Learn More About Smart Meter and Smart Metering Solutions
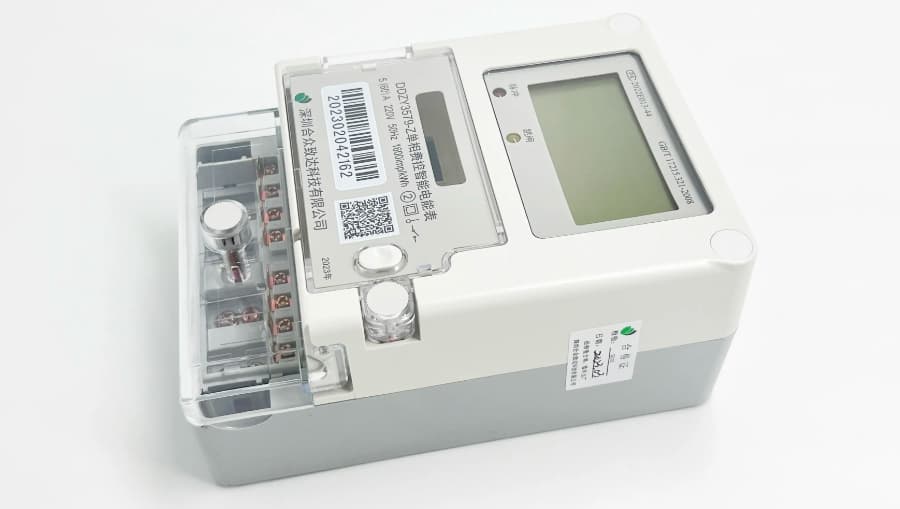

What is a Smart Meter
A Smart Meter is a high-tech metering tool designed to accurately measure and record energy, water, or gas consumption and transmit this critical data to service providers. Thanks to digital and networked technology, it provides customers and energy suppliers with more accurate information on electricity usage. Smart Meter offers significant advantages over conventional meters in terms of intelligence and convenience, providing detailed consumption data, including the exact time and amount of consumption. As a core component of the smart grid, the Smart Meter utilizes Internet technology to enable bi-directional communication, coordination and control of energy distribution and consumption. These features not only greatly improve the efficiency of energy management, but also help users save energy and reduce costs. smart meter plays a crucial role in the smart grid, aiming to optimize the efficiency of energy management and enhance the user experience.

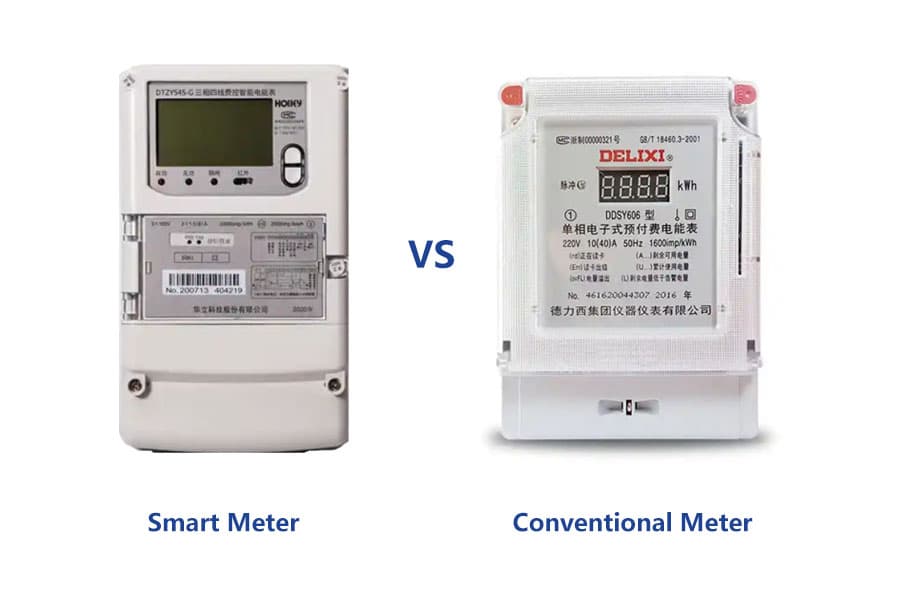
Difference between Smart Meter and ordinary meter
Smart Meter effectively improves the efficiency of both suppliers and users compared to ordinary meters. Smart Meter has real-time monitoring, remote communication, supports peak and valley billing, and promotes energy saving, while ordinary meters only record the total consumption and require manual meter reading, with no real-time data and energy-saving function.
| Features | Smart Meter | Conventional Meter |
|---|---|---|
| Functions | Measure and record power usage in real time | Record only total power consumption |
| Data transmission | Supports remote communication and automatically sends data to energy suppliers | Requires manual reading of data |
| Real-time data | Provides real-time or near-real-time power usage data that can be viewed by the user through an application or display | Real-time data is not available, usually total usage data is provided once a billing cycle |
| Usage Feedback | Provides detailed usage analysis and recommendations to help optimize usage habits | No usage feedback available |
| Billing Mode | Supports time-of-use billing (peak and valley tariffs) | Fixed rate billing only |
| Maintenance and Support | Faults can be detected remotely and automated maintenance is supported | Faults require manual troubleshooting and repair |
| Energy Saving Effect | Helps users understand electricity consumption patterns and promotes energy saving | Cannot help users actively save energy |
| Cost | Higher initial installation and equipment costs, but long-term cost savings | Lower initial costs, but limited long-term energy savings |
| Integration with the energy grid | Can be integrated with the smart grid to support distributed energy management (e.g., solar) | Cannot be seamlessly integrated with the smart grid |
| Data security and privacy | Potential risk of data hacking or misuse | Low risk of data security |
Smart Meter Features
Smart Meter automatically processes data, supports two-way communication, monitors energy consumption in real time, accurate billing, promotes energy conservation, integrates with smart homes, supports renewable energy, and reduces environmental impact.
- Automatic data processing and transmission: Smart Meter can automatically process metering data and transmit it to systems such as distribution network automation.
- Automated management: Smart Meter supports automated management of meters, reducing the need for manual meter reading.
- Bi-directional communication: Smart Meter can realize bi-directional communication between Smart Meter, which improves the efficiency of data interaction.
- Provision of Energy Consumption Information: Smart Meter provides timely and valuable energy consumption information to relevant participants within the smart metering system, including energy consumers.
Disadvantages of Smart Meter
Although Smart Meter has huge advantages over ordinary meters, there are still some barriers to the popularization of Smart Meter, the following are some of the disadvantages of Smart Meter:
- Higher initial investment: the installation cost of Smart Meter is higher than existing meters, which makes the initial investment cost higher and less affordable for ordinary households.
- Lower technological maturity: At present, the technological maturity of Smart Meter is lower, lacks certain reliability, and has certain security risks, which is also one of the reasons why ordinary households are less willing to use Smart Meter.
- Complicated operation: Smart Meter is complicated to operate and requires certain technical support, which makes it difficult for ordinary households to operate and not easy to master.
- Privacy and Data Security Issues: Since Smart Meter needs to collect electricity consumption data from users, protecting user privacy and data security becomes an important task. It may be easy for unauthorized access to occur, leading to leakage of sensitive information about users' habits and lifestyles.
- User resistance: Some users may be concerned about the potential impact of wireless communication technology on privacy, cybersecurity, or health, and therefore may be hesitant to install Smart Meter.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Because Smart Meter are connected to the Internet and often use Wi-Fi to communicate, they are vulnerable to cybersecurity threats such as hacking or denial of service attacks.
- Inaccurate metering: Electricity consumption records are sampled and analyzed through a manganese-copper shunt, and the internal electronics are shot, making metering inaccurate.
- Problems under external strong magnetic field interference: under external strong magnetic field interference (e.g. NdFeB permanent magnets, iron absorbers, etc.) it will disconnect the relay, and can't disconnect the electricity in case of arrears.
- Health concerns: Smart Meter needs to communicate with other electronic devices, so Smart Meter generates high levels of pulsating EMF radiation 24 hours a day, causing health problems such as cancer and heart problems.
Why install Smart Meter

There are certain barriers to the popularity of Smart Meter, but with the advancement of technology, these barriers are being broken through one by one, and by installing Smart Meter, you can achieve a more efficient and environmentally friendly energy management, as well as provide more convenience and control to the users. Here are some of the benefits of installing a Smart Meter in the future:
- Improved billing accuracy: Smart Meter provides accurate billing information rather than estimated billing, reducing the chance of reading errors.
- Energy efficiency and demand management: Smart Meter keeps a close eye on consumers' electricity demand and usage, which can help develop effective energy efficiency programs.
- Remote monitoring and data access: Users can log in and monitor data remotely to detect theft, wasted power or any power-related incidents in a timely manner.
- Improved Electricity Payment: Smart Meter makes it easy for consumers to pay their bills without having to wait for an actual reconciliation meter.
- Enhanced Grid Interaction: Smart Meter works on the basis of two-way communication between the consumer and the grid, providing a better understanding of real-time power usage, power demand and prices.
- Reduced Resource Waste: Smart Meter reduces waste of other resources such as paper and helps reduce maintenance costs and labor expenses.
- Real-time monitoring and metering: Smart Meter is able to monitor and meter a customer's power usage in real-time, including parameters such as current, voltage, and power factor.
- Abnormal event monitoring and alarm: Smart Meter can monitor abnormal events, such as current overload and voltage fluctuation, and send out alarm signals in time.
- Power consumption data analysis and statistics: Smart Meter can analyze and count the power consumption data of users and generate corresponding reports and charts.
- Time-period tariff and billing flexibility: Smart Meter supports the flexible adjustment of time-period tariff and billing strategy to incentivize users to use electricity rationally during peak and valley times.
- Energy saving and emission reduction: Smart Meter plays an important role in energy saving and emission reduction, and promotes the construction of smart grid.
- Technological innovation: The combination of Smart Meter's metering, data transmission, data processing and new technologies generates a variety of new functions and applications.
- Improve energy efficiency: Smart Meter helps to improve the energy efficiency of energy suppliers and end-users. Timely and accurate feedback of energy consumption data will enable users, home automation systems and suppliers to react quickly.
How Smart Meter works
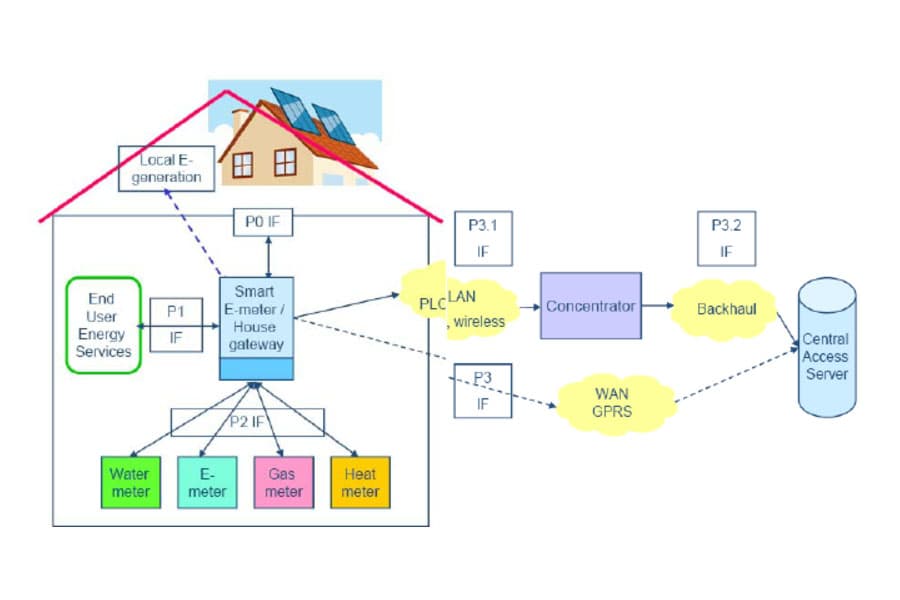
The working principle of the Smart Meter can be summarized as follows:
- Energy metering: Smart Meter accurately measures energy through current and voltage transformers. The current transformer converts the current signal into a low-level signal and the voltage transformer converts the voltage signal into a low-level signal.
- By calculating the frequency and number of pulses of these low-level signals, the exact value of the power can be obtained.
- Data Acquisition: Smart Meter is equipped with a microprocessor and memory inside, which can acquire and store the data of electric energy metering.
- Through the communication with the power metering chip, the power metering data can be read in real time and stored in the internal memory.
- Data processing: Smart Meter processes the collected power metering data through the internal microprocessor.
- It can realize the calculation, statistics and analysis of electric energy, and generate corresponding reports and graphs. At the same time, Smart Meter can also perform load analysis and power factor analysis of electric energy so that users can use electric energy rationally.
- Data communication: Smart Meter transmits the collected power metering data to the remote server through the built-in communication module. Commonly used communication methods include wired communication (e.g. RS485, Modbus, etc.) and wireless communication (e.g. GPRS, NB-IoT, etc.).
- Wireless Sensor Network: Smart Meter transmits the collected power metering data to the remote server via wireless sensor network.
- The wireless sensor network consists of multiple sensor nodes, which enables data interconnection and self-organization between nodes.
- Realization of Remote Meter Reading: Smart Meter realizes accurate metering, remote monitoring and remote meter reading of electric energy by means of digitalization, networking and intelligence.
- Components: Smart Meter is mainly composed of a power module, a metering module, a display module, a communication module, a security module, a clock module, a storage module and a power-on/off module. These modules work together to achieve the functions of power metering, data display, data communication, safety and security, clock synchronization, data storage and power control. The working principle of Smart Meter involves accurate measurement of power, data acquisition and processing, and remote transmission of data, and these functions make Smart Meter play an increasingly important role in modern power systems.
Core Technology Components of Smart Meter
The Smart Meter digitizes the functions of a traditional electricity meter, making it easier for energy suppliers to manage, and helping users to optimize their electricity consumption and achieve more efficient energy use.
| Technical Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Sensor | Measures current, voltage, and calculates power and energy. |
| Microcontroller (MCU) | Processes measurement data, supports logic operations and control. |
| Clock Module | Supports time-of-use billing and time synchronization functions. |
| Storage Unit | Stores historical data and billing data. |
| Communication Module | Enables bidirectional communication with energy companies or smart home devices. |
| Display Module | Displays real-time electricity usage, pricing information, etc. |
What is Smart Metering Solutions?
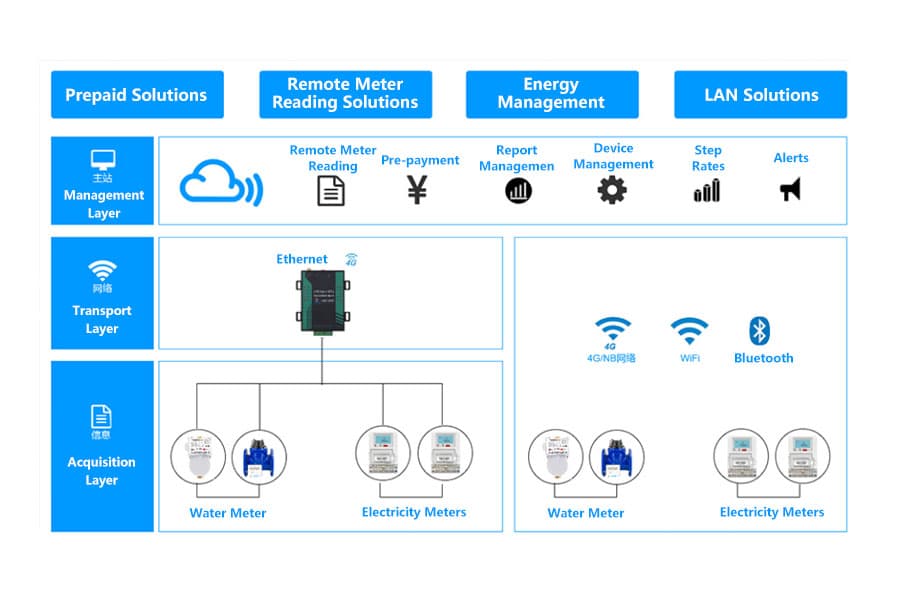
Smart Metering Solutions refer to integrated systems that leverage advanced technologies, such as Smart Meter, communication networks, and data Smart Metering Solutions refer to integrated systems that leverage advanced technologies, such as Smart Meter, communication networks, and data management platforms, to monitor, manage, and optimize energy, water, or gas consumption. These solutions aim to improve resource efficiency, enhance customer service, and support sustainability goals.
-
able energy: Linkage with distributed energy sources (e.g. solar, wind) to support smart grid optimization. Carbon Footprint Reduction: Reduce carbon emissions by optimizing energy usage patterns. Pollution monitoring: Combine environmental data, such as air quality sensors and energy usage data, to jointly analyze urban pollution sources.
-
Transportation and Electric Vehicle Infrastructure
- EV Charging Management: Smart Meter can be used at EV charging stations to monitor charging demand in real time and optimize power distribution.
- Smart Transportation: Regulate power usage by integrating with traffic signals and lighting systems.
-
Public Service Optimization
- Smart Buildings: In residential and commercial buildings, Smart Meter integrates with smart home systems for efficient energy management.
- Street Lighting: Save power by dynamically adjusting the brightness of street lights based on light conditions and foot traffic.
-
Data Analytics and Urban Planning
- Data-driven decision-making: Based on the large amount of data collected by Smart Meter, city managers can optimize energy infrastructure investments and policy making.
- Emergency Response: Smart Meter quickly locates areas of power failure and speeds up the restoration process.
-
Benefits for Residents and Businesses
- Increased Customer Engagement: Residents can view real-time information about their electricity usage through the Smart Meter's user interface and become more aware of energy savings.
- Billing Transparency: Users are billed according to actual usage, avoiding disputes.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA