Understanding the 30uF Capacitor: Types, Applications, and Replacement

In the realm of electrical engineering, the 30uF capacitor is a seemingly small but crucial component found everywhere from your washing machine to industrial machinery. It's a workhorse that stores and releases energy, facilitating smooth operation and preventing malfunctions. Let's dive into the diverse world of 30uF capacitors, uncovering their different types, core applications, and how to address their lifespan, connecting engineering with our daily lives.
What is a 30uF Capacitor?

A 30uF capacitor, or 30 microfarad capacitor, is a fundamental electrical component designed to store electrical energy within an electric field. Its capacitance, quantified in microfarads (µF), defines its capacity to hold an electrical charge. These capacitors are essential components in a variety of electrical circuits and electronic devices, each designed for specific performance characteristics and applications.
Types of 30uF Capacitors

30uF capacitors, characterized by their 30 microfarad capacitance, are integral components in diverse electrical systems. They are not monolithic; rather, they come in several types, each engineered for specific operational requirements. Understanding these types is crucial for effective application and replacement.
| Capacitor Type | Construction | Typical Applications | Key Characteristics |
|---|---|---|---|
| Motor Run Capacitors (CBB60/CBB65) | Film capacitors with metallized polypropylene film as dielectric. | Single-phase AC motors in HVAC systems, appliances, and industrial equipment. | Designed for continuous operation, excellent stability, and self-healing properties. |
| Aluminum Electrolytic Capacitors | Electrolytic capacitor using a layer of aluminum oxide as dielectric. | Power supplies, filtering, and decoupling in various electronic circuits. | High capacitance per volume, but with limited lifespan and temperature range. |
| Ceramic Capacitors | Ceramic materials act as the dielectric. | High-frequency circuits, decoupling, and filtering in electronic circuits. | Small size, high-frequency performance, but limited capacitance. |
| Film Capacitors (other than motor run) | Various film materials like polyester or polycarbonate used as dielectric. | General purpose applications in electronic circuits. | Good stability, moderate size, and moderate cost. |
It’s important to note that while all these capacitors may have the same 30uF rating, their physical construction, voltage ratings, and operational characteristics vary significantly. Therefore, choosing the correct type for an application is essential.
Applications of 30uF Capacitors

30uF capacitors serve as crucial components across a wide array of applications, primarily due to their ability to store and release electrical energy, facilitating essential functions in various devices and systems. Their usage spans from domestic appliances to heavy industrial machinery, highlighting their versatility and importance in modern electrical engineering.
- Motor Starting and Running
30uF capacitors are frequently employed in single-phase AC motors. These capacitors create a phase shift in the electrical current, enabling the motor to generate the torque required for starting and sustained operation. Without this phase shift, these motors would fail to start or run efficiently. This is crucial in pumps, compressors, and fans. - HVAC Systems
In heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems, 30uF capacitors are vital for the operation of fan motors and compressor motors. They ensure the motors start smoothly and run with optimal efficiency, contributing to the overall performance and energy conservation of HVAC units. Specific examples include use in air conditioners, heat pumps, and ventilation systems. - Domestic Appliances
Many household appliances rely on 30uF capacitors. Washing machines, dishwashers, and some types of refrigerators utilize these capacitors to control and optimize the operation of their motors. They are instrumental in ensuring the effective functioning of these appliances, controlling the motor operation. - Industrial Machinery
Industrial equipment utilizes 30uF capacitors in various motor-driven systems to provide reliable power and control. They help manage the higher current requirements of industrial motors, improving operational performance, in applications like conveyor belts, industrial pumps, and various manufacturing machines. - Power Factor Correction
While not their primary role, capacitors can be used for power factor correction. Although a 30uF capacitor itself is a small correction, they are often used in parallel with other capacitors, or in smaller applications, to mitigate reactive power and enhance electrical system efficiency by bringing the power factor closer to 1.
30uF Motor Run Capacitors: How They Work

30uF motor run capacitors are essential components in single-phase AC induction motors, serving the critical function of enabling the motor's start and continuous operation. These capacitors facilitate the creation of a phase shift in the electrical current, a requirement for generating the necessary rotating magnetic field that drives the motor's rotor, ensuring efficient torque production and smooth performance. They are typically designed for continuous use while the motor is running, unlike start capacitors which are only used momentarily during start-up.
| Characteristic | Function | Typical Applications | Voltage Variations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Phase Shifting | Creates a phase difference in the current supplied to the motor's windings, essential for establishing a rotating magnetic field. | Single-phase AC induction motors, HVAC systems, pumps, fans. | 370VAC, 440VAC, 450VAC |
| Continuous Operation | Designed for continuous use while the motor is running. | Applications that require constant motor operation, such as HVAC fans and pump motors. | Specific to application requirements |
| Torque Generation | Assists in producing the initial torque required to start the motor, and also to maintain optimal torque during its operation. | Motor applications where consistent torque output is critical, like compressors and industrial machinery. | Higher voltage ratings may be chosen for robust applications |
Specifically, variations such as 30uF 370VAC and 30uF 450VAC capacitors cater to different motor voltage requirements, ensuring proper functionality and preventing premature capacitor failure. The voltage rating of the capacitor must always meet or exceed the motor’s voltage demand to guarantee safe and efficient motor operation.
30uF Capacitor Voltage Ratings: Choosing the Right One
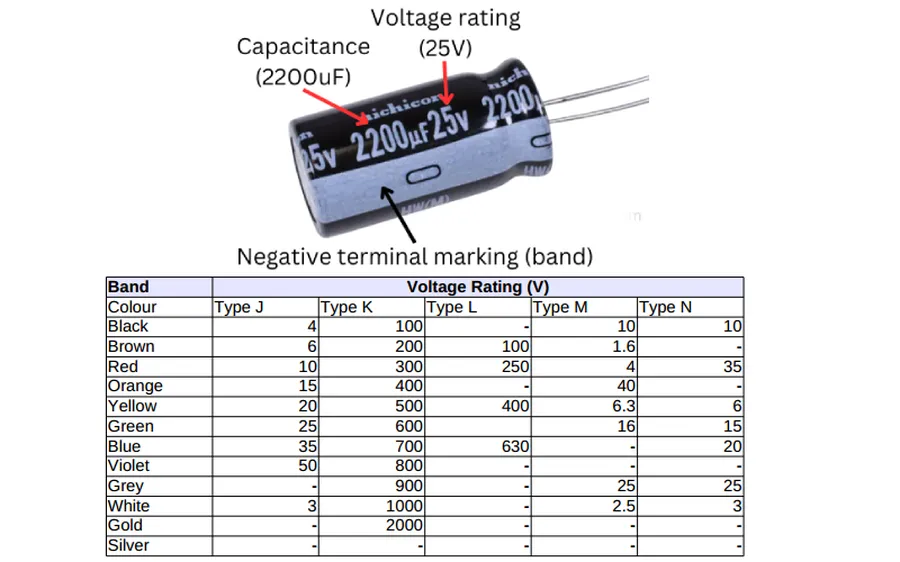
Selecting the appropriate voltage rating for a 30uF capacitor is crucial for ensuring the safety and longevity of electrical systems. A capacitor's voltage rating specifies the maximum voltage it can safely withstand without risking dielectric breakdown and subsequent failure. Using a capacitor with a voltage rating below the circuit's operating voltage can result in catastrophic failure, while using one with a significantly higher rating is generally safe but might come with increased size and cost. Therefore, understanding these ratings is a fundamental aspect of component selection.
| Voltage Rating (VAC) | Typical Applications | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| 240VAC | Small appliances, single-phase motors in domestic settings. | Common in residential applications, check nameplate voltage for precise ratings. |
| 370VAC | HVAC systems (e.g., fans, compressors), medium-duty motor run applications. | Offers a safety margin over 240VAC, suited to more demanding equipment. |
| 440VAC | Industrial machinery, high-torque motors, heavy-duty appliances. | Designed for higher stress and voltage environments. |
| 450VAC | Industrial applications, demanding motor starting applications, heavy duty compressors and pumps. | Provides extra protection and lifespan in high voltage and high heat conditions. |
It is imperative that the selected capacitor's voltage rating meets or exceeds the operational voltage of the intended circuit. Undervolting can lead to premature failure, while selecting an excessive voltage rating, though not detrimental to performance, may lead to unnecessary cost and size considerations. The 30uF capacitors for motor run are more frequently used at voltages between 370VAC and 450VAC, hence it is highly suggested to consult equipment nameplate specifications before buying a replacement.
30uF Capacitor Replacement Guide
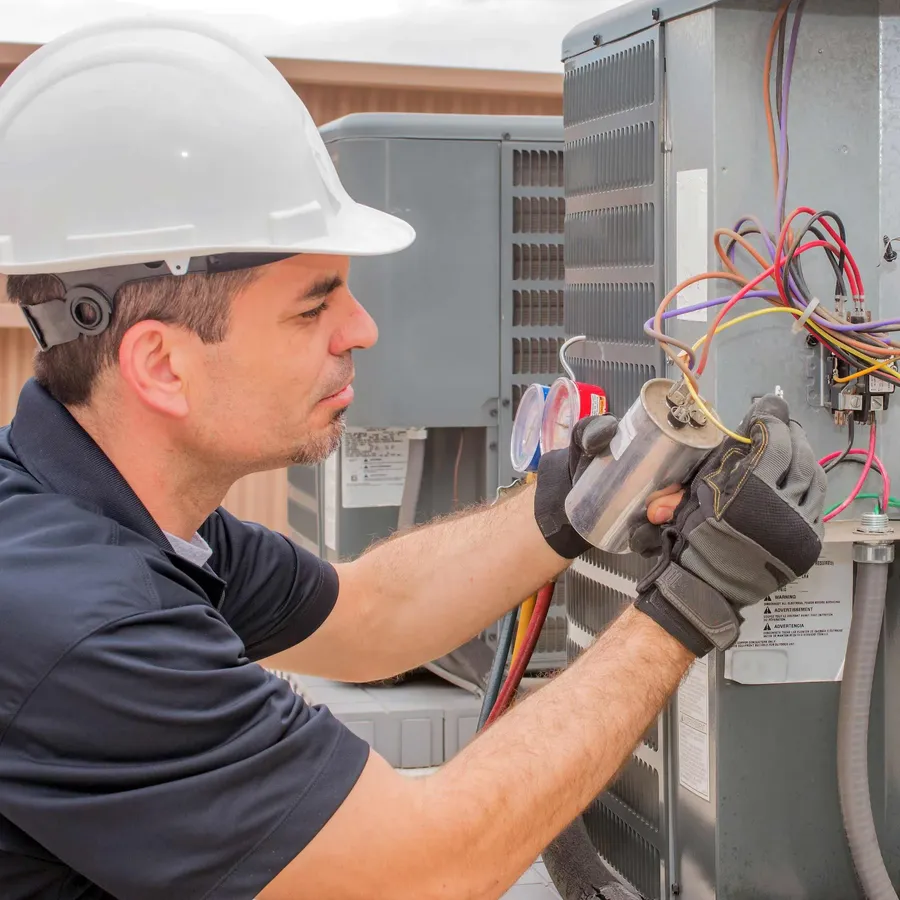

Replacing a 30uF capacitor requires careful attention to safety protocols and proper procedures. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to ensure a safe and effective replacement, minimizing risks and ensuring the proper operation of your equipment.
- Step 1: Gather Necessary Tools and Safety Equipment
Before beginning, ensure you have the appropriate tools and safety gear. This includes insulated screwdrivers, a multimeter, wire strippers, electrical tape, safety glasses, and insulated gloves. Having these ready beforehand will streamline the process and improve safety. - Step 2: Identify the Correct Replacement Capacitor
Carefully examine the existing 30uF capacitor. Note the exact capacitance (30uF), voltage rating (e.g., 370VAC, 440VAC, or 450VAC), and type (e.g., motor run capacitor, CBB60, or CBB65). It is vital to obtain a replacement with identical or higher voltage ratings to ensure compatibility and proper function. Using a lower voltage rated capacitor is extremely dangerous and will likely result in capacitor failure. - Step 3: Safely Discharge the Existing Capacitor
Prior to removal, capacitors MUST be fully discharged. Use a multimeter to check for any residual voltage. If voltage is detected, use a high-value resistor (e.g., 10k ohm, 5W) to discharge it. NEVER touch the capacitor terminals with bare hands or conductive tools while discharging. Discharging a capacitor is critical to prevent electrical shock. - Step 4: Disconnect the Old Capacitor
Once discharged, carefully disconnect the wires from the old capacitor. Take a photo or make a detailed diagram of the wiring before disconnecting to ensure correct connections later. Use wire strippers to cut any wire ties or connectors and note the order of the terminals for re-installation. - Step 5: Install the New Capacitor
Connect the new capacitor, matching the wire positions from the earlier diagram or picture. Ensure all connections are secure by utilizing crimp or screw terminals properly. Loose connections can cause overheating and operational issues. Always double-check your work to prevent wiring errors that could damage equipment or injure personnel. - Step 6: Secure the Capacitor and Test the Circuit
Position the new capacitor securely back to its original location, and ensure it is stable so that it does not move around during operation. Power on the circuit briefly and monitor to see if the new capacitor works. Listen for any unusual sounds or smell for burning smell. Once satisfied that all connections are secured and the new capacitor works as expected, then secure the access panel to prevent accidental contact.
Frequently Asked Questions About 30uF Capacitors
This section addresses common inquiries regarding 30uF capacitors, providing clear and concise answers to ensure a comprehensive understanding of their functionality and usage.
- What does 30 uF mean on a capacitor?
The notation '30 uF' specifies the capacitance of the capacitor, indicating its ability to store an electrical charge. 'uF' stands for microfarads, a unit of capacitance, where one microfarad is equal to one millionth of a farad. A 30uF capacitor can store 30 microfarads of charge at a given voltage. - What does uF stand for on a capacitor?
The abbreviation 'uF' stands for microfarad. A farad (F) is the base unit of capacitance in the International System of Units (SI), and a microfarad (uF) represents one millionth of a farad (10^-6 F). Capacitance measures a component's capacity to store an electric charge. - Is it OK to use a higher uF capacitor?
Generally, using a capacitor with a slightly higher uF value than the original is acceptable in some applications, but it is critical to stay within the recommended tolerance specified by the equipment manufacturer. A significantly higher capacitance can cause issues, such as altered circuit timing, increased inrush current, or in the case of a motor run capacitor, potentially damaging the motor due to changes in the phase shift. Always consult the manufacturer's specifications and guidelines. - What does 1 uF mean on a capacitor?
A '1 uF' marking on a capacitor means it has a capacitance of 1 microfarad, indicating its ability to store 1 millionth of a farad of electrical charge. It's a much lower capacitance than the 30uF capacitor and is used in different applications where smaller charge storage is required. - Can I use a capacitor with a higher voltage rating?
Yes, it is generally safe to use a capacitor with a higher voltage rating than the original capacitor. A higher voltage rating indicates the maximum voltage the capacitor can withstand before dielectric breakdown. Using a higher-rated capacitor will not affect circuit performance negatively, provided the capacitance value remains correct. It provides an extra margin of safety, improving the capacitor's lifespan and ensuring it will not be damaged by transient voltage spikes. - What happens if a capacitor fails?
When a capacitor fails, several consequences can occur depending on the type of failure. Short-circuited capacitors can cause overheating, damage other components, or trigger circuit breakers. Open-circuited capacitors, or capacitors that have lost their capacity, may result in a malfunction of the intended circuit. Common symptoms include motor start failure, flickering lights, overheating and capacitor swelling or bulging. Prompt replacement is essential to maintain system functionality. - Can a 30uF capacitor be used in place of a 25uF capacitor?
Substituting a 30uF capacitor for a 25uF capacitor is generally not recommended without careful consideration. This increase in capacitance can alter the performance of the circuit or the equipment it's part of. In motor applications, an incorrect capacitance can lead to reduced starting torque, inefficient operation, overheating and premature failure of the motor. When replacing a capacitor, it is crucial to use the exact capacitance specified by the manufacturer or consult a qualified technician.
Troubleshooting Common 30uF Capacitor Issues
Effective troubleshooting of 30uF capacitors involves recognizing common failure modes and understanding their impact on circuit operation. Identifying issues early can prevent further damage to connected equipment and ensure safe operation. This section covers visual inspection techniques, performance checks, and diagnostic steps to help you assess the health of your 30uF capacitors.
- Bulging or Swelling
A physically bulging or swollen capacitor casing is a clear sign of internal pressure buildup, often caused by overheating or degradation of the internal dielectric material. Such a capacitor is likely to be out of specification and should be replaced immediately. - Leaking Electrolyte
If you observe any fluid leaking from the capacitor, this indicates a breach in its casing and the loss of its internal electrolytic material. A leaking capacitor is no longer functioning correctly and needs replacement. This is often accompanied by a distinct odor. - Motor Fails to Start
A 30uF capacitor that has degraded may not provide the necessary phase shift to initiate motor rotation. If your motor struggles to start, or simply hums and does not turn, a faulty capacitor may be the cause. Check also for other components failure like the start winding, but a capacitor is a high probability issue - Reduced Motor Torque
A 30uF motor run capacitor may be partially failed. The motor may start, but with reduced torque, indicating the capacitor is not providing the correct phase shift or has lost capacitance. This can lead to increased motor temperature and reduced operational efficiency. - Increased Operating Temperature
A capacitor that is failing internally might heat up excessively during operation. While capacitors are designed to handle some amount of temperature, an overheating capacitor is a sign of degradation. Always disconnect the power before inspection. - Visual Inspection for Damage
Before you start using any measurement tools, check to see if there are any signs of physical damage to the capacitor, such as: cracks, swelling, bulging, or leaks. Any of these things indicate the capacitor needs replacement. - Checking Capacitance with a Multimeter
Use a multimeter with capacitance measurement capability to confirm the value of the capacitor. The measured capacitance should be within the tolerance range indicated on the capacitor label. A reading significantly lower than 30uF suggests the capacitor is failing. Always ensure the capacitor is fully discharged before measurement.
Purchasing 30uF Capacitors: Factors to Consider
Selecting the correct 30uF capacitor involves careful consideration of several factors to ensure optimal performance and longevity. These include voltage rating, capacitor type, brand reputation, and where you ultimately choose to purchase the component.
When purchasing a 30uF capacitor, these are the key factors to consider:
- Voltage Rating
Crucially, the voltage rating of the replacement capacitor must equal or exceed that of the original. Common ratings for 30uF capacitors include 240VAC, 370VAC, 440VAC, and 450VAC. Using a capacitor with an insufficient voltage rating can lead to premature failure, potentially causing a safety hazard. - Capacitor Type
The most common types are motor run capacitors (CBB60 and CBB65). Ensure the replacement is the correct type, especially for motor applications. Using the wrong type can lead to operational issues and reduced performance of the connected device or machinery. - Brand and Quality
Opt for reputable brands that adhere to industry standards for safety and performance. While less expensive alternatives may be tempting, quality issues can reduce the lifespan and impact performance. Investing in a quality capacitor is recommended to minimize the total cost over the long term. - Purchase Location
You have two primary options to purchase a 30uF capacitor: online retailers or physical stores. Online options often provide a wider range of choices, and may have lower prices. However, purchasing locally from physical stores such as electronic component shops, hardware stores or appliance repair shops may allow you to assess the physical condition of the capacitor and obtain it more quickly. When searching online, consider delivery times to ensure minimal downtime for your project or repair. - Price Comparison
Prices can vary significantly between online sellers and local stores, and even between different brands. Carefully compare prices, taking into account quality and warranty. Price should not be the sole factor and must be balanced with quality and durability. A lower-priced capacitor may be a false economy if it has a reduced life span. - Physical Dimensions
Although all replacement capacitors are 30uF it is important to verify that the physical dimensions of the capacitor will fit within the intended space in the device or equipment.
From helping your washing machine spin to powering industrial machinery, the 30uF capacitor is a versatile component. Understanding its different types, voltage ratings, and applications empowers you to maintain and repair your equipment efficiently. Whether you are replacing a motor run capacitor or troubleshooting an electrical issue, knowledge of the 30uF capacitor, a seemingly minor component, is crucial. By integrating engineering know-how into our daily lives, we can extend the lifespan of our devices and ensure optimal performance.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA