6A10 Diode: Powering Your Circuits with Precision

From the smartphones in our pockets to the complex machinery that drives industries, diodes are the unsung heroes of modern electronics. The 6A10 diode, a workhorse in power electronics, is a crucial component for converting AC to DC. This article will delve into the specifications, applications, and practical considerations of using the 6A10 diode, bridging the gap between fundamental science and real-world technology.
Understanding the 6A10 Diode: Basic Function and Specifications

The 6A10 diode is a fundamental semiconductor device categorized as a rectifier diode, specifically engineered for applications demanding substantial current handling capabilities. Its primary function is to act as a one-way electrical valve, allowing current to flow predominantly in one direction while impeding it in the opposite direction. This behavior is crucial in various electronic circuits, particularly in power conversion and rectification.
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Diode Type | Rectifier | Standard rectifier diode for AC to DC conversion |
| Maximum Repetitive Peak Reverse Voltage (VRRM) | 1000V | The maximum reverse voltage the diode can withstand without breakdown |
| Average Forward Current (IF(AV)) | 6A | The maximum average forward current the diode can handle. |
| Forward Voltage Drop (VF) | ~1.1V (at rated current) | Voltage drop across the diode when conducting in the forward direction |
| Package Type | R-6 | Defines physical dimensions and mounting style. |
Key Electrical Characteristics of the 6A10 Diode

The 6A10 diode is characterized by several key electrical parameters that dictate its performance in various circuit applications. Understanding these characteristics is crucial for ensuring proper circuit design and reliable operation. These parameters include Peak Reverse Voltage, Average Rectified Current, Forward Voltage Drop, and Reverse Leakage Current. Each parameter plays a significant role in determining the suitability of the 6A10 for a particular task.
| Parameter | Symbol | Typical Value | Unit | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Reverse Voltage | V_RRM | 1000 | V | The maximum reverse voltage that the diode can withstand without breaking down. |
| Average Rectified Current | I_F(AV) | 6 | A | The maximum average forward current that the diode can handle continuously. |
| Forward Voltage Drop | V_F | 1.1 | V | The voltage drop across the diode when it is conducting current in the forward direction. Note that this value will vary with forward current and junction temperature. |
| Reverse Leakage Current | I_R | 5 | μA | The small current that flows through the diode in the reverse direction when it is reverse biased. Measured at the diode's rated reverse voltage. |
6A10 Diode Packaging and Mounting Considerations
The 6A10 diode typically comes in an R-6 package, a robust, axial-leaded design that is engineered for efficient heat dissipation and ease of mounting, especially in high-current applications. The dimensions and structure of this package are crucial for proper integration into circuits.
The R-6 package dimensions are standardized to ensure consistency across manufacturers. These dimensions usually include the body diameter, lead length, and lead diameter. For example, typical dimensions are around 9mm in body length, 5mm in body diameter, and axial leads at 1.2mm in diameter and 25mm in length. These physical specifications are essential for PCB design and heat management planning.
| Parameter | Typical Value | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Body Length | 9 | mm |
| Body Diameter | 5 | mm |
| Lead Diameter | 1.2 | mm |
| Lead Length | 25 | mm |
Effective thermal management is paramount for the 6A10 diode. As a high-current rectifier, it generates heat during operation due to its forward voltage drop and the current flowing through it. Proper mounting techniques and the use of heatsinks are often necessary to prevent thermal runaway and ensure the diode operates within its safe temperature range. Without proper heat dissipation, the diode's performance will degrade, leading to reduced lifespan and potential failure. Therefore, consider using thermal grease and mounting the diode to a chassis or a heat sink to ensure heat transfer.
Common Applications of the 6A10 Diode
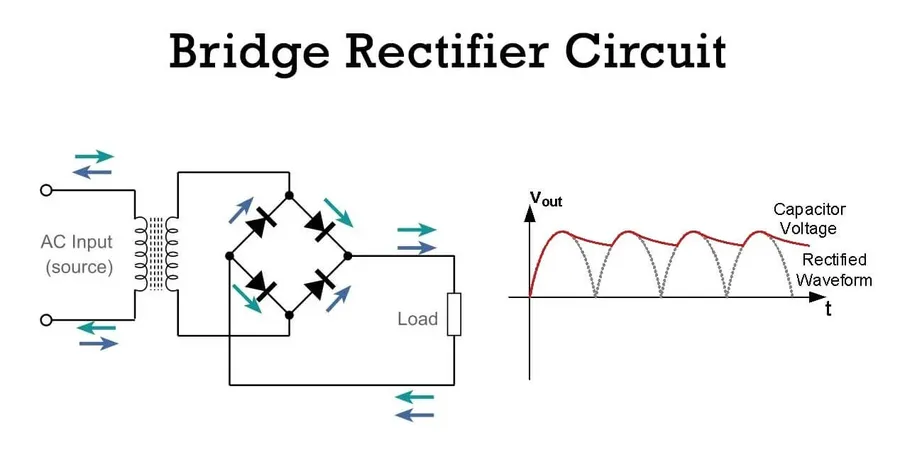
The 6A10 diode, characterized by its robust 6-amp current handling and 1000V peak reverse voltage rating, is a ubiquitous component in various electronic circuits. Its primary role as a rectifier—converting alternating current (AC) to direct current (DC)—makes it indispensable in numerous applications, spanning from basic power supplies to more complex industrial systems.
- Power Supplies
In linear power supplies, the 6A10 diode acts as a critical element in the rectification stage, converting the AC input from the mains into a pulsating DC voltage. This DC voltage is then smoothed by capacitors and regulated by voltage regulators, providing a stable DC output for various electronic devices. Due to its high current rating, the 6A10 is often used in power supplies requiring more than 1A of current. - Battery Charging Circuits
The 6A10 diode is widely used in battery charging circuits to prevent reverse current flow from the battery back into the charger. This ensures that current only flows from the charger to the battery, protecting the charger from damage and ensuring efficient battery charging. Its high current rating makes it suitable for a range of battery types, from smaller portable devices to high capacity automotive batteries. - AC-DC Converters
AC-DC converters, also known as rectifiers, are fundamental components in electronic devices. The 6A10 diode's function in these circuits is to convert AC power into DC power, allowing electronic circuits, which primarily operate using DC, to interface with AC power sources. Whether in adapters for laptops, phones, or other electronic devices, this diode is a standard element. - Industrial Control Systems
The 6A10 finds significant use in industrial control systems for its robust performance and reliability. In industrial settings, the 6A10 is used in applications such as motor drives, welding equipment, and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), where high current capacity and voltage ratings are necessary to cope with the demanding conditions of these applications. - General Purpose Rectification
Beyond specialized applications, the 6A10 is a common choice for general purpose rectification, whether it's in DIY electronic projects or professional circuit designs. Due to its wide availability, cost-effectiveness, and strong specifications, it is a favored choice in any situation requiring a standard rectifier.
6A10 Diode vs. Other Diodes: A Comparative Analysis
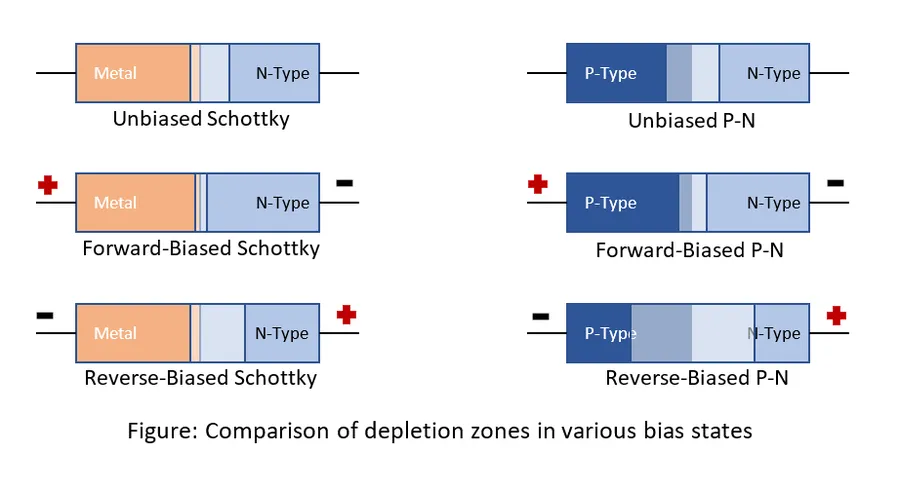
The 6A10 diode, a robust rectifier, is often compared to other diodes, especially when selecting components for power rectification. This section provides a detailed comparison, focusing on key parameters that influence component choice in various applications.
| Parameter | 6A10 Diode | 1N4007 Diode | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peak Reverse Voltage (PRV) | 1000V | 1000V | Both diodes have the same high PRV, suitable for standard mains rectification. |
| Average Rectified Current | 6A | 1A | The 6A10 can handle significantly higher current, useful in high-power applications. |
| Forward Voltage Drop (Typical) | 1.1V | 1.1V | Both diodes have a similar forward voltage drop. |
| Maximum Surge Current | 200A | 30A | The 6A10 has a higher surge current capability. |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C to +150°C | -65°C to +175°C | Both have broad operating temperature ranges, but the 1N4007 may be more suited to very low operating temperatures. |
| Package | R-6 | DO-41 | Different packages affect physical mounting and heat dissipation. |
| Applications | Power Supplies, Battery Chargers, Industrial Control Systems | General Purpose Rectification, Low Current Applications | The 6A10 is suitable for high current applications, while the 1N4007 is better suited for low current rectification. |
The 6A10 excels in high-current scenarios, boasting a 6A continuous current handling capacity. Its higher surge current rating also allows it to withstand momentary overloads. In contrast, the 1N4007, while sharing the same peak reverse voltage rating, is better suited for lower-current applications, typically limited to 1A. When choosing between these diodes, the primary factor should be the current requirement of the specific application. The 6A10 is the preferred choice when dealing with higher-power rectification due to its increased current capacity.
Frequently Asked Questions About the 6A10 Diode
This section addresses common queries about the 6A10 diode, clarifying its operational characteristics, applications, and limitations. We aim to provide precise answers based on fundamental electrical engineering principles to enhance understanding and practical usage.
- What is the primary function of a 6A10 diode?
The 6A10 diode is primarily used as a rectifier, which means its main function is to convert alternating current (AC) into direct current (DC). It acts as a one-way valve for electrical current, allowing it to flow easily in one direction (forward biased) while blocking it in the opposite direction (reverse biased). - What is the typical forward voltage drop of a 6A10 diode?
The forward voltage drop of a 6A10 diode is typically around 1.0 to 1.2 volts when it is conducting its rated current of 6A. This voltage drop is an inherent characteristic of silicon diodes and represents the energy required to overcome the potential barrier at the p-n junction. - How does a 6A10 diode differ from a Schottky diode?
A 6A10 is a standard silicon rectifier diode, whereas a Schottky diode has a metal-semiconductor junction, leading to a significantly lower forward voltage drop (typically 0.2 to 0.4 volts). Schottky diodes are faster but have lower reverse voltage ratings. The choice between them depends on application needs for speed and voltage handling. - Can the 6A10 diode be used in high-frequency circuits?
The 6A10 is not designed for high-frequency applications. Its relatively slow reverse recovery time makes it unsuitable for switching at high frequencies. For high-frequency applications, faster diodes like Schottky diodes or fast recovery diodes are more appropriate. - What is the peak reverse voltage (PRV) rating of the 6A10 diode?
The peak reverse voltage (PRV) rating of the 6A10 diode is 1000V. This is the maximum reverse voltage the diode can withstand without breaking down and conducting in the reverse direction. Exceeding this voltage can cause irreversible damage to the diode. - What are some common applications for the 6A10 diode?
The 6A10 diode is commonly used in power supplies, AC-DC converters, battery charging circuits, and general rectification applications where a high current and relatively low frequency are required. Its robust current handling makes it suitable for medium-power applications. - What are the limitations of the 6A10 diode?
The 6A10 diode is limited by its relatively slow switching speed, which restricts its use in high-frequency circuits, and its forward voltage drop, which leads to some power loss. Also, exceeding the rated reverse voltage or forward current will damage it.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with 6A10 Diode Circuits
Diagnosing issues within 6A10 diode circuits involves understanding common failure modes and employing systematic testing. Identifying problems early can prevent further damage and ensure the reliability of the electronic system.
- Overheating
Excessive heat generation in a 6A10 diode typically indicates it's operating beyond its rated current or experiencing a reverse bias condition. Check the circuit design against the diode's datasheet specifications, verify the presence of adequate heatsinking, and inspect the surrounding components for issues. - Reverse Current Leakage
A malfunctioning 6A10 diode may permit current flow in the reverse direction, disrupting the circuit's intended operation. Employ a multimeter to measure reverse current; significant current flow beyond the datasheet's specified leakage indicates a diode failure. - Open or Short Circuit Failure
A 6A10 diode can fail as an open circuit, blocking current flow entirely, or as a short circuit, allowing unrestricted current flow. Use a multimeter in diode test mode to verify forward voltage drop and continuity in both directions. An open circuit will show no continuity, while a short circuit will measure a very low voltage drop in both directions. - Forward Voltage Drop Anomalies
The forward voltage drop of a 6A10 diode should be consistent, within the expected range based on its current level (typically around 1.1V, but should be verified from the datasheet). Variations can indicate degradation and impending failure. Measure the forward voltage drop with a multimeter while the diode is conducting a known forward current. - Physical Damage
Inspect the diode for any signs of physical damage, such as cracks or burns. These can often be indicative of electrical overstress or improper handling. Such damages can cause intermittent failures or complete malfunction. Replace the component immediately if damage is found.
Effective troubleshooting requires a systematic approach and an understanding of the 6A10 diode's operational characteristics. Always refer to the component's datasheet to confirm expected parameters and operational limits.
Practical Tips for Using and Handling the 6A10 Diode
Proper handling and usage of the 6A10 diode are crucial for ensuring reliable circuit operation and preventing premature failure. These practices encompass careful physical handling, precise soldering techniques, and strategic considerations to extend the diode's operational lifespan.
- Handling Precautions
Avoid dropping or subjecting the 6A10 diode to physical stress, as this can cause internal damage. Store diodes in a dry, antistatic environment to prevent damage from electrostatic discharge (ESD) which can degrade performance or cause failure. When handling, use proper ESD protection such as anti-static wrist straps and mats. - Soldering Techniques
Use a temperature-controlled soldering iron to avoid overheating the diode, which can damage the semiconductor junction. Keep soldering time to a minimum, typically no more than 3-5 seconds, to prevent thermal stress. Ensure that the solder joints are clean and properly formed for reliable electrical connection. Use a flux to assist in solder flow and prevent cold joints. - Heat Management
When operating at or near the diode's maximum rated current, proper heatsinking is essential. Use a heatsink appropriate for the application to dissipate heat and maintain the junction temperature within specified limits. Confirm that the heatsink is securely attached to the diode package using thermal paste for effective heat transfer. - Circuit Design Considerations
Ensure the diode operates within its specified ratings, such as forward current and reverse voltage. Incorporate current limiting resistors in series with the diode to prevent overload. Do not exceed the diode's specified maximum reverse voltage or forward current. When designing circuits where repetitive high reverse voltage is anticipated, consider adding additional components like a TVS diode. - Storage Conditions
Store unused diodes in their original packaging or antistatic bags. Keep the storage environment dry and at a temperature within the manufacturer's recommended range. Avoid exposure to corrosive chemicals or harsh environments.
The 6A10 diode, a fundamental component in power rectification, plays an essential role in our electronic ecosystem. Understanding its capabilities and limitations empowers both hobbyists and professionals to design robust and reliable circuits. From power supplies to battery chargers, the 6A10 diode’s reliability underpins a vast array of applications, and as technology advances, a deeper comprehension of foundational components like this will continue to be key to innovation.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA