Decoding PCB Design Price: Factors, Costs, and Budgeting Tips
In today's world, printed circuit boards (PCBs) are the silent heroes powering our gadgets, from smartphones to spacecraft. But before these intricate boards come to life, they require skilled design, and that comes at a price. This article will dissect the various factors that influence pcb design price, providing you with clear insights and practical tips to budget effectively for your next project. We'll explore everything from hourly rates to complexity levels, so you can make informed decisions when planning your next innovation.
Key Factors Influencing PCB Design Price

The price of PCB (Printed Circuit Board) design is not a fixed value; it is a composite of several interconnected factors, including design complexity, layer count, board size, and component density. These elements directly influence the amount of time, resources, and expertise required, thereby impacting the overall cost. Understanding these key drivers is crucial for effective budgeting and project planning.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Price |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | The intricacy of the circuit design, including the number of unique functions and signal routing requirements. | Higher complexity increases design time and expertise requirements, leading to higher costs. |
| Layer Count | The number of conductive layers within the PCB. Single-layer PCBs are the simplest, while multi-layer PCBs are more complex. | More layers increase manufacturing difficulty and design complexity, thus raising costs. |
| Board Size | The physical dimensions of the PCB. Larger boards require more material and design effort. | Larger boards generally increase material costs and may add to design time, leading to higher prices. |
| Component Density | The number of components and how tightly they are packed on the board. Higher density requires finer trace widths and spacing, increasing design and fabrication challenges. | Higher density demands advanced techniques and precision in both design and manufacturing, resulting in higher costs. |
Hourly Rates vs. Project-Based Pricing

When procuring PCB design services, understanding the pricing structure is crucial for effective budgeting and project management. Two primary models exist: hourly rates and project-based pricing. Each offers distinct advantages and disadvantages that can significantly impact the final cost and the overall process.
| Pricing Model | Description | Pros | Cons | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hourly Rates | Charge based on the actual time spent by the designer. | Transparent cost tracking, suitable for projects with unclear scopes or evolving requirements, flexible in adapting to changes. | Potential for cost overruns if project scope expands, less predictable budgeting, requires detailed time tracking. | Projects with evolving requirements, unclear specifications, or where the scope is difficult to define upfront. |
| Project-Based Pricing | A fixed fee is agreed upon for the entire design project, regardless of the hours spent. | Predictable budgeting, less risk of cost overruns due to time slippage, can be more cost-effective for well-defined projects. | Less flexible to change requests, potential for discrepancies if the initial scope is not accurate, may require significant upfront project definition. | Well-defined projects with specific requirements and limited potential for scope changes. |
Choosing between hourly and project-based pricing depends on several factors. For projects with clear, fixed requirements and minimal anticipated changes, project-based pricing offers budget predictability. Conversely, if the project scope is uncertain or likely to evolve, hourly rates provide the flexibility needed to adapt to changes, albeit with less cost certainty. It is crucial to analyze project needs before selecting a model to mitigate risks and cost.
PCB Design Complexity Levels and Cost Implications
The complexity of a Printed Circuit Board (PCB) design is a primary driver of its cost, with designs categorized into low, medium, and high complexity levels. Each level demands different design efforts, time, and expertise, thus significantly affecting the overall project expenses. Understanding these levels is crucial for accurate budgeting and resource allocation.
| Complexity Level | Characteristics | Design Effort | Cost Implications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Low Complexity | Simple circuits, few components, single or double-sided boards, basic routing, through-hole components, often for educational projects or simple applications. | Minimal design time and effort required. | Lowest design cost, generally a fixed price with little variation unless there are special requests. Ideal for small budget or prototype projects. |
| Medium Complexity | Multiple layers (4-6), moderate component density, surface mount technology (SMT), mixed signal (analog & digital) circuits, some complex routing requirements, may involve specific standards or constraints. | Moderate design time and effort, requiring a professional engineer. | Moderate design cost, typically quoted based on hours or project, prices can vary depending on design complexity. Best for products with standard functionality. |
| High Complexity | High layer count (8+), high component density, high-speed signal routing, impedance matching, advanced packaging (BGA, QFN), rigorous design rules, tight tolerance requirements, often for advanced and industrial applications. | Significant design time and effort, requiring highly experienced engineers and specific software skills. | Highest design cost, often quoted as a premium hourly rate or project with complex requirements. Ideal for highly specific applications with high-performance standards. |
Geographic Location and PCB Design Pricing

The geographic location of PCB design service providers significantly influences pricing due to variations in cost of living and labor rates. These regional differences can lead to substantial price disparities for similar design work.
| Region | Typical Hourly Rate Range (USD) | Cost Drivers | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA/Canada | $80 - $150+ | High cost of living, experienced professionals, advanced technologies | Higher rates but often with robust communication and IP protection |
| Europe | $60 - $120 | Moderate cost of living, experienced engineers, strict quality standards | Balances cost with high-quality outputs |
| Asia (e.g., China, India) | $20 - $60 | Lower cost of living, large pool of engineers, competitive market | Potentially lower rates but may require careful vendor evaluation to ensure quality and clear communication |
For instance, design services in North America or Western Europe typically command higher rates due to higher labor costs and operational overheads. Conversely, outsourcing to regions in Asia may offer lower costs but require diligent evaluation of quality and communication effectiveness. The choice of geographic region should align with a project's budget constraints, required expertise, and desired level of quality assurance.
Software Tools & Expertise Impact on Cost
The selection of software tools and the level of expertise of the PCB designer significantly influence the overall cost of PCB design. Sophisticated software suites and specialized design skills command higher rates due to their enhanced capabilities and the increased complexity they can handle.
Here's a breakdown of how software and expertise impact costs:
- Software Costs
PCB design software ranges from free, open-source options to expensive, professional-grade suites. The cost of the software, including licenses and updates, is often factored into project pricing. Some designers may pass on software costs directly or bundle it into an hourly or project fee. - Professional Software Suites
Industry-standard software like Altium Designer, Cadence Allegro, and Mentor Graphics Xpedition are comprehensive and powerful, offering advanced features for complex designs. These tools come with high licensing fees, which contribute to the higher cost of using a designer proficient in them. - Open-Source and Low-Cost Options
Software like KiCad provides a cost-effective alternative, allowing designers to offer services at more competitive rates. While they may lack some of the advanced features of the high-end tools, they are often suitable for less complex designs. - Specialized Features and Cost
Advanced features, such as signal integrity analysis, thermal simulation, and 3D modeling, within software also contribute to cost. The more complex the design requirements, the more likely a designer needs these features, increasing the cost. - Expertise Level
The proficiency of the PCB designer is a significant cost driver. Highly experienced designers familiar with specific industries, challenging design constraints, and complex software command higher prices for their expertise and the speed at which they can complete projects with minimal errors. This can be a good investment as a well-designed PCB can reduce costs downstream. - Impact of Specialized Knowledge
Expertise in areas like high-speed design, RF design, or impedance control adds to cost. These specialized skills require significant training and experience and can impact project success.
Estimating PCB Design Costs: A Step-by-Step Guide
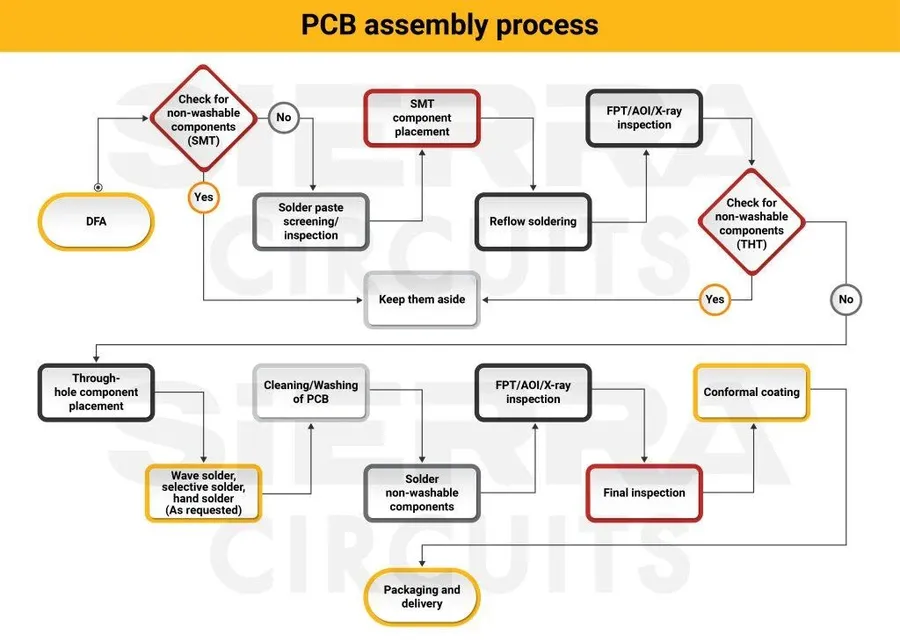
Accurately estimating PCB design costs is crucial for project planning and budget management. This process involves a systematic approach, considering various project specifics, desired turnaround times, and effective negotiation strategies to arrive at a reasonable cost projection.
- Define Project Specifications
Begin by creating a detailed outline of your PCB design requirements. This includes the board's dimensions, layer count, component types and density, technology stack, and any specific performance requirements. Precise specifications significantly reduce estimation errors and subsequent re-designs. - Identify Complexity Level
Assess the complexity of your design (low, medium, high) based on factors such as component count, trace density, and the inclusion of advanced technologies such as high-speed signals or RF components. Higher complexity designs typically incur higher costs due to increased design time and expertise required. - Consider Turnaround Time
Evaluate the desired turnaround time. Expedited services often command premium rates, while standard timelines may allow for more budget-friendly options. Early project planning can allow for standard turnaround times, saving costs. - Research Industry Rates
Gather information on average hourly rates or project-based pricing within the industry. Online platforms and industry publications provide insights into standard pricing. Rates can fluctuate based on geographic location and the designer's experience. - Request Quotations from Multiple Designers
Obtain detailed quotes from several PCB designers or design firms, being sure to provide your defined specifications. This will give you a broader idea of market rates and allow for cost comparisons between firms. - Negotiate Rates
Be prepared to discuss the quoted rates with designers. There may be opportunities for negotiation, especially if you can demonstrate flexibility on timeline or design specifics. It may be beneficial to consider fixed project rates instead of hourly rates for more accurate budget control. - Document Everything
Keep detailed records of your communication, design specifics, and quotations received. Proper documentation can prevent scope creep and disputes during the design process. It will also be useful for future PCB projects.
Frequently Asked Questions About PCB Design Costs
Understanding the costs associated with PCB design can be complex. This section addresses some of the most common questions to help clarify the process and provide realistic expectations about budgeting for your project.
- How much does a PCB designer cost?
The cost of a PCB designer varies widely based on experience, location, and the complexity of the project. Rates can range from $30 to $150+ per hour, or projects may be priced on a fixed basis. More experienced designers or those specializing in high-density or complex designs will naturally command higher rates. It's best to get quotes from multiple designers for a more accurate estimate. - How much should a PCB design cost?
The total cost for PCB design is not a single figure, and it's dependent on several factors such as design complexity, size, layer count, component density, required expertise and turnaround time. Simple designs might cost a few hundred dollars, while complex designs can easily reach into the thousands or even tens of thousands of dollars. It's essential to break down your project needs and get customized quotes. - What is the cost of a single PCB design?
The cost for a single PCB design is the price associated with the design service itself, irrespective of manufacturing. This typically encompasses schematic capture, layout, and design file generation. This cost, as explained above, is variable, but it's essential to obtain a detailed breakdown of the pricing structure from any designer to clarify exactly what's included in that price. - What is the difference between hourly rates and project-based pricing for PCB design?
Hourly rates are suitable for projects with variable scope, where it's difficult to anticipate the full effort. Project-based pricing works best for well-defined projects with clear deliverables, as it provides more cost certainty upfront. When choosing, evaluate whether the project scope is concrete or open to changes. - Does the geographical location of the PCB designer affect pricing?
Yes, the geographic location significantly impacts the cost of PCB design services. Designers in regions with higher costs of living (e.g., North America, Europe) typically charge more than those in regions with lower living costs (e.g., Asia). However, lower cost doesn't always equal lesser quality, so consider experience and references along with the location. - How does the complexity of the PCB design affect the overall cost?
PCB design complexity directly correlates with cost. Higher-complexity designs require more design time, greater expertise, and more sophisticated software. For example, a multi-layer board with high-speed signals and a high component density requires more resources and engineering expertise, hence, higher costs. - Are there any hidden costs associated with PCB design?
While not hidden, be aware of potential additional costs such as design revisions, which can significantly increase expenses. Clarify the scope of included revisions in advance. Also consider the potential need for design modifications due to manufacturing constraints, which may also impact the total cost.
Tips for Reducing PCB Design Costs
Minimizing PCB design costs without sacrificing quality requires a strategic approach, focusing on design efficiency, component selection, and effective vendor negotiation. The key is to identify areas where costs can be reduced without negatively impacting the final product's functionality or reliability.
- Optimize Design Complexity
Reducing unnecessary layers, minimizing trace lengths, and simplifying routing can significantly decrease design time and manufacturing costs. Analyze your design to identify areas where complexity can be reduced without affecting performance. For example, use standard component footprints where feasible. - Accurate Component Selection
Choose components that are readily available and cost-effective. Consider using standard parts instead of specialized ones, as this can reduce both component costs and lead times. Analyze the BOM to find cheaper alternatives without compromising functionality. Avoid over-specifying components, which can lead to unnecessary costs. - Design for Manufacturability (DFM)
Adhering to DFM guidelines can help avoid costly rework and production delays. Ensure that your design adheres to the manufacturer's capabilities, including minimum trace widths, spacing, and via sizes. This avoids manufacturability issues that may require design iterations, impacting both cost and time. - Efficient Panelization
Panelization involves placing multiple PCBs on a single board for manufacturing. Efficient panelization can reduce material waste and manufacturing costs. Collaborate with your manufacturer to ensure that the panelization layout is optimized for their machinery and processes. - Vendor Negotiation
Explore different pricing options from multiple PCB design and manufacturing vendors. Negotiate prices based on volume, lead times, and the complexity of the project. Building long-term relationships with reliable suppliers can also lead to cost savings. Leverage the competition between vendors to secure the best possible rates. - Early Prototyping
Invest in prototypes before committing to high-volume production. This allows for early detection of design issues that could lead to expensive corrections later in the product cycle. The upfront cost of prototyping will be far less expensive than production flaws. - Use Open-Source Tools
Consider using open-source PCB design software to reduce costs associated with licenses for proprietary software. Open-source software options can often provide comprehensive features and capabilities comparable to commercial solutions, with no license fees.
Comparing Quotes and Selecting the Right PCB Designer
Selecting the right PCB designer is crucial for a successful project and involves careful evaluation of multiple quotes. This process extends beyond just price, encompassing expertise, communication skills, and the designer's understanding of your specific needs to ensure a balance of cost-effectiveness, high-quality outcomes, and effective collaboration.
- Detailed Quote Analysis
Don't just look at the bottom line. Scrutinize the breakdown of costs for each phase of the design process. This includes schematic capture, PCB layout, component selection, and any additional services like design for manufacturability (DFM) checks or prototyping. - Evaluate Experience and Expertise
Assess the designer's portfolio and relevant experience, specifically if they have handled similar projects or types of PCBs. Consider their familiarity with the necessary software tools and their understanding of your industry's specific requirements. Verify their expertise with references, if possible. - Assess Communication Proficiency
Effective communication is key for any successful collaborative project. Gauge the designer's responsiveness, their clarity in explaining concepts, and willingness to address your questions thoroughly. - Turnaround Time and Project Timeline
Verify that the estimated turnaround time aligns with your project's deadlines. Discuss how the design phase fits into your overall project timeline, and ensure all critical milestones are clearly established and agreed upon. - Understand the Designer's Process
A clear understanding of how the designer works, their methods, and their internal review process will help you gauge their efficiency and reduce errors. Inquire about the communication protocols they adopt and what tools they plan on using. - Check for Design Flexibility
During the review process, ensure that the designer is open to alterations during the design process, as well as implementing necessary changes based on feedback. Confirm that the design can be modified as needed to improve its performance or functionality. Inquire about the number of revisions included in their quote. - Review Contractual Terms
Before hiring, meticulously review the contract. Verify the scope of work is well defined, timelines are clear, pricing is as discussed, ownership of design is explicitly stated, and if there are any clauses about intellectual property rights.
Understanding pcb design price is essential for any electronics project. By considering factors such as complexity, hourly rates, geographic location, and required expertise, you can better estimate costs and budget accordingly. Armed with these insights, you can confidently navigate the PCB design process and ensure your projects come to fruition within your financial parameters. Remember, investing in quality design is key to long-term success of the final PCB, so choose your designer wisely and plan ahead for a successful venture.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA