Find & Buy Resistors Near You: A Comprehensive Guide

In today's tech-driven world, resistors are the unsung heroes in almost every electronic device. From controlling current flow to dividing voltage, they are indispensable components. Whether you are a hobbyist embarking on a new project or a professional needing a quick replacement, knowing where to buy resistors near you is crucial. This article will guide you through various options, explore different types of resistors, and offer advice on making the right purchase. And yes, we will help you locate where to buy resistors near me.
Understanding Resistors: The Basics

Resistors are fundamental passive electronic components that impede the flow of electrical current within a circuit, effectively acting as a control valve for electron movement. Their primary function is to reduce voltage, limit current, and divide voltage, making them indispensable for a multitude of electronic applications from basic LED circuits to complex computing systems. Selecting the correct resistor type and value is paramount to ensuring circuit functionality, longevity, and safety, as incorrect choices can lead to component damage or circuit malfunction.
Where to Buy Resistors Locally
For immediate access to resistors, several brick-and-mortar options exist, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. This section details where you can buy resistors locally, covering major retailers, specialized electronics stores, and even auto parts shops.
| Store Type | Pros | Cons | Typical Inventory |
|---|---|---|---|
| Major Retailers (e.g., Best Buy, Walmart) | Convenience, often have limited selection, may not have a full range of resistance values | Higher prices, less knowledgeable staff | Basic through-hole resistors, limited value range, commonly used for simple projects |
| Specialized Electronics Stores (e.g., Fry's Electronics, Micro Center) | Wider selection, knowledgeable staff | May be less convenient to visit, variable inventory based on region | Through-hole and SMD resistors, variety of resistance values and power ratings |
| Auto Parts Stores (e.g., AutoZone, Advance Auto Parts) | Some carry resistors for automotive use, readily accessible | Limited selection, primarily high-power resistors, may not be suitable for all electronic projects | High-power resistors, typically wire-wound, for automotive applications |
| Local Hobby Shops | May have a good selection of specialized or hard-to-find resistors, often offers expert advice | Inventory is highly variable, may be more expensive, may not be as conveniently located | Various types, including through-hole, SMD, and sometimes unique or vintage components |
Online Marketplaces for Resistors

The digital landscape offers a plethora of options when sourcing resistors. Online marketplaces like Amazon, eBay, and specialized component sites provide a vast selection, competitive pricing, and convenient shipping, but buyers must also navigate potential risks. This section examines these platforms, highlighting both the advantages and the crucial aspects to consider to make informed purchasing decisions when you buy resistors near me.
| Marketplace | Pros | Cons | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Amazon | Wide variety, often competitive prices, fast shipping for Prime members, customer reviews | Quality can vary significantly among sellers, potential for counterfeit products, shipping costs may apply | Check seller ratings and reviews carefully; prioritize items with high ratings and numerous reviews. |
| eBay | Potentially lower prices, wide range of new and used components, ability to bid for better deals | Seller reliability can vary, shipping times can be longer, risk of scams or misrepresented items | Pay attention to seller feedback scores, check item descriptions and photos meticulously, prefer sellers with high feedback and a history of selling similar items. |
| Specialized Component Sites (e.g., Mouser, Digi-Key) | Extensive technical specifications provided, high-quality components, reliable sourcing and authenticity | Generally higher prices compared to marketplaces, potentially higher shipping cost | Ideal for professional applications requiring precision and component traceability, often offer datasheets and detailed technical information. |
- Price Comparison:
Always compare prices across multiple platforms. Consider total cost, including shipping, taxes, and potential return shipping. - Seller Reputation:
Prioritize sellers with positive reviews and high ratings. Be wary of sellers with little or no feedback. - Product Authenticity:
Look for clear product images and detailed descriptions. Be cautious of items priced too low, as they may be counterfeit. - Shipping and Handling:
Check shipping costs and delivery times. Consider tracking options and any associated fees. - Return Policies:
Understand the return and refund policies of each platform and seller. This is crucial in case of receiving faulty or incorrect items. - Secure Transactions:
Use secure payment methods and be cautious of sellers asking for payment outside of the platform.
Types of Resistors and Their Applications

Resistors, fundamental components in electronic circuits, come in various types, each with unique characteristics and applications. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the correct resistor when you buy resistors near me for your specific project needs. The choice depends on factors like precision, power handling, operating environment and cost considerations.
| Resistor Type | Material | Typical Applications | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film Resistors | Carbon film on a ceramic substrate | General-purpose circuits, low-cost applications | Low cost, good availability | Lower precision, temperature coefficient can be high |
| Metal Film Resistors | Thin metal film on a ceramic substrate | Precision circuits, audio equipment | High precision, low temperature coefficient, low noise | More expensive than carbon film resistors |
| Wire-Wound Resistors | Wire wound around a ceramic or fiberglass core | High-power applications, power supplies, motor control | High power rating, high precision | Larger size, inductive properties |
| SMD Resistors (Surface Mount Device) | Thick or thin film on a ceramic substrate | High-density circuit boards, portable electronics | Small size, easy for automated assembly | Smaller size makes manual handling difficult, requires specific soldering techniques |
Choosing the right resistor type depends on the specific application requirements. For general-purpose use and cost-sensitive projects, carbon film resistors are a suitable option. However, for applications requiring greater precision, metal film resistors are preferred. Wire-wound resistors are essential in high-power situations, and SMD resistors are crucial for modern, compact electronic devices. Always ensure that the resistor you select when you buy resistors near me is appropriate for the intended purpose.
How to Choose the Right Resistor Value
Selecting the correct resistor value is crucial for circuit functionality and safety. This process involves understanding the resistor color code, calculating the required resistance, and considering both tolerance and power rating. This section will guide you through these essential steps to ensure accurate and reliable circuit design.
Resistors are marked with color bands, each representing a numerical value. The color code is standardized and allows for easy identification of a resistor's resistance and tolerance. Typically, a resistor will have four or five bands. The first two (or three in a five-band resistor) indicate the significant digits, the third (or fourth) is a multiplier, and the final band represents the tolerance. The color bands are interpreted based on a standard lookup table.
| Color | Digit Value | Multiplier | Tolerance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | 1 | None |
| Brown | 1 | 10 | 1 |
| Red | 2 | 100 | 2 |
| Orange | 3 | 1000 | None |
| Yellow | 4 | 10000 | None |
| Green | 5 | 100000 | 0.5 |
| Blue | 6 | 1000000 | 0.25 |
| Violet | 7 | 10000000 | 0.1 |
| Grey | 8 | None | 0.05 |
| White | 9 | None | None |
| Gold | None | 0.1 | 5 |
| Silver | None | 0.01 | 10 |
| None | None | None | 20 |
For example, a resistor with bands of Red-Violet-Brown-Gold would have a resistance value calculated as follows: Red (2), Violet (7), Brown (10 multiplier), resulting in 27 * 10^1 = 270 ohms, with a 5% tolerance. Five-band resistors are used for higher precision, where the first three bands represent significant digits.
Besides resistance value, tolerance and power rating are equally important. Tolerance indicates how much the actual resistance value may deviate from the specified value. For example, a 100-ohm resistor with a 5% tolerance could be anywhere between 95 and 105 ohms. Power rating specifies how much power a resistor can dissipate before being damaged. It is expressed in watts. Make sure that the selected resistor has a sufficient power rating for your circuit. A resistor that cannot dissipate the heat generated by the circuit will fail.
When selecting a resistor, start by identifying the required resistance value through circuit analysis, using Ohm's law (V=IR) and Kirchhoff's laws, consider the application to determine the appropriate tolerance and power rating. Always choose a resistor with a tolerance and power rating that meet or exceed the circuit requirements. When in doubt, it's advisable to choose a resistor with a higher power rating to provide additional safety margin.
Frequently Asked Questions About Buying Resistors
This section addresses common queries regarding resistors, aiming to enhance your understanding and make your purchasing process smoother. We'll tackle questions about where to find resistors, alternatives, and even the possibility of creating your own.
- Where can I find resistors to buy?
Resistors are commonly available at various locations including major electronics retailers like Best Buy and Fry's Electronics, specialized electronics supply stores such as Digi-Key and Mouser, and online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay. You can also find them at some auto parts stores, particularly those that cater to custom car audio or electronics. - What can I use as a temporary substitute for a resistor?
While not ideal, you can temporarily use pencil lead as a high resistance substitute. The resistance varies with the thickness and length of the lead. A light bulb can also act as a resistor, though its resistance changes with temperature. Note that these are only for testing and should not be used for permanent solutions. - Where can I find resistors around the house?
Resistors are not commonly found as standalone components within household items. However, electronic devices, such as old circuit boards from discarded appliances or electronics, might contain various resistors that can be salvaged, be cautious when extracting components and ensure you discharge any capacitors to avoid electrical shock. - Can you make a homemade resistor?
While technically possible to create a basic resistor using materials like graphite or thin wire, they are not recommended for precision work due to their instability and poor tolerance. It's far more reliable and safer to buy purpose-built resistors, due to the difficulty in achieving precise resistance values and their potential safety issues, they should be avoided in final projects. - What should I consider when buying resistors?
When buying resistors, consider the resistance value (measured in ohms), tolerance (accuracy of the resistance), power rating (ability to dissipate heat), and physical size or package type. For example, surface-mount device (SMD) resistors are small and used in compact circuits, while axial lead resistors are larger and easier to handle for prototyping. - Can I buy resistors in bulk?
Yes, buying resistors in bulk is a cost-effective approach when you have an ongoing need, such as for regular projects or a small business. You can find discounted prices when purchasing multiple units or complete resistor kits. This is particularly useful for hobbyists and engineers who work on various electronic projects. - Are there any alternatives to buying physical resistors?
Yes, for prototyping, you can use a digital potentiometer, which allows you to digitally set the resistance to the desired value, these are perfect for testing circuit behavior where variable resistance is required but are often not suitable for permanent circuits. Another option in simulation software, where you can test and design circuits without using physical components.
Tips for Storing and Handling Resistors
Proper storage and handling of resistors are crucial for maintaining their integrity and ensuring accurate performance in electronic circuits. Environmental factors and physical stress can alter a resistor's value or even render it unusable. By following some simple best practices, you can significantly extend the lifespan and reliability of your components.
- Storage Environment
Store resistors in a cool, dry place. Avoid areas with high humidity or extreme temperatures, as these conditions can lead to corrosion or changes in resistance values. - Anti-Static Measures
Store resistors in anti-static bags or containers, especially surface mount resistors (SMD). This prevents electrostatic discharge from damaging the components. - Organization
Keep resistors organized by value, using component organizers, labeled boxes, or binders with clear pockets. This makes it easier to find the required resistor quickly and prevents damage from digging around in disorganized storage. Use labels with clear font to ensure rapid identification - Handling Resistors
Always handle resistors with clean, dry hands or with the aid of tweezers, especially when working with SMDs. Avoid touching the conductive leads directly. - Avoid Mechanical Stress
Do not bend or excessively flex the leads of resistors. This can weaken the connections and potentially lead to fractures or changes in resistance, resulting in connection failures. - Avoid Exposure to Corrosive Substances
Keep resistors away from chemicals and corrosive substances. These can damage the materials of the resistor, causing changes in resistance or failure. - Regular Inspections
Periodically inspect stored resistors for any signs of damage such as rust or bent leads. Discard any component that shows signs of damage or is showing an unusual appearance.
DIY Projects and Resistor Applications

Resistors, fundamental components in electronic circuits, are not just passive elements; they are the key to controlling current flow and shaping circuit behavior. This section explores exciting DIY projects that showcase the versatility of resistors, offering practical applications and inspiring your creativity when you buy resistors near me.
- Basic LED Circuit
A foundational project for beginners, this involves using a resistor to limit current flowing through an LED, preventing damage and ensuring proper illumination. This project demonstrates the resistor's current-limiting function, is a must for any electronics novice. Experimenting with different resistor values will show varying brightness. - Voltage Divider for Sensor Readings
A voltage divider is formed by two resistors in series, allowing precise voltage reduction and used to interface sensors with microcontrollers. This basic circuit, central to electronics, uses two resistors to achieve a specific voltage for sensor integration, such as with a temperature sensor, crucial for accurate data collection. - Simple Transistor Switch
Use a resistor to control a transistor's base current, allowing it to function as a switch, which can control larger current flows to power devices such as small motors. This is an initial introduction to transistor circuits, where a resistor manages the transistor's activation. - Light-Sensitive Circuit
Combine a photoresistor with a standard resistor to create a light-sensitive circuit, allowing automated responses based on light level. You can use this principle to make a night-light. By varying the resistance based on light intensity, it provides a responsive control mechanism. - Audio Amplifier
Resistors in this type of circuit set the gain and bias of transistors or op-amps, shaping the amplified sound. While more complex, understanding how resistors are incorporated can provide a better appreciation for sound electronics. - RC Timing Circuit
A resistor combined with a capacitor can create time delay circuits, useful for various electronic functions such as timers or flashing lights. This highlights the role of a resistor in controlling the charging/discharging rates of capacitors in a time-dependent circuit.
Understanding Resistor Markings and Color Codes
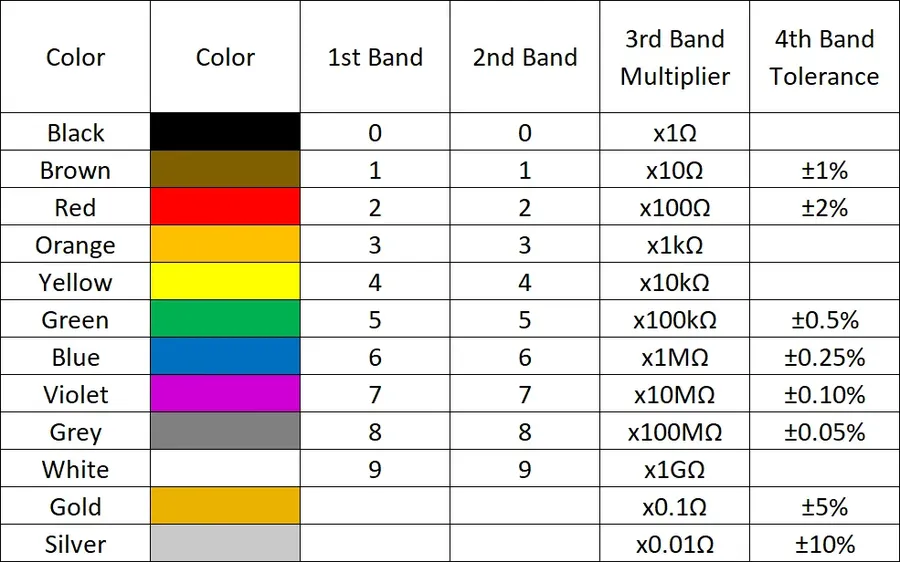
Resistor markings and color codes are essential for identifying a resistor's resistance value, tolerance, and temperature coefficient. This knowledge is crucial for selecting the correct component when you buy resistors, ensuring the proper functionality of electronic circuits. The color-coding system, a standard established by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA), is a universally accepted method for indicating these parameters.
The most common resistor color code uses four or five color bands. Each color corresponds to a numerical digit, a multiplier, or a tolerance value. Understanding this code prevents errors and ensures the accuracy of any electronic design.
| Color | Digit | Multiplier | Tolerance (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | 1 (10⁰) | N/A |
| Brown | 1 | 10 (10¹) | ±1 |
| Red | 2 | 100 (10²) | ±2 |
| Orange | 3 | 1,000 (10³) | N/A |
| Yellow | 4 | 10,000 (10⁴) | N/A |
| Green | 5 | 100,000 (10⁵) | ±0.5 |
| Blue | 6 | 1,000,000 (10⁶) | ±0.25 |
| Violet | 7 | 10,000,000 (10⁷) | ±0.1 |
| Gray | 8 | N/A | ±0.05 |
| White | 9 | N/A | N/A |
| Gold | N/A | 0.1 (10⁻¹) | ±5 |
| Silver | N/A | 0.01 (10⁻²) | ±10 |
| None | N/A | N/A | ±20 |
For a 4-band resistor, the first two bands represent the significant digits of the resistance value, the third band is the multiplier, and the fourth band indicates tolerance. A 5-band resistor includes an additional band for a third significant digit, increasing precision.
For example, a resistor with bands of Brown-Black-Red-Gold represents 10 * 100 = 1000 ohms with a 5% tolerance. A resistor with bands of Brown-Black-Black-Red-Brown represents 100 * 100 = 10000 ohms, 10k ohms with a 1% tolerance.
It is advisable to cross-reference these codes with online resources or resistor calculators, especially when dealing with more complex color codes or less common resistors.
Advanced Resistor Concepts and Considerations
While basic resistors serve fundamental roles in circuits, advanced applications often require more specialized components and configurations. Understanding resistor networks, variable resistors, and specific application considerations is crucial for complex circuit design and troubleshooting. This section delves into these advanced topics, expanding the knowledge of experienced users.
- Resistor Networks
Resistors can be combined in series, parallel, or a combination of both to achieve specific equivalent resistances. Series networks increase the overall resistance, while parallel networks decrease it. Understanding how to calculate equivalent resistance is essential for designing complex circuits. - Variable Resistors (Potentiometers)
Potentiometers allow for manual adjustment of resistance, enabling variable control of current and voltage in circuits. These are crucial in applications such as volume controls, dimmers, and calibration settings. Trimpots, a type of potentiometer, are designed for infrequent adjustments, often during initial setup. - Special Resistor Applications
Certain applications require specialized resistors, such as thermistors (temperature-sensitive resistors), photoresistors (light-sensitive resistors), and varistors (voltage-dependent resistors). These resistors are used in sensors, protection circuits, and other advanced applications where parameters other than resistance are critical factors.
| Concept | Description | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Resistor Networks | Combination of resistors to achieve desired resistance values. | Voltage dividers, current limiting, circuit biasing |
| Potentiometers | Variable resistors with adjustable resistance. | Volume controls, dimmers, calibration circuits |
| Thermistors | Temperature-sensitive resistors. | Temperature sensing, thermal protection |
| Photoresistors | Light-sensitive resistors. | Light detection, automatic light control |
| Varistors | Voltage-dependent resistors. | Overvoltage protection, surge suppression |
These advanced resistor concepts extend beyond basic circuitry. Mastery of these ideas unlocks sophisticated circuit designs and provides a deeper understanding of how resistors can be manipulated for various applications. For engineers and experienced enthusiasts, this represents a deeper level of understanding and application.
Finding the right resistors for your electronics projects is essential for success. Whether you choose to buy resistors near you from local stores or opt for the convenience of online shopping, understanding the basics and choosing the correct values are crucial. This guide has provided you with various avenues to buy resistors near me, as well as valuable information to ensure your projects are both efficient and effective. Armed with this knowledge, you can confidently build and innovate with resistors.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA