Understanding the 33k Resistor: Specs, Uses, and More

In the vast world of electronics, a tiny component like the 33k resistor plays a vital role. Whether you're building a complex audio amplifier or a simple LED circuit, understanding its function and importance is paramount. This article will delve into the specifics of the 33k resistor, exploring its characteristics, applications, and how it fits into the broader landscape of electronics, similar to how a key ingredient shapes a dish.
What is a 33k Ohm Resistor?

A 33k ohm resistor is a fundamental electronic component designed to impede the flow of electrical current by 33,000 ohms. This specific resistance value is crucial for controlling current and voltage within circuits. The physical attributes, such as its size, materials, and construction, are adapted to meet diverse application requirements.
33k Resistor Color Code Explained
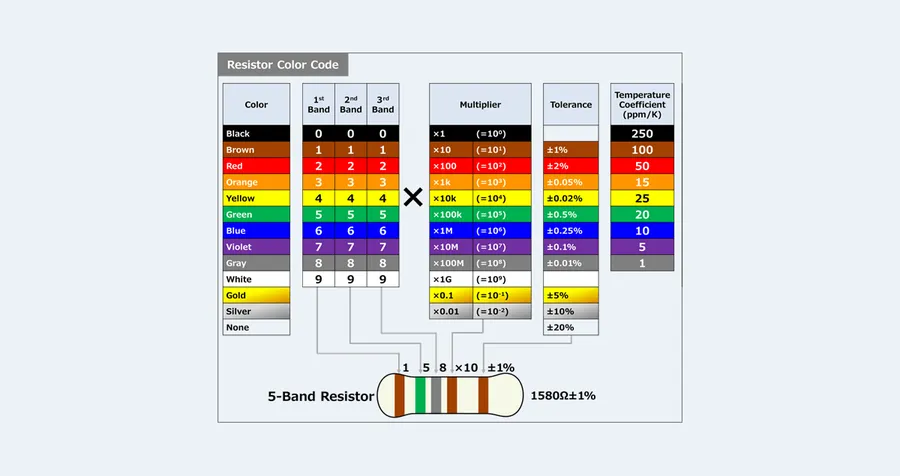
The color code of a 33k ohm resistor is a crucial aspect for identification, typically represented by four color bands: orange, orange, orange, and gold. This standard coding system is foundational in electronics for quickly determining resistance values.
| Band | Color | Value |
|---|---|---|
| 1st Band | Orange | 3 |
| 2nd Band | Orange | 3 |
| 3rd Band | Orange | 1000 (multiplier) |
| 4th Band | Gold | 5% (tolerance) |
Common Types of 33k Resistors

33k resistors are manufactured in several types, each with unique characteristics suited for different applications. The primary types include carbon film, metal film, and wire-wound resistors, each differing in power handling, precision, and temperature stability. Additionally, they are available in both through-hole and surface mount configurations to accommodate various circuit designs.
| Resistor Type | Construction | Typical Tolerance | Power Rating | Temperature Coefficient | Applications | Mounting |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon Film | A thin layer of carbon film on a ceramic substrate | 5% | 1/8W - 1/2W | Moderate | General purpose, cost-sensitive applications | Through-hole |
| Metal Film | A thin layer of metal alloy on a ceramic substrate | 1%, 0.5%, 0.1% | 1/8W - 1W | Low | High-precision circuits, precision measurement, audio circuits | Through-hole & SMD |
| Wire Wound | Fine wire wound around a ceramic core | 1-5% | 1W-10W+ | Very low | High-power applications, precision current sensing | Through-hole |
| Surface Mount (SMD) | Various films or alloys on a ceramic substrate | 1-5% | 1/16W - 1W | Moderate to Low | Modern electronics, high-density circuits, compact devices | Surface Mount |
Key Specifications: Power Rating, Tolerance, and Temperature Coefficient

When selecting a 33k resistor for a specific application, three key specifications must be considered: power rating, tolerance, and temperature coefficient. These parameters determine the resistor's suitability and performance within a circuit. Understanding these specifications ensures the component operates safely and with the desired accuracy.
| Specification | Description | Typical Values for 33k Resistors | Importance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Power Rating | The maximum power the resistor can dissipate without being damaged. | 1/8W, 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, 2W and more | Preventing resistor failure due to overheating. |
| Tolerance | The allowable variation in the actual resistance value from the nominal value. | 5%, 1%, 0.1% or lower | Ensuring circuit accuracy and stability. |
| Temperature Coefficient | The change in resistance value with a change in temperature, usually in parts per million per degree Celsius (ppm/°C). | ±25 ppm/°C to ±200 ppm/°C | Maintaining consistent performance across varying operating temperatures. |
Practical Applications of 33k Resistors
33k resistors serve as fundamental components across a wide array of electronic applications, primarily due to their ability to precisely control current flow and voltage levels within circuits. Their moderate resistance value makes them ideal for scenarios requiring a balance between current limitation and signal integrity.
- Voltage Dividers
33k resistors are frequently employed in voltage divider circuits. In such configurations, two or more resistors are connected in series to proportionally reduce a voltage, providing a smaller, specific voltage to a subsequent component. For example, a 33k resistor coupled with another resistor forms a voltage divider, effectively scaling down an input voltage to a usable level for sensors or microcontrollers. - Current Limiting
These resistors act as current limiting elements. When placed in series with sensitive components like LEDs or transistors, a 33k resistor reduces excessive current, preventing damage. By Ohm's Law (V=IR), the resistor controls the current, ensuring the device operates within its safe current range, crucial for the longevity and functionality of circuit elements. - Feedback Circuits
In circuits using operational amplifiers (op-amps), 33k resistors are commonly used in feedback loops to control the gain and stability of the amplifier. The value of the feedback resistor influences the overall signal amplification and can be selected to achieve a desired performance characteristic. This allows for precise tuning of signal processing capabilities. - Pull-up and Pull-down Resistors
33k resistors are used as pull-up or pull-down resistors in digital logic circuits. These resistors establish a default logic level when inputs are left floating. The choice between pull-up or pull-down is determined by the logic requirements of the circuit. These resistors provide a reliable default signal level to ensure that digital inputs are not in a floating or undefined state. - Audio Circuits
In audio circuits, 33k resistors are used for setting gain and creating bias circuits, controlling signal level, equalization and impedance matching. This is important to create clear signals and the desired audio output.
| Application | Function of 33k Resistor | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Divider | Reduces input voltage | Scaling down voltage for sensors |
| Current Limiting | Limits current flow | Protecting LEDs from overcurrent |
| Feedback Circuits | Controls amplifier gain | Op-amp stabilization and signal control |
| Pull-up/Pull-down | Establishes default logic | Digital input stabilization |
| Audio Circuits | Sets gain and bias | Signal conditioning and impedance control |
33k Resistor vs. Other Common Values (22k, 47k, etc)
Understanding how a 33k ohm resistor behaves relative to other common resistance values, such as 22k, 47k, and even 1k ohms, is crucial for effective circuit design. Each value will create unique current and voltage relationships when placed in a circuit.
| Resistor Value | Current (for a Constant Voltage) | Typical Application Examples | Resistance Change Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1k Ohm | Relatively High | Current limiting, LED circuits | Small change significantly affects current flow |
| 22k Ohm | Moderate | Pull-up and pull-down resistors, feedback networks | Moderate change in current |
| 33k Ohm | Moderate | Audio circuits, op-amp feedback loops, voltage dividers | Moderate change in current, good balance |
| 47k Ohm | Relatively Low | Timing circuits, high impedance inputs | Small change in current flow |
The selection of a resistor value is not arbitrary; it is a fundamental aspect of circuit design. The 33k resistor, for instance, occupies a middle ground in terms of resistance, making it suitable for a variety of general-purpose applications. In contrast, the 1k resistor is more suitable for applications that require significant current flow. 22k and 47k resistors are appropriate where higher resistances are needed and precise current flow is less critical.
Frequently Asked Questions About 33k Resistors
This section addresses common inquiries regarding 33k resistors, providing clear and concise answers to enhance understanding and facilitate effective use in electronic circuit design. The questions and answers provided aim to clarify the value, units, and practical considerations associated with these components.
- What is the precise resistance value of a 33k resistor?
A 33k resistor has a resistance of 33,000 ohms. The 'k' denotes kilo, which represents a multiplication factor of 1,000. Therefore, 33k is equivalent to 33 multiplied by 1,000, resulting in 33,000 ohms. - What does the 'k' signify when referring to a 33k resistor?
In the context of resistors, 'k' is the standard symbol for 'kilo,' a unit prefix in the metric system that denotes a factor of one thousand (1000). Hence, 33k implies 33,000 ohms, which means 33,000 units of electrical resistance. - How is the color code of a 33k resistor determined?
The color code for a 33k resistor is typically orange, orange, orange, and gold (for a 5% tolerance). The first two bands represent the numerical value of the resistance (3 and 3), the third band represents the multiplier (1,000), and the fourth band indicates the tolerance (±5%). - Can I use a 33k resistor in place of a 30k resistor?
The feasibility of replacing a 30k resistor with a 33k resistor depends on the specific application and the tolerance requirements of the circuit. In most cases a 10% change in resistance will have a minimal impact, however, always calculate the circuit performance and take care. - What is the typical power rating for a standard 33k resistor?
The most common power ratings for 33k resistors range from 1/4 watt to 2 watts. The specific power rating needed depends on the amount of current flowing through the circuit. Higher power ratings should be chosen for circuits that experience high current flows. - What is the purpose of tolerance in a 33k resistor?
Tolerance refers to the acceptable variation in the actual resistance value compared to the marked value. A 5% tolerance resistor, for instance, might have a resistance that varies by ±5% of 33k ohms. Always consider the tolerance requirements when designing precise circuitry. - Why is the value of a resistor important for circuit design?
The value of a resistor directly impacts the current flow, voltage division, and overall circuit behavior. Selecting the appropriate resistance ensures the circuit operates within the desired specifications. Using the incorrect resistor value can lead to improper functionality or damage to other components.
Where to Buy 33k Resistors
33k resistors, a fundamental electronic component, are readily accessible through a variety of sources. These components are not exclusive to a single supplier or retailer, ensuring convenient procurement for both hobbyists and professional engineers. The availability of 33k resistors across multiple platforms is a testament to their wide application across various electronic projects and devices.
- Online Electronics Retailers
Numerous online retailers specialize in electronic components, offering a wide selection of 33k resistors. These platforms typically provide detailed product specifications, customer reviews, and competitive pricing, making it easy to find the exact resistor required for a given application. Examples of such retailers include Mouser, Digi-Key, and Newark. - Specialized Component Stores
Dedicated component stores, either online or physical, often carry a diverse inventory of resistors, including various types and tolerances of 33k resistors. These stores are ideal for users seeking specific technical requirements or who need expert advice on the selection of suitable components. - Large E-Commerce Platforms
Major online marketplaces like Amazon and eBay also list 33k resistors from multiple sellers. This option provides convenience and accessibility. It's imperative to scrutinize seller ratings and product specifications before purchasing to verify quality and authenticity, paying close attention to power rating and tolerance specifications.
When purchasing 33k resistors, it's crucial to verify that the specifications for the component, especially the power rating and tolerance, match the requirements of your project. These factors significantly influence the resistor’s performance within the circuit and ensure the longevity and stability of the circuit. Selecting components with adequate specifications ensures the long term reliability of the circuit.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with 33k Resistors
Effective troubleshooting of 33k resistors involves understanding their common failure modes and how they impact circuit behavior. This section provides guidance on identifying potential problems related to wattage, tolerance, and physical damage and how to avoid common pitfalls that can occur during the design and implementation phases.
- Incorrect Wattage Rating
Using a resistor with insufficient power rating can lead to overheating and resistor failure. Confirm that the resistor's power rating meets or exceeds the anticipated power dissipation of the circuit. A 1/4W resistor might be insufficient for some applications, which can cause the resistor to become damaged. - Tolerance Issues
A resistor's tolerance specifies the acceptable variation in its resistance value. If the tolerance is exceeded, the circuit behavior may differ significantly from what was designed and result in the circuit not working as expected, which could be the root of some circuit problems. - Physical Damage
Resistors can be damaged by mishandling, excessive heat, or physical stress. Examine the resistor for any cracks, burns, or broken leads, as even subtle damages could affect its performance and lead to circuit malfunctions. - Incorrect Color Code Identification
Ensure the color bands are properly identified using the correct color code chart. Misreading the color code can lead to using an incorrect resistor value, which can cause circuit malfunction. It is not uncommon to misread a color band, so it is always good to check. - Solder Joint Issues
Cold or poorly made solder joints can increase resistance and lead to unstable circuits. Ensure proper soldering techniques and examine joints with a magnifying glass to identify potential faults. A bad solder joint can be difficult to find and cause intermittent problems. - Environmental Factors
Exposure to moisture or extreme temperatures can affect resistor functionality. Ensure that the resistor is suitable for the operating environment of the application. High humidity or extreme temperature can cause resistors to drift.
The 33k resistor, a seemingly simple component, is a cornerstone of modern electronics, acting as the quiet hero in countless circuits. By understanding its specifications, color codes, applications, and comparison with other resistors, you can leverage its functionality to build a wide range of electronic projects. Just like a 33k resistor precisely controls current, precise knowledge empowers us to construct more accurate and reliable systems. Whether you are a seasoned engineer or a hobbyist, keep the 33k resistor in mind in your design work.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA