Understanding the 470 Ohm Resistor: Applications, Color Code, and More
In the world of electronics, the 470 ohm resistor is a ubiquitous component, often a hidden workhorse in countless devices we use daily. From regulating LED brightness to controlling current in intricate circuits, its role is paramount. This article will dissect the purpose, function, identification using color codes, and practical applications of a 470 ohm resistor. We'll delve into how even a seemingly simple component like the 470 ohm resistor can make a critical difference in the performance and safety of electronic designs, connecting the dots between social science of user needs and the technology that powers our lives.
What is a 470 Ohm Resistor?

A 470 ohm resistor is a fundamental passive electronic component designed to impede the flow of electrical current, presenting a fixed opposition of 470 ohms. This precise resistance value plays a vital role in numerous circuit designs, enabling the control of both current and voltage to ensure proper circuit functionality and component protection.
The Role of a 470 Ohm Resistor in Circuit Design

The 470 ohm resistor is a fundamental component in electronic circuit design, serving primarily to control current and voltage. Its specific resistance value is crucial for a variety of applications, enabling precise and reliable operation of electronic systems.
- Current Limiting
In circuits with light-emitting diodes (LEDs), a 470 ohm resistor is often used to limit the current flowing through the LED, preventing damage from excessive current. This is because LEDs have a low forward voltage drop, and without a current-limiting resistor, they would draw too much current and burn out. - Voltage Dividers
When used in conjunction with other resistors, the 470 ohm resistor can form a voltage divider circuit. This configuration allows for creating specific voltage levels from a higher voltage source, which can be crucial for biasing transistors, sensors, and other components. - Transistor Biasing
For transistor circuits, the 470 ohm resistor is essential for establishing the correct operating point for the transistor. This ensures the transistor functions properly in its active region, allowing it to amplify or switch signals effectively. - RC Circuits
The 470 ohm resistor finds applications in RC (resistor-capacitor) circuits, which are commonly used in timing and filter circuits. By working with capacitors, these resistors determine the time constant, which in turn influences the charging and discharging behavior of the capacitor. - Component Protection
The 470 ohm resistor is also vital in protecting sensitive components from high currents or voltages. By adding resistance in the path of the current, it effectively reduces the load seen by other components, preventing them from being overloaded and damaged.
Decoding the 470 Ohm Resistor Color Code
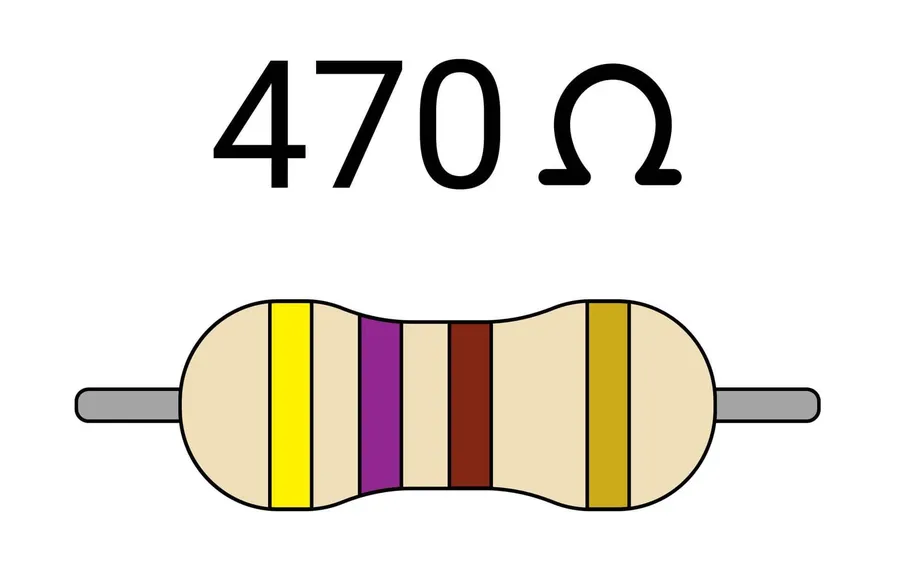
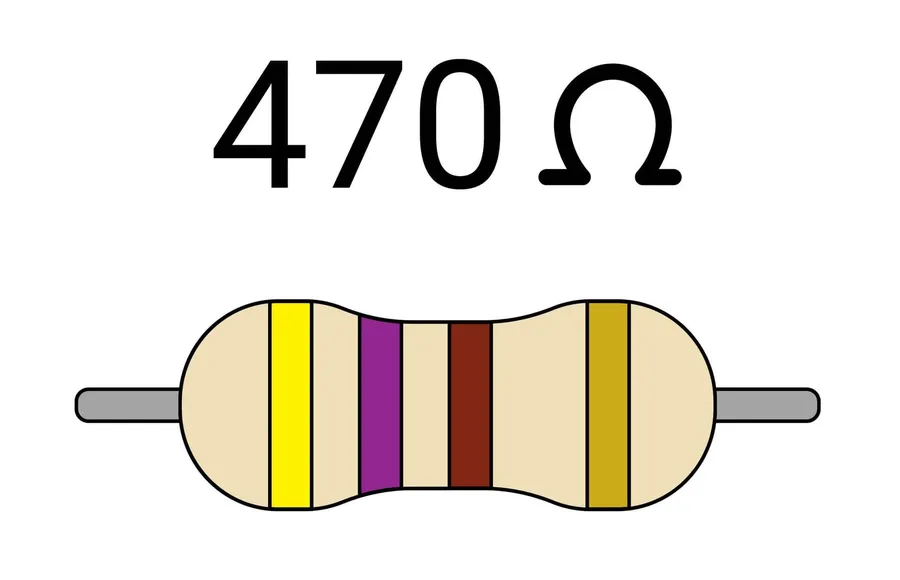
The color code on a 470 ohm resistor is a standardized system for quickly identifying its resistance value and tolerance. Typically, a 470 ohm resistor uses a four-band or five-band system. The color bands are read from left to right, with each color representing a numerical value or a multiplier. Understanding this code is crucial for correctly identifying and using the resistor in circuits.
| Band | 4-Band System | 5-Band System |
|---|---|---|
| First Band | First Digit | First Digit |
| Second Band | Second Digit | Second Digit |
| Third Band | Multiplier | Third Digit |
| Fourth Band | Tolerance | Multiplier |
| Fifth Band | - | Tolerance |
For a standard 470 ohm resistor with 5% tolerance, the color bands in a 4-band system are usually: * **Yellow (4):** The first digit. * **Violet (7):** The second digit. * **Brown (10^1):** Multiplier (multiply by 10). * **Gold (±5%):** Tolerance (deviation from the nominal value). Therefore, the calculation is 47 * 10 = 470 ohms. The tolerance signifies that the actual resistance can vary by ±5% of the nominal value.
In a 5-band system, the 470 ohm resistor uses: * **Yellow (4):** The first digit. * **Violet (7):** The second digit. * **Black (0):** The third digit. * **Brown (10^1):** Multiplier (multiply by 10). * **Gold (±5%):** Tolerance. The calculation is 470 * 10^0 = 470 ohms. The 5-band system often allows for more precise values and tighter tolerances.
| Color | Value (Digit) | Multiplier | Tolerance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Black | 0 | 1 | - |
| Brown | 1 | 10 | ±1% |
| Red | 2 | 100 | ±2% |
| Orange | 3 | 1,000 | - |
| Yellow | 4 | 10,000 | - |
| Green | 5 | 100,000 | ±0.5% |
| Blue | 6 | 1,000,000 | ±0.25% |
| Violet | 7 | 10,000,000 | ±0.1% |
| Grey | 8 | - | ±0.05% |
| White | 9 | - | - |
| Gold | - | 0.1 | ±5% |
| Silver | - | 0.01 | ±10% |
| None | - | - | ±20% |
470 Ohm Resistor Power Ratings and Specifications
The power rating of a 470 ohm resistor is a critical specification that determines how much electrical power it can safely dissipate as heat without damage. Selecting the correct power rating is essential to ensure circuit reliability and prevent component failure.
| Power Rating | Typical Size (Through-Hole) | Application Examples | Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1/8 W | Small, typically 3.2mm long | Low-power circuits, signal conditioning | Suitable for very low current applications, may be harder to find |
| 1/4 W | Standard, 6.35mm long | General-purpose circuits, LED current limiting | Most common for breadboarding and prototyping |
| 1/2 W | Larger, 9.525mm long | Higher current applications, motor control | Good balance of size and power handling, can dissipate more heat |
| 1 W | Larger, 11.9mm long | Power supplies, high current LED circuits | Can handle significant power, may require heatsinking |
| 2 W | Even Larger, typically 15.7mm long | High-power circuits, amplifiers | Can handle substantial power, requires consideration for heat dissipation |
In addition to power ratings, resistors also have tolerance ratings. Tolerance refers to the precision of the resistor's actual resistance value compared to its nominal value. Common tolerances for 470 ohm resistors are 5% and 1%. A 5% tolerance 470 ohm resistor could have actual resistances ranging from 446.5 ohms to 493.5 ohms. A 1% tolerance resistor would have a much narrower range, which is 465.3 ohms to 474.7 ohms. Choosing the correct tolerance depends on the application's sensitivity to resistance variation.
Key specifications also include the temperature coefficient of resistance (TCR). TCR represents how much the resistance changes with temperature variations. Resistors with a low TCR provide more stable resistance across temperature variations. Other specifications may involve noise which is more of a concern for sensitive analog circuits. Physical size, packaging(through-hole or surface mount), maximum operating voltage, are all also considerations to take into account.
Types of 470 Ohm Resistors: Carbon Film vs. Metal Film vs. Metal Oxide

The selection of a 470 ohm resistor often depends on the specific application requirements, especially concerning temperature stability, noise characteristics, precision, and power handling capabilities. This section contrasts carbon film, metal film, and metal oxide resistors, highlighting their respective strengths and weaknesses.
| Characteristic | Carbon Film Resistor | Metal Film Resistor | Metal Oxide Resistor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature Stability | Moderate; resistance drifts more with temperature changes. | Good; exhibits better stability with temperature changes. | Excellent; highly stable at higher temperatures. |
| Noise | Higher noise level due to granular structure. | Lower noise level; better for sensitive circuits. | Low noise level, suitable for precision applications |
| Precision/Tolerance | Typical tolerances are around 5% to 10%. | Higher precision available, typically 1% to 2% tolerance. | High Precision and stability |
| Power Handling | Moderate; power ratings are generally lower. | Good; can handle slightly higher power compared to carbon film. | High; designed for high-power applications. |
| Cost | Generally the least expensive. | Moderately priced. | Generally the most expensive. |
| Applications | General-purpose applications, non-critical circuits. | Precision circuits, audio equipment, instrumentation. | High-temperature applications, power supplies, surge protection. |
Metal film resistors, in particular, offer a superior combination of precision and stability making them a versatile choice for a wide array of applications. Metal oxide resistors, while more expensive, are chosen for their ability to withstand harsh environments and elevated temperatures.
Practical Applications of the 470 Ohm Resistor

The 470 ohm resistor's versatility is showcased in its wide array of practical applications across diverse electronic circuits. Its primary function is to control current flow and voltage levels, ensuring the safe and effective operation of various devices and systems.
- LED Current Limiting
A common use is to limit current flowing through light-emitting diodes (LEDs), preventing damage from overcurrent. The 470 ohm resistor ensures the LED operates within its specified current range, preventing burnout and extending its lifespan. - Audio Amplifier Biasing
In audio amplifier circuits, 470 ohm resistors are often used to establish the correct bias point for transistors or integrated circuits. Correct biasing ensures that the amplifier operates in its linear region for optimal signal amplification with minimal distortion. - Gain Control in Amplifiers
They can be used to control the gain or amplification factor in amplifier circuits. By adjusting the value of resistors in the feedback network of an amplifier, one can effectively manipulate the overall gain of the circuit. - RC Timing Circuits
The 470 ohm resistor finds application in timing circuits, often in conjunction with a capacitor. This resistance-capacitance (RC) combination determines the time constant of the circuit, influencing the rate of charging and discharging, which is used in oscillators and timing devices. - Pull-Up or Pull-Down Resistors
In digital circuits, these resistors may be used as pull-up or pull-down elements. When a logic gate's input is not actively driven high or low, these resistors ensure a defined state, preventing floating inputs and potential malfunctions. The resistor ensures a reliable signal level when an input is not actively driven. - Sensor Circuitry
The 470 ohm resistor can be incorporated into circuits with sensors, where its consistent resistive properties ensure accurate readings. Used in current limiting, biasing or voltage division, this allows for correct interface with analog to digital converters (ADC's) and microcontrollers.
Frequently Asked Questions About 470 Ohm Resistors
This section addresses common queries regarding 470 ohm resistors, providing practical insights into their applications, characteristics, and alternatives.
- What are the primary applications of a 470 ohm resistor?
470 ohm resistors are widely used for current limiting in LED circuits, setting bias points in transistor circuits, creating voltage dividers, and in timing circuits. Their specific resistance value makes them suitable for various precise electronic applications where control of current and voltage is needed. - What is the typical voltage drop across a 470 ohm resistor?
The voltage drop across a 470 ohm resistor is determined by Ohm's Law (V = IR), where 'V' is voltage, 'I' is current, and 'R' is resistance. Therefore, the voltage drop will vary depending on the amount of current flowing through the resistor. For instance, if 20 mA (0.02A) flows through the resistor, the voltage drop would be 0.02A * 470 ohms = 9.4 volts. - What are some suitable alternatives if a 470 ohm resistor is not available?
If a 470 ohm resistor isn't available, you can often use series or parallel combinations of other resistors to approximate the required resistance. For instance, two 235 ohm resistors in series would yield 470 ohms, or two 940 ohm resistors in parallel would also give you the desired 470 ohms. You could also substitute a 430 ohm or a 510 ohm resistor but this will slightly alter your circuit performance. - What is the typical physical size of a 470 ohm resistor?
The physical size of a 470 ohm resistor varies based on its power rating. Common through-hole resistors come in sizes such as 1/4W (approximately 6mm long) and 1/2W (approximately 8-10mm long). Surface mount (SMD) resistors, typically used in miniaturized designs, have sizes like 0805 or 0603, with dimensions in millimeters, where 0805 = 2.0mm x 1.25mm. - How do I choose the correct wattage for a 470 ohm resistor?
The wattage rating of a 470 ohm resistor should be equal to or greater than the power it will dissipate. The power dissipation is calculated using the formula P = I²R (Power = Current squared multiplied by Resistance) or P=V^2/R. For example, if 20 mA flows through the 470 ohm resistor, then the power dissipation would be 0.02^2 * 470 = 0.188 watts. It's good practice to choose a resistor with a power rating at least twice the calculated value to provide a safety margin and prevent overheating or failure. - What does the tolerance of a 470 ohm resistor signify?
The tolerance of a resistor indicates the acceptable range of deviation from the stated resistance value. A 5% tolerance 470 ohm resistor, for example, can have an actual resistance that is within 5% of 470 ohms, between 446.5 ohms and 493.5 ohms. Similarly, a 1% tolerance will have an even tighter range. Choosing the appropriate tolerance is critical for circuit accuracy. - How does temperature affect a 470 ohm resistor?
The temperature coefficient of a resistor describes how much its resistance changes with temperature fluctuations. Metal film resistors exhibit a lower temperature coefficient compared to carbon film resistors, maintaining their resistance value with minimal change across a wider temperature range. Therefore, metal film resistors should be used in applications that demand greater temperature stability.
How to Select a 470 Ohm Resistor for Your Project
Selecting the appropriate 470 ohm resistor is crucial for the reliable performance of any electronic circuit. The selection process involves considering several key factors such as power rating, tolerance, physical size, and mounting method (through-hole vs SMD). Ignoring these parameters can lead to component failure or inconsistent circuit behavior.
- Power Rating
Determine the power dissipation requirement of your circuit. Select a 470 ohm resistor with a power rating significantly higher than the expected power dissipation to ensure safe and reliable operation. Common power ratings include 1/4W, 1/2W, 1W, and 2W. - Tolerance
The tolerance of a resistor specifies the acceptable deviation from its nominal resistance value. For most general-purpose applications, a 5% tolerance is sufficient. However, applications requiring higher precision, such as instrumentation or precision analog circuits, may need resistors with 1% or even tighter tolerances. - Physical Size
The physical size of the resistor is determined by its power rating, and the mounting requirements. Ensure that the size of the chosen resistor matches the available space in your project. Resistors are available in various sizes, which are standardized based on power rating. - Mounting Method
Consider whether through-hole or surface-mount (SMD) resistors are appropriate for your design. Through-hole resistors are typically used for prototype circuits and are easier to handle, while SMD resistors are typically employed in production boards and require reflow soldering.
| Parameter | Consideration |
|---|---|
| Power Rating | Choose a wattage rating higher than calculated to account for heat and current |
| Tolerance | 1%, 5%, or 10%; select based on required precision |
| Physical Size | Consider space constraints of the project and standard resistor sizes. |
| Mounting Method | Through-hole for prototyping or SMD for compact designs |
Where to Buy 470 Ohm Resistors
Purchasing 470 ohm resistors requires consideration of both your project's needs and the reliability of the supplier. Whether you're seeking a single resistor or a bulk quantity, options range from online marketplaces to specialized electronics distributors. This section provides guidance on selecting the right source to meet your specific requirements.
- Online Retailers and Marketplaces
Major online retailers, such as Amazon, eBay, and AliExpress, often carry a wide variety of 470 ohm resistors from different manufacturers. These platforms can be convenient for smaller orders and offer competitive pricing, but verify seller ratings and reviews for product authenticity and quality. - Specialized Electronics Distributors
Reputable electronics distributors like Digi-Key, Mouser Electronics, and Arrow Electronics, are preferred when you need high-quality components and consistent performance. These distributors offer a wide selection, technical specifications, and datasheets, making it easier to choose the appropriate resistor for your design. They often carry resistors from trusted brands with stringent quality control. - Local Electronics Supply Stores
Many cities have local electronics stores, which can be a great option for immediate needs. Though their selection might be smaller than online distributors, they offer the convenience of instant purchase and potential for face-to-face assistance. These are especially suitable for hobbyists and small projects. - Considerations When Purchasing
When buying 470 ohm resistors, pay close attention to power ratings (1/4W, 1/2W, 1W), tolerance (5%, 1%), and resistor type (carbon film, metal film, metal oxide). Ensure the resistor's specifications align with your application requirements and budget constraints. Checking for manufacturer datasheets can help in verifying the quality and reliability of the component. - Bulk Purchases
For larger projects, buying in bulk from distributors often leads to better per-unit pricing. This is especially useful for manufacturers or projects that require a large volume of resistors. Some distributors have specific bulk pricing tiers and purchasing policies. - Verify Resistor Specifications
Regardless of the purchase location, confirm that the resistor's labeling and documentation match the required specifications. This is important to avoid operational failures, project delays, or damage to your equipment. Always prioritize suppliers that offer genuine products and follow industry best practices for quality control and authenticity verification.
The 470 ohm resistor, seemingly simple, is a fundamental building block in countless electronic circuits. Understanding its function, color code, and types ensures you can confidently select and integrate it into your projects. By considering factors such as power ratings, tolerance, and material (e.g. metal film vs carbon film) you can utilize this resistor effectively. From LED circuits to precision analog applications, the 470 ohm resistor plays a crucial role in ensuring circuits function safely and optimally. Next time you're designing or repairing an electronic device, appreciate the unassuming 470 ohm resistor and its contribution to the tech that powers our world.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA