Understanding the Tiny Titan: A Deep Dive into 0402 Resistors

In the ever-shrinking world of electronics, the 0402 resistor stands as a testament to miniaturization. These tiny components, smaller than a grain of rice, are crucial for modern devices, from smartphones to wearable technology. This article delves into the specifics of 0402 resistors, exploring their importance, characteristics, and usage, helping you navigate the nuances of surface-mount technology and understand how these seemingly insignificant parts are indispensable in today's electronics.
What is a 0402 Resistor?

The 0402 resistor is a surface mount device (SMD) characterized by its extremely small physical dimensions of 0.04 inches in length and 0.02 inches in width. These tiny components are fundamental building blocks in modern electronics, enabling miniaturization of circuits and devices.
0402 Resistor Dimensions and Footprint
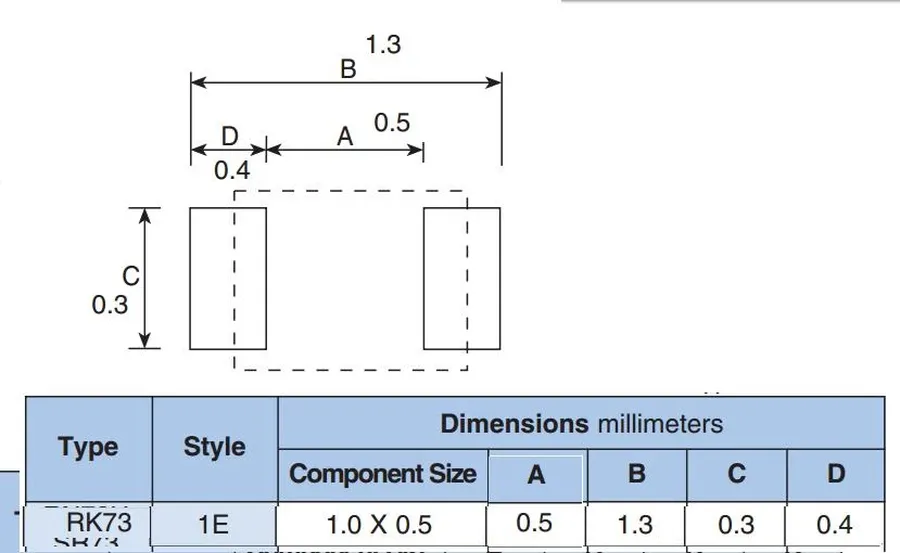
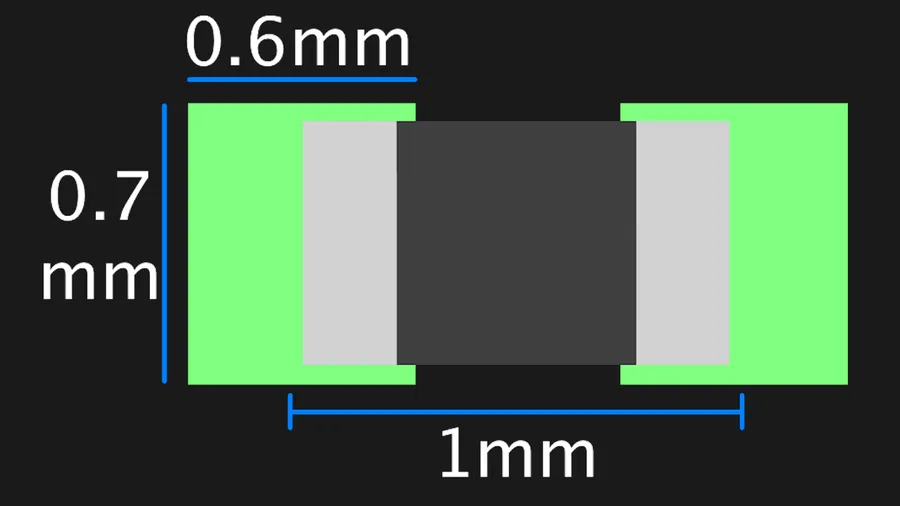
The 0402 resistor, a ubiquitous surface-mount device (SMD), is characterized by its extremely small size, measuring 0.04 inches (1.0 mm) in length and 0.02 inches (0.5 mm) in width. Understanding its precise dimensions and PCB footprint is crucial for accurate circuit design and assembly.
| Parameter | 0402 Resistor | 0603 Resistor | 0201 Resistor |
|---|---|---|---|
| Length (inches) | 0.04 | 0.06 | 0.02 |
| Width (inches) | 0.02 | 0.03 | 0.01 |
| Length (mm) | 1.0 | 1.6 | 0.5 |
| Width (mm) | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.25 |
| Typical PCB Pad Size (mm) | 0.6 x 0.6 | 1.0 x 0.9 | 0.3 x 0.4 |
The table above compares the 0402 resistor with other common SMD resistor sizes, the 0603 and the 0201. Note how the 0402 is smaller than the 0603 and significantly larger than the 0201, each offering a different balance between size and ease of handling. The typical PCB footprint for a 0402 resistor consists of two rectangular pads, allowing for reliable solder joint formation.
Available Resistance Values for 0402 Resistors

0402 resistors, despite their diminutive size, are available in a wide array of resistance values to meet diverse circuit design requirements. These values span from very low resistances, measured in fractions of an ohm, to high resistances reaching megaohms, providing engineers with considerable flexibility. The specific resistance value of a 0402 resistor is typically indicated by a three-digit or four-digit code or an EIA-96 marking, which is often printed on the component itself using extremely precise laser etching techniques, which requires careful decoding.
| Parameter | Description | Typical Values |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance Range | The range of resistance values available for 0402 resistors. | From fractions of an Ohm to several Megaohms (e.g. 0.1 Ohm to 10 Megaohms) |
| Standard Values | Specific values available, usually based on the E-series. | E6, E12, E24, E96 series (e.g., 10Ω, 100Ω, 1kΩ, 10kΩ, 100kΩ) |
| Tolerance | The precision of the resistance value relative to its nominal value. | 1%, 5%, or 0.1% for precision applications |
| Temperature Coefficient | The variation in resistance value per degree change in temperature. | ±25 ppm/°C, ±50 ppm/°C, ±100 ppm/°C |
It's crucial to understand that the availability of specific resistance values within the 0402 package is directly related to its manufacturing process and the precision with which the resistive film can be deposited and trimmed. High precision resistors are typically more difficult and expensive to produce than those with looser tolerances. Tolerance is a critical factor, with standard options such as 1% and 5% being common, but for applications requiring greater accuracy, tighter tolerances like 0.1% are also available.
Power Rating of 0402 Resistors
The power rating of a 0402 resistor is a critical parameter to consider in circuit design, directly influencing its operational reliability and longevity. Due to their diminutive size, 0402 resistors have a very low power handling capacity, typically in the range of 1/16W (0.0625W) or 1/20W (0.05W). Exceeding this rating can lead to overheating, which can cause the resistor to fail, resulting in circuit malfunction or even fire hazards. Therefore, careful consideration of the power dissipation requirements is essential when selecting and implementing 0402 resistors in any application.
| Parameter | Typical Value | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Power Rating | 1/16W (0.0625W) or 1/20W (0.05W) | Very low, needs careful design |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C to +125°C | Temperature derating is critical |
| Voltage Rating | Typically 50V or less | Should be well below rated value |
When incorporating 0402 resistors into a circuit, it is imperative to estimate the power dissipation using Ohm's Law (P = I²R or P=V²/R), where 'P' is power, 'I' is current, 'R' is resistance, and 'V' is voltage. Ensure that the calculated power is substantially below the resistor's maximum power rating to provide a safety margin. Furthermore, it is important to consider the operating temperature of the resistor. The maximum power rating is usually specified at a certain ambient temperature (typically 25°C), and it must be derated at higher temperatures. Therefore, the resistor's ability to dissipate heat effectively should be taken into account, which might include strategies such as increasing pad size or incorporating vias for better heat transfer to a PCB.
Applications of 0402 Resistors
The 0402 resistor, due to its exceptionally small size, finds extensive use in modern electronics where space is at a premium. Its miniature profile allows for high component density on printed circuit boards (PCBs), making it ideal for compact and portable devices.
- Smartphones and Mobile Devices
These devices require increasingly complex circuitry in shrinking form factors. The 0402 resistor is crucial in achieving this level of miniaturization, fitting into tight spaces on the mainboard and daughterboards for functions like signal conditioning and current limiting. - Wearable Technology
Smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearable gadgets rely heavily on small components. The 0402's diminutive size allows designers to maximize functionality while minimizing overall device dimensions, crucial for user comfort and aesthetics. These resistors often perform critical roles in sensor circuits. - Portable Electronics
MP3 players, handheld gaming consoles, and other battery-powered devices benefit from the high density enabled by 0402 resistors. Their small footprint assists in achieving smaller, lighter, and more efficient circuit designs, contributing to longer battery life and device portability. - Medical Devices
Advanced medical devices, such as hearing aids, implantable devices, and portable diagnostic equipment, demand precision and small size. The 0402 resistor provides both, allowing for reliable circuit performance within the stringent size and weight restrictions of medical applications. They are frequently employed in sensitive analog signal processing circuits. - IoT (Internet of Things) Devices
The proliferation of IoT devices, from smart sensors to connected home devices, necessitates cost-effective and space-efficient solutions. The 0402 resistor is a staple in these designs, facilitating compact, cost-effective and reliable functionality for diverse applications. - Automotive Electronics
Modern vehicles incorporate numerous electronic control units (ECUs) that control various functions, such as engine management, braking, and infotainment. In applications with space constraints, the 0402 resistor’s small size is highly advantageous.
The widespread adoption of 0402 resistors is a testament to their necessity in modern electronics. Their ability to deliver reliable performance in extremely compact spaces makes them indispensable for current and future technology.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Using 0402 Resistors
The 0402 resistor, while offering significant benefits in miniaturization, also presents certain challenges. A careful evaluation of these advantages and disadvantages is crucial for effective circuit design and manufacturing.
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Size and Space | Extremely small size enables high component density on PCBs, ideal for miniaturized devices. | Small size makes manual handling and soldering very difficult, requiring specialized equipment and techniques. |
| Cost | Generally cost-effective due to high-volume production and material efficiency. | The cost of specialized equipment for handling and assembly can increase overall project expenses. |
| Electrical Performance | Adequate performance for low-power applications, suitable for signal processing and control circuits. | Limited power handling capability due to small size; easily damaged by overcurrent or overheating. |
| Manufacturing | Allows for automated high-speed assembly processes. | Susceptible to misplacement during pick-and-place operations if not handled with care and precision. |
| Component Density | Contributes to very compact PCB designs, reducing device size. | Requires advanced inspection techniques to verify proper placement and solder joint integrity. |
| Material Efficiency | Minimal material usage due to small size, promoting resource conservation. | Difficult to identify and replace with conventional equipment, resulting in longer troubleshooting processes. |
Where to Buy 0402 Resistors and Kits
Sourcing 0402 resistors requires careful consideration of reliability, quality, and cost. Given their small size, ensuring you obtain components from reputable suppliers is crucial for project success. This section provides guidance on finding suitable sources, including online retailers, distributors, and component suppliers.
The electronic component marketplace provides several options for sourcing 0402 resistors and kits. These sources can generally be categorized into authorized distributors, online marketplaces, and direct manufacturers. Each type of supplier presents unique advantages and disadvantages that must be weighed based on project needs, budget, and timeline.
| Source Type | Description | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|
| Authorized Distributors | Companies like Digi-Key, Mouser, and Arrow Electronics. | High-quality, genuine components; comprehensive datasheets; technical support; traceability. | Higher cost per unit compared to other sources; may have minimum order quantities. |
| Online Marketplaces | Platforms like Amazon, eBay, and AliExpress. | Lower prices; availability of small quantities; wide variety of sellers. | Risk of counterfeit components; varying quality control; less technical support; unclear traceability. |
| Direct Manufacturers | Companies that produce the components themselves | Potentially lower cost in bulk orders; customization options; direct support from the producer. | May require large order quantities; longer lead times; potentially less flexibility in terms of variety. |
When purchasing 0402 resistors, consider the following aspects to ensure you get the right components for your application:
- Resistance Value:
Verify that the resistance value matches your design requirements. Resistors come in a wide range of values, and selecting the correct one is crucial for proper circuit functionality. - Tolerance:
Choose the appropriate tolerance based on your application needs. Common tolerances include 1%, 5%, and 10%, with tighter tolerances providing more precise resistance values. - Packaging:
Consider the packaging method. 0402 resistors are commonly available on reels for automated assembly or in cut tape for prototyping and small-scale projects. - Quantity:
Purchase an adequate quantity to cover your current needs and account for any losses during assembly or testing. It is generally good practice to have a surplus on hand. - Authenticity:
Buy from trusted sources to avoid counterfeit components. Counterfeit parts can cause circuit failures and lead to unreliable performance, especially in critical applications.
Frequently Asked Questions About 0402 Resistors
This section addresses common inquiries about 0402 resistors, providing concise answers to help clarify their characteristics and applications.
- What exactly is a 0402 resistor?
A 0402 resistor is a surface mount device (SMD) with dimensions of 0.04 inches in length and 0.02 inches in width. It's a passive electronic component used to resist the flow of electric current. - What are the physical dimensions of a 0402 resistor in metric units?
The 0402 resistor measures approximately 1.0 mm in length and 0.5 mm in width. - What is the typical power rating of a 0402 resistor?
Due to their small size, 0402 resistors typically have very low power ratings, often in the range of 1/16th of a watt (0.0625W) or 1/20th of a watt (0.05W). Careful consideration of power dissipation is required to prevent overheating and failure. - What is the typical tolerance of a 0402 resistor?
0402 resistors are commonly available with tolerances of 1% or 5%. The tolerance indicates the allowed deviation of the actual resistance from the nominal value. - What is the value of the SMD resistor 402?
The number '402' indicates the size of the resistor, not its resistance value. The resistance of a 0402 resistor is indicated by a separate numerical code or marking system on the component. You need to check the coding to determine the resistance. - What are some of the challenges in handling and soldering 0402 resistors?
The extremely small size of 0402 resistors makes them difficult to handle and solder. Specialized tools, such as fine-tipped tweezers and soldering irons, along with practice, are necessary for successful assembly. The potential for 'tombstoning' during reflow soldering, due to uneven heating, is also a challenge. - Where are 0402 resistors typically used?
0402 resistors are used in space-constrained applications like smartphones, wearable devices, and medical instruments, where component density is critical.
Handling and Soldering Techniques for 0402 Resistors
Due to their diminutive size, handling and soldering 0402 resistors require meticulous technique and specialized tools. These components demand careful consideration to avoid damage and ensure reliable connections, therefore, adhering to best practices is paramount for successful assembly.
- Tools for Handling 0402 Resistors
Fine-tipped tweezers, vacuum pick-up tools, and a magnifying glass or microscope are indispensable for handling these small components. Avoid using fingers directly to prevent contamination or damage. - Preparation Before Soldering
Ensure the PCB pads are clean and have proper solder paste application. Precise solder paste deposition is critical; consider using stencils for accurate placement. It's best practice to bake out the board prior to assembly to avoid trapped moisture. - Soldering Methods for 0402 Resistors
Reflow soldering is typically used for mass production. For manual soldering, use a fine-tipped soldering iron with temperature control. Apply a small amount of solder to one pad, place the resistor using the tools mentioned earlier, and then solder the other pad. - Solder Paste Application
Solder paste should be applied precisely to the PCB pads using a stencil printer or dispenser. The amount of solder paste is crucial; too much can lead to bridging, while too little can result in a weak connection. - Avoiding Common Mistakes
Avoid excessive heat during soldering, as this can damage the resistor. Never apply too much pressure to the component during soldering to avoid causing cracking of the components. Inspect solder joints using a microscope or magnifying glass to verify a quality connection, as this will reduce failure rates.
The 0402 resistor, though small, is a critical component in modern electronics, enabling smaller, more efficient devices. Understanding their specifications, applications, and handling requirements is crucial for any electronics engineer or hobbyist. As technology continues to shrink, components like the 0402 resistor will play an increasingly significant role, driving innovation across industries. Mastering the use of this tiny component opens up a world of possibilities in the design of compact and powerful electronic systems.
 AnyPCBA
AnyPCBA