Understanding the 22k Ohm Resistor: Applications, Types, and Specs

The humble 22k resistor, a ubiquitous component in electronics, plays a vital role in controlling current and voltage in countless circuits. From simple LED circuits to intricate audio amplifiers, understanding the characteristics and applications of a 22k resistor, like a 22k ohm resistor, is essential for any electronics enthusiast or professional. This article will dive into the world of 22k resistors, exploring their types, applications, and how they impact your projects.
What is a 22k Ohm Resistor?

A 22k ohm resistor is a fundamental passive electronic component characterized by a resistance value of 22,000 ohms (22 kiloohms). Its primary function within an electrical circuit is to impede the flow of electrical current, thereby generating a voltage drop across its terminals, a principle governed by Ohm's Law. This controlled impedance is critical for diverse circuit operations, ranging from current limiting and signal conditioning to voltage division.
Types of 22k Ohm Resistors
22k Ohm resistors, crucial for controlling current and voltage in electronic circuits, are manufactured using various technologies, each offering unique characteristics. The selection of a specific type is largely determined by the application's requirements for precision, stability, and power handling.
| Type | Construction | Precision | Temperature Coefficient | Typical Applications | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film | Carbon film deposited on a ceramic substrate | Moderate (typically 5% tolerance) | Moderate (+/- 200 to 400 ppm/°C) | General-purpose applications, hobby electronics | Low |
| Metal Film | Thin metal film deposited on a ceramic substrate | High (typically 1% or 0.1% tolerance) | Low (+/- 25 to 100 ppm/°C) | Precision circuits, audio equipment, instrumentation | Moderate |
| Wire-Wound | Fine wire wound around a ceramic core | Very high (up to 0.01% tolerance) | Very low (+/- 5 to 50 ppm/°C) | High-power applications, current sensing | High |
Among these types, the 1/4 Watt carbon film resistor is frequently used in hobby electronics due to its balance between cost-effectiveness and performance, while metal film resistors provide superior accuracy for more demanding designs. Wire-wound resistors are less common for 22k values because they are typically used for high-power, low-resistance applications, but are available where very high precision and stability are essential, though at a higher cost.
22k Ohm Resistor Color Code
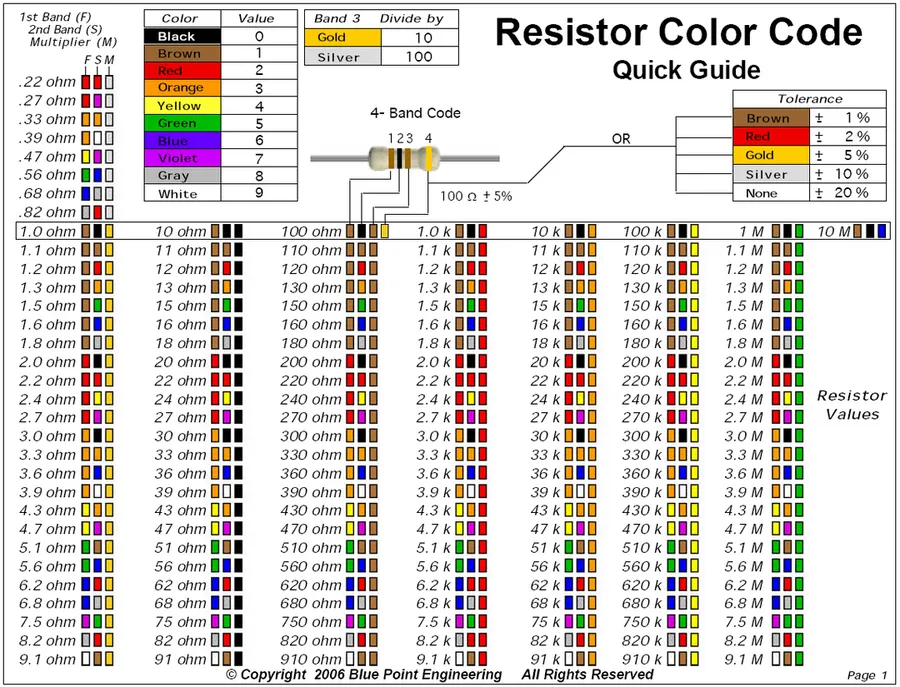
The color code on a 22k ohm resistor is a standardized system that allows for quick identification of its resistance value. This system utilizes a series of colored bands, each representing a numerical value or a multiplier. For a 22k ohm resistor, the color bands are typically arranged as follows: Red, Red, Orange, and Gold.
| Band | Color | Digit/Multiplier | Meaning |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st Band | Red | 2 | First significant digit |
| 2nd Band | Red | 2 | Second significant digit |
| 3rd Band | Orange | 1000 | Multiplier (multiply by 1,000) |
| 4th Band | Gold | ±5% | Tolerance |
Therefore, a 22k ohm resistor with a typical 5% tolerance will have the color bands Red, Red, Orange, and Gold. The reading sequence is important, and should be read from the end of the resistor with the bands closer to the edge. Some resistors may have 5 bands, with the 5th band representing the temperature coefficient, but this is not standard for 22k ohm resistors.
Key Specifications of a 22k Ohm Resistor
Understanding the key specifications of a 22k ohm resistor is crucial for proper circuit design and operation. These specifications include tolerance, power rating, temperature coefficient, and maximum voltage rating. Each parameter plays a vital role in ensuring the resistor functions as intended and prevents potential failures due to overheating or overvoltage.
| Specification | Description | Typical Values for 22k Resistor | Impact on Circuit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerance | The permissible deviation from the stated resistance value. | ±1%, ±5% | Affects the precision of the voltage drop or current limitation. Lower tolerance equals more precise performance. |
| Power Rating | The maximum power the resistor can dissipate without being damaged. | 1/8W, 1/4W, 1/2W | If power rating is exceeded, resistor can overheat leading to failure. Crucial for handling power in the circuit. |
| Temperature Coefficient | The change in resistance per degree Celsius of temperature change. | Typically ±100 ppm/°C to ±200 ppm/°C for carbon film, lower for metal film | Affects resistance value with temperature change; more stable for metal film than carbon film. |
| Maximum Voltage Rating | Maximum voltage that can be applied across the resistor without causing dielectric breakdown. | Dependent on size and type, varies from tens to hundreds of volts. | Exceeding maximum voltage can cause the resistor to fail. |
Applications of 22k Ohm Resistors
22k ohm resistors are versatile components employed across a wide spectrum of electronic circuits due to their ability to limit current and create voltage drops. Their specific resistance value makes them suitable for various applications, including acting as pull-up or pull-down resistors, controlling LED brightness, attenuating signals, and setting gain in amplifier circuits. The 22kΩ resistor plays a crucial role in ensuring circuit functionality and component protection.
- Pull-up and Pull-down Resistors
In digital logic circuits, 22k ohm resistors are frequently used as pull-up or pull-down resistors. These resistors establish a defined logic level (high or low) when an input is left floating. A pull-up resistor connects the input to a voltage source, while a pull-down resistor connects it to ground. 22k ohm resistors offer a balance between current consumption and reliable signal levels. - Current Limiting for LEDs
22k ohm resistors are commonly used in series with light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to limit the current flowing through them. This prevents the LED from drawing excessive current, which could lead to burnout. The specific value of 22kΩ will determine the LED's brightness based on the forward voltage of the LED and the power supply voltage. - Signal Attenuation
In circuits where signal levels need to be reduced, 22k ohm resistors can be used as part of a voltage divider. This is often necessary to interface components with different voltage requirements. The resistor value and the total circuit impedance determine the degree of signal attenuation. - Gain Setting in Amplifiers
Operational amplifiers (op-amps) often use resistors to define the circuit gain. 22k ohm resistors are frequently found in inverting and non-inverting amplifier configurations to establish specific gain levels. The gain is the ratio of the feedback resistance to the input resistance.
22k Resistor Size and Packaging

Understanding the physical dimensions and packaging of a 22k ohm resistor is essential for proper circuit design and assembly. These resistors come in various sizes and packaging styles, each suited for different applications and manufacturing processes.
The most common physical forms are axial lead and surface mount devices (SMD). Axial lead resistors have leads extending from each end, while SMD resistors are designed to be soldered directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB).
| Feature | Axial Lead Resistors | Surface Mount Resistors (SMD) |
|---|---|---|
| Lead Type | Leads extending from both ends | No leads, contacts on the underside |
| Mounting | Through-hole mounting on PCB | Surface mounting on PCB |
| Size | Larger than SMD equivalents | Compact, smaller than axial lead |
| Common Use | Breadboard prototyping, hobby electronics, through-hole circuit boards | Automated assembly, high-density circuit boards |
| Handling | Easier for manual soldering and prototyping | Requires pick-and-place machines and reflow soldering |
Axial lead 22k resistors are commonly available in a 1/4 Watt power rating and are often used in breadboard prototyping due to their easy handling and compatibility with breadboards. Surface mount resistors, available in various sizes such as 0603, 0805, and 1206, are used in more compact, automated electronic assemblies.
Packaging of 22k resistors, for both axial lead and SMD styles, includes options such as individual bags or bulk packaging for small quantities and tape and reel for automated assembly processes. Tape and reel packaging is particularly beneficial for high-volume manufacturing as it facilitates rapid automated placement of resistors onto PCBs.
Frequently Asked Questions About 22k Ohm Resistors
This section addresses common queries regarding 22k ohm resistors, providing clear and concise answers to help users better understand their characteristics and applications.
- What is a 22k ohm resistor typically used for?
A 22k ohm resistor is a versatile component commonly used for current limiting, setting bias voltages, pull-up or pull-down applications, and signal attenuation in electronic circuits. For instance, they are frequently used in series with LEDs to control their brightness and prevent burnout, as well as in amplifier circuits to set the gain. - What does 'k' mean on a resistor?
The letter 'k' on a resistor denotes 'kilo,' which is a metric prefix meaning 1,000. Therefore, a 22k ohm resistor has a resistance of 22,000 ohms (22 x 1000). - What does '2k2' mean on a resistor?
The notation '2k2' on a resistor indicates a resistance of 2.2 kilo-ohms, or 2,200 ohms. The 'k' serves as a decimal point, and thus, '2k2' is different from '22k,' which is 22,000 ohms. - How does a 2k2 resistor relate to a 22k ohm resistor?
While both notations use 'k', they represent different magnitudes of resistance. A 2k2 resistor has a resistance of 2,200 ohms, while a 22k resistor has a resistance of 22,000 ohms. Therefore, a 22k resistor is exactly 10 times the resistance of a 2k2 resistor. - What are the common color bands for a 22k ohm resistor?
A standard 22k ohm resistor has color bands in the sequence: Red, Red, Orange, and Gold. The first two bands (Red, Red) represent the digits 2 and 2; the third band (Orange) is the multiplier 10^3 or 1000, and the fourth band (Gold) represents the tolerance of ±5%. Together, these form 22 x 1000 = 22,000 ohms. - Where can I purchase 22k ohm resistors?
22k ohm resistors are widely available from various electronic component suppliers, both online and in physical stores. Reputable sources include major distributors such as Digi-Key, Mouser Electronics, and Amazon, as well as local electronic stores and hobby shops. Always verify the specifications and source reliability before purchasing. - What power rating should I consider when choosing a 22k ohm resistor?
The power rating is crucial to ensure the resistor doesn't overheat and fail. For most hobbyist and low-power applications, a 1/4 watt or 1/8 watt resistor is sufficient. However, always calculate the power dissipation in the circuit to make sure the resistor's power rating is adequate, accounting for factors such as current and voltage.
Comparison Table: Carbon Film vs. Metal Film 22k Resistors
Selecting the appropriate 22k ohm resistor type is critical for optimal circuit performance. This table provides a detailed comparison between carbon film and metal film resistors, highlighting key differences in their characteristics to aid in informed decision-making.
| Feature | Carbon Film 22k Resistor | Metal Film 22k Resistor |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Precision | Typically 5% tolerance | Typically 1% or better tolerance |
| Tolerance | Wider range, usually 5% or 10% | Tighter tolerance, often 1% |
| Temperature Coefficient | Higher, less stable with temperature changes | Lower, more stable with temperature changes |
| Noise | Higher noise level | Lower noise level |
| Stability | Less stable over time | More stable over time |
| Power Rating | Standard 1/4W, 1/8W options | Standard 1/4W, 1/8W options, higher power ratings available |
The 22k resistor, often a seemingly insignificant component, is a crucial element in countless electronic circuits. From its precise role in current limiting to its contribution in signal processing, understanding this component, and other resistors like it, such as the 22k resistor, is fundamental to circuit design and maintenance. By understanding its different types, specifications, and applications, both hobbyists and professional engineers can confidently integrate the 22k resistor into their projects.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA