Mastering the 7805 Voltage Regulator: A Comprehensive Guide

In our increasingly interconnected world, reliable power sources are the backbone of every electronic device, and the 7805 voltage regulator stands as a foundational component in this realm. This simple yet crucial IC ensures a steady 5V output, powering countless devices from microcontrollers to sensors and beyond. But what makes the 7805 so indispensable, and how can we best utilize it in our projects? This article delves into the intricacies of the 7805 voltage regulator, providing an in-depth exploration of its functionality, applications, and design considerations, empowering you with the knowledge to confidently implement it in your next electronics endeavor.
Understanding the Basics of the 7805 Voltage Regulator

The 7805 voltage regulator is a fundamental component in electronics, renowned for its ability to reliably convert a higher, fluctuating input voltage into a stable 5V output. This linear voltage regulator is crucial for ensuring consistent power delivery to sensitive electronic circuits, preventing damage and guaranteeing optimal performance. Its significance stems from its simplicity and effectiveness in providing a fixed 5V power supply.
At its core, the 7805 is designed to maintain a constant output voltage regardless of variations in the input voltage or load conditions, within its specified operational parameters. It achieves this through a linear regulation mechanism, which dissipates excess voltage as heat. This process makes the 7805 essential in many electronics applications where a stable 5V supply is a requirement.
7805 Pinout and Functionality
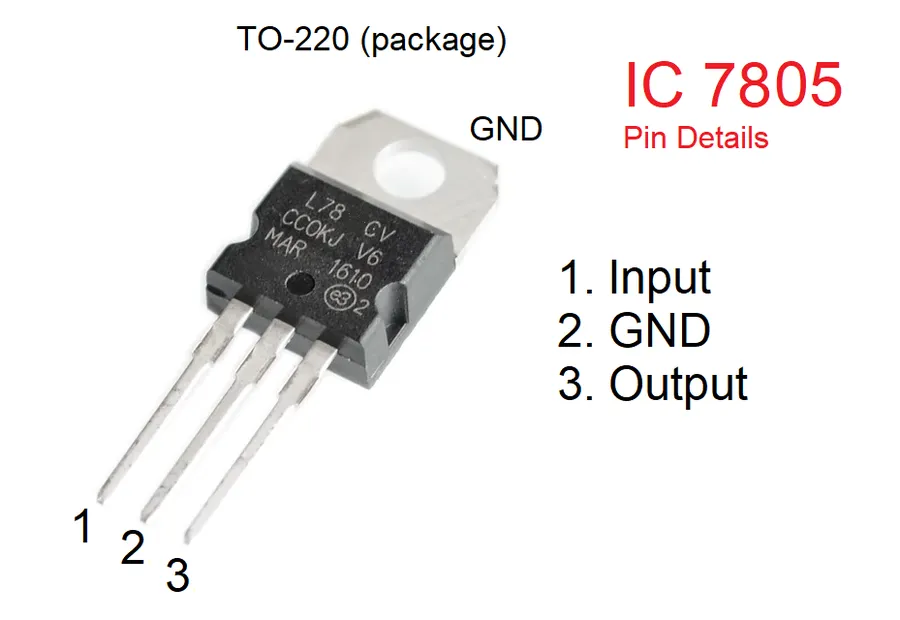
The 7805 voltage regulator is a three-terminal device with a straightforward pin configuration designed to provide a stable 5V output. Understanding the function of each pin is crucial for effective circuit design and operation. The pinout consists of an input pin for the unregulated voltage, an output pin for the regulated 5V supply, and a ground pin for reference.
| Pin Number | Pin Name | Function | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Input (Vin) | Accepts the unregulated DC input voltage. | This pin connects to the source of the voltage that needs to be regulated, which should be higher than the desired 5V output. |
| 2 | Ground (GND) | Provides the common reference point for the input and output voltages. | The ground pin is connected to the 0V reference in the circuit and is necessary for proper operation. |
| 3 | Output (Vout) | Delivers the regulated 5V DC output. | This is the pin where the regulated 5V output is available to power other circuit components. |
Key Specifications of the 7805 Voltage Regulator
The 7805 voltage regulator is a three-terminal positive linear regulator, its key specifications are essential for effective integration into electronic circuits. These specifications primarily govern the operational boundaries of the regulator, including input voltage range, output current capability, and thermal behavior.
| Specification | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Nominal Output Voltage | 5V | The standard, regulated output voltage provided by the 7805. |
| Input Voltage Range | 7V - 25V (Typically) | The range of input voltages that the regulator can safely accept and still maintain its specified output voltage. Some variations may tolerate up to 35V. |
| Maximum Output Current | 1A or 1.5A (Typically) | The maximum current that the regulator can supply to a load without damage or performance degradation. This is dependent on the specific package and heatsinking. |
| Dropout Voltage | ~2V | The minimum voltage difference required between the input and output for the regulator to function correctly (Vin - Vout >= 2V). |
| Quiescent Current | ~5mA (Typically) | The current consumed by the regulator itself for operation. |
| Thermal Resistance | Varies by package | The measure of the ability of the regulator to dissipate heat to the surrounding environment. This value determines the maximum power dissipation and influences the need for a heatsink. |
| Operating Temperature Range | 0°C to +125°C | The range of ambient temperatures under which the regulator can safely and reliably operate. |
It is crucial to operate the 7805 within these specified parameters to ensure reliable performance and prevent damage. Exceeding the maximum input voltage or output current can lead to failure, and proper thermal management is always necessary.
The Internal Mechanism: How the 7805 Achieves Stable Output
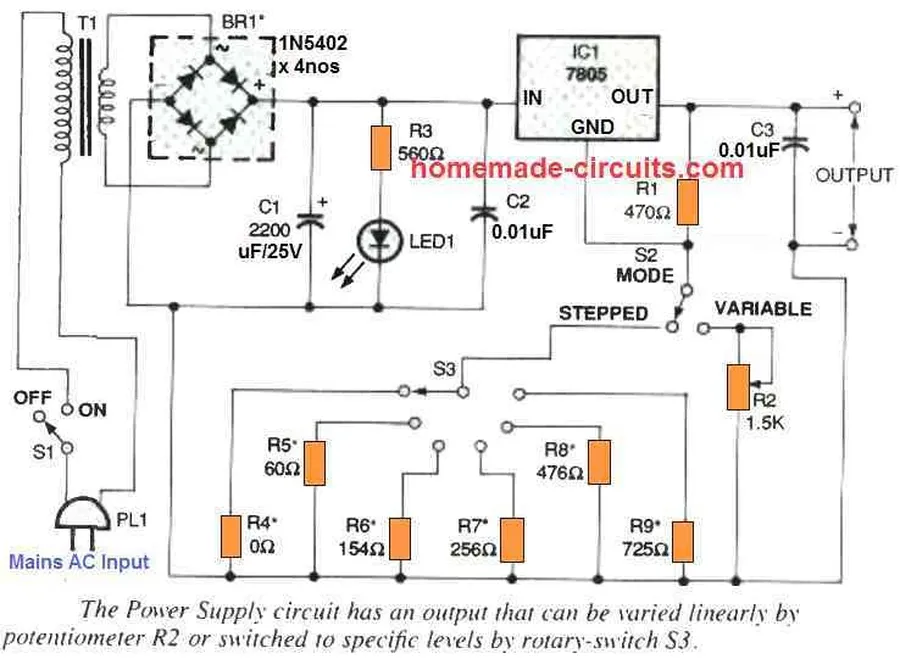
The 7805 voltage regulator employs a linear regulation technique to maintain a consistent 5V output, irrespective of variations in the input voltage or load current. At its core, this process relies on a pass transistor operating in its linear region, coupled with a sophisticated feedback control system.
The regulation process can be broken down into three main stages:
- Reference Voltage Generation
A precise bandgap voltage reference circuit generates a stable reference voltage, typically around 5V. This stable reference is the baseline for the regulation mechanism, against which the output voltage is compared. - Error Amplification
An error amplifier compares the actual output voltage to the stable reference voltage. If there is a deviation, the error amplifier produces a corresponding error signal. This signal indicates the extent of the deviation (either higher or lower) from the desired 5V. - Pass Transistor Control
The error signal then governs a pass transistor, which serves as a variable resistance element. This transistor adjusts its impedance, which modulates the voltage drop, in such a way that it minimizes the difference between the output voltage and the reference voltage. For example, a higher than expected output voltage results in the pass transistor increasing its impedance to reduce the output voltage to the correct level; conversely, a lower than expected output voltage causes the pass transistor's impedance to decrease, increasing the output voltage. This process continues until the output voltage is precisely at 5V.
This negative feedback loop ensures that the 7805 consistently regulates the output voltage at 5V with a high degree of accuracy and stability. However, it’s important to note that linear regulators like the 7805 dissipate excess power as heat, therefore they require careful thermal management especially when dealing with higher input to output voltage differentials or larger currents.
Practical Applications of the 7805 in Circuits
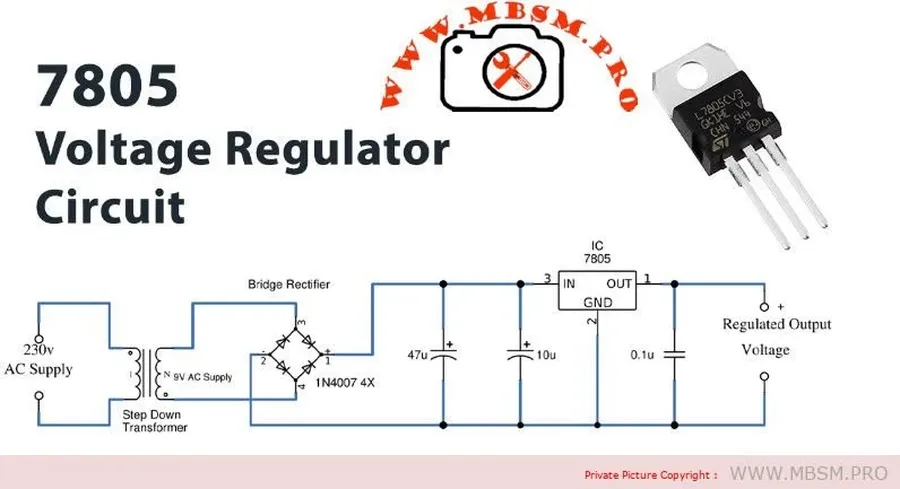
The 7805 voltage regulator's robust and reliable 5V output makes it a cornerstone in numerous electronic applications. Its ability to maintain a stable voltage output from a fluctuating input voltage is crucial for sensitive electronic components, making it a highly versatile tool for both digital and analog circuits.
- Microcontroller Power Supply
The 7805 is extensively used to power microcontrollers, such as the Arduino and ESP32. These devices typically require a stable 5V supply for proper operation, which the 7805 provides efficiently. - Sensor Power Circuits
Many sensors, especially those used in IoT and automation, operate at 5V. The 7805 can serve as a reliable power source for these sensors, ensuring accurate and consistent measurements. - Digital Logic Circuits
The 7805 is often employed in various digital logic circuits, providing the required 5V supply for integrated circuits (ICs) and other digital components. - Analog Circuit Power
In analog circuits, the 7805 provides a stable 5V reference voltage, crucial for biasing transistors and operational amplifiers, and ensuring precise signal processing. - Portable Electronic Devices
The compact form and efficiency of the 7805 make it suitable for portable devices where reliable 5V power is needed, such as custom handheld devices or battery-powered projects. - Educational Electronic Projects
The 7805 is widely used in educational electronics, providing students and hobbyists with a basic voltage regulation solution for various projects.
| Application | Description | Why 7805 is suitable |
|---|---|---|
| Arduino Power | Powering Arduino boards. | Provides stable 5V output. |
| ESP32 Power | Powering ESP32 boards. | Provides stable 5V output. |
| Sensor circuits | Powering various analog and digital sensors. | Ensures stable voltage for accurate measurements. |
| Digital Logic Circuits | Powering ICs and logic gates. | Provides reliable 5V power for digital components. |
| Analog Circuits | Providing reference voltage for op-amps. | Stable 5V ensures precision. |
| Portable Devices | Powering small handheld devices. | Compact and reliable for mobile projects. |
Designing Effective 7805 Circuits: Essential Considerations

Designing robust and reliable circuits with the 7805 voltage regulator requires careful consideration of several key factors. These include selecting the appropriate input voltage, managing heat dissipation with heat sinks, and employing decoupling capacitors for stable operation. Avoiding common design pitfalls ensures the longevity and efficiency of circuits powered by the 7805.
- Choosing the Correct Input Voltage
The input voltage must be within the 7805's specified range, typically 7V to 35V. A voltage too close to the output (5V) will cause poor regulation, while exceeding the maximum rating can damage the regulator. Aim for an input voltage 2-3V higher than the output for efficient operation. For example, for a stable 5V output, a good practice is to use input voltage between 7V and 12V. - Selecting an Appropriate Heat Sink
The 7805 dissipates power as heat, especially at higher input voltages and output currents. The power dissipated is approximately (Vin - Vout) * Iout. For higher power dissipation a heat sink is required to prevent overheating, ensuring the regulator operates within its safe temperature range. Calculate the required thermal resistance of the heatsink based on the power dissipation and ambient temperature. - Adding Decoupling Capacitors
Decoupling capacitors are essential to stabilize the input and output of the 7805. Typically, a 0.33µF ceramic capacitor is placed close to the input pin and a 0.1µF to 1µF capacitor near the output. These capacitors minimize voltage fluctuations and noise, contributing to cleaner power delivery to the connected circuitry. - Considering the Load Requirements
Understanding the maximum current requirements of the load is crucial. The 7805 has a typical maximum output current of 1A or 1.5A. Ensure that the load does not exceed this limit, and consider using a heat sink and proper component selection if a higher current is expected. The continuous current rating should be consider rather than a peak current - Component Placement and Layout
The physical layout of the components impacts circuit performance. Keep input and output capacitors close to the IC pins. Use short, wide traces to reduce parasitic inductance and resistance. Avoid creating ground loops by using a common ground plane. - Overcurrent Protection
Consider using an external fuse or a current limiting circuit to protect the 7805 and the load from overcurrent situations. While 7805 has built-in thermal shutdown and short-circuit protection, adding extra protection is a good practice to enhance circuit reliability
7805 vs Other Voltage Regulators
The 7805 linear voltage regulator, while ubiquitous and simple to use, is not the only solution for stepping down voltage. It is important to compare the 7805 against other popular voltage regulators such as the LM317 adjustable linear regulator and various switching regulators, each exhibiting distinct characteristics in terms of efficiency, heat dissipation, and cost.
| Feature | 7805 | LM317 | Switching Regulator |
|---|---|---|---|
| Type | Fixed Linear Regulator | Adjustable Linear Regulator | Switching Regulator |
| Output Voltage | Fixed 5V | Adjustable (1.25V to ~37V) | Adjustable and Fixed Options |
| Efficiency | Low (especially at large voltage differences) | Low (similar to 7805) | High (typically 70-95%) |
| Heat Generation | High, requires heat sink for higher currents | High, requires heat sink for higher currents | Lower due to higher efficiency |
| Cost | Low | Slightly Higher than 7805 | Higher (component cost and complexity) |
| Complexity | Simple Circuit | Slightly More Complex (requires external resistors) | More complex circuitry (inductors, capacitors, controller IC) |
| Noise | Low | Low | Potentially Higher (can be mitigated) |
| Typical Application | Fixed 5V power for logic circuits, microcontrollers | Adjustable power supplies, battery chargers | High current or battery-powered applications |
The 7805 is advantageous in cost and simplicity. However, its linear regulation leads to substantial power loss as heat, particularly when the input-output voltage difference is large. The LM317 offers flexibility with its adjustable output, but shares the efficiency limitations of linear regulators. Switching regulators, while more complex and costly, provide superior efficiency, making them suitable for battery-powered devices and high current applications. The choice among these voltage regulators should be driven by the specific requirements of the application, including cost, power budget, and thermal management.
Frequently Asked Questions About the 7805 Voltage Regulator
This section addresses common inquiries about the 7805 voltage regulator, providing concise and technically sound answers to ensure a clear understanding of its functionality and application.
- What is the primary function of a 7805 voltage regulator?
The 7805 voltage regulator's primary function is to provide a stable and consistent 5-volt DC output from a higher, unregulated input voltage. This is critical for powering sensitive electronic circuits that require a precise voltage supply. It ensures that voltage fluctuations in the input don't affect the performance or reliability of the connected devices. - What is the maximum output current the 7805 can typically provide?
The standard 7805 voltage regulator typically provides a maximum output current of 1 amp (1A). Some variants, often indicated by an additional suffix (e.g. 7805CT) , can supply up to 1.5 amps (1.5A), however, you must carefully observe datasheet for actual performance under different operation conditions and incorporate proper thermal management to prevent overheating. - What differentiates the 7805 from the 7905 voltage regulator?
The key difference lies in their output polarity. The 7805 provides a positive 5V output, which is commonly used as the power supply for digital ICs and microcontrollers. In contrast, the 7905 outputs a negative 5V, typically used in circuits requiring a negative voltage supply, such as certain operational amplifier configurations or some older analog circuits. - How do you implement a voltage regulator in a circuit?
Implementing a 7805 regulator typically involves connecting the unregulated input voltage to the input pin, connecting the output pin to the circuit requiring 5V, and connecting the ground pin to the common ground of the circuit. It is crucial to include decoupling capacitors at the input and output of the regulator to stabilize operation, and, when needed, a heatsink for temperature management. - Can the output voltage of a 7805 be changed?
The 7805 is designed as a fixed-output voltage regulator. Its output will always be close to 5V provided the input is within its operating range. Unlike adjustable regulators like the LM317, you can't directly alter the output voltage of a 7805 by itself. To obtain a different output voltage, you would need a different regulator with the desired output voltage. - What are some common causes of a 7805 regulator overheating?
Overheating in a 7805 typically results from excessive power dissipation. This occurs when the difference between the input and output voltages, multiplied by the output current, is high. For example, with a high input voltage and high output current the 7805 will produce excess heat which will require heat dissipation management using heatsinks. Using a high current version of the 7805 without heat management when required will cause the part to overheat. Operating the 7805 beyond its rated current will also lead to overheating. You must always carefully review the data sheet to operate within the parameters stated by the manufacturer.
Troubleshooting Common 7805 Voltage Regulator Problems
The 7805 voltage regulator, while robust, can encounter issues such as overheating, unstable outputs, or complete failure. Effective troubleshooting is crucial to ensure proper circuit functionality. This section provides a systematic approach to identifying and resolving these common problems using basic techniques and tools.
- Overheating
Excessive heat generation is a primary concern, particularly when the input voltage is significantly higher than the output or when the regulator is sourcing a high current. To address this, ensure the heat sink is adequately sized and correctly installed, verify input voltage is within the 7805's specified range, and check the output current against the datasheet limits to avoid over current. - Unstable Output Voltage
Fluctuations in the output voltage can result from several factors. Insufficient input voltage, inadequate decoupling, or load variations that exceed the device's current limits can lead to instability. Add bypass capacitor at both input and output close to the regulator to improve stability. Ensure the input voltage is sufficient by checking datasheet. Make sure load variations are within limits of 7805. - No Output Voltage
Absence of output voltage can indicate a total failure of the regulator. Carefully inspect connections to ensure they are secure and correct based on the 7805 pinout. Use a multimeter to check the input voltage and if it exists.If the voltage is correct then the regulator may be damaged, try replacing it. - Incorrect Output Voltage
If the output voltage is not close to 5V, double-check the pin connections, input voltage, and load. If the output is significantly lower or higher than 5V, replace the regulator immediately since it might be damaged. Note that the datasheet may indicate that the output is within a specified range (e.g. 4.8-5.2V). - Oscillations
High frequency oscillations on the output can be caused by instability. Add output bypass capacitor close to the regulator. Sometimes, if not carefully used, electrolytic capacitors can introduce inductance that causes oscilations. Using ceramic capacitors for bypass is generally better. - Noise on the Output
Excessive noise on the output voltage can be due to fluctuations in the input voltage. Add bypass capacitors and ensure that the power supply is clean. If the load is introducing the noise, address the load directly.
The 7805 voltage regulator, despite its simplicity, is an essential component in electronics, providing a reliable 5V output for a variety of applications. Understanding its characteristics and limitations ensures successful implementation and long-term operation of electronic projects. From basic hobby circuits to more complex embedded systems, the 7805 proves to be a workhorse in power regulation. While newer regulators offer greater efficiency, the 7805 remains a fundamental component in electronics due to its low cost, reliability, and ease of use, and provides a solid base for new electronic engineers.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA