Understanding the 2.2 Ohm Resistor: Applications and Selection Guide
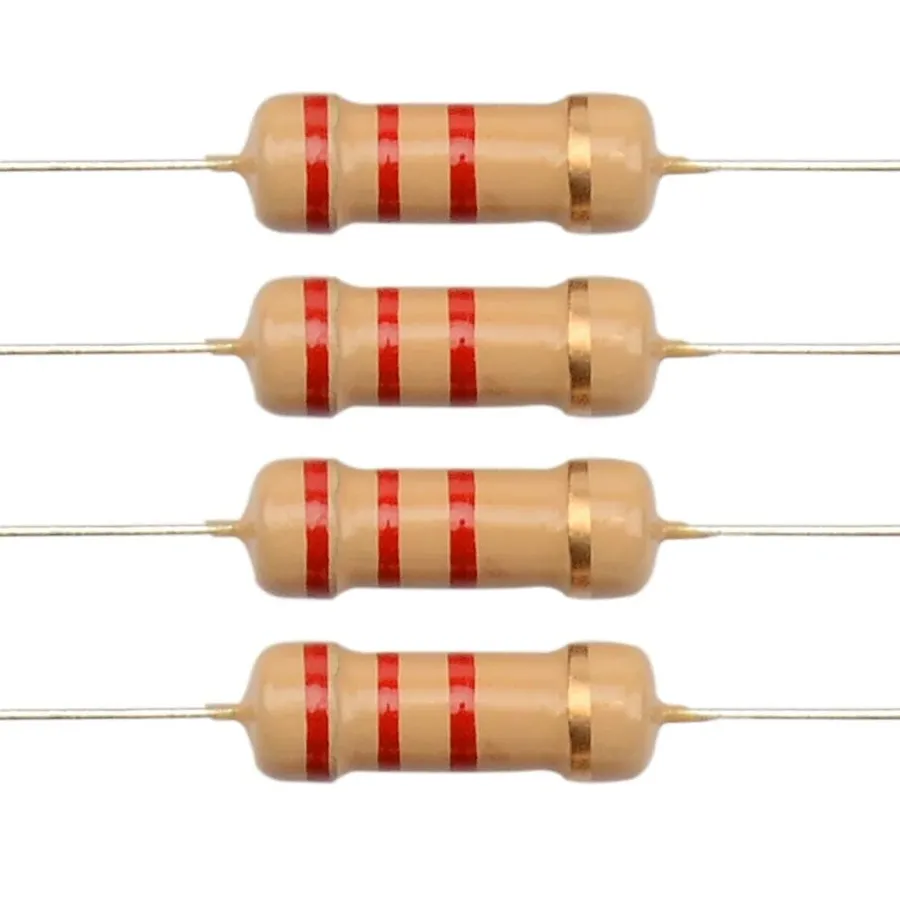
Like a tiny traffic controller in the world of electronics, a 2.2 ohm resistor is a fundamental component. Imagine trying to regulate the flow of water through a pipe—this resistor does the same for electrical current. Whether it's in automotive airbag systems or audio equipment, the 2.2 ohm resistor plays a critical role. This article will demystify its importance and guide you in understanding its applications.
What is a 2.2 Ohm Resistor?

A 2.2 ohm resistor is a fundamental electronic component that provides a precise electrical resistance of 2.2 ohms. This specific resistance value is crucial in controlling the flow of current within a circuit, directly influencing the circuit's overall performance and behavior. The 'ohm' (Ω) is the standard unit of electrical resistance, defined as the resistance between two points of a conductor when a potential difference of one volt applied between these points produces in this conductor a current of one ampere. Resistors, in general, serve to impede current flow, generate heat, or provide a voltage drop within circuits.
Types of 2.2 Ohm Resistors

2.2 ohm resistors are manufactured using various technologies, each offering distinct characteristics suitable for different applications. The primary types include carbon film, metal film, and surface mount devices (SMD), each with its own advantages and limitations concerning power handling, precision, and environmental stability.
| Resistor Type | Construction | Power Rating | Tolerance | Temperature Coefficient | Typical Application | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film | A carbon film deposited on a ceramic substrate | Low to Medium (typically up to 1W) | Relatively high (typically 5% or 10%) | High | General purpose circuits, low-cost applications | Low cost, widely available | Less precise, higher noise |
| Metal Film | A thin metal film deposited on a ceramic substrate | Medium (typically up to 2W) | Lower than carbon film (typically 1% or 2%) | Low | Precision circuits, audio applications | Better precision and stability compared to carbon film | More expensive than carbon film |
| SMD | Thick or thin film deposited on a ceramic substrate, designed for surface mounting | Low (typically under 1W) | Low to Medium (typically 1% or 5%) | Low | Compact electronic devices, high-density circuits | Small size, suitable for automated assembly | Difficult to handle manually |
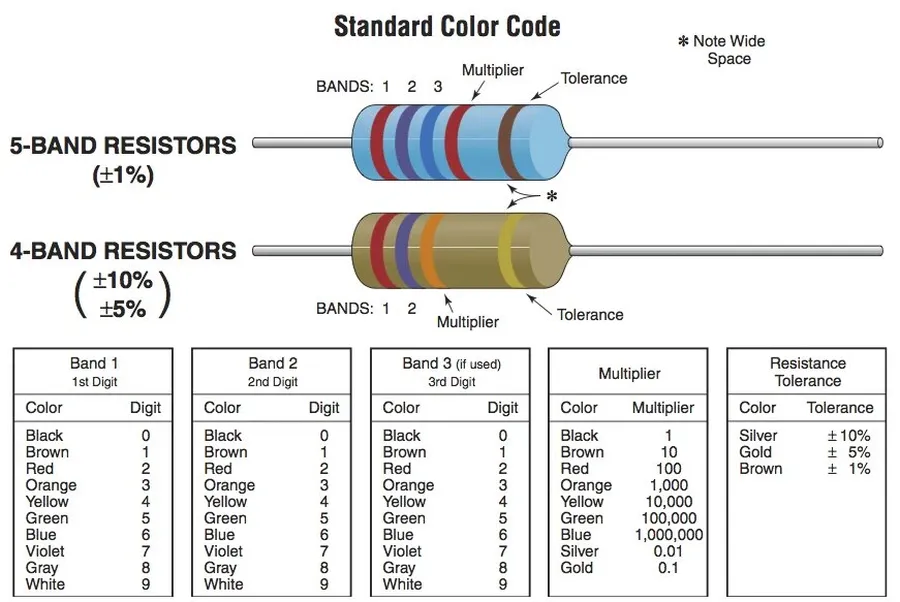
2.2 Ohm Resistor Color Code

The color code on a 2.2 ohm resistor is a critical visual identifier, employing a standardized system to denote its resistance value and tolerance. This system allows for quick identification without needing sophisticated measurement tools. Understanding this color code is fundamental for anyone working with electronics, ensuring accurate circuit implementation.
| Band | Color | Digit/Multiplier/Tolerance |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Band | Red | 2 |
| 2nd Band | Red | 2 |
| 3rd Band | Gold | 0.1 |
| 4th Band | Gold or Silver | 5% or 10% Tolerance |
Therefore, the color bands for a 2.2 ohm resistor are typically: Red, Red, Gold, and either Gold or Silver. The first two bands (Red, Red) represent the significant digits 2 and 2. The third band (Gold) acts as a multiplier, which means multiply by 0.1, hence 22 x 0.1 = 2.2 ohms. The last band represents the tolerance.
Common Applications of 2.2 Ohm Resistors
The 2.2 ohm resistor, while seemingly a very specific value, finds application in a variety of electronic circuits, each leveraging its ability to precisely control current flow. Its common use cases span multiple industries and are integral to the functioning of many devices.
- Airbag System Simulation
In automotive engineering, 2.2 ohm resistors are used to simulate the presence of an airbag during testing or when troubleshooting. This is a critical function, as it ensures that the car's diagnostics don't trigger errors when an airbag is not connected. The precise resistance is crucial for the system to register a proper circuit and avoid false readings. - LED Lighting Circuits
2.2 ohm resistors are frequently used in series with LEDs to limit the current flowing through them. This prevents the LEDs from burning out due to excessive current, ensuring a long and reliable lifespan. The specific resistance value is often chosen based on the forward voltage drop of the LED and the desired operating current. - Audio Equipment
In audio circuits, 2.2 ohm resistors play a role in impedance matching, attenuating signals, and setting bias points for transistors. Their presence ensures that audio signals are processed correctly, maintaining the integrity and fidelity of sound reproduction. - Electronic Prototyping
The 2.2 ohm resistor is a common component in prototyping due to its versatility and the frequency with which it is needed in simple circuits. Its availability and low cost make it ideal for experimenting with various electronic designs. It is used in circuits to set current levels, drop voltages or perform other functions. - Current Sensing
In some specialized applications, a 2.2 ohm resistor can be used as a current-sensing element, where the voltage drop across the resistor is measured and used to calculate the current flowing in the circuit. This method is most commonly used when a low value of resistance is needed for accurate measurement with very low impact on the measured circuit
Selecting the Right 2.2 Ohm Resistor

Choosing the correct 2.2 ohm resistor is crucial for optimal circuit performance and reliability. The selection process involves evaluating several key parameters that align with the specific demands of the application. Ignoring these considerations can lead to malfunctions, circuit damage, or inaccurate results.
The primary factors to evaluate when choosing a 2.2 ohm resistor are power rating, tolerance, and physical size/type. Each will be discussed in detail below:
- Power Rating
The power rating indicates the maximum amount of power (in watts) the resistor can safely dissipate without overheating or failing. Common power ratings for 2.2 ohm resistors include 1/4W, 1/2W, and 1W. Selecting an under-rated resistor will lead to premature failure, therefore it is always good design practice to select a resistor that can handle more power than will be expected to be seen in the circuit. - Tolerance
Tolerance specifies the allowable deviation of the actual resistance value from the nominal 2.2 ohms, it is usually expressed as a percentage (e.g., 1%, 5%). A lower tolerance indicates a more precise resistor, essential for sensitive applications. A tolerance of 1% is usually required in precision circuits, however a tolerance of 5% or greater is acceptable in general purpose applications. - Physical Size and Type
The physical size and type of resistor (leaded or surface mount device (SMD)) must align with the circuit design and application. Leaded resistors are typically used in breadboarding and through-hole circuit construction and SMD components are commonly used for commercial product development where minimizing size and automated assembly is required.
Understanding potential pitfalls and how to avoid them is essential to guarantee the circuit will operate as expected. One common mistake is underestimating the power requirements, which can result in resistor burnout. It is always good practice to calculate the expected power dissipation using Ohm's law and select a resistor with a power rating that is significantly greater. Another common mistake is ignoring the operating environment. High temperatures can affect the resistors performance and can cause it to fail if the resistor's temperature rating is exceeded. Therefore understanding the resistors temperature coefficient is also important. Finally, ensure that the physical package is appropriate for your application.
| Parameter | Description | Typical Values | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Rating | Maximum power the resistor can dissipate | 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, 2W, etc. | Prevents overheating and failure |
| Tolerance | Accuracy of the resistance value | 1%, 5%, 10% | Ensures correct circuit operation |
| Physical Size/Type | Form factor for mounting | Leaded, SMD (various sizes) | Compatibility with circuit design |
| Temperature Coefficient | Change in resistance with temperature | PPM/°C | Ensures stable performance under varying temps |
Frequently Asked Questions About 2.2 Ohm Resistors
This section addresses common questions regarding 2.2 ohm resistors, providing clear and concise answers to aid in your understanding and application of these essential electronic components.
- What is the difference between a 2.2 ohm resistor and a 2.2 k ohm resistor?
A 2.2 ohm resistor has a resistance of 2.2 ohms, while a 2.2 k ohm resistor has a resistance of 2,200 ohms (kiloohms). The 'k' denotes a multiplier of 1000. Therefore, a 2.2 k ohm resistor provides significantly more resistance to current flow than a 2.2 ohm resistor. This difference drastically affects their respective roles within a circuit. - What color bands correspond to a 2.2 ohm resistor?
A standard 2.2 ohm resistor typically has color bands of Red, Red, Gold, Gold or Red, Red, Silver, Gold. The first two bands represent the digits of the resistance value, the third band is the multiplier, and the fourth band represents the tolerance. For 2.2 ohms, the colors directly translate to 2, 2, and 10^-1 for the multiplier (Gold), indicating 22 * 0.1 = 2.2 ohms. Silver can be used for a tolerance of 10%, while gold represents 5% tolerance. - What is the typical voltage drop across a 2.2 ohm resistor?
The voltage drop across a 2.2 ohm resistor depends entirely on the current flowing through it, as dictated by Ohm's Law (V = I * R). To determine the voltage drop, you must first know the current. For example, if 1 amp of current flows through a 2.2 ohm resistor, the voltage drop will be 2.2 volts. If 0.1 amps, the voltage drop will be 0.22 volts. - What are some equivalent resistor combinations for a 2.2 ohm resistor?
Resistors can be combined in series and parallel to achieve the equivalent resistance of 2.2 ohms, although this is typically unnecessary since 2.2 ohm resistors are widely available. Combining two 4.4 ohm resistors in parallel will result in a 2.2 ohm resistance. Conversely, placing two 1.1 ohm resistors in series will also give 2.2 ohms. While parallel and series resistor combinations are typically more common, other combinations can also yield the desired resistance. - Can a 2.2 ohm resistor be used in an automotive airbag system?
Yes, 2.2 ohm resistors are frequently used in automotive airbag systems as a diagnostic and simulation component for testing. The airbag system's electronic control unit (ECU) monitors the airbag squib circuits for proper resistance. If an airbag is removed or faulty, a 2.2 ohm resistor is used to simulate a properly functioning airbag, preventing fault codes being registered with the vehicle's on board diagnostic system. - What power rating should I consider when selecting a 2.2 ohm resistor?
The appropriate power rating depends on the application's power requirements. The power (P) dissipated by a resistor is calculated using P = I^2 * R, where I is the current. Choose a resistor with a power rating well above the calculated value (typically double or more) to avoid overheating and potential failure. Common power ratings for 2.2 ohm resistors include 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, and 2W.
2.2 Ohm Resistor vs Other Resistance Values
While the 2.2 ohm resistor serves specific purposes, understanding how it compares to other resistance values is crucial for informed circuit design. Different resistance values dictate current flow and are selected based on the circuit's functional requirements, leading to different applications.
| Resistance Value | Typical Application | Current Limitation | Power Dissipation Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2.2 Ohm | Airbag system simulation, LED current limiting, low-value shunts for measurement, audio signal path. | Relatively high current flow. | May need higher wattage rating in high current circuits. |
| 1 Ohm | High current sensing, very low value shunts for precise current measurement. | Very high current flow. | Requires higher wattage rating and special resistor types. |
| 10 Ohm | Current limiting for LEDs, pull-up/pull-down resistors in digital circuits, heating elements. | Moderate to high current flow. | Moderate wattage rating. |
| 100 Ohm | General purpose current limiting, signal conditioning, filter circuits. | Moderate current flow. | Lower wattage rating for most applications. |
| 1k Ohm (1000 Ohm) | Current limiting for LEDs, transistor biasing, feedback networks in op-amps, general use. | Lower current flow. | Lower wattage rating. |
| 10k Ohm | Pull-up/pull-down resistors in digital circuits, high-impedance input stages, timing circuits. | Very low current flow. | Low wattage rating. |
| 1M Ohm (1,000,000 Ohm) | High impedance applications, timing circuits, and specialized sensor circuits. | Extremely low current flow. | Low wattage rating. |
Where to Buy 2.2 Ohm Resistors

Sourcing 2.2 ohm resistors requires careful consideration of both the vendor and the component itself. Whether purchasing online or from a local supplier, it is vital to verify the specifications and ensure the resistor meets the requirements of your specific application. Considerations include factors such as the required power rating, the acceptable tolerance, the physical size of the resistor, and whether it is a leaded or surface mount device (SMD).
- Online Retailers
Numerous online platforms offer a wide selection of electronic components, including 2.2 ohm resistors. Reputable sources often include distributors such as Digikey, Mouser Electronics, and Arrow Electronics. These sites typically provide detailed datasheets and specifications for each component, aiding in accurate selection. Be sure to check customer reviews and compare prices before making a purchase. - Local Electronics Suppliers
For immediate needs or smaller quantities, local electronics suppliers can be a valuable resource. These suppliers may include specialized electronics stores or even some hardware stores with an electronics section. Before you buy, ensure that the physical size, the power rating and the tolerance all match your requirements. While the selection may be more limited than online, the convenience of immediate availability can be advantageous. - Component Quality and Authentication
Always prioritize purchasing from reputable sources to avoid counterfeit or substandard components. Confirm that the product descriptions and specifications match your requirement. Verify the manufacturer's part number and any relevant certifications. If possible, check the vendor's history and any available user reviews, as they can offer useful insights into the quality and reliability of the supplier. - Bulk Purchasing
If large quantities of 2.2 ohm resistors are needed, look for distributors that offer volume discounts, which can provide a significant cost saving. Confirm the availability, delivery timeframe and also if the resistors are provided in reels or in other suitable packaging to enable smooth integration in the assembly process. - Physical Inspection upon Receipt
Upon receiving a shipment of resistors, conduct a visual inspection before use. Check the packaging for damage, the color bands for correct value and that the physical dimensions match your specific requirements. Consider using a multimeter to verify the resistance and tolerance of the resistor to ensure it meets the specification. This step can prevent unexpected issues or failures during circuit assembly and testing.
The 2.2 ohm resistor might seem like a small, insignificant component, but its precise function is key to countless electronic devices. From ensuring the safety of airbag systems, to fine tuning audio quality, to prototyping new inventions, the 2.2 ohm resistor plays a big role in our tech-driven world. With this guide, you should now have a comprehensive understanding of this humble yet vital electronic part.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA