Understanding the 20k Ohm Resistor: Uses, Types, and Applications
In the intricate world of electronics, components like the humble 20k ohm resistor are the unsung heroes that make everything from our smartphones to industrial equipment function. Just as the gears within a clock must precisely mesh to tell the time, resistors like the 20k ohm precisely control the flow of electricity in a circuit. This article will delve into the critical role these components play, exploring their various types, applications, and what makes them so indispensable in today's technology.
What is a 20k Ohm Resistor?

A 20k ohm resistor is a fundamental passive electronic component designed to impede the flow of electrical current, providing a resistance of 20,000 ohms. Its core function within a circuit is to regulate electron flow, preventing excessive current that could potentially harm other circuit elements or lead to operational instability. The precise resistive nature of a 20k ohm resistor makes it crucial for a wide array of electronic applications where controlled current and voltage are essential for proper operation.
Key Specifications of a 20k Ohm Resistor

Selecting the appropriate 20k ohm resistor requires a thorough understanding of its key specifications. These specifications, including power rating, tolerance, and material composition, directly impact the resistor's performance, reliability, and suitability for specific applications. Factors such as temperature coefficients and stability are also crucial for critical circuit designs.
| Specification | Description | Typical Values | Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Rating | The maximum power the resistor can dissipate without damage. | 1/8W, 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W | Affects heat dissipation and prevents failure from overheating. |
| Tolerance | The allowable deviation of the actual resistance from the nominal value. | 5%, 1%, 0.1% | Determines precision and accuracy of the circuit. |
| Temperature Coefficient | Change in resistance with temperature variation. | Varies by material | Affects circuit performance in changing thermal environments. |
| Material | The material used in the resistor’s construction. | Carbon film, Metal film, Wirewound | Impacts precision, stability, noise and temperature coefficient |
| Operating Temperature Range | The range of temperatures under which the resistor can operate safely | -55°C to +155°C (typical range, varies by material) | Ensures reliable function within the intended environment. |
| Voltage Rating | Maximum voltage that can be applied without causing damage. | Varies significantly by type, check datasheet | Prevents damage due to voltage breakdown |
Common Types of 20k Ohm Resistors

20k ohm resistors are manufactured using various materials and construction methods, leading to different performance characteristics. The primary types include carbon film, metal film, and surface mount chip resistors. Each type offers unique advantages in terms of cost, precision, and application suitability.
| Resistor Type | Material | Precision | Stability | Cost | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film | Carbon composite | Moderate (typically 5% tolerance) | Moderate | Low | General-purpose circuits, less critical applications |
| Metal Film | Metal alloy | High (typically 1% tolerance or better) | High | Moderate | Precision circuits, audio equipment, measuring instruments |
| Surface Mount (Chip) | Various (thick or thin film) | Moderate to high (depends on specific type) | Moderate to high | Moderate | Modern compact electronics, automated assembly |
The selection of a specific 20k ohm resistor type should be based on the project's demands for precision, environmental conditions, cost constraints and physical size.
Applications of the 20k Ohm Resistor
The 20k ohm resistor's versatility stems from its ability to precisely control current and voltage in various electronic circuits. Its applications span from simple to complex designs, making it a crucial component in numerous electronic systems. This section explores some of the typical scenarios where a 20k ohm resistor is indispensable.
- Pull-Up and Pull-Down Resistors
In digital circuits, 20k ohm resistors are frequently used as pull-up or pull-down resistors. These resistors establish a defined logic state (high or low) when an input is not actively driven. For example, in microcontroller circuits, they ensure a consistent voltage level at input pins. - Current Limiting for LEDs
20k ohm resistors can limit the current flowing through light-emitting diodes (LEDs). By setting the correct resistance, you can protect LEDs from damage due to excessive current. This is essential for ensuring the LED operates at its intended brightness and lifespan. - Voltage Division
In analog circuits, 20k ohm resistors can be used in voltage divider configurations. By combining this resistor with other resistors, we can accurately divide a voltage into smaller, usable voltages. Voltage dividers are fundamental in sensor circuits and signal conditioning. - Sensor Applications
The 20k ohm resistor is commonly used in conjunction with sensors. In some applications, such as with thermistors or photoresistors, these resistors provide a stable reference value. When sensor resistance changes, this allows for accurate measurements by analyzing the voltage changes across the 20k resistor. - Fine Tuning Circuits
20k ohm resistors can be used for fine-tuning in sensitive circuits. The value of this resistor can be used to make minor adjustments to voltage or current levels, allowing for precision in the final output of many electronic devices.
20k Ohm Resistor Color Code
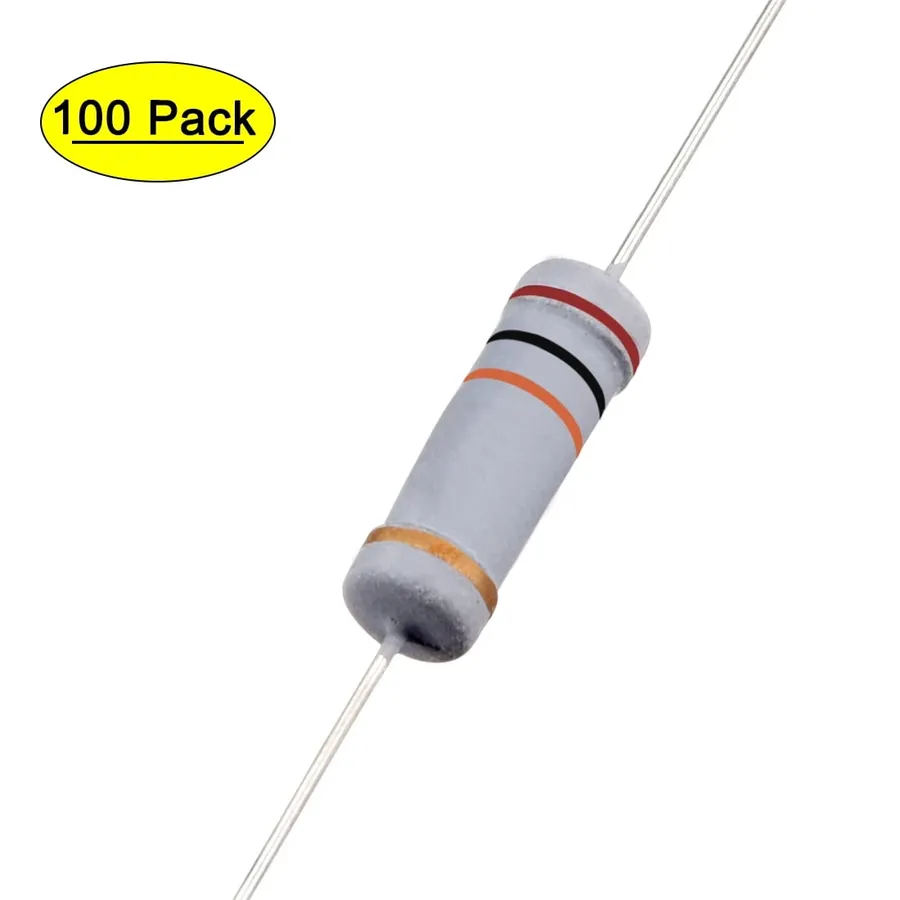

The color code on a 20k ohm resistor is a universal system for quick and accurate identification. Typically, a 20k ohm resistor with a 5% tolerance will display four color bands: Red, Black, Orange, and Gold. This system allows engineers and technicians to easily determine the resistance value without needing to measure each component individually, greatly simplifying circuit construction and maintenance.
| Band | Color | Value/Multiplier | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Band | Red | 2 | N/A |
| 2nd Band | Black | 0 | N/A |
| 3rd Band | Orange | 1000 (Multiplier) | N/A |
| 4th Band | Gold | N/A | 5% |
20k Resistor vs. Other Common Resistors (10k, 1k)
The selection of a resistor value is a critical aspect of circuit design, directly influencing current flow and voltage distribution. A 20k ohm resistor provides a distinct level of resistance compared to other common values such as 10k ohm and 1k ohm resistors, each suited for different applications based on their electrical characteristics.
| Feature | 20k Ohm Resistor | 10k Ohm Resistor | 1k Ohm Resistor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistance | 20,000 ohms | 10,000 ohms | 1,000 ohms |
| Current Flow (for same voltage) | Lower | Medium | Higher |
| Typical Use Cases | Pull-up/pull-down, sensor circuits, voltage dividers | Timing circuits, feedback loops, pull-up/pull-down | Current limiting, load resistors, signal buffering |
| Power Dissipation (for same current) | Higher | Medium | Lower |
| Precision | Dependent on resistor type, metal film better | Dependent on resistor type, metal film better | Dependent on resistor type, metal film better |
The primary difference between these resistors lies in their resistance values. A 20k ohm resistor, with its higher resistance, restricts current flow more significantly compared to the 10k ohm and especially the 1k ohm resistor. This difference makes each resistor suitable for specific circuit roles.
For instance, in a voltage divider circuit, using a 20k ohm resistor in place of a 1k ohm resistor will result in a much larger voltage drop across the 20k ohm resistor and consequently a lower current in the circuit. Conversely, using a 1k ohm resistor where a 20k ohm resistor is needed will lead to excessive current flow and possible damage to other components.
Frequently Asked Questions about 20k Ohm Resistors
This section addresses common questions about 20k ohm resistors, providing clarity on their properties, applications, and handling.
- What is the standard color code for a 20k ohm resistor?
The standard color code for a 20k ohm resistor with 5% tolerance is Red, Black, Orange, and Gold. These bands correspond to the numerical value, multiplier, and tolerance respectively. - How does a 20k resistor compare to a 10k resistor in a circuit?
A 20k resistor offers twice the resistance compared to a 10k resistor. This means, given the same voltage, a 20k resistor will allow half the current flow of a 10k resistor. This difference in resistance is critical for tuning circuit behavior. - What is the common power rating for a 20k ohm resistor?
Common power ratings for 20k ohm resistors are typically 1/4W or 1/2W. The specific power rating required for a given application depends on the current flowing through the resistor and the heat it generates. Always select a resistor with a sufficient power rating to prevent overheating and damage. - Can a 20k resistor be used as a pull-up or pull-down resistor?
Yes, a 20k resistor is frequently used as a pull-up or pull-down resistor in digital logic circuits. Its value is often chosen to provide the correct bias for the logic gates while minimizing power consumption. The specific value may need to be adjusted based on the circuit parameters. - What are the common materials used to make 20k ohm resistors?
20k ohm resistors are commonly made from carbon film or metal film. Carbon film resistors are cost-effective and suitable for general purpose applications. Metal film resistors offer higher precision, better temperature stability, and lower noise, and are therefore preferred in more sensitive circuits. - How do I choose between a carbon film and a metal film 20k ohm resistor?
The choice between carbon film and metal film 20k ohm resistors depends on the application requirements. For basic circuits where precision and stability are not critical, carbon film resistors are appropriate. For more demanding applications, such as precision measurement or sensitive analog circuits, metal film resistors are the preferred choice for their superior performance characteristics. - What happens if I use a 20k resistor with insufficient power rating?
Using a 20k resistor with insufficient power rating can lead to overheating and potential failure. When a resistor's power rating is exceeded, it can heat up significantly, potentially changing its resistance value, or even causing it to burn out. Always ensure the power rating of the resistor exceeds the expected power dissipation to maintain component longevity and circuit stability.
Practical Tips for Using 20k Ohm Resistors
Effective utilization of 20k ohm resistors requires careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity. These include managing heat dissipation, adhering to the power rating, and accounting for environmental conditions. Proper handling during installation and storage, and verifying the resistance value are critical.
- Heat Dissipation
Resistors generate heat as current passes through them. For a 20k ohm resistor, ensure adequate ventilation or heat sinking if operating near its power rating to prevent overheating and potential failure. The power dissipated (P) by a resistor can be calculated by the formula: P = I² * R, where I is the current and R is the resistance. - Power Rating
The power rating of a resistor, typically 1/4W or 1/2W, indicates the maximum power the resistor can safely dissipate without damage. Ensure the 20k ohm resistor's power rating exceeds the calculated power dissipation in your circuit to prevent thermal runaway and premature failure. Selection of a resistor with a higher power rating provides an additional safety margin. - Environmental Conditions
Extreme temperatures and humidity can affect a 20k ohm resistor's performance. High temperatures can increase resistance value drift and cause permanent damage, while humidity can lead to corrosion of the resistor terminals. Choose resistors with appropriate environmental ratings and consider conformal coating in harsh environments to prevent moisture damage. - Handling and Storage
When handling 20k ohm resistors, avoid bending leads too sharply to prevent internal damage. Store resistors in a dry, cool place away from direct sunlight and corrosive materials. Electrostatic discharge (ESD) can damage sensitive resistors, so use ESD-safe handling practices. - Verification with Multimeter
Before installation, always verify the 20k ohm resistor’s value using a calibrated digital multimeter. Tolerance variations and color code misinterpretations can lead to incorrect circuit behavior. Ensure the measured resistance falls within the specified tolerance range. - Proper Soldering Techniques
When soldering 20k ohm resistors onto a PCB or using them in a circuit, apply heat carefully to avoid thermal stress. Excessive soldering heat and duration can alter the resistor's properties. Use a controlled temperature soldering iron, and allow adequate time for cooling to ensure long-term reliability.
Where to Purchase 20k Ohm Resistors
20k ohm resistors are readily accessible through various channels, including major online retailers, specialized electronics distributors, and local stores. When sourcing these components, carefully compare prices and specifications to ensure optimal value and performance. It is always important to verify the 20k resistor's specifications against your project's requirements before making a purchase.
- Online Retailers
Major online platforms like Amazon offer a wide selection of 20k ohm resistors from various manufacturers. These platforms often provide customer reviews and competitive pricing. - Specialized Electronics Distributors
Distributors such as DigiKey and Jameco are reputable sources for electronic components, offering a vast inventory, detailed product specifications, and technical support. - Local Electronics Stores
Local electronics stores provide an option for immediate purchases and can be useful for small-scale or urgent projects. These stores may offer a more limited selection, but they allow for hands-on inspection of the components. - Considerations
When making a purchase, consider the quantity of 20k resistors you need, any special requirements, and the reputation of the supplier. For larger projects, buying in bulk from a trusted supplier can help to reduce costs and ensure a consistent supply of quality components.
The 20k ohm resistor, a small yet powerful component, plays a crucial role in modern electronics. From limiting current in simple circuits to enabling precision in complex systems, understanding the characteristics, types, and proper applications of 20k ohm resistors is essential for anyone working with electronics. They are ubiquitous, vital, and the understanding of their role is the gateway to mastering the world of circuit design, with specific reference to 20k resistor.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA