Understanding the 40uF Capacitor: Uses, Specs, and Replacements
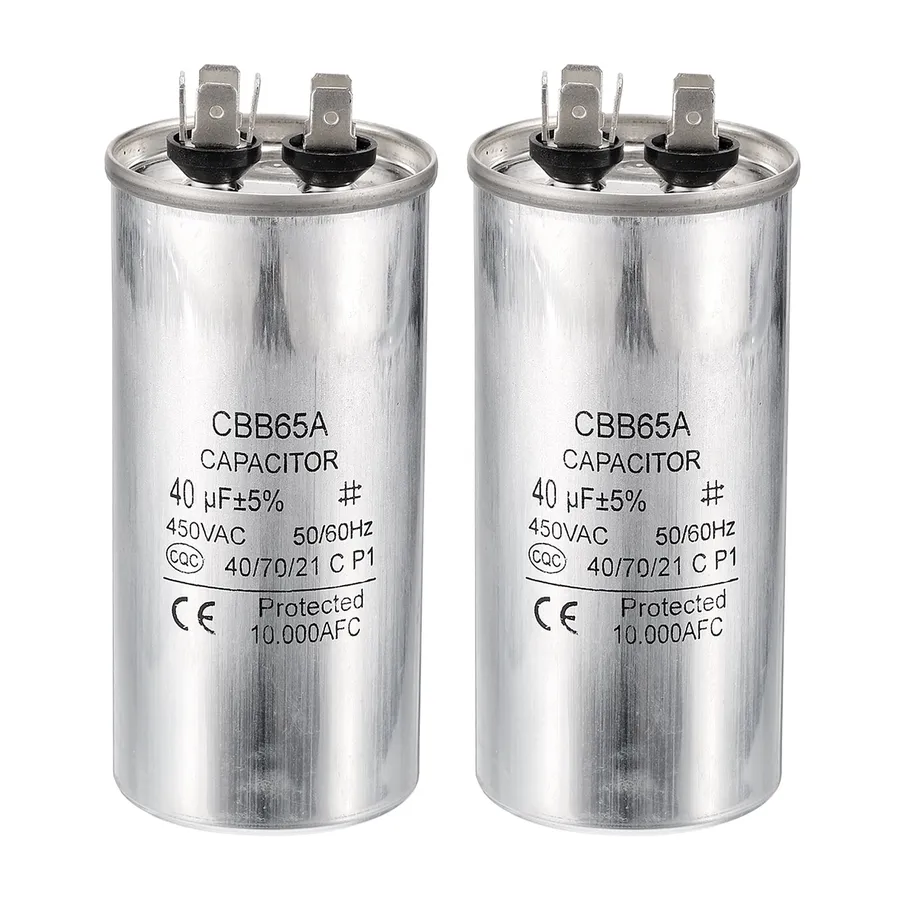

In the realm of electrical components, the 40uF capacitor plays a crucial role in various applications, particularly in motor-driven equipment. Like the heart of an electronic system, this small but mighty component stores and releases electrical energy, ensuring smooth and efficient operation. From air conditioners to washing machines, understanding the specifications and applications of a 40uF capacitor is essential for both technical enthusiasts and those dealing with household appliances. This article will delve deep into the 40uF capacitor, exploring its various facets to empower you with the knowledge for making informed decisions.
What is a 40uF Capacitor?

A 40uF capacitor is an electrical component designed to store energy in an electric field. The '40uF' designation indicates its capacitance, which is 40 microfarads (µF). Capacitance quantifies the capacitor's ability to store charge; a higher capacitance value means the capacitor can store more charge at a given voltage. These capacitors are fundamental in various electrical circuits for purposes including power factor correction, motor starting, and filtering.
Common Applications of 40uF Capacitors

40uF capacitors, characterized by their 40 microfarad capacitance, are essential components in various electrical systems, primarily functioning to store and release electrical energy. Their specific capacitance value makes them well-suited for applications requiring moderate energy storage, playing a critical role in starting and running motors, improving power factor, and enabling smooth operation in numerous devices.
- Motor Start and Run Capacitors
40uF capacitors are commonly used as run capacitors in single-phase AC motors, such as those found in compressors, pumps, and fans. They provide the necessary phase shift to generate a rotating magnetic field, enabling the motor to start and operate efficiently. - HVAC Systems
In Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems, 40uF capacitors are frequently employed in both the fan motors and compressor motors. These capacitors help in maintaining the smooth operation and longevity of the system, ensuring reliable performance. - Power Factor Correction
Capacitors, including 40uF units, play a role in power factor correction, which increases the efficiency of the electrical system by reducing reactive power, thereby minimizing energy waste. While not a primary application, they contribute to optimized power utilization. - Industrial Machinery
Many industrial machines utilize 40uF capacitors for various motor-related tasks. These could be in machinery for manufacturing, agriculture, or other industrial processes, ensuring the smooth start and operation of equipment which are essential for productivity. - Pumps
Pumps, used in diverse applications from water supply to industrial processes, frequently rely on 40uF capacitors to ensure proper operation of their electric motors, preventing start-up issues and maintaining continuous, efficient operation.
Key Specifications: Voltage, Type, and Size

Understanding the key specifications of a 40uF capacitor is crucial for ensuring its proper function and safe operation within a circuit. These specifications primarily revolve around voltage rating, capacitor type, and physical dimensions, each of which influences its suitability for specific applications.
| Specification | Description | Typical Values for 40uF Capacitors |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | The maximum voltage the capacitor can safely withstand. Exceeding this can lead to failure. | Commonly 250VAC, 370VAC, 440VAC, or 450VAC. The specific rating must match or exceed the application's voltage. |
| Capacitor Type | Refers to the capacitor's construction and intended use. | Typically a run capacitor, designed for continuous operation in AC circuits. Often made with film dielectric. |
| Physical Dimensions | The size and shape of the capacitor, impacting its fit within the application. | Dimensions vary but are often cylindrical. Diameter and height must fit the application's housing or space limitations. |
It's crucial to select a 40uF capacitor with a voltage rating that matches or exceeds the voltage of the circuit it will be used in. Using a capacitor with a lower voltage rating than the circuit can lead to capacitor failure, potentially causing damage or fire. The type of capacitor, such as a 'run capacitor', should also match the original unit or the application's requirements to ensure optimal performance and reliable operation. Finally, ensure that the physical dimensions fit within the given space constraints.
Decoding Capacitor Markings
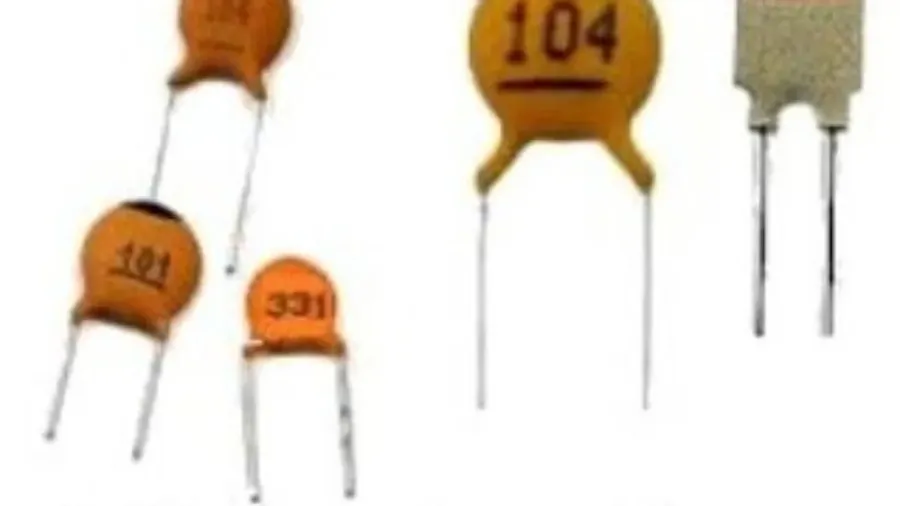

Understanding the markings on a 40uF capacitor is crucial for proper identification and safe installation. These markings provide essential information about the capacitor's electrical characteristics, manufacturer, and safety ratings, ensuring correct usage and preventing potential damage or hazards.
Capacitor markings typically include:
- Capacitance Value
Indicates the capacitor's storage capacity, in this case, 40uF (microfarads). It's always indicated with a number and followed by a 'uF', 'µF', or 'MFD'. A tolerance might be added next to this value using letter codes (e.g., 'J' for ±5%). - Voltage Rating
This indicates the maximum voltage that the capacitor can safely withstand, expressed in Volts AC (VAC) or Volts DC (VDC). Typical values for 40uF capacitors could be 250VAC, 370VAC, 440VAC, or higher. Exceeding this rating can lead to capacitor failure. - Capacitor Type
The type of capacitor is usually mentioned (e.g., 'Run' for motor run capacitors), this helps identify the main usage of capacitor. - Manufacturer's Identification
A logo or the company's name can be found on the capacitor, providing a way to trace it to its maker. - Operating Temperature Range
Indicates the range of temperatures within which the capacitor will perform within its specified ratings. This is usually listed with a minimum and a maximum operating temperature. - Terminal Markings
Run capacitors have two terminals without polarity, making them interchangeable. - Safety Certifications
Marks from recognized organizations such as UL, CE, or CSA are used to signify that the capacitor meets established safety standards. - Date Code
Usually in the format of YYWW (year, week) or similar, the date code tells you when the capacitor was manufactured. It's beneficial to understand this especially for long-term storage or comparison to lifespan.
Identifying a Faulty 40uF Capacitor
A malfunctioning 40uF capacitor can manifest in several ways, often impacting the performance of the equipment it's integrated into. Identifying these symptoms early is crucial for preventing further damage and ensuring safe operation. These signs range from subtle performance degradations to outright failure.
- Motor Humming or Buzzing
A common indicator of a failing capacitor in motor applications is a persistent humming or buzzing sound, which is a result of the motor struggling to start or run efficiently due to insufficient power. - Slow or Delayed Start
If a motor takes an unusually long time to start or requires manual assistance to get going, this could point to a weakened capacitor. The capacitor's inability to deliver the necessary charge can cause such delays. - Reduced Motor Performance
A capacitor losing capacitance results in decreased motor torque and speed, leading to reduced efficiency, and slower operation, this is most noticeable in appliances such as fans, pumps and air compressors. - Overheating
If the capacitor becomes excessively hot during operation, this is a strong indication that the internal resistance is increasing, which can indicate a failing capacitor. This can also lead to further component damage. - Physical Damage
Visible signs of damage, such as bulging, cracking, leaking, or any deformation of the capacitor housing, are clear indicators of a failing or failed capacitor. Immediate replacement is necessary. - Complete Failure
The most definitive sign is when the equipment stops functioning entirely. This indicates a complete failure of the capacitor, requiring immediate attention.
Diagnosing a faulty capacitor often requires a multimeter capable of measuring capacitance and a visual inspection for physical damage. If any of the aforementioned symptoms are observed, replacement is usually the most effective solution. Always disconnect power before inspection.
Selecting the Correct 40uF Capacitor Replacement
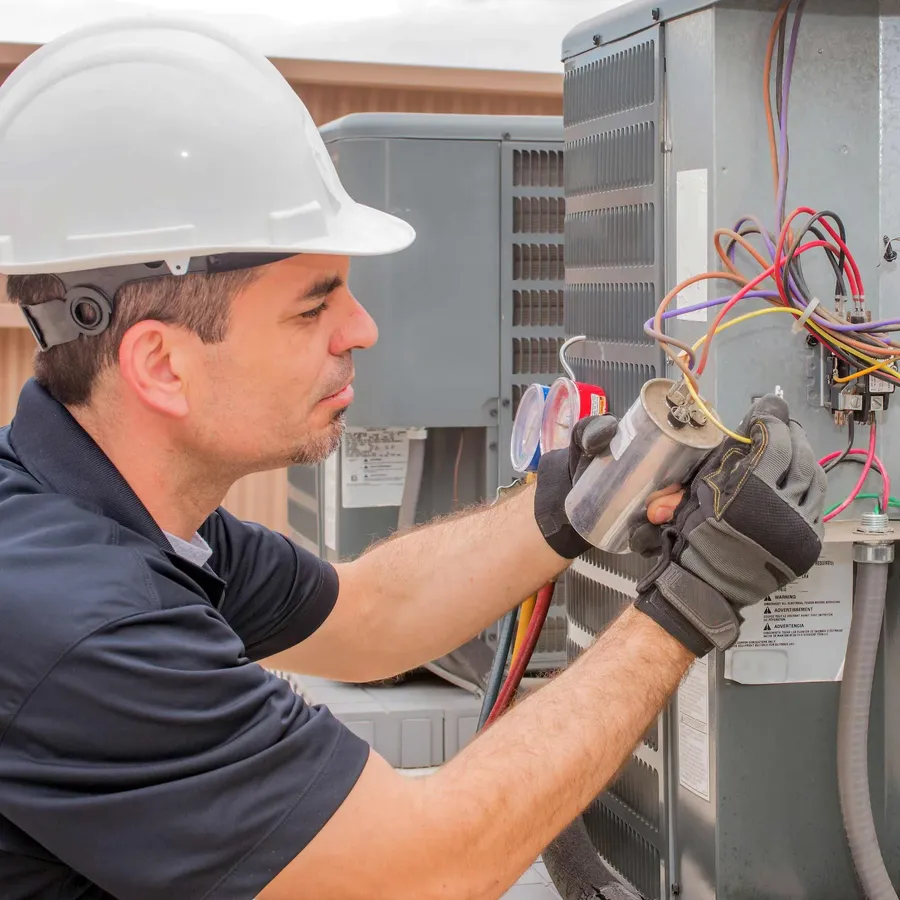

Selecting the correct replacement for a 40uF capacitor is crucial for ensuring the proper functioning and longevity of the equipment it serves. Mismatched specifications can lead to performance issues or even damage to the device. The replacement process should be approached with careful attention to detail, focusing on matching the original capacitor's parameters and using cross-referencing techniques.
- Match Capacitance:
The replacement capacitor must have the same capacitance value, in this case, 40uF (microfarads). Slight variations are acceptable if specified by the equipment manufacturer; however, exact matches are generally preferred. - Voltage Rating:
The voltage rating of the replacement capacitor should be equal to or greater than the original. Never use a capacitor with a lower voltage rating. Common ratings for 40uF capacitors include 250VAC, 370VAC, and 440VAC. - Capacitor Type:
Ensure you are replacing the correct type of capacitor. For instance, many 40uF capacitors are motor run capacitors, which are designed for continuous operation. Do not substitute with a start capacitor. - Physical Dimensions:
The dimensions of the replacement capacitor should be compatible with the available space within the equipment. Check the diameter and length to ensure a proper fit. - Terminal Type:
Verify that the terminal type (e.g., spade terminals, screw terminals) matches the original for ease of installation. - Operating Temperature:
Ensure the operating temperature range of the replacement capacitor meets or exceeds the application’s environment.
Cross-referencing is an effective strategy for identifying suitable replacements. Online databases and manufacturer resources can assist in finding equivalent capacitors based on model numbers or specifications.
| Parameter | Importance | Action |
|---|---|---|
| Capacitance | Critical for Proper Operation | Must match original value (40uF). |
| Voltage Rating | Prevent Capacitor Failure | Should be equal to or greater than the original rating (e.g., 250VAC, 440VAC). |
| Capacitor Type | Ensures Functionality | Replace with the same type (e.g., run capacitor). |
| Dimensions | Facilitates Installation | Must fit available space. |
| Terminals | Ease of Wiring | Should match the type of the original capacitor. |
| Operating Temperature | Reliability | Should meet or exceed the application’s environment. |
Step-by-Step Guide: Replacing a 40uF Capacitor
Replacing a 40uF capacitor, while seemingly straightforward, requires careful execution to ensure both personal safety and the proper functioning of the equipment. This section provides a detailed guide, covering essential precautions and the necessary steps to complete the replacement process effectively.
- Gather Necessary Tools and Materials
Before starting, ensure you have the correct replacement 40uF capacitor, an insulated screwdriver (preferably non-magnetic), a pair of insulated pliers, a digital multimeter, and safety glasses. Consider also having a camera to document the original wiring before disconnecting. - Safety First: Disconnect Power
The most crucial step is to completely disconnect the power supply to the appliance or motor. Verify that the power is OFF using a multimeter. Failure to do so can result in severe electrical shock. - Discharge the Old Capacitor
Even when disconnected, capacitors can retain a dangerous charge. Carefully discharge the old capacitor using an insulated screwdriver with a resistor attached across the terminals if necessary. Shorting the terminals without a resistor can lead to a dangerous arc. This can be done by touching the screw driver to each terminal after the power is disconnected. Verify the capacitor is discharged using the multimeter setting. - Document the Existing Wiring
Before disconnecting any wires, take photos or make a detailed diagram of the capacitor's wiring. This ensures that you connect the replacement capacitor correctly. Note the position of each wire in relation to the capacitor terminals. - Remove the Old Capacitor
Carefully disconnect the wires from the old capacitor using insulated pliers or screwdriver. If the terminals are corroded, clean them lightly with a wire brush. Remove the capacitor from its housing or mounting brackets. - Install the New Capacitor
Place the new 40uF capacitor into the housing and secure it. Attach the wires to the corresponding terminals as documented in step 4, ensuring that the wires are securely connected to the terminals. - Double-Check Connections
Before powering up, review your connections again against your documentation. Ensure the correct wires are connected to the right terminals of the new capacitor. - Restore Power and Test the Appliance
Once confident that everything is correctly wired, restore power and test the appliance or motor. If the motor starts correctly without humming or any other unusual noises, the replacement process was successful. If you have any issues review all the steps or seek a qualified technician.
Frequently Asked Questions About 40uF Capacitors
This section addresses common queries regarding 40uF capacitors, providing clear and concise answers to ensure a comprehensive understanding of their function and application.
- What does '40 uF' mean on a capacitor?
The designation '40 uF' indicates the capacitance of the capacitor, specifically 40 microfarads. Capacitance is a measure of a capacitor's ability to store an electrical charge. A higher capacitance value implies a greater charge storage capacity. - Is it acceptable to use a capacitor with a higher uF rating than the original?
While using a capacitor with a slightly higher uF rating *might* seem permissible in some limited cases, it's generally not recommended and can lead to operational problems or equipment damage. Using a lower uF rating is almost always detrimental. It’s crucial to match the capacitor's uF rating to ensure correct functionality and longevity of the equipment. - What does 'mF' stand for on a capacitor?
The abbreviation 'mF' stands for millifarad, which is equal to one thousandth of a farad (1 mF = 0.001 F). This unit is sometimes used for larger capacitors, although microfarads (uF) are more common for the applications we discuss here. - What does 'uF' mean on a capacitor?
The symbol 'uF' stands for microfarad, which is a unit of capacitance equal to one millionth of a farad (1 uF = 0.000001 F). It is a common unit for measuring capacitance in electronic circuits and devices such as motors and HVAC systems. - Can I replace a 40uF capacitor with a capacitor of a different voltage rating?
It is *essential* to use a replacement capacitor that meets or exceeds the original capacitor's voltage rating. Using a capacitor with a lower voltage rating can cause the capacitor to fail catastrophically, potentially damaging connected equipment and posing a safety risk. Always prioritize matching or exceeding the voltage rating during replacement. - What are common failure modes of 40uF capacitors?
Typical failure modes include a decrease in capacitance (leading to poor motor starting or running), increased equivalent series resistance (ESR), physical swelling or bulging of the capacitor casing, or complete open/short circuit. Visual inspection can often provide clues to a faulty capacitor. - How do I verify the condition of a 40uF capacitor?
The most accurate method is to measure its capacitance using a dedicated capacitance meter or a multimeter with a capacitance measuring function. You should also check the capacitor's ESR and compare it to the manufacturer's specifications if available. Visual inspection for physical damage is also recommended.
40uF Capacitor Price and Where to Buy
The cost of a 40uF capacitor can vary significantly based on several factors, including the voltage rating, brand, type (e.g., motor run vs. start), and the vendor from which it's purchased. This section provides an overview of pricing considerations and where to find these components.
When considering the price of a 40uF capacitor, it's essential to factor in both the initial cost and the long-term value. While cheaper options might seem appealing initially, they may compromise on durability, reliability, and lifespan, potentially leading to higher replacement costs in the future. Purchasing from reputable suppliers can provide the assurance of quality and adherence to industry standards.
| Factor | Impact on Price | Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| Voltage Rating | Higher voltage ratings typically increase the price. | Ensure the replacement matches or exceeds the original capacitor's voltage rating. |
| Capacitor Type | Motor run capacitors generally cost more than start capacitors. | Select the correct capacitor type (run or start) for the application. |
| Brand | Established brands often cost more due to reputation and reliability. | Balance cost and reputation when selecting a brand. |
| Supplier Type | Online retailers may offer competitive pricing, while local suppliers might offer immediate availability and better customer support. | Consider the trade-offs between price, availability, and support. |
| Quantity | Bulk purchases can lower the price per unit. | Consider bulk purchasing if multiple replacements are needed. |
When sourcing a 40uF capacitor, both online retailers and local suppliers have their unique advantages.
- Online Retailers
Often offer a wide selection and competitive pricing, sometimes lower than local stores, and the convenience of home delivery. Examples include Amazon, eBay, and specialized electronics component websites. However, shipping times may vary, and there may be return hassles. Ensure to check for supplier reviews for reliability, shipping, and warranty before purchase. - Local Suppliers
Local electrical supply houses or hardware stores can offer immediate availability, which is important when quick replacement is needed. Local suppliers may have knowledgeable staff who can offer advice and support, but prices may be slightly higher. Also, you have the ability to physically examine components before purchasing them.
The 40uF capacitor is an indispensable component in many everyday electrical devices, from the hum of your air conditioner to the spin of your washing machine. Understanding its role, specifications, and proper replacement procedures can save you time and money. This guide has provided valuable insights into the 40uF capacitor, empowering you to maintain and repair your own equipment with confidence. When handling electrical components like a 40uF capacitor, remember that safety comes first. Always disconnect the power source and refer to expert advice when needed. By understanding the significance of the 40uF capacitor, you can keep your essential appliances running smoothly and efficiently, and even expand your knowledge in the world of electrical components.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA