Decoding Capacitor Prices: A Comprehensive Guide for 2024
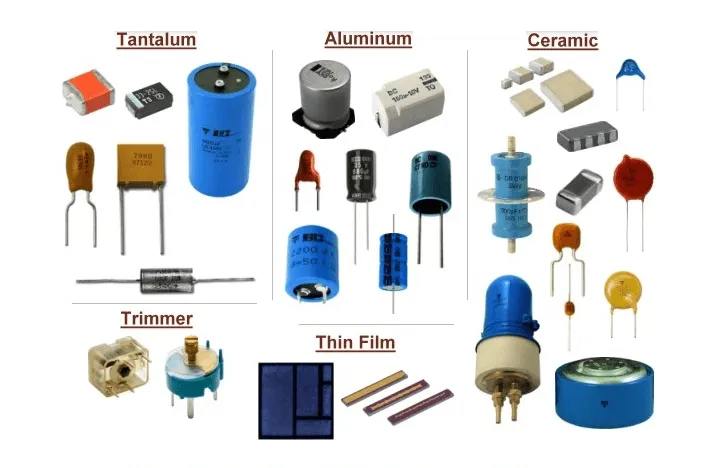
Capacitors, essential components in countless devices from the AC in your home to the computer on your desk, come with a surprising range of prices. This article demystifies capacitor pricing, exploring the factors influencing these costs and offering practical guidance for homeowners, hobbyists, and professionals alike. The average price of a capacitor can range from $10 to $400 or more, depending on its type and purpose, so stay tuned for a deeper dive into understanding the true value of capacitors.
Capacitor Price Ranges: An Overview

Capacitor prices exhibit a wide range, primarily influenced by the capacitor's material, capacitance, voltage rating, and intended application. This section provides an overview of this price spectrum, highlighting the differences between inexpensive ceramic capacitors and the more costly AC dual run capacitors.
The cost of a capacitor can range from a few cents for basic ceramic types used in low-power electronics, to several hundred dollars for specialized high-voltage or high-capacitance units. Understanding these cost variations requires looking into the factors that dictate pricing.
- Material:
The dielectric material used (e.g., ceramic, electrolytic, film, tantalum) significantly affects the capacitor's performance characteristics and cost. - Capacitance:
Measured in farads (F), or more commonly microfarads (µF), higher capacitance generally leads to higher prices for comparable types of capacitors. - Voltage Rating:
Capacitors designed to withstand higher voltages are typically more expensive due to specialized construction and materials. - Application:
Capacitors intended for high-reliability applications or extreme conditions (high temperature, humidity) often come at a premium. For example, AC run capacitors for motors are more expensive than general-purpose capacitors.
AC Capacitor Costs: Factors Influencing Price
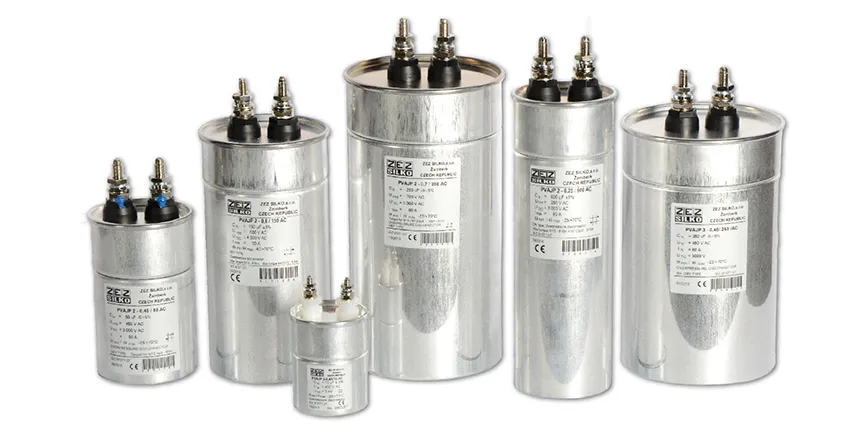

The cost of an AC capacitor is not a fixed value but rather a dynamic figure influenced by several key factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for both consumers looking to replace a capacitor and professionals seeking to make informed purchasing decisions. The price of an AC capacitor is fundamentally determined by its electrical specifications and its intended application within an HVAC system.
The following are key elements influencing the price of AC capacitors:
- Microfarad Rating (MFD)
The microfarad (MFD or µF) rating signifies the capacitance of the component, a measure of its ability to store an electrical charge. Higher MFD ratings generally correlate with higher prices, as they indicate a greater storage capacity. For instance, a 60 MFD capacitor will invariably cost more than a 30 MFD capacitor of similar voltage and type. - Voltage
The voltage rating of the capacitor is the maximum voltage it can withstand without failing. Higher voltage ratings, such as 440 VAC versus 370 VAC, typically translate to higher costs. The voltage rating must match the requirements of the AC system to ensure safe operation, therefore, higher rated voltage capacitor have a higher price point. - Type (Single or Dual Run)
AC capacitors come in two primary types: single-run and dual-run capacitors. Single-run capacitors serve one motor (either the fan or compressor), whereas dual-run capacitors serve both. Dual-run capacitors have more terminals and are physically larger, thus they typically cost more than single-run types. - Physical Size and Dimensions
Capacitors of same capacitance and voltage may still vary in price due to different physical sizes and dimensions. Larger capacitors may require more material and different manufacturing process, therefore they may be priced higher. Considerations must include case material and terminal type, as this can also affect price. - Brand
Reputable brands often command higher prices due to perceived reliability and quality. While some generic brands might offer lower prices, these may compromise on quality, therefore, brand is a major price factor.
These factors are not isolated; they interact to determine the final price of an AC capacitor. For example, a high-MFD, high-voltage, dual-run capacitor from a leading brand will naturally cost more than a low-MFD, low-voltage, single-run capacitor from a generic manufacturer. Also, the technology used in the capacitor design can greatly affect price, with more advanced design and production processes typically reflecting higher price.
| Factor | Impact on Price | Technical Detail |
|---|---|---|
| Microfarad (MFD) | Higher MFD = Higher Price | Capacity to store electrical charge |
| Voltage Rating | Higher Voltage = Higher Price | Maximum voltage the capacitor can withstand |
| Type | Dual-Run > Single-Run | Functionality (single or dual motor) |
| Brand | Reputable Brands = Higher Price | Quality, reliability, warranty |
| Physical Size | Larger Size = Higher Price | Material usage and manufacturing process |
AC Capacitor Replacement Costs: Labor and Parts

Replacing an AC capacitor involves both the cost of the component itself and the labor required for installation. Understanding this breakdown is crucial for budgeting and deciding between a DIY approach and hiring a professional. The total cost can vary significantly depending on the complexity of the system and the technician's rates.
| Cost Component | Typical Price Range | Factors Influencing Price |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitor (Part) | $10 - $50 | Microfarad rating (MFD), voltage, type (single or dual run), brand, quality |
| Labor | $90 - $200+ | Technician experience, geographic location, complexity of the job, call-out fees |
| Total Replacement Cost | $100 - $250+ | Combined costs of parts and labor |
AC capacitor part costs typically range from $10 to $50. This price fluctuation is driven by factors such as microfarad (MFD) rating, voltage, whether it’s a single or dual run capacitor, the brand, and the overall quality of the component. Higher MFD and voltage ratings generally correlate with higher prices. Dual run capacitors, which serve both the compressor and the fan motor, usually cost more than single run capacitors.
Labor costs for AC capacitor replacement are quite variable, typically ranging from $90 to over $200. Factors influencing these costs include the technician’s experience level, geographical location, and the complexity of the AC unit. Some technicians may charge by the hour, while others may have a flat rate for the service. Additional costs might include call-out or diagnostic fees. In areas with higher costs of living, labor expenses will likely be higher.
The decision between DIY and professional installation often comes down to a balance between cost, skills, and safety. While DIY can potentially save on labor costs, it carries inherent risks, especially due to the high voltages in AC systems. Professional technicians provide expertise and typically warranty their work, ensuring proper installation and function of the system. DIY solutions might be suitable for someone who is mechanically inclined, understands the electrical components and safety precautions, and has the right tools.
- DIY Replacement Advantages:
Lower cost by avoiding labor charges; potential for learning and gaining practical experience. - DIY Replacement Disadvantages:
Risk of improper installation or electric shock; potential to void warranties; no labor guarantees. - Professional Technician Advantages:
Ensured proper installation and electrical safety; warranties on parts and labor; troubleshooting and diagnostic abilities. - Professional Technician Disadvantages:
Higher cost due to labor charges; potential for scheduling delays.
Different Types of Capacitors and Their Prices
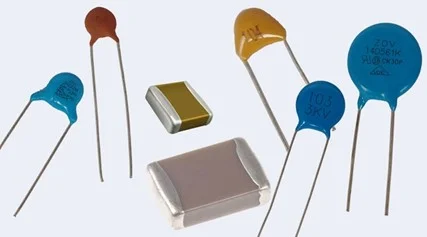
Capacitors, essential components in electronic circuits, come in various types, each with distinct characteristics, applications, and price points. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the appropriate capacitor for specific needs. This section explores the common types of capacitors, highlighting their cost variations and typical uses.
| Capacitor Type | Typical Applications | Price Range (USD) | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic | Bypassing, decoupling, general-purpose applications. | $0.01 - $0.50 | Small size, low cost, limited temperature range, moderate stability. |
| Electrolytic (Aluminum) | Power supply filtering, energy storage in low-frequency circuits. | $0.10 - $5.00 | High capacitance, polarized, limited lifespan, sensitive to temperature and reverse voltage. |
| Electrolytic (Tantalum) | Filtering, decoupling, and energy storage in space-constrained and high-reliability applications. | $0.20 - $10.00 | Compact size, relatively stable over temperature, but sensitive to reverse voltage. |
| Film | High-frequency applications, precision timing circuits, audio equipment. | $0.20 - $15.00 | High precision, good stability, moderate to high-temperature resistance. |
| Supercapacitor (Ultracapacitor) | Energy storage for short-term power delivery, regenerative braking, backup power. | $1.00 - $50.00+ | Very high capacitance, long cycle life, relatively low voltage rating. |
| AC Run Capacitor | Motor starting and running in AC units, refrigerators, and other motor-driven appliances. | $10 - $50+ | High voltage rating, designed for continuous duty in AC applications. |
The price ranges provided are approximate and can vary based on factors like manufacturing quality, brand, tolerances, and quantity purchased. For example, high-precision film capacitors used in audio equipment can be significantly more expensive than standard film capacitors used in general electronics.
Let's further explore some of these common types of capacitors:
- Ceramic Capacitors
These are the most common and inexpensive type, often used for general-purpose applications. Their small size and low cost make them ideal for decoupling and bypassing in electronic circuits. However, their capacitance is typically limited, and they may not be as stable as other types under temperature variations. - Electrolytic Capacitors
Electrolytic capacitors, especially aluminum types, offer high capacitance values, making them suitable for filtering and energy storage in power supplies. However, they are polarized, meaning they must be connected with the correct polarity, and they have a limited lifespan, especially at elevated temperatures. Tantalum capacitors are a more expensive option that offers a smaller, more stable option over temperature compared to aluminum electrolytic. - Film Capacitors
Film capacitors are known for their high precision, good stability, and ability to handle higher frequencies. They are widely used in timing circuits, audio equipment, and other applications where accuracy and reliability are crucial. Film capacitors come in various constructions, such as polyester, polypropylene, and polystyrene, each with its own performance characteristics and cost. - Supercapacitors (Ultracapacitors)
Supercapacitors stand out with their exceptional capacitance and rapid charging/discharging capabilities. While they are not typically designed for voltage regulation like other capacitors, their primary use lies in energy storage and short-term power delivery in applications like regenerative braking and backup power systems. They come at a higher price compared to other capacitor types.
Where to Buy Capacitors: Online vs. Local Stores
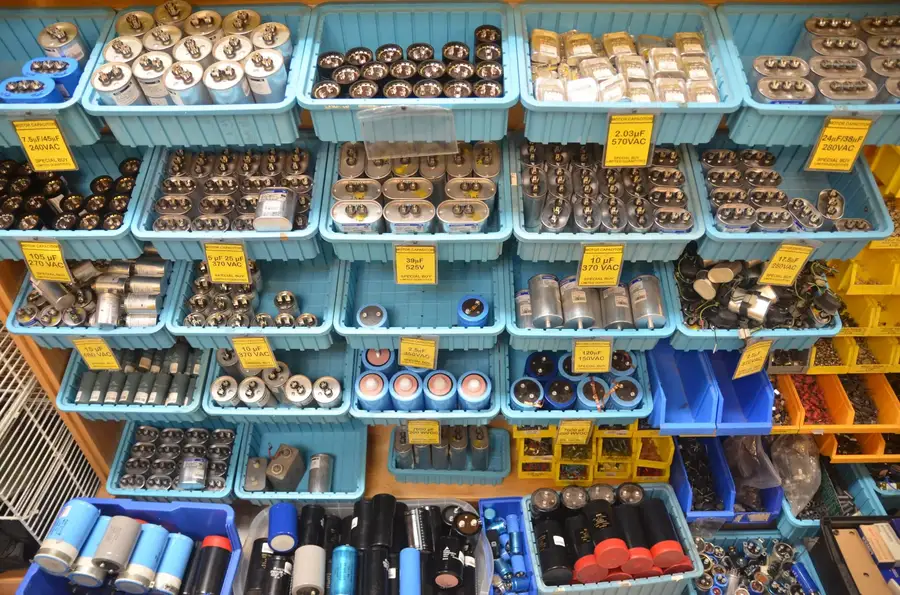

The decision of where to purchase capacitors, whether online or from local stores, significantly impacts cost, convenience, and availability. Understanding the nuances of each option is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions.
Online retailers like Amazon, Home Depot, and specialized electronics distributors offer a broad selection, while local stores provide immediate availability and potential for in-person support.
| Feature | Online Retailers | Local Stores |
|---|---|---|
| Selection | Wide variety of capacitors, including specialized types. | Limited selection, primarily common capacitor types. |
| Price | Competitive pricing, often with discounts and promotions. | Potentially higher prices due to overhead costs. |
| Convenience | Easy to browse, compare prices, and purchase from home. | Requires travel to the store, potentially inconvenient. |
| Availability | Generally good, with options for expedited shipping. | May be limited by stock, requiring multiple trips or phone calls. |
| Expertise & Support | Limited in-person expert support, but typically includes online customer reviews and FAQs. | Opportunity for face-to-face interaction with store staff for advice. |
| Shipping Time | Requires lead-time for shipping. | Immediate availability of the part. |
| Return Policy | Typically good return policy with refunds or exchanges. | Return policies can be more restrictive. |
- Online Retailers: Advantages
Extensive selection, competitive pricing, convenient shopping experience, and detailed product information. Often provides customer reviews to aid decision-making. - Online Retailers: Disadvantages
Lack of in-person support and product inspection before purchase, potential shipping delays, and less immediate access to the component. - Local Stores: Advantages
Immediate availability, face-to-face interaction with staff, potential for personalized advice, and ability to inspect product before purchase. - Local Stores: Disadvantages
Limited stock, higher prices due to overhead, and less convenience, requiring travel.
When considering where to purchase your capacitors, assess the urgency of your project, your budget, and your need for specialized components. If immediate replacement is crucial and price is secondary, a local store may be optimal. For cost-conscious buyers seeking a broad array of choices, online retailers are often the better path.
Capacitor Price and Quality: Striking the Right Balance

Selecting a capacitor involves more than just finding the lowest price; it's crucial to balance cost with quality to ensure long-term reliability and performance. Opting for the cheapest capacitors can often lead to premature failure, resulting in additional expenses for replacements and potential damage to the equipment they are intended to protect. A careful evaluation of quality standards and brand reputation is essential for a cost-effective solution.
The price of a capacitor can be indicative of several factors that relate to its overall quality. Lower cost capacitors often compromise on materials, manufacturing tolerances and quality control processes. This can result in a shorter lifespan, higher failure rates, and instability in operation.
- Material Quality
High-quality capacitors utilize superior dielectric materials and conductive elements which contribute to better performance and longevity. - Manufacturing Precision
Precise manufacturing processes and tight tolerances ensure that the capacitor meets its specified performance metrics and can withstand rated operating conditions. - Quality Control
Reputable manufacturers implement stringent quality control procedures that include testing at various stages of production, resulting in components that are less likely to fail prematurely.
When choosing a capacitor, pay attention to the brand's reputation and adherence to quality standards. Industry-recognized certifications, such as those from ISO or specific electronics standards organizations, can serve as an indication of a manufacturer’s commitment to quality. Additionally, product datasheets provide critical information, including operating temperature ranges, voltage ratings, and life expectancy data.
It is often advantageous to choose capacitors from manufacturers with a proven track record of producing reliable components. While initially more costly, high-quality capacitors offer a better return on investment through reduced replacement frequencies and lower risk of system downtime. For instance, a capacitor that adheres to strict UL standards may be more expensive, but is likely to operate reliably for longer, reducing the total cost of ownership compared to an inexpensive, uncertified component.
In conclusion, while price is undoubtedly a factor, it should not be the primary determinant when selecting a capacitor. A balanced approach that prioritizes quality ensures long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness, minimizing the risk of premature failure and subsequent maintenance costs.
Frequently Asked Questions About Capacitor Prices
Understanding capacitor pricing can be complex, given the variety of types and applications. This section addresses common questions related to capacitor costs, aiming to provide clarity for both consumers and professionals. We delve into the factors affecting price, potential issues, and operational considerations.
- How much does a capacitor cost?
Capacitor costs vary widely based on type, capacitance, voltage rating, and application. Simple ceramic capacitors can cost less than $0.10 each, while specialized AC run capacitors can range from $10 to $50 or more. Electrolytic capacitors often fall in the $1-$10 range, with film capacitors varying more widely, and supercapacitors often being the most expensive. The precise cost hinges on the specific requirements of the application. - What happens when an AC capacitor goes bad?
A failing AC capacitor can lead to a variety of issues. Typically, a bad capacitor will prevent the compressor or fan motor from starting properly, resulting in a humming noise and the inability to cool. In some cases, a bad capacitor can also lead to overheating and eventual motor failure. Other symptoms include intermittent operation and reduced performance, such as less cooling or airflow. - How to tell if a capacitor is bad?
Visually, a bad capacitor may exhibit signs of physical damage, such as a bulging case, leaking fluid, or burnt terminals. Electrically, a multimeter can be used to measure capacitance and confirm whether it matches the rated value (with a tolerance). An ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) meter can detect the presence of short circuits, which is a more precise method. If the capacitance value is significantly lower than the stated rating or is reading near 0, the capacitor is likely faulty. - Can I run my AC without a capacitor?
No, an AC unit cannot run without a functioning capacitor. The capacitor provides the initial boost of energy needed to start the compressor and fan motors, which require a significant amount of power initially. Attempting to bypass the capacitor can lead to damage or premature failure of the motors due to excessive startup current. In essence, the capacitor is a critical component of an AC unit's starting circuit. The motors will experience increased stress and won't start correctly without the capacitor's help. - Are more expensive capacitors always better?
While price is often correlated with quality, the most expensive capacitor isn't always the best choice for every application. High-quality capacitors from reputable manufacturers often have tighter tolerances, greater lifespan, and more robust construction. However, selecting a capacitor that meets the specific technical requirements of your application is crucial. Over-specifying a capacitor won't provide added performance and would be a waste of cost. Consider the voltage, capacitance, temperature requirements, expected lifespan, and environmental conditions when choosing a capacitor, rather than strictly looking at price. - Do all capacitors have the same lifespan?
No, capacitors have varying lifespans, which depend on the capacitor type, operating conditions, and quality. Electrolytic capacitors, for instance, have a limited lifespan due to the liquid electrolyte, which can dry out, especially at high temperatures. Film capacitors generally have a longer lifespan, while ceramic capacitors are more robust and less sensitive to temperature changes. Environmental factors such as heat, humidity, and voltage surges can significantly reduce the lifespan of any capacitor, so ensure adequate ventilation and proper component ratings for extended performance.
DIY Capacitor Replacement: Risks and Considerations
While replacing a capacitor might seem like a straightforward DIY task, it's crucial to acknowledge the potential risks involved, particularly when dealing with high-voltage systems commonly found in air conditioning units. Incorrect handling or misdiagnosis can lead to personal injury, equipment damage, or further complications.
This section outlines the key risks associated with DIY capacitor replacement and provides a checklist to help determine if you should attempt the repair yourself or call in a professional technician.
- High Voltage Hazards
AC capacitors store a significant electrical charge, even when the power is disconnected. Mishandling can result in severe electrical shock, burns, or even death. Improper discharging techniques are a major risk factor. - Equipment Damage
Incorrect installation or selection of the wrong capacitor can damage your AC unit, potentially leading to costly repairs beyond the simple capacitor replacement. This includes damage to the compressor and fan motors. - Misdiagnosis
A faulty capacitor may exhibit symptoms similar to other electrical issues within the AC system. Attempting to fix the system based on an incorrect diagnosis can worsen the problem or lead to further damage. - Safety Risks
Working with electrical components requires knowledge of safety practices and the use of proper personal protective equipment (PPE), such as insulated gloves and safety glasses. Failure to do so increases the risk of injury.
Given these risks, it's essential to assess your capabilities and the potential dangers carefully before proceeding with a DIY capacitor replacement. Here's a checklist to help you make an informed decision:
- Safety Knowledge
Do you have a clear understanding of electrical safety practices, including how to safely discharge a capacitor? - Proper Tools
Do you possess the necessary tools, including insulated screwdrivers, a multimeter, and potentially a capacitor discharge tool? - Technical Proficiency
Are you comfortable working with electrical components and following diagrams? - System Knowledge
Do you understand the specific electrical requirements of your AC unit, including the correct capacitor specifications (microfarads and voltage)? - Risk Tolerance
Are you comfortable with the potential risks of electrical shock and equipment damage?
If you answer 'no' to any of these questions, it is highly recommended to contact a qualified HVAC technician to handle the capacitor replacement. Professionals have the necessary training, experience, and equipment to complete the job safely and efficiently.
Capacitor Pricing Table: A Comparison Guide
Understanding the diverse landscape of capacitor pricing requires a structured comparison. This table provides a consolidated view of different capacitor types, their typical applications, and key considerations to aid in selection based on project or repair requirements. The price ranges are approximate and can vary based on supplier, specifications, and quantity.
| Capacitor Type | Typical Capacitance Range | Typical Voltage Range | Typical Applications | Approximate Price Range (USD) | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceramic Capacitors | 1 pF to 10 μF | Few volts to several kV | Bypassing, coupling, filtering in general electronics. | $0.01 - $1.00 | Small size, low cost, good for high frequency applications, but lower accuracy and stability |
| Electrolytic Capacitors | 0.1 μF to several Farads | Few volts to hundreds of volts | Power supply filtering, energy storage, decoupling. | $0.10 - $5.00 | High capacitance, polarized (polarity matters), shorter lifespan, susceptible to heat and temperature |
| Film Capacitors | 1 nF to 100 μF | Few volts to several kV | Audio equipment, power electronics, high-frequency circuits. | $0.20 - $10.00 | High precision, stable, long lifespan, good high-frequency performance, but larger size |
| AC Run Capacitors (Single) | 1 μF to 100 μF | 250VAC to 600 VAC | Single phase AC motor run applications, air conditioners, refrigerators | $10 - $30 | Designed for AC operation, specific voltage and capacitance ratings are required |
| AC Run Capacitors (Dual) | 2.5+ μF to 80+ μF | 250VAC to 450 VAC | Dual motor run applications, AC units with fan and compressor | $15 - $50 | Designed for AC operation, three terminals for dual motor operation, capacitance and voltage requirements are critical |
| Supercapacitors (Ultracapacitors) | 1 F to thousands of Farads | Few volts | Energy storage, battery backup, regenerative braking. | $5.00 - $100+ | Extremely high capacitance, very high charge-discharge cycles, lower voltage ratings, expensive |
Understanding capacitor prices is essential for making informed purchasing decisions and budgeting for repairs. Whether you are replacing an AC capacitor for approximately $180 on average or stocking up on electronic components, consider type, quality, and application. While a cheaper option might be tempting, investing in quality capacitors ensures reliability and longevity, ultimately saving you money in the long run. The capacitor market is vast and variable, so keep informed and always prioritize safety when handling electrical components.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA