogen-free materials that reduce toxic byproducts. Research and development are focused on materials that meet stringent performance criteria and adhere to environmental regulations. - High-Performance Materials for Advanced Applications
The demand for advanced electronics in 5G, automotive, and aerospace sectors is driving the need for high-performance CCLs. This involves using materials with improved thermal management characteristics, lower dielectric constants, and enhanced signal integrity, such as advanced ceramic-filled resins and low-loss laminates. These are designed to meet the requirements of higher frequencies and complex circuit designs. - Advanced Manufacturing Techniques
Innovations in manufacturing are improving the efficiency and precision of CCL production. This includes continuous lamination techniques, automated production lines, and advanced quality control using machine vision and artificial intelligence. These methods ensure consistent quality and reduce production costs. - Integration of Smart Technologies
Integrating sensors and smart features directly into CCLs is becoming more common. This allows for real-time monitoring of parameters such as temperature and humidity in electronic devices. This trend is opening avenues for intelligent material science in PCB design. - Miniaturization and Flexible Substrates
The demand for smaller and more flexible electronic devices is pushing the development of thinner and flexible CCLs. This involves materials with high flexibility and durability, such as flexible polymers, and thin copper foil. Flexible and bendable boards are essential for new generations of wearables and flexible displays.
In conclusion, choosing the right copper clad board manufacturer is vital for the success of any electronic project. By understanding the different types of materials, manufacturing processes, and available suppliers, you can make informed decisions that ensure both quality and performance. From everyday electronics to cutting-edge technology, the copper clad board is a vital component, and partnering with the correct manufacturer, for example, a copper clad board manufacturer specializing in a unique area will make a vast difference. Consider this guide as a resource to navigate the options and choose a partner who can deliver the materials your designs need, now and into the future.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA