The Ultimate Guide to 270 Ohm Resistors: Applications, Color Codes, and More
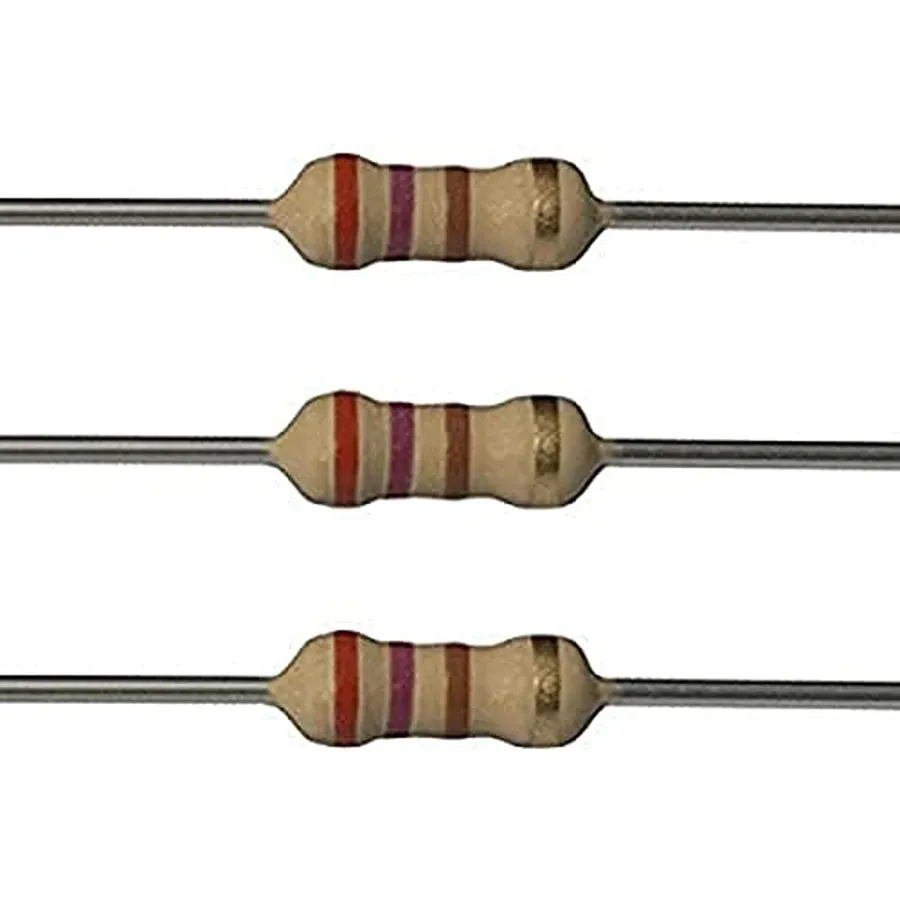

In the realm of electronics, a 270 ohm resistor, seemingly a tiny component, plays a critical role in controlling the flow of electricity, much like traffic signals guide cars. This little workhorse is used everywhere, from simple LED circuits to complex audio equipment and robotics. Like a well-placed speed bump slowing down a car, a 270 ohm resistor helps to regulate electrical currents, ensuring that our devices operate safely and efficiently. This article will guide you through the essential details of this fundamental component, including its various types, how to identify one by its color bands, and practical applications in our everyday world.
What is a 270 Ohm Resistor?

A 270 ohm resistor is a fundamental passive electronic component designed to impede the flow of electrical current, presenting a specific resistance of 270 ohms. This resistance, a property of the material, limits the current flow and converts electrical energy into heat as electrons move through the resistor. This conversion follows Joule's first law. The precise 270 ohm value makes these resistors crucial in a wide range of applications where specific current or voltage levels are necessary. In practical terms, a 270-ohm resistor functions as a controlled impediment in an electrical pathway, crucial for maintaining circuit integrity and functionality.
270 Ohm Resistor Color Code: Decoding the Bands
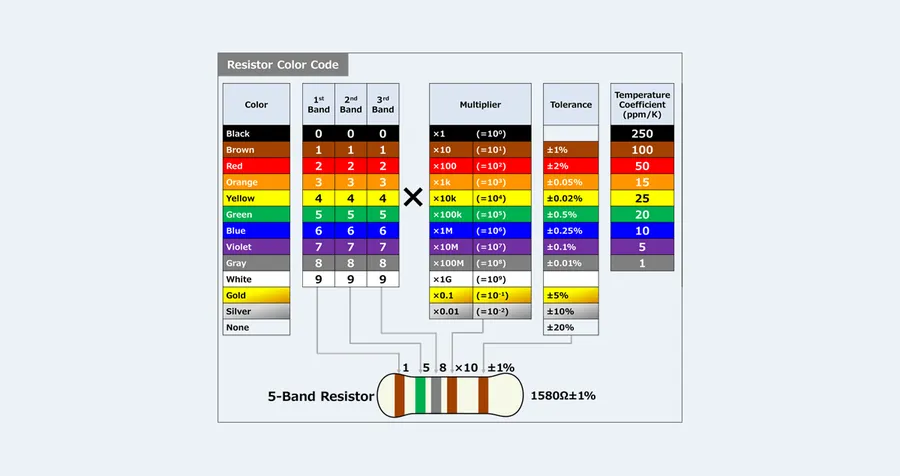
The color code on a 270 ohm resistor is a standardized system that allows for quick identification of its resistance value and tolerance. This is crucial for circuit design and troubleshooting. The color bands are read from left to right, with each color corresponding to a specific numerical value.
For a standard 4-band 270 ohm resistor, the color bands are typically: Red, Violet, Brown, and Gold. Here's a breakdown of what each color means:
When these colors are combined, the calculation is performed as follows: (27 * 10^1) ohms ±5%, which gives us 270 ohms with a 5% tolerance.
For a 5-band 270 ohm resistor, the color bands would be: Red, Violet, Black, Black, and Brown. Here's how the 5-band code works:
The calculation is then: 270 * 10^0 ohms ±1%, which is again 270 ohms but with a tighter tolerance of ±1%.
Types of 270 Ohm Resistors

270 Ohm resistors are manufactured in various types, each with unique characteristics that make them suitable for different applications. These types primarily differ in the materials used for their resistive element, which significantly impacts their performance characteristics like power rating, accuracy, temperature stability, and cost. Common types include carbon film, metal film, wirewound, and surface mount (SMD) resistors.
| Resistor Type | Material | Power Rating | Accuracy | Temperature Coefficient | Cost | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film | Carbon composition | Low to Medium | Moderate | High | Low | General-purpose, low-cost applications |
| Metal Film | Metal alloy | Low to Medium | High | Low | Medium | Precision circuits, stable performance |
| Wirewound | Metallic wire | High | Moderate | Moderate | High | High-power applications, current sensing |
| Surface Mount (SMD) | Thick/thin film | Low | Moderate to High | Moderate | Low to Medium | Automated PCB assembly, compact designs |
Understanding the nuances of each resistor type allows engineers and hobbyists to select the most appropriate component for a specific design, ensuring optimal performance, reliability, and cost-effectiveness.
Applications of 270 Ohm Resistors
270 ohm resistors are fundamental components in a wide array of electronic circuits, serving diverse roles from simple current limitation to intricate signal conditioning. Their specific resistance value makes them suitable for applications where a moderate level of current restriction is needed, balancing performance and efficiency.
- LED Current Limiting
One of the most common uses of a 270 ohm resistor is to limit the current flowing through an LED. Without a current-limiting resistor, an LED connected directly to a power source would draw excessive current, leading to its rapid failure. The 270 ohm resistor drops the voltage to an optimal level, ensuring the LED operates at its rated brightness and prolongs its lifespan. - Op-Amp Circuits
In operational amplifier (op-amp) circuits, 270 ohm resistors can be used in feedback loops to set the gain of the amplifier or in input stages to limit current or create voltage dividers. These resistors allow for precise control over circuit behavior, enabling reliable signal processing and conditioning. Their role is to modify the amplification or bias the circuit as needed. - Voltage Dividers
270 ohm resistors are often paired with other resistors to form voltage dividers, which are circuits used to create a specific voltage output that is proportional to the input voltage. These dividers can be used in sensor circuits, reference voltage generation or in the bias of transistor circuits. - Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors
In digital logic circuits, 270 ohm resistors may be employed as pull-up or pull-down resistors. These resistors ensure a defined logic state (high or low) when the input is left floating. This prevents indeterminate behavior, ensuring the logic circuit works as expected. - Basic Electronic Circuits
The 270 ohm resistor also finds use in more basic circuits, including simple transistor circuits, where they provide base current limiting, or in timer circuits, where they form an essential part of the time constant calculation. These applications show their versatility in different circuit designs.
Selecting the Right 270 Ohm Resistor: Key Considerations
Selecting the correct 270 ohm resistor for a specific application is crucial to ensure circuit performance and reliability. Several key factors must be taken into account, including power rating, tolerance, temperature coefficient, physical size, and mounting style. Each parameter plays a vital role in the function of the resistor.
| Factor | Description | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Power Rating (Wattage) | The maximum power the resistor can dissipate without overheating or damage. | Ensures the resistor can handle the expected power load; using one with insufficient wattage can lead to failure. |
| Tolerance | The permissible variation in the actual resistance value from the nominal (270 ohms) value. | Impacts the precision of the circuit; tighter tolerance is needed for more sensitive applications. |
| Temperature Coefficient | Indicates how much the resistance changes with temperature. | Crucial in environments with temperature fluctuations; a lower coefficient provides more stable performance. |
| Physical Size | The physical dimensions of the resistor. | Important for PCB layout and assembly, surface mount device (SMD) is ideal for compact designs and automated assembly. |
| Mounting Type | How the resistor is attached to the circuit board (e.g., through-hole, SMD). | Impacts the assembly process; SMD for automated assembly, through-hole for manual soldering. |
For example, in high-temperature environments, choosing a metal film resistor with a low-temperature coefficient is vital to ensure stable performance. In contrast, a carbon film resistor, although economical, might exhibit significant changes in resistance under similar conditions. Careful consideration of all these factors is essential for selecting the right 270 ohm resistor.
270 Ohm Resistors: Practical Tips and Best Practices
Working with 270 ohm resistors, like any electronic component, requires attention to detail to ensure their longevity and proper function within a circuit. This section provides practical advice on handling, measurement, and storage.
- Proper Handling During Soldering
When soldering, use appropriate temperature settings and avoid prolonged exposure to heat. Excessive heat can alter the resistor's properties, potentially changing its resistance or causing it to fail. Use a heat sink on the resistor leads during soldering to dissipate heat. - Avoiding Overheating
Resistors generate heat while in operation. Always ensure the chosen resistor's power rating (wattage) is sufficient for the circuit to avoid overheating and potential failure. If a resistor becomes excessively hot during operation, re-evaluate your circuit design or choose a resistor with a higher wattage rating. - Measuring Resistance with a Multimeter
To verify the resistance of a 270 ohm resistor, use a digital multimeter set to the ohms (Ω) range. Connect the multimeter probes across the resistor leads, ensuring good contact. The measurement should be within the resistor’s specified tolerance range. For a 270 ohm resistor with 5% tolerance, the measured value should ideally be between 256.5 and 283.5 ohms. - Proper Storage
Store resistors in a dry, cool environment, away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Humidity and temperature fluctuations can degrade a resistor's performance over time. When storing in bulk, use compartmentalized organizers to prevent mixing of different resistor values. Anti-static containers are especially recommended for handling and storage of surface mount (SMD) resistors.
Frequently Asked Questions About 270 Ohm Resistors
This section addresses common inquiries regarding 270 ohm resistors, aiming to provide clarity on their characteristics, applications, and related concepts.
- What is the color code for a 270 ohm resistor?
For a standard 4-band 270 ohm resistor, the color code is Red-Violet-Brown-Gold. The first two bands (Red and Violet) represent the significant digits 2 and 7, the third band (Brown) is the multiplier of 10^1, and the fourth band (Gold) signifies a ±5% tolerance. For a 5-band resistor, it would be Red-Violet-Black-Black-Brown, where the first three bands are the significant digits, the fourth band is the multiplier, and the fifth band is the tolerance. - What is the color code for a 270K ohm resistor?
The color code for a 270 kiloohm (270,000 ohms) resistor using 4 bands is Red-Violet-Yellow-Gold. The Red and Violet bands represent the digits 2 and 7, the Yellow band is the multiplier 10^4 (10,000), and the Gold band indicates a 5% tolerance. If using a 5 band resistor the code would be Red-Violet-Black-Orange-Brown, with the red, violet and black giving 2,7 and 0 respectively, the orange as the multiplier 10^3 and the brown as the tolerance of 1%. - What is a suitable equivalent for a 270 ohm resistor?
While exact replacements are ideal, in practice, resistors with slightly higher or lower values can sometimes be used, depending on the circuit's tolerance. Common alternatives include 220 ohm, 250 ohm or 330 ohm resistors. However, it is critical to analyze the circuit requirements thoroughly as using the incorrect value can affect circuit performance, potentially causing overheating or improper functionality. Always verify component specifications and circuit needs. - Why would you use a 270 ohm resistor?
270 ohm resistors are used in various electronic circuits to limit current, divide voltage, and provide a known resistance value. A common example is in LED circuits, where they limit the current to a level safe for the LED, preventing damage while ensuring proper brightness. In other applications they can be used in op-amp circuits, as pull-up or pull-down resistors, and in sensor circuits where a known resistance is needed. - Why use a 250 ohm resistor?
A 250 ohm resistor is often used in similar applications as a 270 ohm resistor, such as in LED current limiting and in various analog circuit designs. The difference in resistance value will cause a slightly different current flow, which in practice may or may not be significant depending on the design parameters. It is essential to check circuit parameters when deciding between a 250 ohm and 270 ohm resistor. - What is the color code for a 250 ohm resistor?
The color code for a 250 ohm resistor with 4 bands is Red-Green-Brown-Gold. The Red and Green bands represent the digits 2 and 5, the Brown band is the multiplier of 10^1, and the Gold band indicates a 5% tolerance. A 5-band resistor would be Red-Green-Black-Black-Brown. The first three bands give the digits, 2, 5 and 0, the fourth is the multiplier and the fifth is the tolerance.
Comparative Analysis: 270 Ohm Resistor vs. Similar Values

When designing electronic circuits, selecting the correct resistor value is crucial for optimal performance. While a 270 ohm resistor serves specific needs, understanding its behavior in relation to adjacent values, such as 220 ohm and 330 ohm resistors, is essential. These slight differences in resistance have an impact on voltage, current, and circuit behavior.
| Characteristic | 220 Ohm Resistor | 270 Ohm Resistor | 330 Ohm Resistor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance (Ω) | 220 | 270 | 330 |
| Current (for a given voltage) | Higher Current | Medium Current | Lower Current |
| Voltage Drop (for a given current) | Lower Voltage Drop | Medium Voltage Drop | Higher Voltage Drop |
| LED Brightness (as current limiter) | Brighter (potentially damaging) | Optimal Brightness | Dimmer |
| Use case Examples | Some LED circuits, current sensing applications | Most common LED circuits, sensor circuits | Less common LED circuits, higher voltage circuits |
| Effect on circuit | May cause excess current, overheating, reduced component life | Provides optimal current and voltage regulation | May result in lower current/voltage, affecting component performance |
Where to Buy 270 Ohm Resistors
Sourcing 270 ohm resistors requires consideration of factors beyond just price. Availability, reliability, and delivery times also significantly influence the purchasing decision. Reputable vendors, whether online or local, offer components that adhere to specified tolerances, ensuring proper circuit functionality.
- Online Retailers
Major online retailers such as Amazon, Digikey, Mouser, Newark, and Tayda Electronics provide a wide range of 270 ohm resistors. These platforms offer varied stock levels, pricing, and shipping options. Look for vendors with high ratings and positive customer reviews to ensure the components meet their specifications. - Local Electronics Stores
Local electronics retailers and hobby shops may carry 270 ohm resistors, making it easier to purchase with immediate availability. It’s important to know the quality and brands stocked by these vendors to ensure you buy reliable components. Prices and selection can vary significantly depending on your location. - Key factors for online shopping
When shopping online, pay close attention to the price of the resistors, in addition to availability and current stock level. Check customer ratings and reviews to determine component quality. Delivery time varies, consider this depending on your project requirements, especially in case of limited availability. Also note any handling or shipping costs.
In conclusion, the humble 270 ohm resistor is an indispensable element in modern electronics. It’s important to understand the types, color codes, and key characteristics to select the right resistor for any project. Its ability to precisely control electrical current, like regulating water flow in a pipe, makes it critical in the function of numerous devices we use every day. By mastering the basics of the 270 ohm resistor, from its color bands to its role in various circuits, you will be able to tackle a wide array of electronic challenges with confidence and precision. Whether you are a beginner or an experienced electronics hobbyist, the 270 ohm resistor is a core component in your toolbox. Understanding its operation is key to mastering electronic design.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA