Understanding the 470uF 16V Capacitor: Specs, Uses, and Replacements
The 470uF 16V capacitor, a small but mighty component in the world of electronics, plays a crucial role in stabilizing voltage and filtering current in various devices. Much like the role of water reservoirs in maintaining a steady flow, capacitors like this 470uf 16v variant store and release electrical energy, ensuring smooth operation. From the circuits powering our smartphones to those within larger appliances, this capacitor type is a workhorse of the modern technological landscape. This article will delve into the intricacies of this capacitor, its applications, and how it performs in various scenarios, providing you with comprehensive knowledge, so you can make an informed selection when the need arises. We’ll also address the common questions that might arise when working with 470uF 16V capacitors.
What is a 470uF 16V Capacitor?

A 470uF 16V capacitor is an electronic component characterized by its ability to store electrical energy, with a capacitance of 470 microfarads (µF) and a maximum voltage rating of 16 volts. It's fundamental to many electronic circuits, functioning as a temporary energy reservoir and filter. Typically, these are electrolytic capacitors, known for their relatively high capacitance in a small physical size, but also notable for their polarity requirements.
- Capacitance
The 470uF indicates the capacitor's ability to store charge. A higher capacitance means it can store more energy. - Voltage Rating
The 16V rating specifies the maximum voltage the capacitor can safely withstand. Exceeding this voltage can damage the capacitor. - Electrolytic Type
Most 470uF 16V capacitors are electrolytic, utilizing a liquid electrolyte to achieve high capacitance. Electrolytic capacitors are polarized, requiring correct orientation in a circuit. - Energy Storage
These capacitors store energy in an electric field between two conductive plates separated by a dielectric material. This stored energy can be released when needed by the circuit.
Key Specifications of the 470uF 16V Capacitor
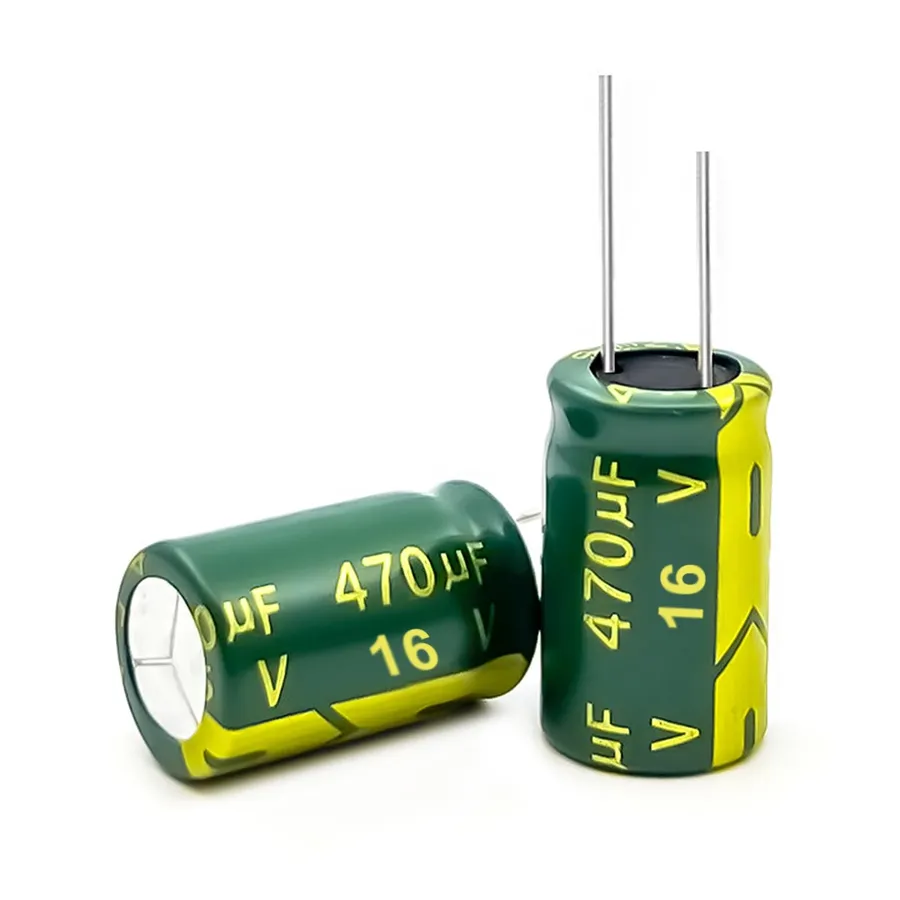

Understanding the detailed specifications of a 470uF 16V capacitor is crucial for proper selection and application. Beyond the core values of 470 microfarads (µF) capacitance and 16 volts (V) voltage rating, several other parameters influence its performance and suitability for different electronic circuits.
| Specification | Description | Typical Value |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance | The amount of electrical charge the capacitor can store. | 470 µF |
| Voltage Rating | The maximum voltage the capacitor can withstand without damage. | 16 V |
| Capacitance Tolerance | The acceptable variation in the actual capacitance value. | ±20% (Common) |
| Operating Temperature Range | The temperature range within which the capacitor will function correctly. | -40°C to +85°C (Typical) |
| Dimensions | Physical size of the capacitor, which can be influenced by lead type. | 8mm x 12mm (Common Radial) |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | The internal resistance of the capacitor which is important for filtering and power applications | Variable, often specified in datasheets |
| Leakage Current | A measure of current flowing through the capacitor dielectric when the capacitor is fully charged. | A few microamps or less, specified in datasheets |
| Lead Type | The configuration of the leads for connection | Radial or Axial |
Capacitance tolerance, typically ±20% for electrolytic capacitors, indicates that the actual capacitance can vary from 376uF to 564uF for a nominal 470uF capacitor. The operating temperature range is crucial since capacitor performance degrades at extreme temperatures. For instance, the electrolyte in electrolytic capacitors may freeze at very low temperatures. Capacitors also have a specified lifespan, which depends on factors such as operating temperature and ripple current.
The physical dimensions, such as 8x12 mm, refer to a typical radial-leaded capacitor, which means the leads extend from the base. Axial-leaded capacitors, conversely, have leads extending from either end and will have different dimensions. The leads are important for installation into a circuit board, and the choice depends on the board and application type. Furthermore, ESR is an important factor in circuits that carry high-frequency signals or have a high ripple current. Low ESR capacitors are required in those specific applications to avoid overheating and improve efficiency.
Common Applications of 470uF 16V Capacitors

470uF 16V capacitors are ubiquitous in modern electronics, serving crucial roles in various applications due to their ability to store and release electrical energy. Their primary functions include smoothing power fluctuations and filtering out unwanted noise, thus contributing to the stability and reliability of electronic circuits.
- Power Supplies
These capacitors are vital in power supply circuits for smoothing the rectified DC output. They help to reduce voltage ripple, providing a cleaner and more stable power source for sensitive electronic components. The 470uF capacity and 16V rating are common in low-voltage power supplies for various devices. - Audio Equipment
In audio circuits, 470uF 16V capacitors are often used for coupling and decoupling signals, filtering out unwanted low-frequency noise, and stabilizing amplifier circuits. They contribute to the clarity and quality of audio reproduction by ensuring a stable power supply to audio components. - LCD Monitors
These capacitors play an essential role in the power and backlight circuits of LCD monitors. They help to regulate the voltage supply to the display panel and the backlight LEDs, ensuring a consistent and stable display output. They are part of the power management system that can affect the brightness and stability of the display. - Game Consoles
Similar to LCD monitors, game consoles rely on 470uF 16V capacitors for power regulation and noise filtering. They are frequently used in various sub-systems, including power supply, audio output and data processing circuits, thus ensuring stable operation during intensive gaming sessions. These components are crucial for both performance and reliability. - General Electronics
Beyond specific devices, these capacitors are used in many general-purpose electronics for filtering, decoupling, timing and energy storage within power circuits. Their compact size and suitable electrical specifications make them a standard choice in a multitude of applications, emphasizing their versatility in general circuit design. Examples can include motor control circuits, small microcontroller based projects, and sensor circuits.
Choosing the Right 470uF 16V Capacitor: What to Consider?

Selecting the appropriate 470uF 16V capacitor requires careful consideration of several key factors to ensure optimal performance and reliability in your application. These include temperature requirements, physical size constraints, expected lifespan, and the crucial parameter of Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR).
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Requirements | The operating temperature range the capacitor will be subjected to. Capacitors have defined limits, exceeding which can result in performance degradation or failure. | Critical; Ensure the capacitor's temperature range meets or exceeds the expected operating conditions. |
| Physical Size | The physical dimensions of the capacitor (e.g., diameter and height). Space constraints on the circuit board can limit the size of the capacitor. | Important; Consider available space and package options to ensure a proper fit. |
| Lifespan | The expected operational lifetime of the capacitor. Electrolytic capacitors, especially, have a finite lifespan that is influenced by temperature and applied voltage. | Very Important; Choose a capacitor with a suitable lifespan for the intended application; lifespan is inversely proportional to the temperature of operation. |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | The internal resistance of the capacitor. ESR affects the capacitor's ability to handle ripple current and can generate heat. | Crucial for specific applications; High ESR can lead to increased heat, reduced efficiency, and potential premature failure, especially in power applications |
| Capacitance Tolerance | The acceptable variation in the actual capacitance value from the stated 470uF. Common tolerances are ±20% or ±10%. | Important, higher tolerance means more variation in capacitance, and can effect the performance of the device. Consider the circuit sensitivity to capacitance variation when selecting your capacitor. |
Can I Use a Capacitor With Higher uF or Voltage Rating?
When replacing a 470uF 16V capacitor, it's crucial to understand the implications of using components with different ratings. While it may seem convenient to substitute with a higher capacitance (uF) or voltage rating, it’s important to understand the nuances to ensure proper circuit function and longevity.
- Higher Voltage Rating
Using a capacitor with a higher voltage rating (e.g., 25V instead of 16V) is generally safe. A capacitor's voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage it can withstand without damage. Utilizing a higher-rated capacitor will not negatively impact the circuit. It simply means the capacitor has a higher safety threshold. It is crucial to never use a lower rated voltage as this will cause the capacitor to fail and potentially cause damage. - Higher Capacitance Rating
Using a capacitor with a higher capacitance (uF) rating is more nuanced. While some applications can tolerate a slightly higher capacitance, other circuits are dependent on specific timings. The capacitance value plays a crucial role in setting timing constants in circuits. Increasing the capacitance, without a deep understanding of the effect of the change, will alter the timing and may prevent the circuit from functioning correctly. If the goal of the capacitor is simply energy storage for decoupling and filtering purposes, a higher capacitance is acceptable, and may have some positive benefits such as a longer lifespan. - When to be cautious
When dealing with timing circuits, such as oscillators or filters, it’s important to closely adhere to the original capacitor's specification. A higher capacitance may result in reduced frequency operation or non-optimal filter performance. In these cases, it's best to use the exact capacitance value of the original capacitor, but with a higher voltage rating if that suits.
Replacing a 470uF 16V Capacitor: Step-by-Step Guide

Replacing a faulty 470uF 16V capacitor requires careful execution to ensure the proper function of your electronic device. This guide outlines the necessary steps, tools, and safety precautions for a successful replacement, emphasizing correct polarity and handling.
- Gather Necessary Tools
Ensure you have the following tools readily available: a soldering iron with a fine tip, desoldering braid or a desoldering pump, needle-nose pliers or tweezers, and a new 470uF 16V capacitor. Additionally, have safety glasses, a well-ventilated workspace, and appropriate safety equipment. - Prepare the Work Area
Work in a well-lit and well-ventilated space. Place the circuit board containing the faulty capacitor on a stable surface. Avoid working near flammable materials or where you could accidentally bump into sensitive components. - Identify the Faulty Capacitor
Visually inspect the circuit board to locate the 470uF 16V capacitor. Note its physical orientation and polarity. The polarity is usually marked with a stripe on one side of the capacitor which represents the negative pin, and the circuit board typically has markings indicating the correct orientation. Take a photo as a reference if needed. - Desolder the Old Capacitor
Heat the solder joints of the capacitor leads using a soldering iron. Once the solder melts, use desoldering braid or a desoldering pump to remove the solder from the pad. This may require multiple attempts and carefully avoid overheating the board or lifting the pad, especially on a double sided board. Once the solder is removed from both leads, gently remove the old capacitor using pliers or tweezers. - Prepare the New Capacitor
Ensure the new capacitor is the correct type. Bend the leads if necessary to match the spacing of the holes on the circuit board. Double check the polarity and orientation of the new capacitor before installation. - Install the New Capacitor
Insert the leads of the new capacitor into the corresponding holes, making sure the orientation matches the old capacitor and the markings on the board. Gently push the component completely into the board. Bend the leads slightly on the back of the board so the component does not fall out while soldering. - Solder the New Capacitor
Heat the solder joints of the capacitor leads and apply solder. Ensure a strong connection but avoid applying too much solder. Allow each joint to cool before moving on to the next. - Inspect the Solder Joints
Once the solder cools, inspect the joints for smooth connections. Make sure there are no cold solder joints, where there is a weak and dull connection. If there are any issues then reheat the solder and try again. Remove any sharp lead or solder spikes with small flush cutters. - Test the Circuit
Before reassembling your device, perform a quick test to ensure that the repair was successful, and that the device is working as expected.
Always exercise caution when working with electronic components. Double check all steps to avoid any mishaps and ensure a successful replacement. If you are uncomfortable with the repair process, it is best to consult a qualified technician.
470uF 16V Capacitor Datasheet Analysis
A capacitor datasheet is a critical document for understanding the specific characteristics and limitations of a capacitor. For the 470uF 16V capacitor, it provides vital information beyond just the capacitance and voltage rating. This section will guide you through the key parameters typically found in a datasheet, enabling informed decision-making for your applications.
| Parameter | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance | Rated value of 470uF | Primary value; actual value within tolerance. |
| Voltage Rating | Maximum voltage (16V) capacitor can withstand | Exceeding rating damages capacitor. |
| Capacitance Tolerance | Allowable deviation from the nominal 470uF. | Critical for accuracy in timing and filtering circuits. |
| Operating Temperature Range | Temperature range within which the capacitor operates correctly. | Affects lifespan and performance. |
| Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) | Internal resistance of the capacitor. | Important in high-frequency and power-related applications. |
| Ripple Current | The alternating current a capacitor can handle without degradation. | Essential in switching power supply applications. |
| Leakage Current | DC current that flows through the capacitor when voltage is applied. | Can affect long-term performance. |
| Lifetime | Expected operational life of the capacitor at rated conditions. | Important for reliability, varies with temp |
| Physical Dimensions | Size and lead configurations, e.g., 8x12mm radial. | Critical for space-constrained designs. |
Datasheets for 470uF 16V capacitors are readily available from component manufacturers. Some common manufacturers include: Panasonic, Nichicon, and Rubycon. Refer to their websites for the most current data on their components. These documents provide comprehensive information including test conditions, reliability data, and specific application guidelines for their capacitors, ensuring that you choose the appropriate component for your design.
Where to Buy 470uF 16V Capacitors

Sourcing genuine 470uF 16V capacitors is crucial for reliable electronic projects and repairs. This section guides you to reputable suppliers, both online and local, and provides tips to help you avoid counterfeit components, ensuring you obtain high-quality capacitors.
- Online Retailers
Several online retailers specialize in electronic components, offering a wide selection of capacitors. Major online retailers include, but are not limited to Amazon, Mouser, DigiKey, and Tayda Electronics. These platforms provide user reviews and detailed product information. - Local Electronics Suppliers
Local electronic component stores can be a good option if you need the capacitors quickly. These stores often allow you to visually inspect components before purchase. The downside is often the price is slightly higher. - Authorized Distributors
Purchasing from authorized distributors of major capacitor manufacturers is highly recommended for ensuring component authenticity and quality. These distributors usually guarantee genuine products, but may have higher minimum order quantities or be more geared toward business clients rather than hobbyists.
| Retailer | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Amazon | Wide variety, often quick delivery, customer reviews | Risk of counterfeit components, inconsistent quality |
| Mouser | Extensive selection, high-quality components, authorized distributor | Higher prices, may have minimum order quantities, shipping can be expensive for small orders |
| DigiKey | Similar to Mouser, wide selection, excellent technical resources, authorized distributor | Higher prices, may have minimum order quantities, shipping can be expensive for small orders |
| Tayda Electronics | Competitive pricing, good for small quantities, good for hobbyists | Can be limited selection, can be lower quality than name brands. |
| Local Electronics Stores | Immediate availability, visual inspection possible | May have limited selection, could be more expensive than online |
When choosing a supplier, prioritize reputable sources and check for customer reviews, and if the supplier is an authorized distributor of a capacitor manufacturer. If possible, visually inspect the capacitors for any obvious defects, such as bulging or corrosion, as a further precaution against counterfeit or defective components. Always compare prices, shipping costs, and delivery times between different retailers to optimize your purchasing decision. Be aware of the source of the product ( direct from manufacturer, third party seller), and how this may influence product authenticity.
Troubleshooting Issues with 470uF 16V Capacitors
Diagnosing problems with 470uF 16V capacitors is crucial for maintaining the functionality of electronic devices. Common failure modes include physical damage, such as bulging or leaking, and electrical degradation, which manifests as changes in capacitance or increased Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR). Identifying these issues early can prevent further damage to the circuit and ensure proper operation.
- Visual Inspection
Begin by visually inspecting the capacitor for any signs of damage. Look for a bulging top or bottom, which indicates internal pressure build-up, often due to overheating or overvoltage. Leaking electrolyte, a sticky or oily substance around the capacitor, is another clear sign of failure. Discoloration or burn marks on the capacitor body or surrounding board are further evidence of potential issues. - Capacitance Measurement
Use a multimeter with a capacitance measurement function to determine if the capacitor's value has deviated significantly from its 470uF rating. A significant drop in capacitance is an indicator of degradation, while extremely low capacitance may indicate an open circuit. Note that most multimeters will only give an approximate reading, and an LCR meter is required for precision measurements. - ESR Measurement
Changes in Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR) can also indicate capacitor degradation. Increased ESR often results in heat generation and poor circuit performance. An ESR meter provides a method for measuring this value; low ESR is generally desirable, while high ESR usually implies a faulty capacitor. Note that accurate ESR measurements require specialized meters and may not be possible with standard multimeters. - Multimeter Testing (Basic)
For a basic check, set the multimeter to the resistance setting (typically the highest range first). Connect the probes to the capacitor leads. In the case of a polarized capacitor, the positive lead of the meter will correspond to the positive lead of the capacitor. Initially, the resistance reading should start low, and as the capacitor charges through the multimeter, the resistance reading should gradually increase towards infinity. A reading of '0' or an unchanging low resistance indicates a short, while an unchanging high resistance indicates a open capacitor. - Component location and circuit performance
Note the location of the capacitor within the circuit, and how any failure affects that circuit's functionality. Capacitors in power rails will cause power issues, while capacitors in audio circuits may cause noise and distortion.
In conclusion, the 470uF 16V capacitor is a versatile and essential component in various electronic circuits. Understanding its specifications, applications, and proper handling is crucial for both hobbyists and professionals. When replacing this capacitor, it is imperative to observe correct polarity. Whether you're repairing existing devices or designing new circuits, a solid understanding of how this workhorse of a component, the 470uf 16v capacitor, functions will greatly enhance the success of your electronics projects. By considering the information provided, you'll be better equipped to make informed decisions, ensuring the reliable operation of your devices.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA